 développement back-end
développement back-end
 Tutoriel C#.Net
Tutoriel C#.Net
 Explication détaillée de la façon d'utiliser les expressions régulières .net ?
Explication détaillée de la façon d'utiliser les expressions régulières .net ?
Explication détaillée de la façon d'utiliser les expressions régulières .net ?
L'essence des expressions régulières est d'utiliser une série de modèles de caractères spéciaux pour représenter un certain type de chaîne. Les expressions régulières sont sans aucun doute l'outil le plus puissant pour traiter du texte, et la classe System.Text.RegularExpressions.Regex fournie par la bibliothèque de classes System.dll de .NET implémente des méthodes de vérification des expressions régulières. La classe Regex représente des expressions régulières immuables (en lecture seule). Il contient également diverses méthodes statiques qui permettent d'utiliser d'autres classes d'expressions régulières sans créer explicitement d'instances d'autres classes.
Explication de la représentation des caractères de l'expression régulière :
Caractère |
Explication |
caractère d'échappement, échapper un caractère avec une fonction spéciale en un caractère ordinaire, ou vice versa |
|
^ |
Correspond au début de la chaîne d'entrée |
$ |
correspond à la position finale de la chaîne d'entrée |
* |
Correspond à la sous-expression précédente zéro ou plusieurs fois |
+ |
Correspond à la sous-expression précédente Une ou plusieurs sous-expressions de |
? |
correspond au zéro ou à une sous-expression précédente La formule |
{n} |
n est un entier non négatif, correspondant à la deuxième sous-expression du n précédent |
{n,} |
n est un entier non négatif, correspondant au moins à la deuxième sous-expression de la formule n précédente |
{n,m> |
m et n sont tous deux des entiers non négatifs, où n<=m , correspond au moins n fois et au plus m fois |
? | lorsque le caractère est immédiatement suivi par d'autres restricteurs (*,+,? ,{n},{n,},{n,m}), le modèle correspondant correspond le moins possible à la chaîne recherchée |
. | correspond à n'importe quel caractère sauf "n" |
(motif) | Faites correspondre le modèle et obtenez cette correspondance |
(?:pattern) | Faites correspondre le modèle mais n'obtenez pas le résultat correspondant |
(?=motif) | Pré-vérification avant, correspond à la chaîne de recherche |
(?!modèle) | négatif au début de tout modèle de correspondance de chaîne Pour regarder vers l'avant, faites correspondre la chaîne de recherche |
x|y | <🎜 au début de toute chaîne qui ne correspond pas au motif >match x ou y. Par exemple, « z|food » peut correspondre à « z » ou « food ». '(z|f)ood' correspond à 'zood' ou 'food' |
| [xyz] | Caractère collection. Correspond à l'un des caractères contenus. Par exemple : '[abc]' peut correspondre à 'a' dans "plain" |
| [^xyz] | Jeu de caractères de valeur négative. Correspond à n’importe quel caractère contenu à l’intérieur. Par exemple : '[^abc]' peut correspondre à 'p' dans "plain" |
| [a-z] | Faire correspondre n'importe quel caractère dans la plage spécifiée. Par exemple : « [a-z] » peut correspondre à n'importe quel caractère alphabétique minuscule compris entre « a » et « z » |
| [^a-z] | correspond à tout caractère ne se trouvant pas dans la plage spécifiée. Par exemple : '[^b-z]' peut correspondre à n'importe quel caractère ne faisant pas partie de la correspondance b~z |
