Notes d'étude CodeIgniter Item5 - AR dans CI
AR (Active Record)
Lorsque AR est activé (CI3.0 est démarré par défaut et n'a aucun élément de configuration), vous pouvez utiliser la méthode get de
$this->db
Obtenir l'ensemble de résultats d'une table
[code]// AR会自动加上表前缀,因此get方法中的表名不用加上表前缀
$res = $this->db->get('user');
foreach ($res->result() as $item)
{
echo $item->name . "
";
}
Vous pouvez simplement insérer un enregistrement via la méthode insert. Les paramètres sont le nom de la table et le tableau associatif
<🎜. >
[code]$data = array('name'=>'mary', 'password'=>md5('mary'));
$result = $this->db->insert('user', $data); Modifier l'enregistrement via la méthode de mise à jour. Le premier paramètre est l'indication, le deuxième paramètre est le contenu modifié, représenté par un tableau associatif, et le troisième paramètre est la condition de requête.
[code]$data = array ('email'=>'mary@gmail.com', 'password'=>md5('123456'));
$this->db->update('user', $data, array('name'=>'mary'));Supprimer un enregistrement via la méthode de suppression. Le premier paramètre est le nom de la table et le deuxième paramètre est la condition de requête
<🎜. >
[code]$this->db->delete('user', array('name'=>'mary'));
Opération continue, pour des instructions SQL plus complexes, vous pouvez utiliser l'opération cohérente fournie par AR pour interroger
[code]$result = $this->db->select('id, name')
->from('user')
->where('id >=', 1)
->limit(3,1)
->order_by('id desc ')
->get();
Comment. pour écrire l'instruction Where dans différentes conditions de requête
[code]where('name', 'mary')或where('name =', 'mary'):表示查询条件是name字段值是mary where(array('name'=>'mary', 'id >'=>'1'));:表示查询条件有两个,name字段值是mary并且id字段值是1
[code]$this->db->last_query();
select data
Les fonctions suivantes vous aident à créer des instructions SQL SELECT.
Remarque : Si vous utilisez PHP5, vous pouvez utiliser la syntaxe de chaîne dans des situations complexes. Des descriptions détaillées sont fournies au bas de cette page.
[code]$this->db->get();
[code]$query = $this->db->get('mytable');
// Produces: SELECT * FROM mytable
[code]$query = $this->db->get('mytable', 10, 20);
// Produces: SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 20, 10 (in MySQL. Other databases have slightly different syntax)
Vous remarquerez que la fonction ci-dessus est constituée d'une variable $ query
Execution, cette $query
peut être utilisée pour afficher l'ensemble de résultats.
[code]$query = $this->db->get('mytable');
foreach ($query->result() as $row)
{
echo $row->title;
}
[code]$this->db->get_where();[code]$query = $this->db->get_where('mytable', array('id' => $id), $limit, $offset);[code]$this->db->select();
[code]$this->db->select('title, content, date');
$query = $this->db->get('mytable');
// Produces: SELECT title, content, date FROM mytable$this->db->select()
[code]$this->db->select('(SELECT SUM(payments.amount) FROM payments WHERE payments.invoice_id=4') AS amount_paid', FALSE);
