 développement back-end
développement back-end
 Tutoriel C#.Net
Tutoriel C#.Net
 Explication détaillée du code graphique de Thread, Task, Async/Await, IAsyncResult en C#
Explication détaillée du code graphique de Thread, Task, Async/Await, IAsyncResult en C#
Explication détaillée du code graphique de Thread, Task, Async/Await, IAsyncResult en C#
Cet article présente principalement les connaissances pertinentes de Thread, Task, Async/Await, IAsyncResult en C#. Il a une certaine valeur de référence, jetons un oeil avec l'éditeur ci-dessous
En parlant d'asynchrone, Thread, Task, async/await, IAsyncResult, ces choses sont définitivement incontournables. Parlons-en tour à tour aujourd'hui
1. Thread
L'importance du multi-threading est que dans une application, plusieurs parties d'exécution peuvent être exécutées en même temps pour des opérations plus chronophages (pour exemple, io,httpopérations de base de données ), ou en attente d'une réponse (telle comme communication WCF) L'opération peut être effectuée en démarrant le thread d'arrière-plan séparément, afin que le thread principal ne soit pas bloqué et puisse continuer à s'exécuter en attendant que le thread d'arrière-plan soit terminé, puis en informant le thread principal, puis en effectuant le correspondant ; opération
en C# ! Il est relativement simple de démarrer un nouveau thread enstatic void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("主线程开始");
//IsBackground=true,将其设置为后台线程
Thread t = new Thread(Run) { IsBackground = true };
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine("主线程在做其他的事!");
//主线程结束,后台线程会自动结束,不管有没有执行完成
//Thread.Sleep(300);
Thread.Sleep(1500);
Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");
}
static void Run()
{
Thread.Sleep(700);
Console.WriteLine("这是后台线程调用");
}
1.1 Thread Pool
Imaginez s'il y a un un grand nombre de tâches à traiter, telles que Pour le traitement des requêtes HTTP en arrière-plan du site web, est-il nécessaire de créer un thread en arrière-plan pour chaque requête ? C'est évidemment inapproprié. Cela prendra beaucoup de mémoire, et. le processus de création fréquent affectera également sérieusement la vitesse. Alors, que dois-je faire ? Le but du pool est de résoudre ce problème. Il stocke les threads créés pour former un pool de threads (avec plusieurs threads). à traiter, s'il y a des threads inactifs dans le pool de threads (une fois l'exécution de la tâche précédente terminée, le thread ne sera pas recyclé et mis à l'état inactif), puis appelez directement l'exécution du thread dans le pool de threads ( par exemple, l'objet Applicationdans le mécanisme de traitement asp.net),
Exemple d'utilisation :for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(m =>
{
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
});
}
Console.Read();
1.2 Sémaphore .
Sémaphore est responsable de la coordination des threads et peut limiter le nombre de threads accédant à une certaine ressource Voici un exemple simple d'utilisation de la classe SemaphoreSlim : static SemaphoreSlim semLim = new SemaphoreSlim(3); //3表示最多只能有三个线程同时访问
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
new Thread(SemaphoreTest).Start();
}
Console.Read();
}
static void SemaphoreTest()
{
semLim.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("线程" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString() + "开始执行");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString() + "执行完毕");
semLim.Release();
}

2.Task
La tâche a été ajoutée dans .NET4.0. Elle a des fonctions similaires au pool de threads ThreadPool. Lorsque vous utilisez Task pour démarrer une nouvelle tâche, il sera tiré du pool de threads appelant et Thread créera un nouveau thread à chaque fois qu'il sera instancié.Console.WriteLine("主线程启动");
//Task.Run启动一个线程
//Task启动的是后台线程,要在主线程中等待后台线程执行完毕,可以调用Wait方法
//Task task = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { Thread.Sleep(1500); Console.WriteLine("task启动"); });
Task task = Task.Run(() => {
Thread.Sleep(1500);
Console.WriteLine("task启动");
});
Thread.Sleep(300);
task.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
new Thread(Run1).Start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Task.Run(() => { Run2(); });
}
}
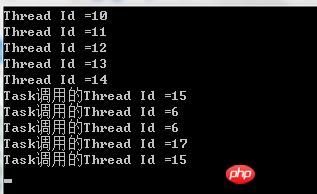
static void Run1()
{
Console.WriteLine("Thread Id =" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
static void Run2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Task调用的Thread Id =" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
2.1 Task
Console.WriteLine("主线程开始");
//返回值类型为string
Task<string> task = Task<string>.Run(() => {
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString();
});
//会等到task执行完毕才会输出;
Console.WriteLine(task.Result);
Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");
3. async/await
async/await a été introduit en C# 5.0, première utilisation :static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------主线程启动-------");
Task<int> task = GetStrLengthAsync();
Console.WriteLine("主线程继续执行");
Console.WriteLine("Task返回的值" + task.Result);
Console.WriteLine("-------主线程结束-------");
}
static async Task<int> GetStrLengthAsync()
{
Console.WriteLine("GetStrLengthAsync方法开始执行");
//此处返回的<string>中的字符串类型,而不是Task<string>
string str = await GetString();
Console.WriteLine("GetStrLengthAsync方法执行结束");
return str.Length;
}
static Task<string> GetString()
{
//Console.WriteLine("GetString方法开始执行")
return Task<string>.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "GetString的返回值";
});
}await必须用来修饰Task或Task
看看运行结果:

可以看出来,main函数调用GetStrLengthAsync方法后,在await之前,都是同步执行的,直到遇到await关键字,main函数才返回继续执行。
那么是否是在遇到await关键字的时候程序自动开启了一个后台线程去执行GetString方法呢?
现在把GetString方法中的那行注释加上,运行的结果是:

大家可以看到,在遇到await关键字后,没有继续执行GetStrLengthAsync方法后面的操作,也没有马上反回到main函数中,而是执行了GetString的第一行,以此可以判断await这里并没有开启新的线程去执行GetString方法,而是以同步的方式让GetString方法执行,等到执行到GetString方法中的Task
那么await的作用是什么呢?
可以从字面上理解,上面提到task.wait可以让主线程等待后台线程执行完毕,await和wait类似,同样是等待,等待Task
那么await是怎么做到的呢?有没有开启新线程去等待?