| b | Une limite de mot fait référence à la position entre les mots et les espaces |
| B | correspond aux limites non-mots
|
| d | correspond à un caractère numérique, équivalent à [0-9] |
| D | correspond à un caractère non numérique, équivalent à [^0-9] |
| f | correspond à un fil de formulaire |
| n | correspond à un caractère de nouvelle ligne |
| r | correspond à un caractère de retour chariot |
| s | correspond à n'importe quel caractère d'espacement, y compris les espaces, les tabulations, les sauts de formulaire, etc. |
S | correspond à n'importe quel caractère autre qu'un espace |
t | correspond à un caractère de tabulation |
v | correspond à un caractère de tabulation verticale, équivalent à x0b et cK |
w | correspond à n'importe quel caractère de mot, y compris un trait de soulignement. Équivalent à '[A-Za-z0-9_]' |
W | correspond à n'importe quel caractère autre qu'un mot , équivalent à '[^A-Za-z0-9_]' |
注意:
由于在正则表达式中“ \ ”、“ ? ”、“ * ”、“ ^ ”、“ $ ”、“ + ”、“(”、“)”、“ | ”、“ {
”、“ [ ”等字符已经具有一定特殊意义,如果需要用它们的原始意义,则应该对它进行转义,例如希望在字符串中至少有一个“ \
”,那么正则表达式应该这么写: "\\+"
Regex类常用的方法
1、静态Match方法
使用静态Match方法,可以得到源中第一个匹配模式的连续子串。
静态的Match方法有2个重载,分别是:
Regex.Match(string input, string pattern); //第一种重载的参数表示:输入、模式 Regex.Match(string input, string pattern, RegexOptions options); //第二种重载的参数表示:输入、模式、RegexOptions枚举的“按位或”组合。
RegexOptions枚举的有效值是:
1、None:指定不设置选项。表示无设置,此枚举项没有意义
2、IgnoreCase:指定不区分大小写的匹配。
3、Multiline:多行模式。更改 ^ 和 $ 的含义,使它们分别在任意一行的行首和行尾匹配,而不仅仅在整个字符串的开头和结尾匹配。表示多行模式,改变元字符^和$的含义,它们可以匹配行的开头和结尾
4、ExplicitCapture:指定有效的捕获仅为形式为 (?
5、Compiled:指定将正则表达式编译为程序集。这会产生更快的执行速度,但会增加启动时间。在调用
System.Text.RegularExpressions.Regex.CompileToAssembly(System.Text.RegularExpressions.RegexCompilationInfo[],System.Reflection.AssemblyName)方法时,不应将此值分配给
System.Text.RegularExpressions.RegexCompilationInfo.Options属性。
6、Singleline :指定单行模式。更改点 (.) 的含义,使它与每一个字符匹配(而不是与除 \n 之外的每个字符匹配)。表示单行模式,改变元字符.的意义,它可以匹配换行符
7、IgnorePatternWhitespace:
消除模式中的非转义空白并启用由 #
标记的注释。但是,System.Text.RegularExpressions.RegexOptions.IgnorePatternWhitespace值不会影响或消除字符类中的空白。表示去掉模式中的非转义空白,并启用由#标记的注释
8、RightToLeft:指定搜索从右向左而不是从左向右进行。表示从右向左扫描、匹配,这时,静态的Match方法返回从右向左的第一个匹配
9、ECMAScript:
为表达式启用符合 ECMAScript 的行为。该值只能与
System.Text.RegularExpressions.RegexOptions.IgnoreCase、System.Text.RegularExpressions.RegexOptions.Multiline和
System.Text.RegularExpressions.RegexOptions.Compiled
值一起使用。该值与其他任何值一起使用均将导致异常。表示符合ECMAScript,这个值只能和IgnoreCase、Multiline、Complied连用
10、CultureInvariant: 指定忽略语言中的区域性差异 RegularExpressions Namespace。表示不考虑文化背景
注意:Multiline在没有ECMAScript的情况下,可以和Singleline连用。Singleline和Multiline不互斥,但是和ECMAScript互斥。
2、静态的Matches方法
这个方法的重载形式同静态的Match方法,返回一个MatchCollection,表示输入中,匹配模式的匹配的集合。
3、静态的IsMatch方法
此方法返回一个bool,重载形式同静态的Matches,若输入中匹配模式,返回true,否则返回false。
可以理解为:IsMatch方法,返回Matches方法返回的集合是否为空。
Regex类常用的方法的例子:
1、字符串替换:
//例如我想把如下格式记录中的NAME值修改为YONG
string line = "ADDR=5449919;NAME=LINJIE;PHONE=45859";
Regex reg = new Regex("NAME=(.+);");
string modifiedStr = reg.Replace(line, "NAME=YONG;");
2、字符串匹配:
string line = "ADDR=5449919;NAME=LINJIE;PHONE=45859";
Regex reg = new Regex("NAME=(.+);");
//例如我想提取line中的NAME值
Match match = reg.Match(line);
string value = match.Groups[1].Value;
Console.WriteLine("value的值为:{0}", value);
3、Match方法的实例
//文本中含有"speed=68.9mph",需要提取该速度值,但是速度的单位可能是公制也可能是英制,mph,km/h,m/s都有可能;另外前后可能有空格。
string line = "lane=5;speed=68.9mph;acceleration=3.6mph/s";
