
Contexte (background) est une partie très importante du CSS et l'une des connaissances de base du CSS Passons maintenant en revue les 5 attributs en CSS2 et les 3 nouveaux en CSS3. attributs et 2 fonctions.
La famille background (background) se compose de 5 attributs d'arrière-plan principaux en CSS2, qui sont :
background-color 指定填充的背景颜色 background-image 引用图片作为背景图 background-position 指定元素背景图片的位置 background-repeat 决定背景图是不是平铺 background-attachment 背景图是否滚动
Si vous voulez connaître l'identité détaillée des cinq membres majeurs de la famille, si vous voulez connaître les détails, trouvez vite un siège et asseyez-vous et écoutez mes vantardises tranquillement !
Ce membre ne peut remplir l'arrière-plan qu'avec une couleur unie.
background-color: colorName ;
colorName的取值: (1)颜色名 : red、green、blue、skyblue…… (2)rgb() : rgb(255,255,255)、rgb(12,202,29)…… (3)十六进制颜色值 : #000000、#ffffff、#ff6600…… 特别取值(默认): (4)透明 : transparent; //背景透明
Ce membre vous permet de spécifier une image comme arrière-plan.
background-image:url(imagePath) ; //imagePath指图片路径(相对路径和绝对路径)
Bonne pratique : utilisez-le en conjonction avec (background-color) pour garantir que la couleur d'arrière-plan peut être remplie dans les situations suivantes :
a> 图片出不来(可能路径错、图片不存在); b> 图片被误删除; c> 图片在不平铺的情况下覆盖不了整个盒子;
Lors de la définition d'une image d'arrière-plan, le membre mosaïquera l'image horizontalement et verticalement pour couvrir toute la boîte par défaut.
background-repeat: propertyValue ; //propertyValue指属性值
propertyValue的取值: (1)repeat : (默认)平铺 (2)no-repaet : 不平铺 (3)repeat-x : 水平方向平铺 (4)repeat-y : 垂直方向平铺
background-position background positionnement
Ce membre contrôle la position de l'image de fond dans la boîte, c'est-à-dire : la position du coin supérieur gauche de l'image de fond par rapport au coin supérieur gauche de la boîte.
background-position:X-coordinate Y-coordinate ; //(水平方向坐标 垂直方向坐标)
属性的取值: (1)百分比:10% …… (2)像素值:10px …… (3)方位名词: 水平方向:left right center 垂直方向:top bottom center
Il existe trois expressions de valeurs par défaut :
background-position: left top ; background-position: 0px 0px ; background-position: 0% 0% ;
Remarque :
Lors de l'utilisation de pourcentages pour le positionnement en arrière-plan, le navigateur utilise une case Le La valeur en pourcentage de la taille est utilisée pour définir la position de l'image. Par exemple :
background-position: 40% 50% ; 40%指:背景图在水平方向40%的位置,对应到该盒子水平方向40%的位置 50%指:背景图在垂直方向50%的位置,对应到该盒子垂直方向50%的位置
background-attachment Pièce jointe en arrière-plan
Ce membre détermine si l'image d'arrière-plan est fixe ou suit la page Le reste du défilement.
background-attachment:status //背景依附状态
status的取值: (1)scroll : 滚动(默认),背景图会随着页面其余部分的滚动而滚动 (2)fixed : 固定,当页面的其余部分滚动时,背景图不会滚动 (3)inherit: 从父元素继承background-attachment属性的设置(很少用)
background-origin) :
-webkit-background-origin: ; -moz-background-origin: ; -ms-background-origin: ; -o-background-origin: ; //加上浏览器私有前缀的写法 background-origin: ; //W3C写法,必须带上
background-origin 背景起源 background-size 背景大小 background-clip 背景裁切
-webkit-background-origin: positionArea ; //positionArea指定位区域 -moz-background-origin: positionArea ; -ms-background-origin: positionArea ; -o-background-origin: positionArea ; background-origin: positionArea ;
positionArea的取值: (1)padding-box : 背景图相对于盒子的内边距进行定位(默认) (2)border-box : 背景图相对于盒子的边框进行定位 (3)content-box : 背景图相对于盒子的内容进行定位
Contenu) remplissage (marge intérieure)
marge(outer margin); background-size background size Le membre décide La taille de l'image d'arrière-plan ne modifie cependant pas la taille originale de l'image. l'image elle-même.
