引言
NOKIA 有句著名的广告语:“科技以人为本”。任何技术都是为了满足人的生产生活需要而产生的。具体到小小的一个手机,里面蕴含的技术也是浩如烟海,是几千年来人类科技的结晶,单个人穷其一生也未必能掌握其一角。不过个人一直认为基本的技术和思想是放之四海而皆准的,许多技术未必需要我们从头到尾再研究一遍,我们要做的就是站在巨人的肩膀上,利用其成果来为人们的需求服务。
随着移动互联网时代的大潮,越来越多的App不光是需要和网络服务器进行数据传输和交互,也需要和其他 App 进行数据传递。承担App与网络来进行传输和存储数据的一般是XML或者JSON。在移动互联网时代,XML和JSON很重要。
最近一段时间,个人综合了之前对XML、JSON的一些了解,参考了相关资料,再结合视频的代码,把自己的一些思考融入了这篇总结文档中,同时尝试用通俗诙谐的语言风格来阐述,期望能给感兴趣的读者带来帮助。
为了不和时代落伍,我们必须要学习 XML 和 JSON,但同时它们也很容易学习,Let's start:–)
一、XML
XML即可扩展标记语言(eXtensible Markup Language)。标记是指计算机所能理解的信息符号,通过此种标记,计算机之间可以处理包含各种信息的文章等。如何定义这些标记,既可以选择国际通用的标记语言,比如HTML,也可以使用象XML这样由相关人士自由决定的标记语言,这就是语言的可扩展性。XML是从SGML中简化修改出来的。它主要用到的有XML、XSL和XPath等。
上面这段是对XML的一个基本定义,一个被广泛接受的说明。简单说,XML就是一种数据的描述语言,虽然它是语言,但是通常情况下,它并不具备常见语言的基本功能——被计算机识别并运行。只有依靠另一种语言,来解释它,使它达到你想要的效果或被计算机所接受。
记住以下几点就行了:
XML是一种标记语言,很类似HTML
XML的设计宗旨是传输数据,而非显示数据
XML标签没有被预定义。您需要自行定义标签。
XML被设计为具有自我描述性。
XML是W3C的推荐标准
总结:
XML是独立于软件和硬件的信息传输工具。 目前,XML在Web中起到的作用不会亚于一直作为 Web 基石的 HTML。 XML无所不在。XML是各种应用程序之间进行数据传输的最常用的工具,并且在信息存储和描述领域变得越来越流行。
1.1 XML属性
1.1.1 XML与HTML的主要差异
XML不是HTML的替代。
XML和HTML为不同的目的而设计。
XML被设计为传输和存储数据,其焦点是数据的内容。
HTML被设计用来显示数据,其焦点是数据的外观。
HTML旨在显示信息,而 XML 旨在传输信息
1.1.2 XML是不作为的。
也许这有点难以理解,但是XML不会做任何事情。XML被设计用来结构化、存储以及传输信息。
下面是John写给George的便签,存储为XML:
<note> <to>George</to> <from>John</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget the meeting!</body> </note>
上面的这条便签具有自我描述性。它拥有标题以及留言,同时包含了发送者和接受者的信息。但是,这个 XML 文档仍然没有做任何事情。它仅仅是包装在XML标签中的纯粹的信息。我们需要编写软件或者程序,才能传送、接收和显示出这个文档。
1.1.3 XML仅仅是纯文本
XML没什么特别的。它仅仅是纯文本而已。有能力处理纯文本的软件都可以处理XML。 不过,能够读懂 XML 的应用程序可以有针对性地处理 XML 的标签。标签的功能性意义依赖于应用程序的特性。
1.1.4 XML允许自定义标签
上例中的标签没有在任何XML标准中定义过(比如和)。这些标签是由文档的创作者发明的。这是因为XML没有预定义的标签。
在HTML中使用的标签(以及HTML的结构)是预定义的。HTML文档只使用在HTML标准中定义过的标签(比如
,
XML允许创作者定义自己的标签和自己的文档结构。
1.1.5 XML不是对HTML的替代
XML是对HTML的补充。
XML不会替代HTML,理解这一点很重要。在大多数 web 应用程序中,XML用于传输数据,而HTML用于格式化并显示数据。
1.2 XML的语法
XML的语法规则很简单,且很有逻辑。这些规则很容易学习,也很容易使用。
1.2.1 所有元素都必须有关闭标签
在XML中,省略关闭标签是非法的。所有元素都必须有关闭标签。 在HTML,经常会看到没有关闭标签的元素:
<p>This is a paragraph <p>This is another paragraph
在XML中,省略关闭标签是非法的。所有元素都必须有关闭标签:
<p>This is a paragraph</p> <p>This is another paragraph</p>
注释:您也许已经注意到XML声明没有关闭标签。这不是错误。声明不属于XML本身的组成部分。它不是XML元素,也不需要关闭标签。
1.2.2 XML标签对大小写敏感
XML元素使用XML标签进行定义。
XML标签对大小写敏感。在XML中,标签与标签是不同的。
必须使用相同的大小写来编写打开标签和关闭标签:
<Message>这是错误的。</message> <message>这是正确的。</message>
1.2.3 XML标签对大小写敏感
在 HTML 中,常会看到没有正确嵌套的元素:
<b><i>This text is bold and italic</b></i>
在 XML中,所有元素都必须彼此正确地嵌套:
<b><i>This text is bold and italic</i></b>
在上例中,正确嵌套的意思是:由于元素是在元素内打开的,那么它必须在元素内关闭。
