
Nous présenterons quelques détails d'utilisation de include* require*,
et analyserons l'implémentation et le processus d'appel de PHP zend respectivement du point de vue de l'__autoload application et du spl_autoload_register code source.
Le but de l'analyse est d'approfondir votre compréhension de ces détails et de mieux comprendre le Zend code source.
PHP 版本:`php-5.6` 核心方法:` spl_autoload_register`
Chargement manuel
__autoload
spl_autoload_register
inclure : include include_once requice requice_one
La documentation suivante s'applique également aux exigences.
Le fichier inclus est d'abord recherché selon le chemin donné par le paramètre. Si aucun répertoire n'est donné (uniquement le nom du fichier), il est recherché selon le répertoire spécifié par include_path. Si le fichier n'est pas trouvé sous include_path, include recherchera finalement dans le répertoire où se trouve le fichier de script appelant et dans le répertoire de travail actuel. La construction include émet un avertissement si le fichier n'est pas trouvé à la fin ; ceci est différent de require, qui émet une erreur fatale.Si un chemin est défini - qu'il s'agisse d'un chemin absolu (commençant par une lettre de lecteur ou sous Windows, commençant par / sous Unix/Linux) ou d'un chemin relatif vers le répertoire courant (commençant par . ou . .) - --include_path sera complètement ignoré. Par exemple, si un fichier commence par ../, l'analyseur recherchera le fichier dans le répertoire parent du répertoire courant.
Exemple de code :
FICHIER : run.php
<?php
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// 直接包含
$ret = include 'class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo();
// 包含不存在的文件
$ret1 = include './class1.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret1, gettype($ret1));
// 重复包含
$ret2 = include './class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo();FICHIER : class.php
<?php
class Foo
{
static public function getFoo()
{
echo "I am foo!\n";
}
} Résultat : 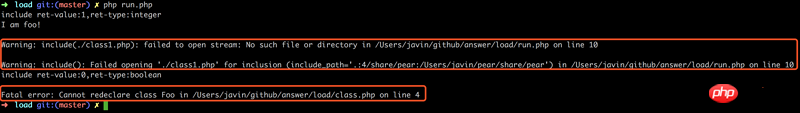
Conclusion :
include Valeur de retour réussie : 1, Valeur de retour d'échec : false
include L'échec aura warning et le processus ne sera pas interrompu
include_oncese comporte de la même manière que l'instruction include, la seule différence est que si le fichier a déjà été inclus, il ne le sera pas à nouveau.
Modifier run.php comme suit :
<?php
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// 直接包含
$ret = include 'class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo();
// 重复包含
$ret2 = include_once './class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo(); Résultat : 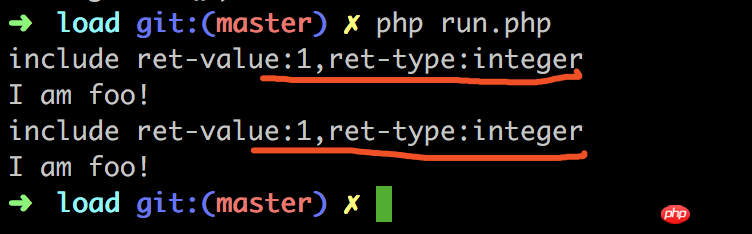
Conclusion :
include_once Lorsqu'il est inclus à plusieurs reprises, 1 sera renvoyé directement, et cette opération d'inclusion sera ignorée, et l'exécution continuera
requireetincludesont presque identiques, maisrequireproduitE_COMPILE_ERRORerreurs de niveau en cas d'erreur. (Le script cessera de s'exécuter)
Modifiez run.php comme suit :
<?php
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// 直接包含
$ret = require 'class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo();
// 包含不存在的文件
$ret1 = require './class1.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret1, gettype($ret1)); Résultat : 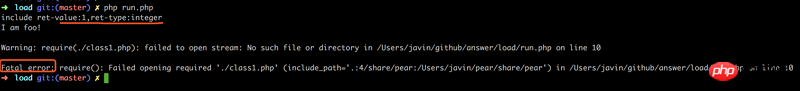
Conclusion :
require contient le succès, identique à include, valeur de retour : 1
require contient S'il échoue, Fatal error est lancé directement et le processus est terminé.
