
1) Copiez le package jar dans le répertoire du projet
2) Ajoutez le package jar à la variable d'environnement buildpath du projet afin que le chemin de classe soit également cohérent avec le buildpath Cohérent, permettant au chargeur de classe de charger facilement des sous-classes spécifiques
3) Chargez de manière réfléchie la classe de pilote et le pilote sera automatiquement enregistré4) Obtenez la connexion via le gestionnaire de pilotes.
Créer le fichier jdbc.properties sous le projet en cours dont le contenu est le suivant (les quatre paramètres requis pour se connecter aux bases de données Oracle et MySql sont : chargement du driver, obtention de l'IP et du port pour se connecter à la base de données), nom d'utilisateur, mot de passe), le but est de faciliter les appels et les modifications !
#driverClass = oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver #url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl #user = scott#password = tigerdriverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/companyuser = root password = 123456
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 获取连接
* 1) 把jar包复制到项目目录下
* 2) 把jar包加入项目的buildpath环境变量中, 使得classpath也和buildpath一致, 让类加载器便于加载具体子类
* 3) 反射加载驱动程序类, 会自动注册驱动程序
* 4) 通过驱动程序管理器获取连接.
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class DriverTest {
// 使用Properties类对象的getPropety方法与FileInputStream方法获取文件中的内容,从而创建Connection对象
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
}Puisque chaque opération jdbc doit établir une connexion, nous mettons la méthode d'établissement de la connexion et la méthode de fermeture de la ressource comme méthodes fixes dans JdbcUtil classe pour une utilisation facile :
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtil {
// 获取建立连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
// 关闭资源
public static void close(Connection connection) {
close(connection, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
close(connection, statement, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}La connexion est établie avec succès. Nous pouvons maintenant communiquer avec la base de données. Pour communiquer avec la base de données, nous devons d'abord utiliser la classe Statement. créez une classe User pour communiquer avec la base de données entreprise créée dans la classe Statement Correspondant à la table user :
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class User {
private String user;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String user, String password) {
super();
this.user = user;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [user=" + user + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}Utilisez Statement pour créer la table user. et insérez trois lignes de données :
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
// 使用Statement执行创建user表,并插入三行数据
public class StatementTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();// 获取执行体对象
// 执行SQL
// 创建user表
String sql = "create table if not exists user(user varchar(50), password varchar(100))";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 执行的DDL语句, 还可以执行DML
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('admin','admin')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user1','user1')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user2','123456')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, statement);
}
}
}Cependant, La déclaration présente inconvénients : elle nécessite non seulement épeler les instructions SQL, mais a également le problème de l'injection SQL. Les problèmes spécifiques sont reflétés dans le petit exemple suivant
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestStatement {
// 弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题
@Test
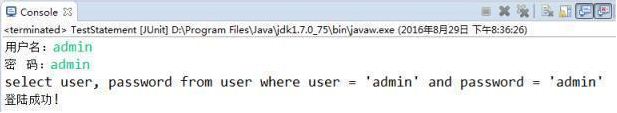
public void testLogin() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("密 码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
String sql = "select user, password from user where user = '"
+ userName + "' and password = '" + password + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
User user = get(sql, User.class);
if(user != null){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else{
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
public <T> T get(String sql, Class<T> clazz) {// (sql, Customer.class)
T t = null;
Connection conn = null;
Statement stam = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
stam = conn.createStatement();
rs = stam.executeQuery(sql);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// //1. 获取列的名称
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 1. 获取列的别名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 注意:
// 获取结果集中(相当于数据表)列的名称(别名)
// 2. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(columnName);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 注意:反射根据Java中类的属性获取Field对象
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//JDBCUtils.close(rs, stam, conn);
}
return t;
}
}
Pour cela. programme, nous devons utiliser le nom d'utilisateur correct et le mot de passe correspondant pour nous connecter avec succès Grâce au programme ci-dessus, nous pouvons connaître le nom d'utilisateur et les mots de passe sont :
----- -- ----------
| utilisateur | mot de passe
------- -------- --
| administrateur |
| utilisateur1 |
|
------- ----------
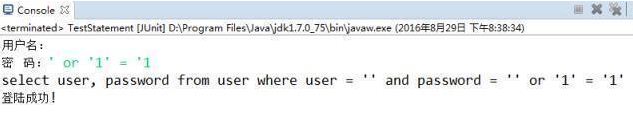
Afin d'éviter les problèmes d'injection SQL, nous devons utiliser sa sous-classe PreparedStatement pour précompiler le corps d'exécution. Ensuite, nous pratiquerons PreparedStatement :
// Écrire une classe Customer, incluant les attributs nom, sexe, téléphone
Utiliser l'objet exécutable PreparedStatment dans la classe de test pour créer le tableau correspondant et insérer 2 données.
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String gender;
private String phone;
public Customer(String name, int age, String gender, String phone,) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Customer() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", phone=" + phone + "]";
}
}public class PreparedStatementTest {
@Test
public void exer1() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "create table if not exists customer(name varchar(30), gender enum('男','女') default '男', phone varchar(20))";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement); // 在获取新的预编译对象前,一定要先关闭原来的.
String sql2 = "insert into customer(name, gender, phone) values(?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); // 要想重新执行新的SQL,必须再次预编译
preparedStatement.setString(1, "张三");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "13343493434");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
preparedStatement.setString(1, "李四");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "1322243434");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
// 并通过客户端验证.