1.2.4 XML文档必须有根元素
XML文档必须有一个元素是所有其他元素的父元素。该元素称为根元素。
<root> <child> <subchild>.....</subchild> </child> </root>
1.2.5 XML的属性值须加引号
与 HTML 类似,XML 也可拥有属性(名称/值的对)。 在 XML 中,XML 的属性值须加引号。请研究下面的两个 XML 文档。第一个是错误的,第二个是正确的:
<note date=08/08/2008> <to>George</to> <from>John</from> </note> <note date="08/08/2008"> <to>George</to> <from>John</from> </note>
1.2.6 实体引用
在 XML 中,一些字符拥有特殊的意义。 如果你把字符 “<” 放在 XML 元素中,会发生错误,这是因为解析器会把它当作新元素的开始。 这样会产生 XML 错误:
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>
为了避免这个错误,请用实体引用来代替 “<” 字符:
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>
在 XML 中,有 5 个预定义的实体引用:
< < 小于 > > 大于 & & 和号 ' ' 单引号 " " 引号
注释:在 XML 中,只有字符 “<” 和 “&” 确实是非法的。大于号是合法的,但是用实体引用来代替它是一个好习惯。
1.2.7 XML中的注释
在 XML 中编写注释的语法与 HTML 的语法很相似:
<!-- This is a comment -->
在 XML 中,空格会被保留 HTML 会把多个连续的空格字符裁减(合并)为一个:
HTML: Hello my name is David.
输出: Hello my name is David. 在 XML 中,文档中的空格不会被删节。
1.2.8 以 LF 存储换行
在 Windows 应用程序中,换行通常以一对字符来存储:回车符 (CR) 和换行符 (LF)。这对字符与打字机设置新行的动作有相似之处。在 Unix 应用程序中,新行以 LF 字符存储。而 Macintosh 应用程序使用CR来存储新行。
1.3 XML CDATA
所有XML文档中的文本均会被解析器解析。
只有CDATA区段(CDATA section)中的文本会被解析器忽略。
1.3.1 PCDATA
PCDATA指的是被解析的字符数据(Parsed Character Data)。
XML解析器通常会解析XML文档中所有的文本。 当某个XML元素被解析时,其标签之间的文本也会被解析:
<message>此文本也会被解析</message>
解析器之所以这么做是因为 XML 元素可包含其他元素,就像这个例子中,其中的元素包含着另外的两个元素(first和last):
<name><first>Bill</first><last>Gates</last></name>
而解析器会把它分解为像这样的子元素:
<name> <first>Bill</first> <last>Gates</last> </name>
1.3.2 转义字符
非法的XML字符必须被替换为实体引用(entity reference)。
假如您在XML文档中放置了一个类似 “<” 字符,那么这个文档会产生一个错误,这是因为解析器会把它解释为新元素的开始。因此你不能这样写:
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>
为了避免此类错误,需要把字符 “<” 替换为实体引用,就像这样:
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>
在 XML 中有 5 个预定义的实体引用:
< < 小于 > > 大于 & & 和号 ' ' 省略号 " " 引号
注释:严格地讲,在XML中仅有字符”<“和”&“是非法的。省略号、引号和大于号是合法的,但是把它们替换为实体引用是个好的习惯。
1.3.3 CDATA
术语CDATA指的是不应由XML解析器进行解析的文本数据(Unparsed Character Data)。
在 XML 元素中,”<“ 和 ”&“ 是非法的。
“<” 会产生错误,因为解析器会把该字符解释为新元素的开始。 “&” 也会产生错误,因为解析器会把该字符解释为字符实体的开始。
某些文本,比如 JavaScript 代码,包含大量 “<” 或 “&” 字符。为了避免错误,可以将脚本代码定义为 CDATA。 CDATA 部分中的所有内容都会被解析器忽略。 CDATA 部分由 “” 结束:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <response> <header> <respcode>0</respcode> <total>1736</total> </header> <result> <album> <album_id>320305900</album_id> <title> <![CDATA[ 电影侃侃之初恋永不早 ]]> </title> <tag> <![CDATA[ 18岁以上 当代 暧昧 华语 ]]> </tag> <img>http://pic9.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/ec/e0/v_108639906_m_601_120_160.jpg</img> <img180236>http://pic9.