Modifier
require_onceest exactement la même que l'instruction <🎜. > déclaration, la seule différence estrequireVérifie si le fichier a déjà été inclus, si c'est le cas, il ne l'inclura pas à nouveau.PHP
comme suit : run.php
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// 直接包含
$ret = require_once 'class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo();
// 重复包含
$ret2 = require_once './class.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret, gettype($ret));
Foo::getFoo();
// 包含不存在的文件
$ret1 = require_once './class1.php';
echo sprintf("include ret-value:%d,ret-type:%s\n", $ret1, gettype($ret1));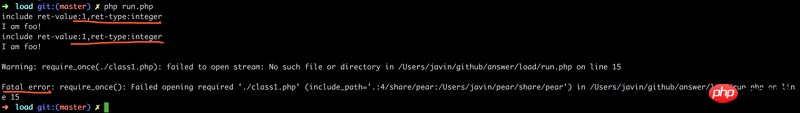
1
et ignorez cette inclusion 1
include include_once requice En cas de succès, requice_one sera renvoyé La différence réside dans le traitement de l'échec de l'inclusion et de l'inclusion répétée 1
Tentative de charger une classe non définie. Cette fonction sera obsolète dansExplication du code PHPExemple d'utilisation :.
PHP 7.2.0
FILE :foo.php
<?php
class Foo
{
static public function getFoo()
{
echo "I am foo!\n";
}
}FILE :run.php
<?php
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
function __autoload($classname)
{
$filename = "./". lcfirst($classname) .".php";
include_once($filename);
}
Foo::getFoo();➜ load git:(master) ✗ php run.php I am foo!
rencontre une classe non confinée, elle déclenchera
le chargement, si toutes les règles de chargement sont présentes ce n'est pas une telle chose, alors __autoload. Fatal error
下面,我们来看一下 Zend 引擎是如何触发 __autoload 调用的。
利用 vld 来查看刚才执行过程中产生的 opcode,结果如下: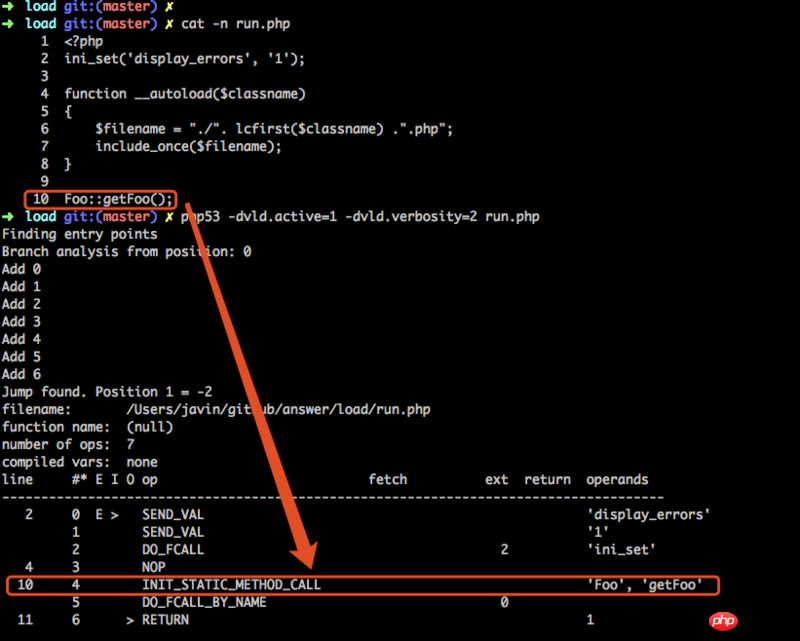
我们看到,PHP 运行到第 10 行时,所生成的 opcode 为:INIT_STATIC_METHOD_CALL,两个操作数都为常量(CONST)。
根据 opcode 的处理函数对应规则,我们利用 命名法 可以确定,
处理函数为:ZEND_INIT_STATIC_METHOD_CALL_SPEC_CONST_CONST_HANDLER
源码位置为:vim Zend/zend_vm_execute.h +3819
源码如下:
static int ZEND_FASTCALL ZEND_INIT_STATIC_METHOD_CALL_SPEC_CONST_CONST_HANDLER(ZEND_OPCODE_HANDLER_ARGS)
{
USE_OPLINE
zval *function_name;
zend_class_entry *ce;
call_slot *call = EX(call_slots) + opline->result.num;
SAVE_OPLINE();
if (IS_CONST == IS_CONST) {
/* no function found. try a static method in class */
if (CACHED_PTR(opline->op1.literal->cache_slot)) {
ce = CACHED_PTR(opline->op1.literal->cache_slot);
} else {
ce = zend_fetch_class_by_name(Z_STRVAL_P(opline->op1.zv), Z_STRLEN_P(opline->op1.zv), opline->op1.literal + 1, opline->extended_value TSRMLS_CC);
if (UNEXPECTED(EG(exception) != NULL)) {
HANDLE_EXCEPTION();
}
if (UNEXPECTED(ce == NULL)) {
zend_error_noreturn(E_ERROR, "Class '%s' not found", Z_STRVAL_P(opline->op1.zv));