Regex reg = new Regex(@"speed\s*=\s*([\d\.]+)\s*(mph|km/h|m/s)*");
Match match = reg.Match(line);
//那么在返回的结果中match.Groups[1].Value将含有数值,而match.Groups[2].Value将含有单位。
var value = match.Groups[1].Value;
var unit = match.Groups[2].Value;
Console.WriteLine("speed的值为:{0} speed的单位是:{1}", value, unit);
4、解码gps的GPRMC字符串
//就可以获得经度、纬度值 Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\$GPRMC,[\d\.]*,[A|V],(-?[0-9]*\.?[0-9]+),([NS]*),(-?[0-9]*\.?[0-9]+),([EW]*),.*");
5、提取[]里面的值
string pattern = @"(?is)(?<=\[)(.*)(?=\])";
string result = new Regex(pattern).Match("sadff[我要提取你了]sdfdsf").Value;6、提取()里面的值
string pattern= @"(?is)(?<=\()(.*)(?=\))";
string result = new Regex(pattern).Match("sad(我提取到了)dsf").Value;7、提取{}里面的值
string pattern = @"(?is)(?<=\{)(.*)(?=\})";
string result = new Regex(pattern).Match("sadff[{的d你]srd}sf").Value;
System.Text.RegularExpressions命名空间的说明
该名称空间包括8个类,1个枚举,1个委托。他们分别是:
Capture: 包含一次匹配的结果;
CaptureCollection: Capture的序列;
Group: 一次组记录的结果,由Capture继承而来;
GroupCollection:表示捕获组的集合
Match: 一次表达式的匹配结果,由Group继承而来;
MatchCollection: Match的一个序列;
MatchEvaluator: 执行替换操作时使用的委托;
RegexCompilationInfo:提供编译器用于将正则表达式编译为独立程序集的信息
RegexOptions 提供用于设置正则表达式的枚举值
Regex类中还包含一些静态的方法:
Escape: 对字符串中的regex中的转义符进行转义;
IsMatch: 如果表达式在字符串中匹配,该方法返回一个布尔值;
Match: 返回Match的实例;
Matches: 返回一系列的Match的方法;
Replace: 用替换字符串替换匹配的表达式;
Split: 返回一系列由表达式决定的字符串;
Unescape:不对字符串中的转义字符转义。
常用的正则表达式:
1、数字验证的表达式:
//数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]*$");
//n位的数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d{n}$");
//至少n位的数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d{n,}$");
//m-n位的数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d{m,n}$");
//零和非零开头的数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$");
//非零开头的最多带两位小数的数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^([1-9][0-9]*)+(.[0-9]{1,2})?$");
//带1-2位小数的正数或负数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(\-)?\d+(\.\d{1,2})?$");
//正数、负数、和小数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(\-|\+)?\d+(\.\d+)?$");
//有两位小数的正实数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{2})?$");
//有1~3位小数的正实数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{1,3})?$");
//非零的正整数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^([1-9][0-9]*){1,3}$ 或 ^\+?[1-9][0-9]*$");
//非零的负整数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\-[1-9][]0-9″*$ 或 ^-[1-9]\d*$");
//非负整数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d+$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*|0$");
//非正整数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^-[1-9]\d*|0$ 或 ^((-\d+)|(0+))$");
//非负浮点数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d+(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0$");
//非正浮点数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^((-\d+(\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$ 或 ^(-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*))|0?\.0+|0$");
//正浮点数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$");
//负浮点数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*)$ 或 ^(-(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)))$");
//浮点数
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^-?([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0)$");2、字符验证常用正式表达式:
//汉字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{0,}$");
//英文和数字
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[A-Za-z0-9]{4,40}$");