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/ec/e0/v_108639906_m_601_180_236.jpg</img180236> <img11577>http://pic9.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/ec/e0/v_108639906_m_601_115_77.jpg</img11577> <img220124>http://pic9.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/ec/e0/v_108639906_m_601_284_160.jpg</img220124> <category_id>1</category_id> <score>0.0</score> <voters>0</voters> <tv_sets>0</tv_sets> <duration>00:38:57</duration> <year> <![CDATA[ 2014 ]]> </year> <tv_focus>跟爱情片学把妹心经</tv_focus> <episode_count>1</episode_count> <directors> <![CDATA[ 关雅荻 ]]> </directors> <mainactors> <![CDATA[ 关雅荻 ]]> </mainactors> <actors> <![CDATA[ ]]> </actors> <vv2> <![CDATA[ 15 ]]> </vv2> <timeText> <![CDATA[ 今天 ]]> </timeText> <first_issue_time> <![CDATA[ 2014-10-16 ]]> </first_issue_time> <up>0</up> <down>0</down> <download>1</download> <purchase_type>0</purchase_type> <hot_or_new>0</hot_or_new> <createtime>2014-10-16 12:25:08</createtime> <purchase>0</purchase> <desc> <![CDATA[ 本期节目主持人介绍新近上映的口碑爱情片,。主持人轻松幽默的罗列出胡鳄鱼导演拍摄的爱情片越来越接地气,博得观众的认同和追捧,更提出“初恋永远不嫌早”的口号。观众可以跟着爱情片学习把妹心经。 ]]> </desc> <ip_limit>1</ip_limit> <episodes/> </album> </result> </response>
这是展示一部电影的具体数据,包括标题、介绍、内容、导演、演员、时长、上映年份等很多内容。
1.5 XML树结构
XML文档形成了一种树结构,它从“根部”开始,然后扩展到“枝叶”。
1.5.1 一个XML文档实例
XML使用简单的具有自我描述性的语法:
<note> <to>George</to> <from>John</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget the meeting!</body> </note>
第一行是XML声明。它定义XML的版本(1.0)和所使用的编码(ISO-8859-1=Latin-1/西欧字符集)。
下一行描述文档的根元素(像在说:“本文档是一个便签”):
<note>
接下来 4 行描述根的 4 个子元素(to, from, heading 以及 body):
<to>George</to> <from>John</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget the meeting!</body>
最后一行定义根元素的结尾:
</note>
从本例可以设想,该XML文档包含了John给George的一张便签。
XML具有出色的自我描述性,你同意吗?
XML文档形成一种树结构
XML文档必须包含根元素。该元素是所有其他元素的父元素。
XML文档中的元素形成了一棵文档树。这棵树从根部开始,并扩展到树的最底端。
所有元素均可拥有子元素:
<root> <child> <subchild>.....</subchild> </child> </root>
父、子以及同胞等术语用于描述元素之间的关系。父元素拥有子元素。相同层级上的子元素成为同胞(兄弟或姐妹)。
所有元素均可拥有文本内容和属性(类似HTML中)。
1.6 XML DOM
想到这里,大家都有点迫不及待了,XML 文件到底如何解析呢?
但是,别急,让子弹先飞会儿:–)
在XML解析之前,我们必须系统性的学习一下 XML DOM 知识:
1.6.1 定义
XML DOM(XML Document Object Model) 定义了访问和操作XML文档的标准方法。
DOM把XML文档作为树结构来查看。能够通过DOM树来访问所有元素。可以修改或删除它们的内容,并创建新的元素。元素,它们的文本,以及它们的属性,都被认为是节点。
XML DOM是:
用于XML的标准对象模型
用于XML的标准编程接口
中立于平台和语言
W3C的标准
XML DOM定义了所有XML元素的对象和属性,以及访问它们的方法(接口)。
换句话说:
XML DOM是用于获取、更改、添加或删除XML元素的标准
DOM将XML文档作为一个树形结构,而树叶被定义为节点。
1.6.2 总结
XML DOM其实比较复杂,在这么短的篇幅里也无法一一进行讲解。想详细了解XML DOM可以好好去学习下
1.7 XML如何解析?
上面讲了这么多关于XML的东西,那么XML文件应该如何解析呢?