}
CACHE_PTR(opline->op1.literal->cache_slot, ce);
}
call->called_scope = ce;
} else {
ce = EX_T(opline->op1.var).class_entry;
if (opline->extended_value == ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_PARENT || opline->extended_value == ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_SELF) {
call->called_scope = EG(called_scope);
} else {
call->called_scope = ce;
}
}
if (IS_CONST == IS_CONST &&
IS_CONST == IS_CONST &&
CACHED_PTR(opline->op2.literal->cache_slot)) {
call->fbc = CACHED_PTR(opline->op2.literal->cache_slot);
} else if (IS_CONST != IS_CONST &&
IS_CONST == IS_CONST &&
(call->fbc = CACHED_POLYMORPHIC_PTR(opline->op2.literal->cache_slot, ce))) {
/* do nothing */
} else if (IS_CONST != IS_UNUSED) {
char *function_name_strval = NULL;
int function_name_strlen = 0;
if (IS_CONST == IS_CONST) {
function_name_strval = Z_STRVAL_P(opline->op2.zv);
function_name_strlen = Z_STRLEN_P(opline->op2.zv);
} else {
function_name = opline->op2.zv;
if (UNEXPECTED(Z_TYPE_P(function_name) != IS_STRING)) {
if (UNEXPECTED(EG(exception) != NULL)) {
HANDLE_EXCEPTION();
}
zend_error_noreturn(E_ERROR, "Function name must be a string");
} else {
function_name_strval = Z_STRVAL_P(function_name);
function_name_strlen = Z_STRLEN_P(function_name);
}
}
if (function_name_strval) {
if (ce->get_static_method) {
call->fbc = ce->get_static_method(ce, function_name_strval, function_name_strlen TSRMLS_CC);
} else {
call->fbc = zend_std_get_static_method(ce, function_name_strval, function_name_strlen, ((IS_CONST == IS_CONST) ? (opline->op2.literal + 1) : NULL) TSRMLS_CC);
}
if (UNEXPECTED(call->fbc == NULL)) {
zend_error_noreturn(E_ERROR, "Call to undefined method %s::%s()", ce->name, function_name_strval);
}
if (IS_CONST == IS_CONST &&
EXPECTED(call->fbc->type <= ZEND_USER_FUNCTION) &&
EXPECTED((call->fbc->common.fn_flags & (ZEND_ACC_CALL_VIA_HANDLER|ZEND_ACC_NEVER_CACHE)) == 0)) {
if (IS_CONST == IS_CONST) {
CACHE_PTR(opline->op2.literal->cache_slot, call->fbc);
} else {
CACHE_POLYMORPHIC_PTR(opline->op2.literal->cache_slot, ce, call->fbc);
}
}
}
if (IS_CONST != IS_CONST) {
}
} else {
if (UNEXPECTED(ce->constructor == NULL)) {
zend_error_noreturn(E_ERROR, "Cannot call constructor");
}
if (EG(This) && Z_OBJCE_P(EG(This)) != ce->constructor->common.scope && (ce->constructor->common.fn_flags & ZEND_ACC_PRIVATE)) {
zend_error_noreturn(E_ERROR, "Cannot call private %s::__construct()", ce->name);
}
call->fbc = ce->constructor;
}
if (call->fbc->common.fn_flags & ZEND_ACC_STATIC) {
