
Reprendre les bases de Java (12) : Résumé du type de Java String le plus couramment utilisé
Présentation de la classe String
Caractère char Un caractère '' String String Un ou plusieurs ""
2. String est un type de données de référence et appartient au package java.lang
.3. Table de codage ascii unicode
4. Le langage Java prend en charge l'unicode
2. Méthode de construction
空构造 public String()
String s1=new String();
System.out.println(s1);
输出结果为空。
参数为字符串
public String(String s)
String s2=new String("hello"); //String s2="hello";
System.out.println(s2);
输出结果为 hello
参数为字节数组
public String( byte[] bytes ) 转换
byte[] t={97,98,99,'d'}; //byte b='d';
String s3=new String(t);
System.out.println(s3);
输出结果为 abcd 它是将byte数组类型转化为ASCII
表对应的字符
参数为字符数组 public String( char[] value ) 转换
char[] c={'a','b','c',100}; //char d=100;
String s4=new String(c);
System.out.println(s4);
输出结果为 abcd 它是将char数组类型转化为ASCII
表对应的字符。3. String est un type de référence spécial
1. 它支持两种写法:
String s="hello"; //s也是对象
String s=new String("hello");
注意:
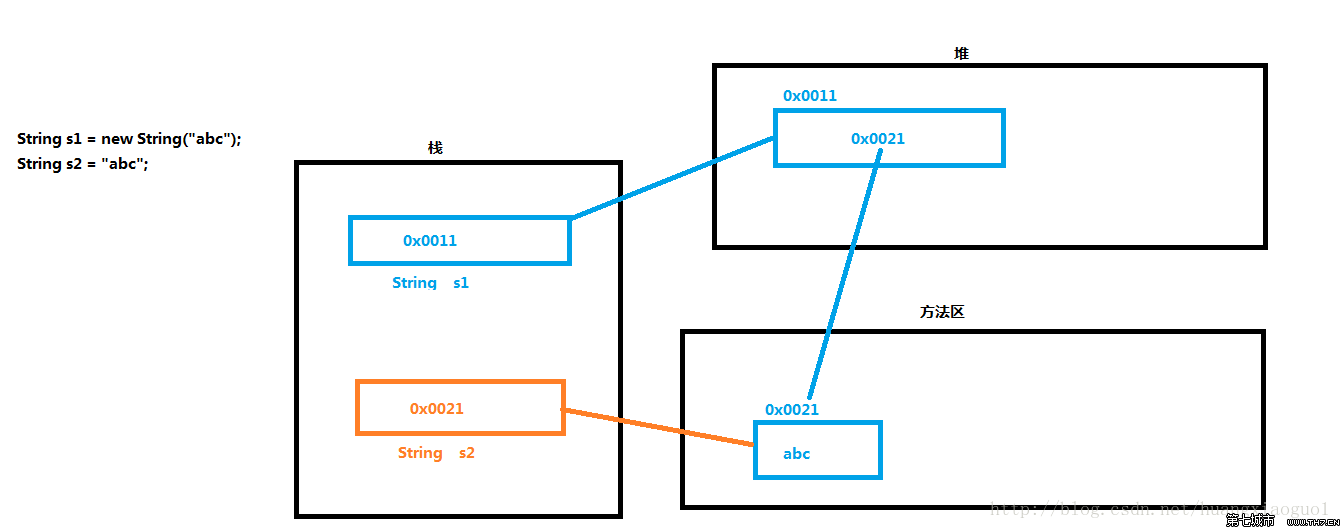
String s1="hello";String s2="hello";这时有三个对象
s1、s2、hello2. 画内存分配图carte d'allocation de mémoire de la nouvelle chaîne

Allocation de mémoire de manière nouvelle et non nouvelle
Vide
3. Une constante de chaîne peut être utilisée directement comme objet
4.