-webkit-background-size: widthSize heightSize ; //(宽度尺寸 高度尺寸) -moz-background-size: widthSize heightSize ; -ms-background-size: widthSize heightSize ; -o-background-size: widthSize heightSize ; background-size: widthSize heightSize ;
background-size: auto auto ; //背景图会以自身大小呈现
background-size: 50px 50px ; //背景图会以指定值呈现
background-size: 50% 50% ; //背景图会以相对于盒子尺寸的百分比大小呈现
background-size:contain ; //在保证显示完整背景图的情况下,缩放背景图到与盒子等宽或等高
最佳实践:
图片私有特性:只要设置图片宽高中的任何一个值,图片就会等比缩放,这样可以保证图片不变形不失真;
因此,通常利用图片这一特性,在不知道图片等比例缩放尺寸的情况下,background-size只给图片宽高中的任何一个设置值,另外一个设置为auto。
该成员规定背景(背景图or背景色)的绘制区域。
-webkit-background-clip : clipArea ; //clipArea指绘制区域 -moz-background-clip : clipArea ; -ms-background-clip : clipArea ; -o-background-clip : clipArea ; background-clip : clipArea ;
clipArea的取值: (1)border-box : 背景从盒子边框开始裁切 (默认) (2)padding-box : 背景从盒子内边距开始裁切 (3)content-box : 背景从盒子内容开始裁切
瞧瞧css3都给背景家族扩展了哪两个功能!
a> 多个背景图 b> 背景渐变
感觉高大上的样子,到底是什么神秘功能,赶紧来一起分析分析!
css3中可以让一个元素盒子应用一个或多个图片作为背景,而且多个背景之间用逗号","隔开,而且图片按照书写顺序显示!
background:url(./images/01.png),url(./images/02.png),url(./images/03.png);
特别说明:
a> 从IE9开始支持;
b> 不需要加上浏览器私有前缀;
c> 如果content-box、padding-box和border-box一同设置,需要把content-box写在最前面,padding-box写在第二,border-box写在最后;
background:url(./images/01.png) content-box , url(./images/02.png) padding-box , url(./images/03.png) border-box;
注:在这里content-box、padding-box和border-box,既是background-clip的属性值,也是background-origin的属性值;
css3中可以让一个元素盒子设置背景色渐变,而不是单纯的只能设置纯色作为盒子的背景色或者指定图片作为盒子的背景!切记这里的背景渐变是背景色!背景色!不是背景图!!
又称为直线渐变。
background-image:-webkit-linear-gradient(startLocal , color1 , color2 , color3); background-image:-moz-linear-gradient(startLocal , color1 , color2 , color3); background-image:-ms-linear-gradient(startLocal , color1 , color2 , color3); background-image:-o-linear-gradient(startLocal , color1 , color2 , color3); //加上浏览器私有前缀的写法 background-image:linear-gradient(startLocal , color1 , color2 , color3); //W3C写法
color1表示颜色值:
(1)如果后面没有加上百分比或者像素值: a> color1将在起始位置显示; b> color3将在最后位置显示; c> color2将在中间等分点显示; (2)如果后面加上百分比或者像素值,表示给颜色将在盒子的该位置显示;
startLocal表示起始位置,可取值:
(1)方位名词:
top: 从上到下渐变(默认) (等价于to bottom) left:从左到右渐变 (等价于to right) right:从右到左渐变 (等价于to left) bottom:从下到上渐变 (等价于to top) top left:从左上角开始渐变
(2)度数degree:
在背景渐变中,W3C和WHATWG的标准不一样:数轴不一样,起始位置不同,旋转方向不同。因此,度数是不一样的!具体:
a> W3C中,0deg是在X轴(水平方向)的左边,顺时针旋转;
b> WHATWG中,0deg是在Y轴(垂直方向)的下方,逆时针旋转;
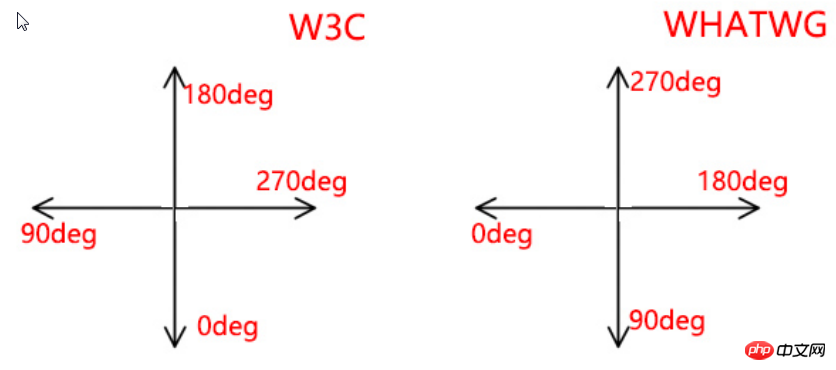
background-image:-webkit-linear-gradient(270deg, red, blue); background-image:-moz-linear-gradient(270deg, red, blue); background-image:-ms-linear-gradient(270deg, red, blue); background-image:-o-linear-gradient(270deg, red, blue); background-image:linear-gradient(180deg, red, blue); /*deg 表示degree 度数*/
特别地,W3C不支持方位名词的写法,但是支持度数的写法
又称圆心渐变
background-image:-webkit-radial-gradient(start_X start_Y , color1 , color2 , color3); background-image:-moz-radial-gradient(start_X start_Y , color1 , color2 , color3); background-image:-ms-radial-gradient(start_X start_Y , color1 , color2 , color3); background-image:-o-radial-gradient(start_X start_Y , color1 , color2 , color3); //加上浏览器私有前缀的写法 background-image:radial-gradient(start_X start_Y , color1 , color2 , color3); //W3C写法
说明:径向渐变的起始位置的取值不支持度数的写法!