//长度为3-20的所有字符
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^.{3,20}$");
//由26个英文字母组成的字符串
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[A-Za-z]+$");
//由26个大写英文字母组成的字符串
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[A-Z]+$");
//由26个小写英文字母组成的字符串
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[a-z]+$");
//由数字和26个英文字母组成的字符串
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[A-Za-z0-9]+$");
//由数字、26个英文字母或者下划线组成的字符串
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\w+$ 或 ^\w{3,20}$");
//中文、英文、数字包括下划线
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9_]+$");
//中文、英文、数字但不包括下划线等符号
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]{2,20}$");
//可以输入含有^%&’,;=?$\”等字符
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[^%&’,;=?$\x22]+");
//禁止输入含有~的字符
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[^~\x22]+");3、一些特殊的正则表达式:
//Email地址
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$");
//域名
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62}(/.[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62})+/.?");
//InternetURL
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[a-zA-z]+://[^\s]* 或 ^http://([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]+(/[\w-./?%&=]*)?$");
//手机号码
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(13[0-9]|14[5|7]|15[0|1|2|3|5|6|7|8|9]|18[0|1|2|3|5|6|7|8|9])\d{8}$");
//电话号码(“XXX-XXXXXXX”、”XXXX-XXXXXXXX”、”XXX-XXXXXXX”、”XXX-XXXXXXXX”、”XXXXXXX”和”XXXXXXXX)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^($$\d{3,4}-)|\d{3.4}-)?\d{7,8}$");
//国内电话号码(0511-4405222、021-87888822)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"\d{3}-\d{8}|\d{4}-\d{7}");
//身份证号(15位、18位数字)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d{15}|\d{18}$");
//短身份证号码(数字、字母x结尾)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^([0-9]){7,18}(x|X)?$ 或 ^\d{8,18}|[0-9x]{8,18}|[0-9X]{8,18}?$");
//帐号是否合法(字母开头,允许5-16字节,允许字母数字下划线)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{4,15}$");
//密码(以字母开头,长度在6~18之间,只能包含字母、数字和下划线)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[a-zA-Z]\w{5,17}$");
//强密码(必须包含大小写字母和数字的组合,不能使用特殊字符,长度在8-10之间)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,10}$");
//日期格式
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}");
//一年的12个月(01~09和1~12)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(0?[1-9]|1[0-2])$");
//一个月的31天(01~09和1~31)
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^((0?[1-9])|((1|2)[0-9])|30|31)$");
//钱的输入格式:
//有四种钱的表示形式我们可以接受:”10000.00″ 和 “10,000.00”, 和没有 “分” 的 “10000” 和 “10,000”
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[1-9][0-9]*$");
//这表示任意一个不以0开头的数字,但是,这也意味着一个字符”0″不通过,所以我们采用下面的形式
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$");
//一个0或者一个不以0开头的数字.我们还可以允许开头有一个负号
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(0|-?[1-9][0-9]*)$");
//这表示一个0或者一个可能为负的开头不为0的数字.让用户以0开头好了.把负号的也去掉,因为钱总不能是负的吧.下面我们要加的是说明可能的小数部分
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]+(.[0-9]+)?$");
//必须说明的是,小数点后面至少应该有1位数,所以”10.”是不通过的,但是 “10” 和 “10.2” 是通过的
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{2})?$");
//这样我们规定小数点后面必须有两位,如果你认为太苛刻了,可以这样
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{1,2})?$");
//这样就允许用户只写一位小数。下面我们该考虑数字中的逗号了,我们可以这样
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^[0-9]{1,3}(,[0-9]{3})*(.[0-9]{1,2})?$");
//1到3个数字,后面跟着任意个 逗号+3个数字,逗号成为可选,而不是必须