$query = $this->db->get('mytable');[code]$array = array('title' => $match, 'page1' => $match, 'page2' => $match);
$this->db->like($array);
// WHERE title LIKE '%match%' AND page1 LIKE '%match%' AND page2 LIKE '%match%'
$this->db->or_like();[code]$this->db->like('title', 'match');
$this->db->or_like('body', $match);
// WHERE title LIKE '%match%' OR body LIKE '%match%'[code]$this->db->not_like();
[code]$this->db->not_like('title', 'match');
// WHERE title NOT LIKE '%match%
$this->db->or_not_like();[code]$this->db->like('title', 'match');
$this->db->or_not_like('body', 'match');
// WHERE title LIKE '%match%' OR body NOT LIKE '%match%'
$this->db->group_by();[code]$this->db->group_by("title");
// 生成: GROUP BY title[code]$this->db->group_by(array("title", "date"));
// 生成: GROUP BY title, date[code]$this->db->distinct();
[code]$this->db->distinct();
$this->db->get('table');
// 生成: SELECT DISTINCT * FROM table
$this->db->having();[code]$this->db->having('user_id = 45');
// 生成: HAVING user_id = 45
$this->db->having('user_id', 45);
// 生成: HAVING user_id = 45
你也可以把多个值通过数组传递过去:
[code]$this->db->having(array('title =' => 'My Title', 'id <' => $id));
// 生成: HAVING title = 'My Title', id < 45[code]$this->db->having('user_id', 45);
// 生成: HAVING `user_id` = 45 (在诸如MySQL等数据库中)
$this->db->having('user_id', 45, FALSE);
// 生成: HAVING user_id = 45
$this->db->or_having();[code]$this->db->order_by();
[code]$this->db->order_by("title", "desc");
// 生成: ORDER BY title DESC[code]$this->db->order_by('title desc, name asc');
// 生成: ORDER BY title DESC, name ASC[code]$this->db->order_by("title", "desc");
$this->db->order_by("name", "asc");
// 生成: ORDER BY title DESC, name ASC
Remarque : actuellement, les pilotes Oracle et MSSQL ne prennent pas en charge le tri aléatoire et seront définis par défaut sur « ASC » (ordre croissant).
[code]$this->db->limit();
[code]$this->db->limit(10); // 生成: LIMIT 10
[code]$this->db->limit(10, 20); // 生成: LIMIT 20, 10 (仅限MySQL中。其它数据库有稍微不同的语法) $this->db->count_all_results();
允许你获得某个特定的Active Record查询所返回的结果数量。可以使用Active Record限制函数,例如 where(),or_where()
, like(), or_like() 等等。范例:
[code]echo $this->db->count_all_results('my_table');
// 生成一个整数,例如 25
$this->db->like('title', 'match');
$this->db->from('my_table');
echo $this->db->count_all_results();
// 生成一个整数,例如 17插入数据
[code]$this->db->insert();
生成一条基于你所提供的数据的SQL插入字符串并执行查询。你可以向函数传递 数组 或一个 对象。下面是一个使用数组的例子:
[code]$data = array(
'title' => 'My title' ,
'name' => 'My Name' ,
'date' => 'My date'
);
$this->db->insert('mytable', $data);
// Produces: INSERT INTO mytable (title, name, date) VALUES ('My title', 'My name', 'My date')第一个参数包含表名,第二个是一个包含数据的关联数组。
下面是一个使用对象的例子:
[code]/*
class Myclass {
var $title = 'My Title';
var $content = 'My Content';
var $date = 'My Date';
}
*/
$object = new Myclass;
$this->db->insert('mytable', $object);
// Produces: INSERT INTO mytable (title, content, date) VALUES ('My Title', 'My Content', 'My Date')
第一个参数包含表名,第二个是一个对象。(原文有错:The first parameter will contain the table name, the second is an associative array of values.)