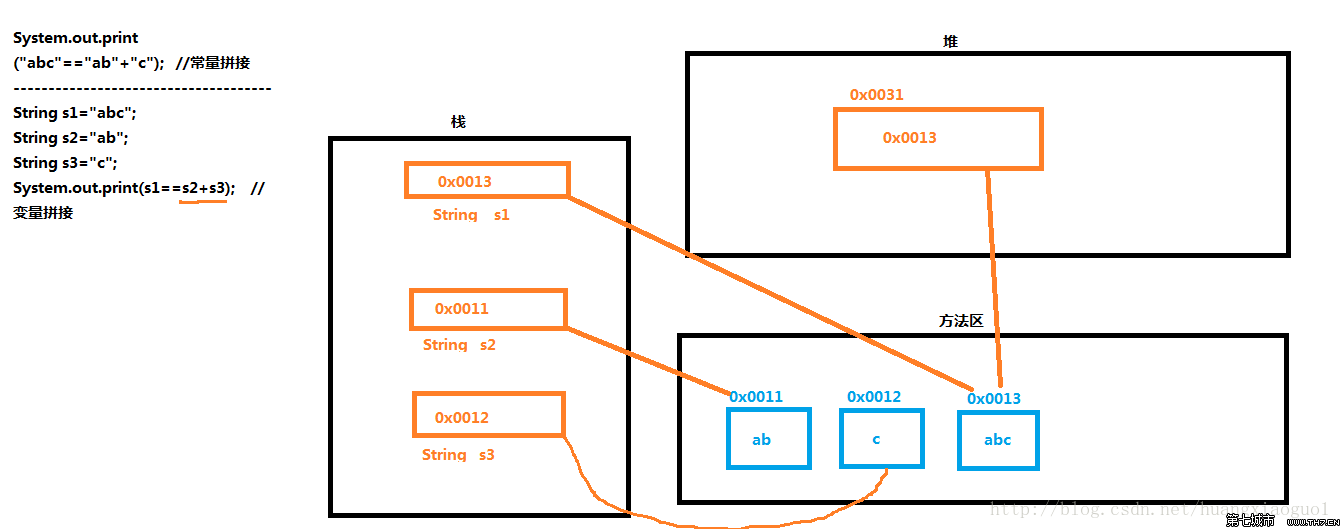
Les cordes d'épissage ne peuvent épisser que des cordes
2. Si une chaîne est épissée avec une non-chaîne, Java convertira automatiquement la non-chaîne en chaîne, puis la raccordera
3. Remarque : lors de l'utilisation de chaînes épissées Allocation de mémoire map (Les objets String sont immuables)
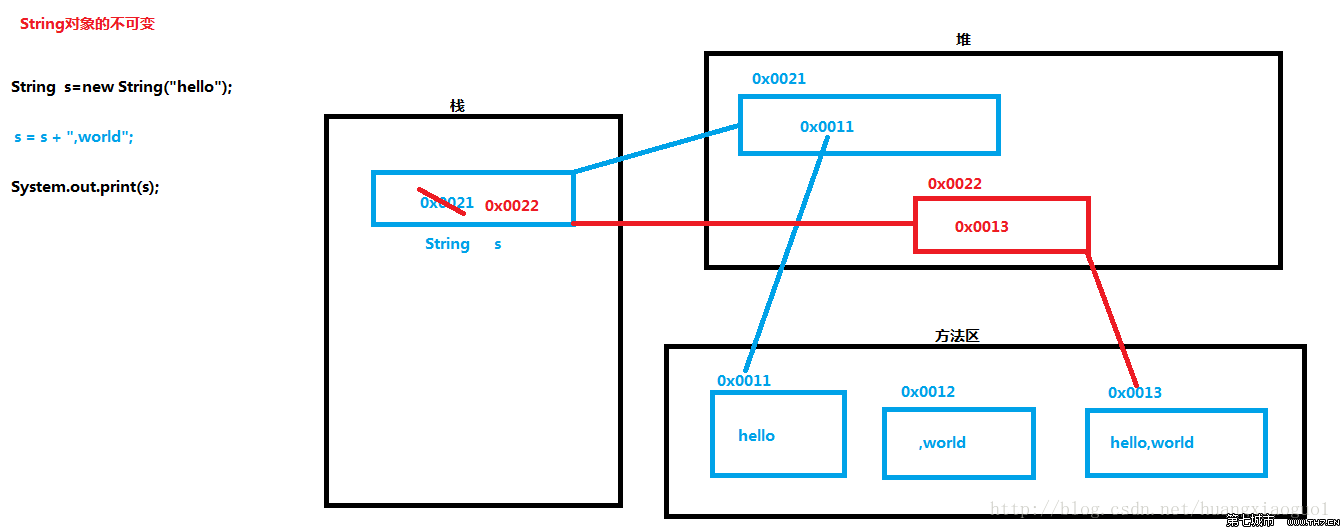
4. Même si l'objet String n'est pas nouveau, alors le caractère Lorsque les chaînes sont épissées, un nouvel espace mémoire est ouvert dans le tas à chaque fois
5 Lorsque les constantes de chaîne sont épissées, un nouvel espace mémoire n'est pas ouvert dans le tas (souligné)
5. Méthodes pour déterminer les fonctions liées
boolean equals(Object obj)
String s1="hello";
String s2=new String("HellO");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
输出结果为 false false ;
equals比较的是内容区分大小写boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str)String s3="hello";
String s4="Hello";System.out.println(s3==s4);
System.out.println(s3.equalsIgnoreCase(s4));
輸出結果為 false true ;
equalsIgnoreCase比较的是内容不区分大小写boolean contains(String str)String s1="hello";
System.out.println(s1.contains("ho"));输出结果为 false 这个方法是看“hello”中是否包含ho
记得不能分开,如果是he的话结果就是 trueboolean startsWith(String str)System.out.println(s1.startsWith("he"));
输出结果是:true
这个方法是求输入的这个字符串是否
以你定义的这个字符串开头的!
这里就是看 “hello”是否以he开头
如果换成e 结果就为false了。
boolean endsWith(String str)
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("llo"));
输出结果为:true 这个方法是求输入的这个字符串是否
以你定义的这个字符串结尾的!
这里就是看 “hello”是否以lo结尾
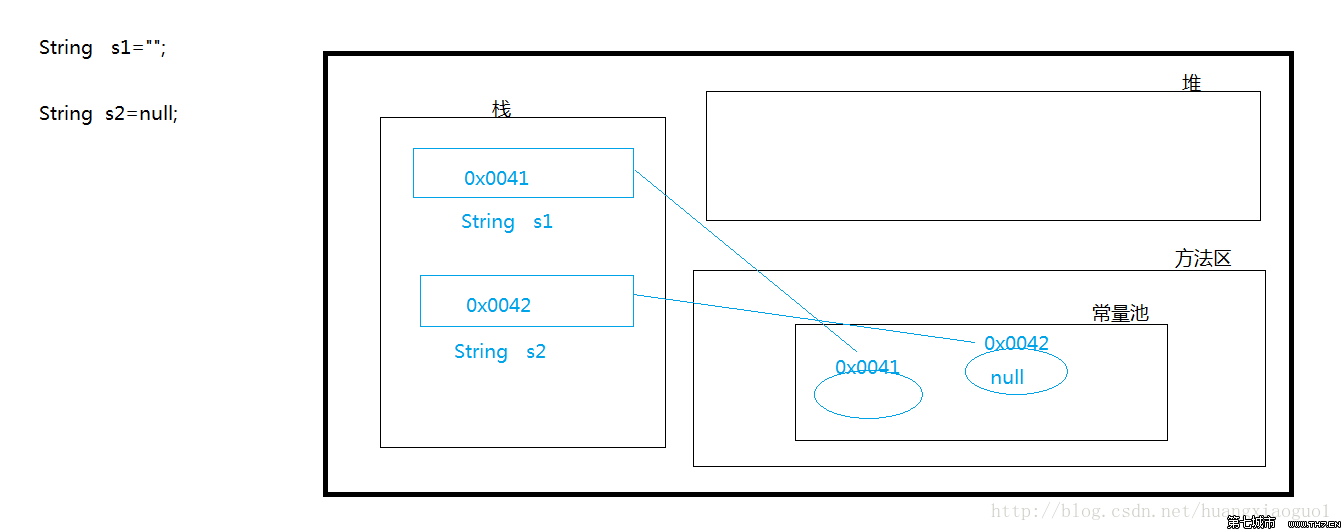
如果换位ll 结果就为false了。boolean isEmpty() "" null
s1="";System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());