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^([0-9]+|[0-9]{1,3}(,[0-9]{3})*)(.[0-9]{1,2})?$");
//备注:这就是最终结果了,别忘了”+”可以用”*”替代。如果你觉得空字符串也可以接受的话(奇怪,为什么?)最后,别忘了在用函数时去掉去掉那个反斜杠,一般的错误都在这里
//xml文件
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^([a-zA-Z]+-?)+[a-zA-Z0-9]+\\.[x|X][m|M][l|L]$");
//中文字符的正则表达式
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[\u4e00-\u9fa5]");
//双字节字符
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[^\x00-\xff] (包括汉字在内,可以用来计算字符串的长度(一个双字节字符长度计2,ASCII字符计1))");
//空白行的正则表达式,可用来删除空白行
Regex reg = new Regex(@"\n\s*\r");
//HTML标记的正则表达式
Regex reg = new Regex(@"<(\S*?)[^>]*>.*?</\1>|<.*? />");// (网上流传的版本太糟糕,上面这个也仅仅能部分,对于复杂的嵌套标记依旧无能为力)
//首尾空白字符的正则表达式
Regex reg = new Regex(@"^\s*|\s*$或(^\s*)|(\s*$)");// (可以用来删除行首行尾的空白字符(包括空格、制表符、换页符等等),非常有用的表达式)
//腾讯QQ号
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[1-9][0-9]{4,}"); //(腾讯QQ号从10000开始)
//中国邮政编码
Regex reg = new Regex(@"[1-9]\d{5}(?!\d)");// (中国邮政编码为6位数字)
//IP地址
Regex reg = new Regex(@"\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+");// (提取IP地址时有用)
//IP地址
Regex reg = new Regex(@"((?:(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|[01]?\\d?\\d)\\.){3}(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|[01]?\\d?\\d))");Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)

Sujets chauds
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 Exemples SVM en Python
Jun 11, 2023 pm 08:42 PM
Exemples SVM en Python
Jun 11, 2023 pm 08:42 PM
Support Vector Machine (SVM) en Python est un puissant algorithme d'apprentissage supervisé qui peut être utilisé pour résoudre des problèmes de classification et de régression. SVM fonctionne bien lorsqu'il s'agit de données de grande dimension et de problèmes non linéaires, et est largement utilisé dans l'exploration de données, la classification d'images, la classification de textes, la bioinformatique et d'autres domaines. Dans cet article, nous présenterons un exemple d'utilisation de SVM pour la classification en Python. Nous utiliserons le modèle SVM de la bibliothèque scikit-learn
 Quelles sont les perspectives d'emploi du C# ?
Oct 19, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Quelles sont les perspectives d'emploi du C# ?
Oct 19, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Que vous soyez débutant ou professionnel expérimenté, la maîtrise du C# ouvrira la voie à votre carrière.
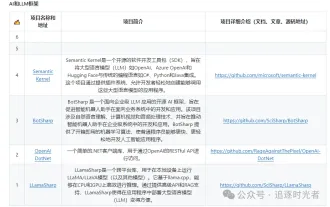 Partagez plusieurs frameworks de projets open source .NET liés à l'IA et au LLM
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Partagez plusieurs frameworks de projets open source .NET liés à l'IA et au LLM
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Le développement des technologies d’intelligence artificielle (IA) bat son plein aujourd’hui et elles ont montré un grand potentiel et une grande influence dans divers domaines. Aujourd'hui, Dayao partagera avec vous 4 cadres de projets liés au modèle d'IA open source .NET LLM, dans l'espoir de vous fournir une référence. https://github.com/YSGStudyHards/DotNetGuide/blob/main/docs/DotNet/DotNetProjectPicks.mdSemanticKernelSemanticKernel est un kit de développement logiciel (SDK) open source conçu pour intégrer de grands modèles de langage (LLM) tels qu'OpenAI, Azure
 Comment faire correspondre plusieurs mots ou chaînes à l'aide de l'expression régulière Golang ?