只有两个线程(主线程和Task开启的线程)!至于怎么做到的(我也不知道......>_<),大家有兴趣的话研究下吧!
4.IAsyncResult
IAsyncResult自.NET1.1起就有了,包含可异步操作的方法的类需要实现它,Task类就实现了该接口
在不借助于Task的情况下怎么实现异步呢?
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("主程序开始--------------------");
int threadId;
AsyncDemo ad = new AsyncDemo();
AsyncMethodCaller caller = new AsyncMethodCaller(ad.TestMethod);
IAsyncResult result = caller.BeginInvoke(3000,out threadId, null, null);
Thread.Sleep(0);
Console.WriteLine("主线程线程 {0} 正在运行.",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId)
//会阻塞线程,直到后台线程执行完毕之后,才会往下执行
result.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("主程序在做一些事情!!!");
//获取异步执行的结果
string returnValue = caller.EndInvoke(out threadId, result);
//释放资源
result.AsyncWaitHandle.Close();
Console.WriteLine("主程序结束--------------------");
Console.Read();
}
}
public class AsyncDemo
{
//供后台线程执行的方法
public string TestMethod(int callDuration, out int threadId)
{
Console.WriteLine("测试方法开始执行.");
Thread.Sleep(callDuration);
threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId;
return String.Format("测试方法执行的时间 {0}.", callDuration.ToString());
}
}
public delegate string AsyncMethodCaller(int callDuration, out int threadId);关键步骤就是红色字体的部分,运行结果:
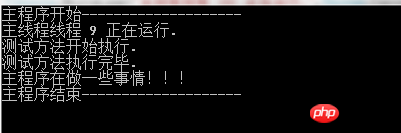
和Task的用法差异不是很大!result.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne()就类似Task的Wait。
5.Parallel
最后说一下在循环中开启多线程的简单方法:
Stopwatch watch1 = new Stopwatch();
watch1.Start();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
Console.Write(i + ",");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
watch1.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(watch1.Elapsed);
Stopwatch watch2 = new Stopwatch();
watch2.Start();
//会调用线程池中的线程
Parallel.For(1, 11, i =>
{
Console.WriteLine(i + ",线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
});
watch2.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(watch2.Elapsed);运行结果:
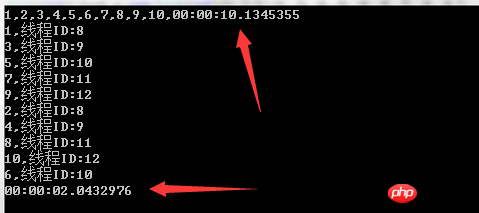
循环List
List<int> list = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
Parallel.ForEach<int>(list, n =>
{
Console.WriteLine(n);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
});Action[] actions = new Action[] {
new Action(()=>{
Console.WriteLine("方法1");
}),
new Action(()=>{
Console.WriteLine("方法2");
})
};
Parallel.Invoke(actions);Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Active Directory avec C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Active Directory avec C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide d'Active Directory avec C#. Nous discutons ici de l'introduction et du fonctionnement d'Active Directory en C# ainsi que de la syntaxe et de l'exemple.
 Sérialisation C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Sérialisation C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Guide de sérialisation C#. Nous discutons ici de l'introduction, des étapes de l'objet de sérialisation C#, du fonctionnement et de l'exemple respectivement.
 Générateur de nombres aléatoires en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Générateur de nombres aléatoires en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide du générateur de nombres aléatoires en C#. Nous discutons ici du fonctionnement du générateur de nombres aléatoires, du concept de nombres pseudo-aléatoires et sécurisés.
 Vue Grille de données C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Vue Grille de données C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Guide de la vue Grille de données C#. Nous discutons ici des exemples de la façon dont une vue de grille de données peut être chargée et exportée à partir de la base de données SQL ou d'un fichier Excel.
 Modèles en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Modèles en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide des modèles en C#. Nous discutons ici de l'introduction et des 3 principaux types de modèles en C# ainsi que de ses exemples et de l'implémentation du code.
 Nombres premiers en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Nombres premiers en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Guide des nombres premiers en C#. Nous discutons ici de l'introduction et des exemples de nombres premiers en c# ainsi que de l'implémentation du code.
 Factorielle en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Factorielle en C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide de Factorial en C#. Nous discutons ici de l'introduction de factorial en c# ainsi que de différents exemples et de l'implémentation du code.
 La différence entre le multithreading et le C # asynchrone
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
La différence entre le multithreading et le C # asynchrone
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
La différence entre le multithreading et l'asynchrone est que le multithreading exécute plusieurs threads en même temps, tandis que les opérations effectuent de manière asynchrone sans bloquer le thread actuel. Le multithreading est utilisé pour les tâches à forte intensité de calcul, tandis que de manière asynchrone est utilisée pour l'interaction utilisateur. L'avantage du multi-threading est d'améliorer les performances informatiques, tandis que l'avantage des asynchrones est de ne pas bloquer les threads d'interface utilisateur. Le choix du multithreading ou asynchrone dépend de la nature de la tâche: les tâches à forte intensité de calcul utilisent le multithreading, les tâches qui interagissent avec les ressources externes et doivent maintenir la réactivité de l'interface utilisateur à utiliser asynchrone.