输出结果为:true 这个方法是看 s1这个字符串是否为""
如果是就为true
注意:null1.null在Java中是作为常量存在的2.它表示对象不存在3.一个是可以作为初始值来用,一个是可以加快垃圾回收的速度6. Méthodes pour obtenir les fonctions liées
int length()
String s1="heloool";System.out.println(s1.length());
输出结果为:7
这个方法是来求一个字符串的长度的。
char charAt(int index)
System.out.println(s1.charAt(0));
输出结果为 h 这个方法是用来输入字符串的某个字符的地址坐标来
输出这个坐标所对应的值;如果输入2的话输出应该为l。
int indexOf(int ch) 和int indexOf(String str);
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("he"));
输出结果为 0 这个方法是用来寻找输入的字符串(例如he)在当前字
符串(heloool)中首次出现的,首个字符的位置。
注意he要连写,并且不能为ho这种形式 他们都会
输出 -1
int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)和int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("l",4));
输出结果为 6 这个方法是用来寻找输入的字符串(例如l)在当前字
符串(heloool)中你定义的从哪个地址坐标(4)开始
出现的,首个字符的位置。
String substring(int start)和
String substring(int start,int end)
////
String substring(int start)
System.out.println(s1.substring(3));
输出结果为:oool 这个方法是为了求出 s1这个字符串中 从3开始
包括(3)这个坐标,开始输出字符串,一直到结尾。
//
String substring(int start,int end)
System.out.println(s1.substring(2,5));
输出结果为 loo 这个方法是为了求出 s1这个字符串中 从2开始
包括(2)这个坐标,开始输出字符串,一直到5(不包括5
这个坐标)。
注意:java有两个原则 一、就近原则;二、顾前不顾后原则。7. Méthodes pour convertir les fonctions
byte[] getBytes()
String s1="abcde";
byte[] b=s1.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
System.out.println(b[i]);}输出结果为:97 98 99 100 101(竖着写)
这个方法表示将一个String 类型的字符串转化为:byte
类型的数组;对应的值为ASCII表值。
char[] toCharArray()
char[] c=s1.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
System.out.println(c[i]);}输出结果为:a b c d e (竖着写)这个方法表示将一个字符转变为数组 。
注意 数组类型为charstatic String valueOf(char[] chs) //相当于 new String(char[] c)
String s2=String.valueOf(c);