May 31, 2024 am 10:32 AM
Comment faire correspondre plusieurs mots ou chaînes à l'aide de l'expression régulière Golang ?
May 31, 2024 am 10:32 AM
Les expressions régulières Golang utilisent le caractère barre verticale | pour faire correspondre plusieurs mots ou chaînes, séparant chaque option comme une expression OU logique. Par exemple : correspond à "fox" ou "dog" : fox|dog correspond à "quick", "brown" ou "lazy" : (quick|brown|lazy) correspond à "Go", "Python" ou "Java" : Go| Python |Java fait correspondre des mots ou des codes postaux à 4 chiffres : ([a-zA
 Découvrez des exemples de bonnes pratiques de conversion de pointeur dans Golang
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
Découvrez des exemples de bonnes pratiques de conversion de pointeur dans Golang
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
Golang est un langage de programmation puissant et efficace qui peut être utilisé pour développer diverses applications et services. Dans Golang, les pointeurs sont un concept très important, qui peut nous aider à exploiter les données de manière plus flexible et plus efficace. La conversion de pointeur fait référence au processus d'opérations de pointeur entre différents types. Cet article utilisera des exemples spécifiques pour découvrir les meilleures pratiques de conversion de pointeur dans Golang. 1. Concepts de base Dans Golang, chaque variable a une adresse, et l'adresse est l'emplacement de la variable en mémoire.
 Exemple de démarrage de VUE3 : création d'un lecteur vidéo simple
Jun 15, 2023 pm 09:42 PM
Exemple de démarrage de VUE3 : création d'un lecteur vidéo simple
Jun 15, 2023 pm 09:42 PM
Alors que la nouvelle génération de frameworks front-end continue d'émerger, VUE3 est apprécié comme un framework front-end rapide, flexible et facile à utiliser. Ensuite, apprenons les bases de VUE3 et créons un simple lecteur vidéo. 1. Installez VUE3 Tout d'abord, nous devons installer VUE3 localement. Ouvrez l'outil de ligne de commande et exécutez la commande suivante : npminstallvue@next. Ensuite, créez un nouveau fichier HTML et introduisez VUE3 : <!doctypehtml>
 Exemple de développement d'un robot d'exploration Web simple PHP
Jun 13, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
Exemple de développement d'un robot d'exploration Web simple PHP
Jun 13, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
Avec le développement rapide d’Internet, les données sont devenues l’une des ressources les plus importantes à l’ère de l’information d’aujourd’hui. En tant que technologie qui obtient et traite automatiquement les données du réseau, les robots d'exploration Web attirent de plus en plus d'attention et d'applications. Cet article explique comment utiliser PHP pour développer un robot d'exploration Web simple et réaliser la fonction d'obtention automatique de données réseau. 1. Présentation de Web Crawler Le robot d'exploration Web est une technologie qui obtient et traite automatiquement les ressources réseau. Son principal processus de travail consiste à simuler le comportement du navigateur, à accéder automatiquement aux adresses URL spécifiées et à extraire toutes les informations.
 Exemple d'algorithme VAE en Python
Jun 11, 2023 pm 07:58 PM
Exemple d'algorithme VAE en Python
Jun 11, 2023 pm 07:58 PM
VAE est un modèle génératif, son nom complet est VariationalAutoencoder, qui se traduit en chinois par auto-encodeur variationnel. Il s'agit d'un algorithme d'apprentissage non supervisé qui peut être utilisé pour générer de nouvelles données, telles que des images, de l'audio, du texte, etc. Comparés aux auto-encodeurs ordinaires, les VAE sont plus flexibles et plus puissants et peuvent générer des données plus complexes et plus réalistes. Python est l'un des langages de programmation les plus utilisés et l'un des principaux outils d'apprentissage en profondeur. En Python, il existe de nombreux excellents outils d'apprentissage automatique et profonds.