终于到了我们的重头戏了
下面以视频项目为例,展示如何解析XML文件:
1.7.1 Step 1
XML文件是一棵树,首先需要找到对应的节点,然后从节点开始解析,比如搜索找到的就是result/weights/weight 和result/weights/weight 2个节点,分别从这个开始解析:
public ResultInfo onParser(Element rootElement) {
int resp = -1;
try {
String elName = "header/respcode";
resp = Integer.parseInt(selectNodeString(rootElement, elName));
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Log.d(TAG, "resp= " + resp);
if (resp != 0) {
return null;
}
ResultInfo searchResultInfo = new ResultInfo();
// Parse Search Weight
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
final List weights = rootElement.selectNodes(rootElement.getPath() + "/"
+ "result/weights/weight");
ResultInfo[] resultFilterInfos = parseVideos(weights);
if (resultFilterInfos != null) {
ResultInfo weight = new ResultInfo();
weight.putResultInfoArray(ResultInfo.KEY_VIDEOS, resultFilterInfos);
searchResultInfo.putResultInfo(ResultInfo.KEY_WEIGHT, weight);
}
// Parse Albums
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
final List albums = rootElement.selectNodes(rootElement.getPath() + "/"
+ "result/albums/album");
ResultInfo[] resultInfos = parseVideos(albums);
if (resultInfos != null) {
ResultInfo album = new ResultInfo();
album.putResultInfoArray(ResultInfo.KEY_VIDEOS, resultInfos);
searchResultInfo.putResultInfo(ResultInfo.KEY_SEARCH, album);
}
return searchResultInfo;
}
1.7.2 Step 2
找到了对应的Node,即从对应的Node开始递归的查找,直到找到最小的节点,也就是最基本的单元Element。再对每一个Element进行解析:
private ResultInfo[] parseVideos(final List nodes) {
if (nodes != null && nodes.size() > 0) {
final int size = nodes.size();
final ResultInfo[] vis = new ResultInfo[size];
int i = 0;
for (Object o : nodes) {
if (o instanceof Element) {
final Element videoElement = (Element) o;
ResultInfo vi = parseVideo(videoElement);
vis[i] = vi;
}
i++;
}
return vis;
}
return null;
}
1.7.3 Step 3
针对获取到的Element,解析出对应的String将数据传递给VideoInfo这个类:
private ResultInfo parseVideo(final Element videoElement) {
final String id = videoElement.elementText("album_id");
final String title = videoElement.elementText("title");
final String categoryId = videoElement.elementText("category_id");
final String categoryName = videoElement.elementText("category_name");
final String count = videoElement.elementText("count");
final String imgUrl = videoElement.elementText("img180236");
final String duration = videoElement.elementText("duration");
final String mainactors = videoElement.elementText("mainactors");
final String sitename = videoElement.elementText("site_name");
final String videourl = videoElement.elementText("vedio_url");
final String sort = videoElement.elementText("sort");
final String tv_id = videoElement.elementText("tv_id");
ResultInfo vi = new ResultInfo();
vi.putString(VideoInfo.ID, id);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.TITLE, title);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.CATEGORY_ID, categoryId);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.CATEGORY_NAME, categoryName);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.COUNT, count);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.IMG_URL, imgUrl);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.DURATION, duration);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.MAINACTORS, mainactors);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.SITENAME, sitename);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.VIDEOURL, videourl);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.SORT, sort);