call->object = NULL;
} else {
if (EG(This) &&
Z_OBJ_HT_P(EG(This))->get_class_entry &&
!instanceof_function(Z_OBJCE_P(EG(This)), ce TSRMLS_CC)) {
/* We are calling method of the other (incompatible) class,
but passing $this. This is done for compatibility with php-4. */
if (call->fbc->common.fn_flags & ZEND_ACC_ALLOW_STATIC) {
zend_error(E_DEPRECATED, "Non-static method %s::%s() should not be called statically, assuming $this from incompatible context", call->fbc->common.scope->name, call->fbc->common.function_name);
} else {
/* An internal function assumes $this is present and won't check that. So PHP would crash by allowing the call. */
zend_error_noreturn(E_ERROR, "Non-static method %s::%s() cannot be called statically, assuming $this from incompatible context", call->fbc->common.scope->name, call->fbc->common.function_name);
}
}
if ((call->object = EG(This))) {
Z_ADDREF_P(call->object);
call->called_scope = Z_OBJCE_P(call->object);
}
}
call->num_additional_args = 0;
call->is_ctor_call = 0;
EX(call) = call;
CHECK_EXCEPTION();
ZEND_VM_NEXT_OPCODE();
}通过以上源码,我们发现关键方法为 zend_fetch_class_by_name,跟进此方法:
zend_class_entry *zend_fetch_class_by_name(const char *class_name, uint class_name_len, const zend_literal *key, int fetch_type TSRMLS_DC) /* {{{ */
{
zend_class_entry **pce;
int use_autoload = (fetch_type & ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_NO_AUTOLOAD) == 0;
if (zend_lookup_class_ex(class_name, class_name_len, key, use_autoload, &pce TSRMLS_CC) == FAILURE) {
if (use_autoload) {
if ((fetch_type & ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_SILENT) == 0 && !EG(exception)) {
if ((fetch_type & ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_MASK) == ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_INTERFACE) {
zend_error(E_ERROR, "Interface '%s' not found", class_name);
} else if ((fetch_type & ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_MASK) == ZEND_FETCH_CLASS_TRAIT) {
zend_error(E_ERROR, "Trait '%s' not found", class_name);
} else {
zend_error(E_ERROR, "Class '%s' not found", class_name);
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
return *pce;
}我们发现是通过 zend_lookup_class_ex 来获取类,继续跟进:
ZEND_API int zend_lookup_class_ex(const char *name, int name_length, const zend_literal *key, int use_autoload, zend_class_entry ***ce TSRMLS_DC) /* {{{ */
{
...
/* 注意:在 类的符号表 中没有找到示例中调用的类 foo */
if (zend_hash_quick_find(EG(class_table), lc_name, lc_length, hash, (void **) ce) == SUCCESS) {
if (!key) {
free_alloca(lc_free, use_heap);
}
return SUCCESS;
}
...