注意: 所有的值已经被自动转换为安全查询。
[code]$this->db->set();
本函数使您能够设置inserts(插入)或updates(更新)值。
它可以用来代替那种直接传递数组给插入和更新函数的方式:
[code]$this->db->set('name', $name);
$this->db->insert('mytable');
// 生成: INSERT INTO mytable (name) VALUES ('{$name}')如果你多次调用本函数,它们会被合理地组织起来,这取决于你执行的是插入操作还是更新操作:
[code]$this->db->set('name', $name);
$this->db->set('title', $title);
$this->db->set('status', $status);
$this->db->insert('mytable');
set() 也接受可选的第三个参数($escape),如果此参数被设置为 FALSE,就可以阻止数据被转义。为了说明这种差异,这里将对 包含转义参数 和 不包含转义参数 这两种情况的 set() 函数做一个说明。
[code]$this->db->set('field', 'field+1', FALSE);
$this->db->insert('mytable');
// 得到 INSERT INTO mytable (field) VALUES (field+1)
$this->db->set('field', 'field+1');
$this->db->insert('mytable');
// 得到 INSERT INTO mytable (field) VALUES ('field+1')你也可以将一个关联数组传递给本函数:
[code]$array = array('name' => $name, 'title' => $title, 'status' => $status);
$this->db->set($array);
$this->db->insert('mytable');或者一个对象也可以:
[code]/*
class Myclass {
var $title = 'My Title';
var $content = 'My Content';
var $date = 'My Date';
}
*/
$object = new Myclass;
$this->db->set($object);
$this->db->insert('mytable');更新数据
[code]$this->db->update();
根据你提供的数据生成并执行一条update(更新)语句。你可以将一个数组或者对象传递给本函数。这里是一个使用数组的例子:
[code]$data = array(
'title' => $title,
'name' => $name,
'date' => $date
);
$this->db->where('id', $id);
$this->db->update('mytable', $data);
// 生成:
// UPDATE mytable
// SET title = '{$title}', name = '{$name}', date = '{$date}'
// WHERE id = $id或者你也可以传递一个对象:
[code]/*
class Myclass {
var $title = 'My Title';
var $content = 'My Content';
var $date = 'My Date';
}
*/
$object = new Myclass;
$this->db->where('id', $id);
$this->db->update('mytable', $object);
// 生成:
// UPDATE mytable
// SET title = '{$title}', name = '{$name}', date = '{$date}'
// WHERE id = $id说明: 所有值都会被自动转义,以便生成安全的查询。
你会注意到
$this->db->where()
[code]$this->db->update('mytable', $data, "id = 4");或者是一个数组:
[code]$this->db->update('mytable', $data, array('id' => $id));
在进行更新时,你还可以使用上面所描述的 $this->db->set() 函数。
删除数据
[code]$this->db->delete();
生成并执行一条DELETE(删除)语句。
[code]$this->db->delete('mytable', array('id' => $id));
// 生成:
// DELETE FROM mytable
// WHERE id = $id第一个参数是表名,第二个参数是where子句。你可以不传递第二个参数,使用 where() 或者 or_where() 函数来替代它:
[code]$this->db->where('id', $id);
$this->db->delete('mytable');
// 生成:
// DELETE FROM mytable
// WHERE id = $id
如果你想要从一个以上的表中删除数据,你可以将一个包含了多个表名的数组传递给delete()函数。
[code]$tables = array('table1', 'table2', 'table3');
$this->db->where('id', '5');
$this->db->delete($tables);如果你想要删除表中的全部数据,你可以使用 truncate() 函数,或者 empty_table() 函数。
[code]$this->db->empty_table();
生成并执行一条DELETE(删除)语句。
[code] $this->db->empty_table('mytable');
// 生成
// DELETE FROM mytable
$this->db->truncate();
生成并执行一条TRUNCATE(截断)语句。
[code]$this->db->from('mytable');
$this->db->truncate();
// 或
$this->db->truncate('mytable');
// 生成:
// TRUNCATE mytable说明: 如果 TRUNCATE 命令不可用,truncate() 将会以 “DELETE FROM table” 的方式执行。
链式方法
链式方法允许你以连接多个函数的方式简化你的语法。考虑一下这个范例:
[code]$this->db->select('title')->from('mytable')->where('id', $id)->limit(10, 20);
$query = $this->db->get(); 以上就是CodeIgniter学习笔记 Item5--CI中的AR的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Xu Chi, fondateur de XREAL : Apple permet à tout le monde de voir l'avenir de l'informatique spatiale, et nous travaillons dur pour permettre à tout le monde de voir le présent de l'informatique spatiale.