vi.putString(VideoInfo.TV_ID, tv_id);
return vi;
}
1.7.4 Step 4
当使用XML解析器将XML数据解析出来之后。需要将这些数据提取出来,也是通过连续2层提取,将数据定位到每个video, 将每个video里的数据传递给SearchVideoInfo这个ArrayList,然后将ArrayList中的数据和对应的Adapter数据关联起来:
public static ArrayList<SearchVideoInfo> getSearchVideoInfo(ResultInfo searchResultInfo) {
ResultInfo resultInfo = null;
ResultInfo[] videos = null;
ArrayList<SearchVideoInfo> searchVideoInfos = null;
if (searchResultInfo != null) {
resultInfo = searchResultInfo.getResultInfo(ResultInfo.KEY_SEARCH);
}
if (resultInfo != null) {
videos = resultInfo.getResultInfoArray(ResultInfo.KEY_VIDEOS);
}
if (videos != null && videos.length > 0) {
searchVideoInfos = new ArrayList<SearchVideoInfo>(videos.length);
for (ResultInfo video : videos) {
SearchVideoInfo searchInfo = new SearchVideoInfo();
searchInfo.setAlbum_id(video.getString(VideoInfo.ID));
searchInfo.setTitle(video.getString(VideoInfo.TITLE));
searchInfo.setChannel_id(video.getString(VideoInfo.CATEGORY_ID));
searchInfo.setImgUrl(video.getString(VideoInfo.IMG_URL));
searchInfo.setDuration(video.getString(VideoInfo.DURATION));
searchInfo.setMainActors(video.getString(VideoInfo.MAINACTORS));
searchInfo.setSiteName(video.getString(VideoInfo.SITENAME));
searchInfo.setVideo_url(video.getString(VideoInfo.VIDEOURL));
searchInfo.setOrder(video.getString(VideoInfo.SORT));
searchInfo.setTv_id(video.getString(VideoInfo.TV_ID));
// searchInfo.setContinueType(video.getString(VideoInfo.CONTINUETYPE));
searchVideoInfos.add(searchInfo);
}
}
if (searchVideoInfos == null) {
MyLog.e(TAG, "error, getSearchVideoInfo, can not get info");
}
return searchVideoInfos;
}
以上就是搜索数据的XML的解析和数据展示过程。
二、JSON
XML很好很强大,但是最近有另外一个时代弄潮儿,这就是JSON。现在JSON的光环已经逐渐超越了XML,各大网站提供的数据接口一般都是JSON。下面我们就来学习下JSON。
2.1 JSON是什么?
JSON:JavaScript对象表示法(JavaScript Object Notation), 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式, 易于人阅读和编写, 同时也易于机器解析和生成。
JSON是存储和交换文本信息的语法,类似XML。
JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但是也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯(包括C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python等)。 这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言
2.2 JSON格式
JSON构建于两种结构:
“名称/值”对的集合(A collection of name/value pairs)。不同的语言中,它被理解为对象(object),纪录(record),结构(struct),字典(dictionary),哈希表(hash table),有键列表(keyed list),或者关联数组(associative array)。
值的有序列表(An ordered list of values)。在大多数语言中,它被理解为数组(array)、矢量(vector), 列表(list)或者是序列(sequence)。
JSON具有以下这些形式:
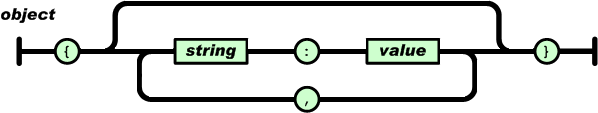
对象是一个无序的“'名称/值'对”集合。一个对象以“{”(左括号)开始,“}”(右括号)结束。每个“名称”后跟一个“:”(冒号);“‘名称/值' 对”之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。
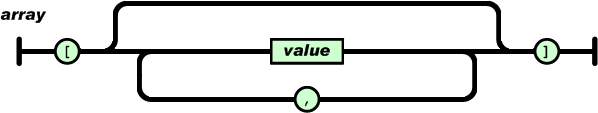
数组是值(value)的有序集合。一个数组以“[”(左中括号)开始,“]”(右中括号)结束。值之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。
JSON Array
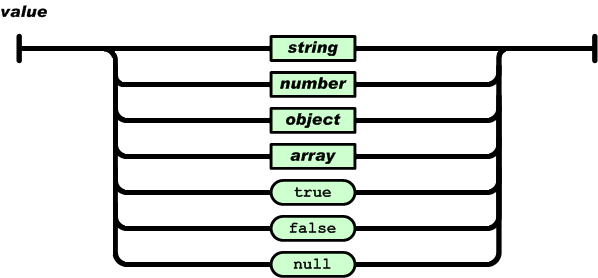
值(value)可以是双引号括起来的字符串(string)、数值(number)、true、false、 null、对象(object)或者数组(array)。这些结构可以嵌套。
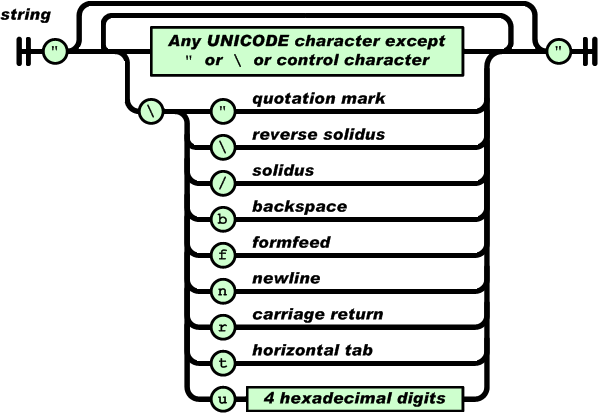
字符串(string)是由0到多个Unicode字符组成的序列,封装在双引号(”“)中, 可以使用反斜杠(‘\')来进行转义。一个字符可以表示为一个单一字符的字符串。
数字(number)类似C或者Java里面的数,没有用到的8进制和16进制数除外。
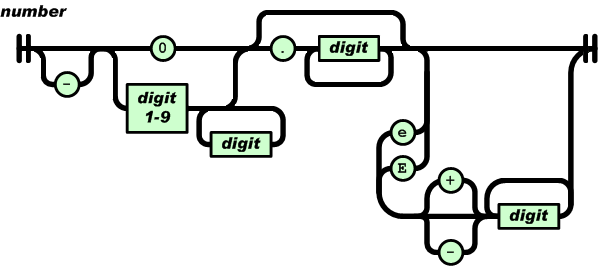
2.3 举个例子
上面关于JSON讲了这么多,大家都表示一头雾水了吧?