/*
* ZVAL_STRINGL 为 zval (即 PHP 类型的实现基础 zvalue_value)赋值宏,
* 此处实现了 把 ZEND_AUTOLOAD_FUNC_NAME 值 赋给 autoload_function
* #define ZEND_AUTOLOAD_FUNC_NAME "__autoload"
*/
ZVAL_STRINGL(&autoload_function, ZEND_AUTOLOAD_FUNC_NAME, sizeof(ZEND_AUTOLOAD_FUNC_NAME) - 1, 0);
...
fcall_info.size = sizeof(fcall_info);
fcall_info.function_table = EG(function_table);
fcall_info.function_name = &autoload_function;
fcall_info.symbol_table = NULL;
fcall_info.retval_ptr_ptr = &retval_ptr;
fcall_info.param_count = 1;
fcall_info.params = args;
fcall_info.object_ptr = NULL;
fcall_info.no_separation = 1;
fcall_cache.initialized = EG(autoload_func) ? 1 : 0;
fcall_cache.function_handler = EG(autoload_func); /* 留意此处 */
fcall_cache.calling_scope = NULL;
fcall_cache.called_scope = NULL;
fcall_cache.object_ptr = NULL;
...
retval = zend_call_function(&fcall_info, &fcall_cache TSRMLS_CC); /* 调用自动加载函数 */
...
EG(autoload_func) = fcall_cache.function_handler;
zval_ptr_dtor(&class_name_ptr);
zend_hash_quick_del(EG(in_autoload), lc_name, lc_length, hash);
...
}我们发现是通过 zend_call_function 出发了自动加载函数,而且看到了加载方法的名字 __autoload (宏:ZEND_AUTOLOAD_FUNC_NAME)
zend_call_function 中会做一下检测并调用等,而且我们看到 zend_lookup_class_ex 的返回结果即为 zend_call_function 的返回结果。
接下来我们逐步退出函数调用栈:
假设 zend_call_function 调用失败,返回 FALSE,
则 zend_lookup_class_ex 返回 FALSE;
则 zend_fetch_class_by_name 返回 NULL;
则 ZEND_INIT_STATIC_METHOD_CALL_SPEC_CONST_CONST_HANDLER 抛出异常 Class ** not found,如下图所示: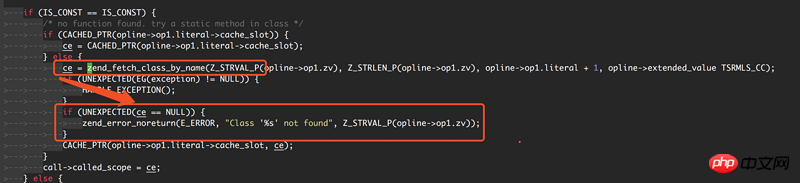
至此,我们通过 PHP 代码 Zend 源码 了解了 __autoload 的调用过程。
我们知道 __autoload 现在已并不推荐使用,
它的缺点也很明显,不支持多个自动加载函数。
将函数注册到SPL __autoload函数队列中。如果该队列中的函数尚未激活,则激活它们。如果在你的程序中已经实现了__autoload()函数,它必须显式注册到__autoload()队列中。
使用示例:
FILE:foo.php
(同上 __autoload)
FILE:foo2.class.php
<?php
class Foo2
{
static public function getFoo2()
{
echo "I am foo2!\n";
}
}FILE:run.php
<?php
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
$my_autoload1 = function ($classname)
{
echo "entry my_autoload1 \n";
$filename = "./". lcfirst($classname) .".php";
include_once($filename);
};
$my_autoload2 = function ($classname)
{
echo "entry my_autoload2 \n";
$filename = "./". lcfirst($classname) .".class.php";
include_once($filename);
};
spl_autoload_register($my_autoload1);
spl_autoload_register($my_autoload2);
Foo::getFoo();
Foo2::getFoo2();结果如下: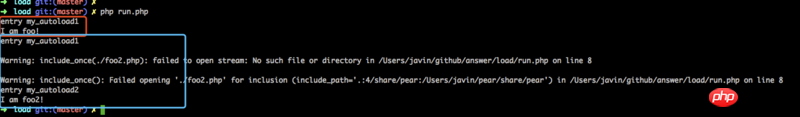
我们看到,调用 getFoo2 时,会先调用第一个注册的 autoload 方法,如果没找到对应的类,会产生 warning 并继续调用后边注册的 autoload 方法。
说明了 PHP 内核中为通过 spl_autoload_register 注册的 autoload 方法维护了一个队列,当前文件为包含调用类,便会触发此队列,并依次调用,直到队列结束 或者 找到对应类。
首先,我们看一下 PHP 文件生成的 opcode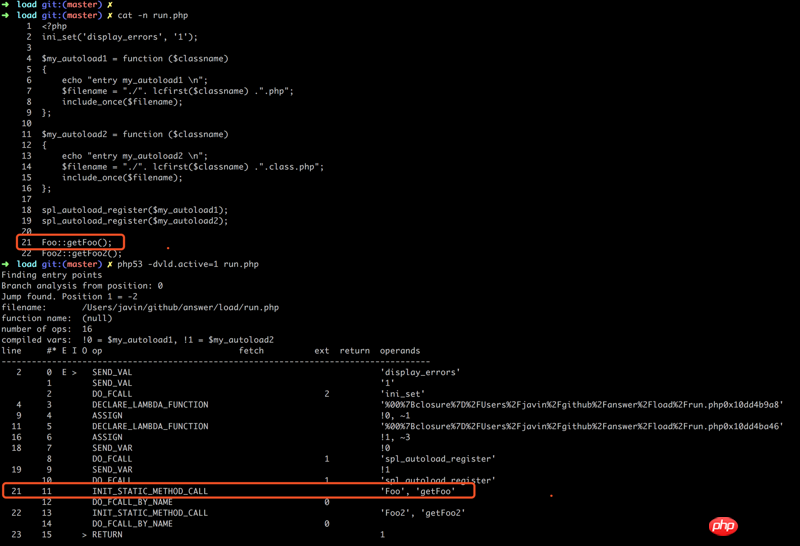
我们发现,其方法调用所生成的 opcode 跟 __autoload 一样,