}
}Ajoutez à chaque fois le même code que ci-dessus. Ici, nous définissons une opération de mise à jour universelle et la stockons dans la classe CommonUtil en tant qu'opération de mise à jour universelle pour les classes d'outils. L'implémentation spécifique est la suivante :
public class PreparedStatementTest {
// 在Customer类中添加属性int age,double weight,给Customer表中添加对应的列,并添加记录
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add age int after name";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "alter table customer add weight double";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 50);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "134234234234");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 98.5);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 添加记录
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add birthdate date";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "赵六");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 60);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "13882342323");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 40);
preparedStatement.setString(6, "1960-2-3");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 再添加记录
@Test
public void test5() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "张七");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 20);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "1343434343");
preparedStatement.setObject(5, 58.8);
preparedStatement.setObject(6, "1980-3-8");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (rows == 1) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
}package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class CommonUtil {
/**
* 通用更新操作
* @param sql 一个可以包含?的SQL语句
* @param values SQL中有多少个?,可变参数就有多少个具体值
* @return 更新以后影响的记录数
*/
public static int commonUpdate(String sql, Object... values) throws FileNotFoundException,
ClassNotFoundException, IOException,
SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection(); // 获取连接
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 把带有?的SQL编译
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) { // 可变参数的长度就是?的个数
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, values[i]); // 统一给所有的?替换成具体的值
}
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 替换完?或没有?, 执行更新操作
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement); // 关闭资源
}
}
}package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.util.List;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ResultSetTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
// select * from customer; 结果如下
/*
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
| name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
| 张七 20 | 女 | 1343434343 | 58.8 | 1980-03-08 |
| 张九 | 40 | 男 | 1349932423 | 78.2 | 1977-08-08 |
| 张三 | 3 | 女 | 1332324234 | 70 | 1979-08-08 |
+------+------+--------+------------+--------+------------+
*/
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 调用PreparedStatement对象的executeQuery方法产生ResultSet对象
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
System.out.println(resultSet);
while (resultSet.next()) { // 根据列的<span style="color:#ff0000;">序号</span>,
先检测当前游标的下一行是否有数据, 如果有数据则移动游标,并返回true, 如果没有数据,直接返回false
String name = resultSet.getString(1); // 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第1列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt(2);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第2列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString(3);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第3列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString(4);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第4列的值
double weight = resultSet.getDouble(5);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第5列的值
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate(6);// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的第6列的值
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age + "\t" + gender + "\t" + phone + "\t" + weight + "\t" + birthDate);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 我们改变查询列名的顺序进行查询操作,使用下标不能实现了,我们需要根据虚表中的<span style="color:#ff0000;">列名</span>
进行查询,并将查询结果封装成对象,添加到list集合中
@Test
public void test2() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
List<Customer> list = new ArrayList<Customer>();
// 基于虚表的结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("custName");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为name列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为age列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为gender列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
double weight = resultSet.getDouble("weight");
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthDate); // 封装成对象 O/R mapping
list.add(customer);
}
// 遍历集合
for (Customer cust : list) {
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 我们改变查询列名的顺序进行查询年龄大于任意数的操作,使用下标不能实现了,我们需要根据<span style="color:#ff0000;">虚表中的列名</span>
进行查询,并将查询结果封装成对象,添加到list集合中
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer where age > ?";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
prepareStatment.setObject(1, 20);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
List<Customer> list = new ArrayList<Customer>();
// <span style="color:#ff0000;">基于虚表的结果集</span>
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("custName");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的
<span style="color:#ff0000;">虚表</span>中名字为name列的值
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为age列的值
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");// 获取到的是当前游标指向的行的虚表中名字为gender列的值
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
double weight = resultSet.getDouble("weight");
Date birthDate = resultSet.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthDate); // 封装成对象 O/R mapping
list.add(customer);
}
// 遍历集合
for (Customer cust : list) {
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
// 获取查询结果,若查询结果并没有类与其对应,就需要获取虚表的表结构进行查询操作的打印输出
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatment = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
// name | age | gender | phone | weight | birthdate |
String sql = "select name custName, gender, age, weight, phone, birthdate birth from customer";
prepareStatment = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = prepareStatment.executeQuery();
/*
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
| custName | gender | age | weight | phone | birth |
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
| 张七 | 女 | 20 | 58.8 | 1343434343 | 1980-03-08 |
| 张九 | 男 | 40 | 78.2 | 1349932423 | 1977-08-08 |
| 张三 | 女 | 30 | 70 | 1332324234 | 1979-08-08 |
+----------+--------+------+--------+------------+------------+
*/
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); // 获取虚表的表结构对象
int cols = metaData.getColumnCount(); // 获取虚表共有多少列
//System.out.println(cols);
String colName = metaData.getColumnName(3);// 获取基表的列名, 参数中的是第几列
//System.out.println(colName);
colName = metaData.getColumnName(6);// 获取基表列名, 参数中的是第几列
//System.out.println(colName);
String colLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(6); // 获取虚表列名, 参数是第6列
//System.out.println(colLabel);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 列的索引总是从1开始
System.out.print(columnLabel + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
while (resultSet.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 先获取列的别名
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); // 根据列的别名再获取对应的值
System.out.print(value + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, prepareStatment, resultSet);
}
}
}Ce qui précède est le contenu de l'implémentation du code spécifique à Jdbc, plus Pour le contenu associé, veuillez faire attention au site Web PHP chinois (www.php.cn) !