没关系,我们来举个栗子,让大家有个直观的感受:–)
以目前视频使用的iQiyi提供的频道接口为例:
iQiyi提供的电影频道的JSON电影数据如下:
"code": 1,
"data": 0,
"albumIdList": [
{
"totalidnum": 2000,
"idlist": [
"319281600"
]
}
],
"albumArray": {
"319281600": {
"_as": "",
"_blk": 0,
"_cid": 1,
"_ct": "2014-10-10 17:55:06",
"_da": "",
"_dl": 0,
"_dn": "7296",
"_id": 319281600,
"_img": "http://pic2.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/19/ca/v_108628048_m_601_m1_120_160.jpg",
"_ip": 1,
"_ma": "",
"_pc": 2,
"_pid": 0,
"_reseftv": 959,
"_t": "末代独裁",
"_tvct": 1,
"_tvs": 1,
"_vt": 0,
"a_av": 1,
"a_pro": "",
"bpt": "0",
"clm": "",
"cn_year": "0",
"co_album_id": "0",
"ctype": 0,
"desc": "",
"down": 0,
"down2": "0",
"drm": 0,
"fst_time": "2014-10-16",
"h1_img": "http://pic2.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/19/ca/v_108628048_m_601_m1_180_236.jpg",
"h2_img": "http://pic2.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/19/ca/v_108628048_m_601_m1_195_260.jpg",
"is_h": 0,
"is_n": 0,
"is_zb": 0,
"k_word": "",
"language": 0,
"live_center": 0,
"live_start_time": 0,
"live_stop_time": 0,
"logo": 1,
"m_av": 1,
"p_av": 1,
"p_s": 0,
"p_s_1": 0,
"p_s_4": 0,
"p_s_8": 0,
"qiyi_pro": 0,
"qiyi_year": "0",
"qt_id": "1005722",
"s_TT": "",
"songname": "",
"t_pc": 1,
"tag": "当代 美国 乡村 大片",
"tv_eftv": 1,
"tv_pha": "",
"tv_pro": "",
"tv_ss": "",
"tvfcs": "雄心壮志背后的真相",
"up": 0,
"up2": "0",
"upcl": "",
"v2_img": "http://pic2.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/19/ca/v_108628048_m_601_m1_284_160.jpg",
"v3_img": "http://pic2.qiyipic.com/image/20141016/19/ca/v_108628048_m_601_m1_480_270.jpg",
"vv": "1",
"year": "2007",
"tv_id": "0",
"vv_p": 0,
"vv_f": 2,
"vv_m": 0,
"_sc": 8
}
},
"changeAlbum": null,
"category": null,
"before": "2~4~1~7~3",
"latest_push_id": "655",
"up_tm": "1413441370874",
"recommend_attach": "",
"preset_keys": null,
"category_group": null,
"exp_ts": 120,
"stfile_path": "/data/view/online5/0/1/2.1.8.5.1.txt"
}从上面的例子可以很清晰的看出JSON是如何展示一个电影的数据的,当然这是JSON格式化之后的数据。JSON的元数据是不便于阅读的。
2.4 如何解析JSON?
Android JSON所有相关类,都在org.json包下。
包括JSONObject、JSONArray、JSONStringer、JSONTokener、JSONWriter、JSONException。
<1>. 常见方法
目前JSON解析有2种方法,分别是get和opt方法,可以使用JSON
那么使用get方法与使用opt方法的区别是?