但是我们之前调用了 `spl_autoload_register,
那么,看一下 spl_autoload_register 的源码:
FILE: ext/spl/php_spl.c*
PHP_FUNCTION(spl_autoload_register)
{
char *func_name, *error = NULL;
int func_name_len;
char *lc_name = NULL;
zval *zcallable = NULL;
zend_bool do_throw = 1;
zend_bool prepend = 0;
zend_function *spl_func_ptr;
autoload_func_info alfi;
zval *obj_ptr;
zend_fcall_info_cache fcc;
if (zend_parse_parameters_ex(ZEND_PARSE_PARAMS_QUIET, ZEND_NUM_ARGS() TSRMLS_CC, "|zbb", &zcallable, &do_throw, &prepend) == FAILURE) {
return;
}
if (ZEND_NUM_ARGS()) {
if (Z_TYPE_P(zcallable) == IS_STRING) {
if (Z_STRLEN_P(zcallable) == sizeof("spl_autoload_call") - 1) {
if (!zend_binary_strcasecmp(Z_STRVAL_P(zcallable), sizeof("spl_autoload_call"), "spl_autoload_call", sizeof("spl_autoload_call"))) {
if (do_throw) {
zend_throw_exception_ex(spl_ce_LogicException, 0 TSRMLS_CC, "Function spl_autoload_call() cannot be registered");
}
RETURN_FALSE;
}
}
}
if (!zend_is_callable_ex(zcallable, NULL, IS_CALLABLE_STRICT, &func_name, &func_name_len, &fcc, &error TSRMLS_CC)) {
alfi.ce = fcc.calling_scope;
alfi.func_ptr = fcc.function_handler;
obj_ptr = fcc.object_ptr;
if (Z_TYPE_P(zcallable) == IS_ARRAY) {
if (!obj_ptr && alfi.func_ptr && !(alfi.func_ptr->common.fn_flags & ZEND_ACC_STATIC)) {
if (do_throw) {
zend_throw_exception_ex(spl_ce_LogicException, 0 TSRMLS_CC, "Passed array specifies a non static method but no object (%s)", error);
}
if (error) {
efree(error);
}
efree(func_name);
RETURN_FALSE;
}
else if (do_throw) {
zend_throw_exception_ex(spl_ce_LogicException, 0 TSRMLS_CC, "Passed array does not specify %s %smethod (%s)", alfi.func_ptr ? "a callable" : "an existing", !obj_ptr ? "static " : "", error);
}
if (error) {
efree(error);
}
efree(func_name);
RETURN_FALSE;
} else if (Z_TYPE_P(zcallable) == IS_STRING) {
if (do_throw) {
zend_throw_exception_ex(spl_ce_LogicException, 0 TSRMLS_CC, "Function '%s' not %s (%s)", func_name, alfi.func_ptr ? "callable" : "found", error);
}
if (error) {
efree(error);
}
efree(func_name);
RETURN_FALSE;
} else {
if (do_throw) {
zend_throw_exception_ex(spl_ce_LogicException, 0 TSRMLS_CC, "Illegal value passed (%s)", error);
}
if (error) {
efree(error);
}
efree(func_name);
RETURN_FALSE;
}
}
alfi.closure = NULL;
alfi.ce = fcc.calling_scope;
alfi.func_ptr = fcc.function_handler;
obj_ptr = fcc.object_ptr;
if (error) {
efree(error);
}
lc_name = safe_emalloc(func_name_len, 1, sizeof(long) + 1);
zend_str_tolower_copy(lc_name, func_name, func_name_len);
efree(func_name);
if (Z_TYPE_P(zcallable) == IS_OBJECT) {
alfi.closure = zcallable;
Z_ADDREF_P(zcallable);