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:55 PM
Xu Chi, fondateur de XREAL : Apple permet à tout le monde de voir l'avenir de l'informatique spatiale, et nous travaillons dur pour permettre à tout le monde de voir le présent de l'informatique spatiale.
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:55 PM
XREAL a lancé un nouveau produit - XREALBeamPro lors de la conférence de lancement de nouveaux produits d'informatique spatiale, au prix de 1 299 yuans. Selon l'introduction officielle, XREALBeamPro est un terminal informatique qui libère progressivement des applications 2D dans l'espace 3D. Equipé de lunettes XREALAR, il formera un « système informatique spatial AR grand public complet » et minimisera le coût de migration des utilisateurs depuis le téléphone mobile. côté. En termes de design, XREALBeamPro ressemble à un smartphone, mais ce n'est pas un produit de téléphonie mobile, mais un terminal informatique spatial équipé d'un écran tactile. Il se positionne officiellement comme un « terminal informatique spatial AR comme un téléphone ». Lors de la conférence de presse, le fondateur et PDG de XREAL, Xu Chi, a exprimé son enthousiasme pour les capacités de BeamPro.
 Comment implémenter un middleware personnalisé dans CodeIgniter
Jul 29, 2023 am 10:53 AM
Comment implémenter un middleware personnalisé dans CodeIgniter
Jul 29, 2023 am 10:53 AM
Comment implémenter un middleware personnalisé dans CodeIgniter Introduction : Dans le développement Web moderne, le middleware joue un rôle essentiel dans l'application. Ils peuvent être utilisés pour exécuter une logique de traitement partagé avant ou après que la demande atteigne le contrôleur. CodeIgniter, en tant que framework PHP populaire, prend également en charge l'utilisation de middleware. Cet article explique comment implémenter un middleware personnalisé dans CodeIgniter et fournit un exemple de code simple. Présentation du middleware : le middleware est une sorte de requête
 Comment créer des applications AR/VR en utilisant PHP
Jun 11, 2023 pm 07:22 PM
Comment créer des applications AR/VR en utilisant PHP
Jun 11, 2023 pm 07:22 PM
Avec le développement de l’AR (Réalité Augmentée) et de la VR (Réalité Virtuelle), ces deux technologies sont devenues un élément important de l’innovation et de l’expérience. Avec la popularité de PHP en tant que langage de programmation réseau, PHP est devenu un choix réalisable pour développer des applications AR/VR. Cet article explique comment utiliser PHP pour créer des applications AR/VR. 1. Comprendre les technologies AR et VR Avant de commencer à créer des applications AR/VR, nous devons comprendre les différentes technologies et bibliothèques. La technologie AR permet à des objets ou informations virtuels d'interagir avec des environnements du monde réel. V
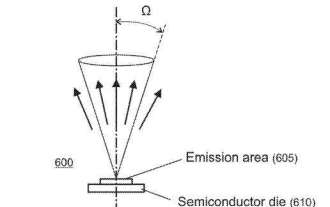 Microsoft explore les brevets AR/VR utilisant des réseaux de microlentilles pour la manipulation de l'angle de rayon principal à large plage
Sep 30, 2023 pm 09:29 PM
Microsoft explore les brevets AR/VR utilisant des réseaux de microlentilles pour la manipulation de l'angle de rayon principal à large plage
Sep 30, 2023 pm 09:29 PM
(Nwe le 26 septembre 2023) Microsoft estime que MicroLED présente les caractéristiques d'une petite taille, d'un poids léger, d'une luminosité élevée et d'une densité d'emballage élevée, et peut être particulièrement adapté aux appareils montés sur la tête qui nécessitent une haute résolution, une petite taille et un poids léger. . moniteur. Dans une demande de brevet intitulée « Microlentilles fournissant une manipulation de l'angle de rayon principal à large plage pour l'affichage sur panneau », Microsoft a présenté une microlentille qui permet une manipulation de l'angle de rayon principal à large plage pour l'affichage sur panneau, ainsi qu'un système d'affichage configuré avec le réseau de microlentilles. Chaque microlentille du réseau correspond à un pixel respectif du panneau d'affichage. Les microlentilles sont configurées en fonction de leur