System.out.println(s2);输出结果为:abcde
这个方法是将c这个数组转化为字符串
static String valueOf(基本数据类型 i)
int j=100;
s2=String.valueOf(j); //s2=j+"";
System.out.println(s2+100); 输出结果为:100100 这个方法是将基本数据类型转化为字符串。
注意 : 我们一般将基本数据类型转化为字符串类型一般用
s2=j+"";String toLowerCase()
String s3="hElLo";
System.out.println(s3.toLowerCase());输出结果为:hello
这个方法是将字符串统一为小写形式。
String toUpperCase()System.out.println(s3.toUpperCase());输出结果为:HELLO
这个方法是将字符串统一为大写形式。
String concat(String str) “+”
String s4=s3.concat(",world");
System.out.println(s4);
输出结果为:hElLo,world
这个方法是将字符串进行拼接。8. Autres fonctions de la classe String
替换String replace(String old,String new)
String s1="helloe";
s1=s1.replace("l", "123");
System.out.println(s1);输出结果为:he123123oe
这个方法是将字符串中的l全部用123来替换。分割
String[] split(String regex)
String s2="abcdeffcdtt";
String[] ss=s2.split("cd");
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
System.out.println(ss[i]);
}输出结果为:ab eff tt(竖着写)
这个方法是从cd分割,且不要cd 其前与后都
分别存入数组。
去除字符串两端的空格
String trim()
String s3=" he llo world ";
s3=s3.trim();
System.out.println(s3);输出结果为:he llo world
这个方法是将s3字符串两端的空格去掉!
s3=s3.replace(" ", "");
System.out.println(s3); 输出结果为:helloworld
注意: 用""来替换" " 这样就起到了删除效果补充:
int lastIndexOf(int ch)int lastIndexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)int lastIndexOf(String s)
String s4="hello";
System.out.println(s4.indexOf("l")); //输出为2 这个是从前向后找
System.out.println(s4.lastIndexOf("l")); //输出为3 这个是从后向前找!
int lastIndexOf(String s,int fromIndex)Ce qui précède est le résumé de Retrouver les bases de Java (12) : les plus couramment utilisées type de chaîne dans le contenu Java, veuillez faire attention au site Web PHP chinois (www.php.cn) pour plus de contenu connexe !