lc_name = erealloc(lc_name, func_name_len + 2 + sizeof(zend_object_handle));
memcpy(lc_name + func_name_len, &Z_OBJ_HANDLE_P(zcallable),
sizeof(zend_object_handle));
func_name_len += sizeof(zend_object_handle);
lc_name[func_name_len] = '\0';
}
if (SPL_G(autoload_functions) && zend_hash_exists(SPL_G(autoload_functions), (char*)lc_name, func_name_len+1)) {
if (alfi.closure) {
Z_DELREF_P(zcallable);
}
goto skip;
}
if (obj_ptr && !(alfi.func_ptr->common.fn_flags & ZEND_ACC_STATIC)) {
/* add object id to the hash to ensure uniqueness, for more reference look at bug #40091 */
lc_name = erealloc(lc_name, func_name_len + 2 + sizeof(zend_object_handle));
memcpy(lc_name + func_name_len, &Z_OBJ_HANDLE_P(obj_ptr), sizeof(zend_object_handle));
func_name_len += sizeof(zend_object_handle);
lc_name[func_name_len] = '\0';
alfi.obj = obj_ptr;
Z_ADDREF_P(alfi.obj);
} else {
alfi.obj = NULL;
}
if (!SPL_G(autoload_functions)) {
ALLOC_HASHTABLE(SPL_G(autoload_functions));
zend_hash_init(SPL_G(autoload_functions), 1, NULL, (dtor_func_t) autoload_func_info_dtor, 0);
}
zend_hash_find(EG(function_table), "spl_autoload", sizeof("spl_autoload"), (void **) &spl_func_ptr);
if (EG(autoload_func) == spl_func_ptr) { /* registered already, so we insert that first */
autoload_func_info spl_alfi;
spl_alfi.func_ptr = spl_func_ptr;
spl_alfi.obj = NULL;
spl_alfi.ce = NULL;
spl_alfi.closure = NULL;
zend_hash_add(SPL_G(autoload_functions), "spl_autoload", sizeof("spl_autoload"), &spl_alfi, sizeof(autoload_func_info), NULL);
if (prepend && SPL_G(autoload_functions)->nNumOfElements > 1) {
/* Move the newly created element to the head of the hashtable */
HT_MOVE_TAIL_TO_HEAD(SPL_G(autoload_functions));
}
}
if (zend_hash_add(SPL_G(autoload_functions), lc_name, func_name_len+1, &alfi.func_ptr, sizeof(autoload_func_info), NULL) == FAILURE) {
if (obj_ptr && !(alfi.func_ptr->common.fn_flags & ZEND_ACC_STATIC)) {
Z_DELREF_P(alfi.obj);
}
if (alfi.closure) {
Z_DELREF_P(alfi.closure);
}
}
if (prepend && SPL_G(autoload_functions)->nNumOfElements > 1) {
/* Move the newly created element to the head of the hashtable */
HT_MOVE_TAIL_TO_HEAD(SPL_G(autoload_functions));
}
skip:
efree(lc_name);
}
if (SPL_G(autoload_functions)) {
zend_hash_find(EG(function_table), "spl_autoload_call", sizeof("spl_autoload_call"), (void **) &EG(autoload_func)); /* 注意此处 */
} else {
zend_hash_find(EG(function_table), "spl_autoload", sizeof("spl_autoload"), (void **) &EG(autoload_func));
}
RETURN_TRUE;
} /* }}} */通过分析源码,我们发现 spl_autoload_register 会把注册的自动加载函数添加到 autoload_functions 中,最后将 autoload_functions 赋值给 EG(autoload_func) (上方源码倒数第一个 if 判断逻辑中)。