JsonObject方法,opt与get建议使用opt方法,因为get方法如果其内容为空会直接抛出异常。不过JsonArray.opt(index)会有越界问题需要特别注意。
opt、optBoolean、optDouble、optInt、optLong、optString、optJSONArray、optJSONObject get、getBoolean、getDouble、getInt、getLong、getString、getJSONArray、getJSONObject
<2>. Android中如何创建JSON?
在Android中应该如何创建JSON呢?
下面展示了一个如何创建JSON的例子:
private String createJson() throws JSONException {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("intKey", 123);
jsonObject.put("doubleKey", 10.1);
jsonObject.put("longKey", 666666666);
jsonObject.put("stringKey", "lalala");
jsonObject.put("booleanKey", true);
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
jsonArray.put(0, 111);
jsonArray.put("second");
jsonObject.put("arrayKey", jsonArray);
JSONObject innerJsonObject = new JSONObject();
innerJsonObject.put("innerStr", "inner");
jsonObject.put("innerObjectKey", innerJsonObject);
Log.e("Json", jsonObject.toString());
return jsonObject.toString();
}其输出结果如下所示:
{"intKey":123, "doubleKey":10.1, "longKey":666666666, "stringKey":"lalala", "booleanKey":true, "arrayKey":[111,"second"], "innerObjectKey":{"innerStr":"inner"}}
<3>. 如何解析JSON?
下面以视频中解析iQiyi的每个视频album数据为例来说明如何解析JSON:
第一步,需要从网络服务器上发起请求,获取到JSON数据:
JsonObjectRequest jsonObjRequest = new JsonObjectRequest(Request.Method.GET, url, null,
new Response.Listener<JSONObject>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(JSONObject response) {
try {
MyLog.d(TAG, "response=" + response);
parseiQiyiInterfaceResponse(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
/*
* if (error instanceof NetworkError) { } else if (error
* instanceof ClientError) { } else if (error instanceof
* ServerError) { } else if (error instanceof
* AuthFailureError) { } else if (error instanceof
* ParseError) { } else if (error instanceof
* NoConnectionError) { } else if (error instanceof
* TimeoutError) { }
*/
MyLog.e(TAG, "onErrorResponse, error=" + error);
}
}) {
@Override
public Map<String, String> getHeaders() throws AuthFailureError {
HashMap<String, String> headers = new HashMap<String, String>();
headers.put("t", iQiyiInterface.getEncryptTimestamp());
headers.put("sign", iQiyiInterface.getSign());
return headers;
}
};
第二步,获取到对应的对应的JSONObject数据:
public void getJsonObjectString(String url) {
mQueue = VideoApplication.getInstance().getRequestQueue();
JsonObjectRequest jsObjRequest = new JsonObjectRequest(Request.Method.GET, url, null,
new Response.Listener<JSONObject>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(JSONObject response) {
MyLog.e(TAG, "response = " + response.toString());
JSONArray jsonArray = null;
JSONObject jsonObject = null;
try {
jsonObject = response.getJSONObject("response");
jsonArray = jsonObject.getJSONObject("result").getJSONArray("album");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (jsonArray == null) {
return;
}
mChannelList = VideoUtils.parseVideoJsonArray(jsonArray);
if (isLoading) {
isLoading = false;
if (mIsGrid) {
mChannelGridAdapter.appendChannelVideoInfo(mChannelList);
} else {
mChannelListAdapter.appendChannelVideoInfo(mChannelList);
}
} else {
if (mIsGrid) {
mChannelGridAdapter.setChannelVideoInfo(mChannelList);
showOppoGrid();
} else {
mChannelListAdapter.setChannelVideoInfo(mChannelList);
showOppoList();
}
}
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
MyLog.e(TAG, "error = " + error);
}
});
jsObjRequest.setTag(TAG);
jsObjRequest.setShouldCache(true);
mQueue.add(jsObjRequest);
mQueue.start();
}
获取到JSON Object之后,就对这个JSONObject进行解析:
private ArrayList<VideoConstant> parseVideoAlbumJsonObject(JSONObject albumJSONObject, ArrayList<Integer> albumIdJSONArrayList) {
MyLog.d(TAG, "parseVideoAlbumJsonObject, length=" + albumJSONObject.length());
if (albumJSONObject.length() < 1) {
return null;
}
ArrayList<VideoConstant> videos = new ArrayList<VideoConstant>();
try {
for (int index = 0; index < albumJSONObject.length(); index++) {