在css中,可以用background复合属性在一个声明中设置所有的背景属性(包括css3新增属性),而不用单独去写某个背景属性,可以设置的背景属性:
background-color background-position background-repeat background-attachment background-image background-origin background-size background-clip
是不是感觉很牛逼,但是这里几个坑,值得我们注意!
(1)通常所说的background复合属性,是针对CSS2中5个背景属性而言,不包含CSS3中新增3个背景属性!
background: background-image background-repeat background-position background-attachment background-color ;
a> 不存在严格意义上的书写顺序(上面是老司机的书写顺序);
b> 如果某个属性没有书写,那么将自动采用默认值;
那么background复合属性,为啥不包含CSS3中的3个属性呢?理由有下:
a> css2中的背景属性,已经得到各大浏览器支持,不存在兼容性,不需要写浏览器私有前缀! b> css3中新增背景属性,存在一定兼容性,且需要带上各大浏览器的私有前缀才能得到支持!
(2)还记得CSS3给背景家族新增加多个背景图的功能么,该功能也是以background开头!
那么问题来了!
如果在一个元素中我们既要用background复合属性来简写CSS2的背景属性,又要添加多个背景图,怎么办?
a> 优先用background复合属性添加多个背景图; b> 背景属性只能单独写,不能用background复合属性来简写! c> 单独写的背景属性,必须写在background复合属性的后面!
肯定又有同学要问,为什么单独背景属性必须写在background复合属性之后?
css三大特性之层叠性!熟悉么?长江后浪推前浪,前浪死在沙滩上!
这个家族成员比较牛逼,当然也比较复杂!
(1)可以覆盖多个背景图的background复合属性!
在同一个元素中:
将导致多个背景图效果失效
p{ width:300px; height:300px; background:url(images/30/ab.png) content-box,url(images/30/xiaoming.jpg) padding-box; background-image:url(images/30/ab.png);
}在嵌套的父子级元素中:
a> 如果子元素的背景图尺寸小于父元素的尺寸,那么父元素的多个背景图效果的多余部分会显示出来!
b> 如果子元素的背景图尺寸大于等于父元素的尺寸,那么父元素的多个背景图效果会被覆盖!
p{ width:300px; height:300px; background:url(images/30/ab.png) content-box,url(images/30/xiaoming.jpg) padding-box;
}p span{ display: block; width:300px; height:300px; background-image: url(images/02.jpg);
}(2)背景渐变与背景图共用background-image属性!
a> 在同一元素中,两者不能共存,谁在前面,谁先死;
b> 在嵌套的父子级元素中,子元素的样式只会覆盖父元素的样式;
(1)插入图片占位;背景图不占位
(2)插入图片语义高,可以被搜索引擎收录到;背景图语义低,不可以被搜索引擎搜录到
(3)插入图片不容易定位;背景图容易定位,因为有background-position属性
(4)插入图片不可以用精灵图;背景图可以用精灵图
(5)插入图片有一个bug,下方带缝隙
(1)在同一个元素中,background复合属性写在前面,单独需要设置的背景属性写最后面;
理由:长江前浪推后浪,前浪死在沙滩上
(2)在同一元素中添加了多个背景图,其他背景属性只能单独写,不能在用复合属性简写;
(3)在嵌套的父子级元素中,不建议写同名属性
理由:在子元素尺寸大于等于父元素尺寸的情况下,父元素的样式会被子元素覆盖;
(4)在实际工作中,多用背景图,少用插入图片;
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 Quelle est la différence entre le protocole TCP et le protocole UDP ?
Quelle est la différence entre le protocole TCP et le protocole UDP ?
 comment créer un site Web
comment créer un site Web
 Comment intégrer des styles CSS dans HTML
Comment intégrer des styles CSS dans HTML
 WeChat Moments, deux tirets et un point
WeChat Moments, deux tirets et un point
 qu'est-ce que le framework vue
qu'est-ce que le framework vue
 Comment se connecter pour accéder à la base de données en VB
Comment se connecter pour accéder à la base de données en VB
 Moyenne du tableau
Moyenne du tableau
 Quelles sont les méthodes de détection des vulnérabilités ASP ?
Quelles sont les méthodes de détection des vulnérabilités ASP ?