而有印象的同学会发现,EG(autoload_func) 在分析 __autoload 调用源码时出现过(可以划到之前的分析查看),它是执行环境全局结构体中的成员,出现调用大概源码如下:
ZEND_API int zend_lookup_class_ex(const char *name, int name_length, const zend_literal *key, int use_autoload, zend_class_entry ***ce TSRMLS_DC)
{
...
fcall_info.size = sizeof(fcall_info);
fcall_info.function_table = EG(function_table);
fcall_info.function_name = &autoload_function;
fcall_info.symbol_table = NULL;
fcall_info.retval_ptr_ptr = &retval_ptr;
fcall_info.param_count = 1;
fcall_info.params = args;
fcall_info.object_ptr = NULL;
fcall_info.no_separation = 1;
fcall_cache.initialized = EG(autoload_func) ? 1 : 0;
fcall_cache.function_handler = EG(autoload_func); /* 注意这里 */
fcall_cache.calling_scope = NULL;
fcall_cache.called_scope = NULL;
fcall_cache.object_ptr = NULL;
zend_exception_save(TSRMLS_C);
retval = zend_call_function(&fcall_info, &fcall_cache TSRMLS_CC);
zend_exception_restore(TSRMLS_C);
...
return retval;
}分析到这里,我们已经知道了,spl_autoload_register 注册的函数是如何在 PHP 代码调用时被触发的。
感兴趣的同学可以继续查看一下 zend_call_function 的源码,了解具体的调用方式。
Enregistrez la fonction de chargement automatique via spl_autoload_register et maintenez une file d'attente Zend dans le moteur autoload Vous pouvez ajouter plusieurs fonctions autoload et appeler celle actuelle dans PHP. Lorsque la classe du fichier est inconnue, l'appel de autoload_func est déclenché.
Dans le même temps, les étudiants attentifs découvriront également dans le code source spl_autoload_register que lorsque la méthode transmise lors de l'inscription ne peut pas être appelée, si spl_autoload est implémentée, elle sera enregistrée dans le autoload file d'attente.
Recommandations associées :
javaScript et jQuery réalisent le chargement automatique
Exemples détaillés de trois façons de charger automatiquement les classes PHP
Comment comprendre l'opération de chargement automatique de la classe php
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 Comment ouvrir le fichier php
Comment ouvrir le fichier php
 Comment supprimer les premiers éléments d'un tableau en php
Comment supprimer les premiers éléments d'un tableau en php
 Que faire si la désérialisation php échoue
Que faire si la désérialisation php échoue
 Comment résoudre le problème que les CSS ne peuvent pas être chargés
Comment résoudre le problème que les CSS ne peuvent pas être chargés
 Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
 Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
 Comment télécharger du HTML
Comment télécharger du HTML
 Que faire si le CSS ne peut pas être chargé
Que faire si le CSS ne peut pas être chargé