 Middleware CodeIgniter : accélère la réactivité des applications et le rendu des pages
Jul 28, 2023 pm 06:51 PM
Middleware CodeIgniter : accélère la réactivité des applications et le rendu des pages
Jul 28, 2023 pm 06:51 PM
Middleware CodeIgniter : accélère la réactivité des applications et le rendu des pages Présentation : À mesure que les applications Web continuent de gagner en complexité et en interactivité, les développeurs doivent utiliser des solutions plus efficaces et évolutives pour améliorer les performances et la réactivité des applications. CodeIgniter (CI) est un framework léger basé sur PHP qui fournit de nombreuses fonctionnalités utiles, dont le middleware. Le middleware est une série de tâches effectuées avant ou après que la demande parvienne au contrôleur. Cet article explique comment utiliser
 La technologie Mojie a fait ses débuts au CES pour la première fois, menant la tendance de l'innovation AR !
Jan 14, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
La technologie Mojie a fait ses débuts au CES pour la première fois, menant la tendance de l'innovation AR !
Jan 14, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Du 9 au 12 janvier, plus de 4 000 exposants étaient réunis au CES, le « Spring Festival Gala » de l'électronique grand public. En tant qu'entreprise innovante dans le domaine de la RA grand public, Mojie Technology a participé au CES pour la première fois, démontrant pleinement la forte force des entreprises chinoises de RA en matière de dispositifs de base, de solutions de machines complètes et de services personnalisés. Sur le stand Mojie, les lunettes AR basées sur un guide de lumière à diffraction en résine binoculaire + MicroLED ont été exposées, ce qui a suscité l'intérêt de nombreux visiteurs, qui les ont essayées et expérimentées leurs fonctions. Ces lunettes AR possèdent de nombreuses fonctionnalités pratiques. Premièrement, le porteur peut visualiser le contenu du texte en temps réel à travers la lentille des lunettes, ce qui rend la lecture plus pratique. Deuxièmement, les lunettes disposent de microphones intégrés qui peuvent collecter des informations vocales et les convertir en texte dans la langue spécifiée grâce à la fonction de traduction instantanée.
 NTT QONOQ Devices dévoile les lunettes XR sans fil Mirza pour smartphones
Sep 09, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
NTT QONOQ Devices dévoile les lunettes XR sans fil Mirza pour smartphones
Sep 09, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
NTT QONOQ Devices a dévoilé les lunettes XR sans fil Mirza pour smartphones, évitant ainsi aux utilisateurs d'avoir à se débattre avec des cordons. Les lunettes peuvent afficher du contenu AR virtuel dans des espaces du monde réel comme Pokemon Go ou le contenu de leur téléphone sur un grand écran virtuel.
 Comment utiliser le générateur de requêtes de base de données (Query Builder) dans le framework CodeIgniter
Jul 28, 2023 pm 11:13 PM
Comment utiliser le générateur de requêtes de base de données (Query Builder) dans le framework CodeIgniter
Jul 28, 2023 pm 11:13 PM
Introduction à la méthode d'utilisation du générateur de requêtes de base de données (QueryBuilder) dans le framework CodeIgniter : CodeIgniter est un framework PHP léger qui fournit de nombreux outils et bibliothèques puissants pour faciliter les développeurs dans le développement d'applications Web. L'une des fonctionnalités les plus impressionnantes est le générateur de requêtes de base de données (QueryBuilder), qui fournit un moyen concis et puissant de créer et d'exécuter des instructions de requête de base de données. Cet article expliquera comment utiliser Co