VideoConstant video = new VideoConstant();
JSONObject itemJsonObject;
itemJsonObject = albumJSONObject.getJSONObject(albumIdJSONArrayList.get(index)
.toString());
MyLog.d(TAG, "string=" + albumIdJSONArrayList.get(index).toString());
video.mAlbumId = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.ID);
video.mAtitle = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.TITLE);
video.mEpisodeCount = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.UPDATE_SET);
video.mTvSets = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.TV_SETS);
video.mDesc = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.DESCRIPTION);
video.mCid = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.CATEGORY_ID);
video.mImg = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.IMG);
video.mHighimg = itemJsonObject
.optString(InterfaceParameterName.HIGH_RESO_PORT_IMG);
video.mHoriImg = itemJsonObject
.optString(InterfaceParameterName.HIGH_RESO_HORI_IMG);
video.mScore = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.SCORE);
video.mMainActors = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.MAIN_ACTOR);
video.mCreateTime = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.CREATE_TIME);
video.mDuration = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.DURATION);
video.mTag = itemJsonObject.optString(InterfaceParameterName.TAG);
MyLog.d(TAG, "id=" + video.mAlbumId + ",title=" + video.mAlbumTitle + ",img="
+ video.mHighimg + ",tvsets=" + video.mTvSets);
videos.add(video);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return videos;
}
<4>. Android JSON解析库
上面介绍都是使用Android提供的原生类解析JSON,最大的好处是项目不需要引入第三方库,但是如果比较注重开发效率而且不在意应用大小增加几百K的话,有以下JSON可供选择:
Jackson
google-gson
Json-lib
大家可以去对应的官网下载并学习:)
三、 JSON vs. XML
JSON和XML就像武林界的屠龙刀和倚天剑,那么他们孰强孰弱?
XML长期执数据传输界之牛耳,而JSON作为后起之秀,已经盟主发起了挑战。
那就让他们来进行PK一下:
<1>. JSON相比XML的不同之处
没有结束标签
更短
读写的速度更快
能够使用内建的 JavaScript eval() 方法进行解析
使用数组
不使用保留字
总之: JSON 比 XML 更小、更快,更易解析。
<2>. XML和JSON的区别:
XML的主要组成成分:
XML是element、attribute和element content。
JSON的主要组成成分:
JSON是object、array、string、number、boolean(true/false)和null。
XML要表示一个object(指name-value pair的集合),最初可能会使用element作为object,每个key-value pair 用 attribute 表示:
<student name="John" age="10"/>
但如个某个 value 也是 object,那么就不可以当作attribute:
<student name="John" age="10"> <address> <country>China</country> <province>Guang Dong</province> <city>...</city> <district>...</district> ... </address> </student>
那么,什么时候用element,什么时候用attribute,就已经是一个问题了。
而JSON因为有object这种类型,可以自然地映射,不需考虑上述的问题,自然地得到以下的格式。
{
"name": "John",
"age" : 10,
"address" : {
"country" : "China",
"province" : "Guang Dong",
"city" : "..",
"district" : "..",
...
}
}
One More Thing…
XML需要选择怎么处理element content的换行,而JSON string则不须作这个选择。
XML只有文字,没有预设的数字格式,而JSON则有明确的number格式,这样在locale上也安全。
XML映射数组没大问题,就是数组元素tag比较重复冗余。JSON 比较易读。
JSON的true/false/null也能容易统一至一般编程语言的对应语义。
XML文档可以附上DTD、Schema,还有一堆的诸如XPath之类规范,使用自定义XML元素或属性,能很方便地给数据附加各种约束条件和关联额外信息,从数据表达能力上看,XML强于Json,但是很多场景并不需要这么复杂的重量级的东西,轻便灵活的Json就显得很受欢迎了。
打个比方,如果完成某件事有两种方式:一种简单的,一个复杂的。你选哪个?
我只想杀只鸡罢了,用得着牛刀?
JSON与XML相比就是这样的。
四、总结
这篇文章只是对XML和JSON这2种目前主流使用的数据格式进行了解释,并系统的学习了其中的语法及如何进行解析,同时在最好针对XML和JSON做了对比,了解其不同点和各自的优势。
期望有需要的朋友有所帮助:–)
 vue fait référence aux fichiers js
vue fait référence aux fichiers js
 Comment verrouiller l'écran sur oppo11
Comment verrouiller l'écran sur oppo11
 Comment exprimer des espaces dans des expressions régulières
Comment exprimer des espaces dans des expressions régulières
 Comment résoudre le problème car il ne peut pas démarrer
Comment résoudre le problème car il ne peut pas démarrer
 utilisation de la fonction memset
utilisation de la fonction memset
 Trois frameworks majeurs pour le développement Android
Trois frameworks majeurs pour le développement Android
 Comment accélérer les pages Web
Comment accélérer les pages Web
 Comment résoudre l'erreur http 503
Comment résoudre l'erreur http 503