Explication détaillée de l'utilisation du gradient linéaire
Cette fois, je vais vous apporter une explication détaillée de l'utilisation du dégradé linéaire. Quelles sont les précautions lors de l'utilisation du dégradé linéaire. Voici des cas pratiques, jetons un coup d'œil.
Le dégradé CSS3 est divisé en dégradé linéaire (dégradé linéaire) et dégradé radial (dégradé radial). Aujourd’hui, nous analysons principalement son utilisation spécifique pour les dégradés linéaires. Afin de mieux appliquer CSS3 Gradient, nous devons d'abord comprendre le cœur de plusieurs navigateurs modernes, principalement Mozilla (Firefox, Flock, etc.), WebKit (Safari, Chrome, etc.), Opera (navigateur Opera), Trident (Annoying Navigateur IE).
Cet article ignore IE comme d'habitude. Nous examinons principalement les applications sous Mozilla, Webkit et Opera. Bien sûr, il peut également être implémenté sous IE. Il doit être implémenté via des filtres spécifiques à IE. sera répertorié plus tard. La syntaxe d'utilisation des filtres ne sera pas présentée en détail. Si vous êtes intéressé, vous pouvez rechercher des documents techniques pertinents.
1. Application du dégradé linéaire sous Mozilla
Syntaxe :
-moz-linear-gradient( [<point> || <angle>,]? <stop>, <stop> [, <stop>]* )
Paramètres : Il y en a trois au total Paramètres, le premier paramètre représente la direction du dégradé linéaire, le haut va de haut en bas, la gauche va de gauche à droite, s'il est défini comme haut gauche, c'est du coin supérieur gauche au coin inférieur droit. Les deuxième et troisième paramètres sont respectivement la couleur de début et la couleur de fin. Vous pouvez également insérer davantage de paramètres entre eux pour représenter des dégradés de plusieurs couleurs. Comme le montre l'image :

D'après l'introduction ci-dessus, regardons d'abord un exemple simple :
HTML :
<p class="example example1"></p>
CSS :
.example {
width: 150px;
height: 80px;
}Sauf indication contraire, nos exemples suivants utilisent tous ce code de base html et css.
Maintenant, nous appliquons un style de dégradé simple à ce p :
.example1 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient( top,#ccc,#000);
}L'effet est le suivant :

2. Application du dégradé linéaire sous Webkit
Syntaxe :
-webkit-linear-gradient( [<point> || <angle>,]? <stop>, <stop> [, <stop>]* )//最新发布书写语法 -webkit-gradient(<type>, <point> [, <radius>]?, <point> [, <radius>]? [, <stop>]*) //老式语法书写规则
Paramètres : -webkit - Le dégradé est le paramètre d'implémentation du dégradé du moteur du webkit. Il y en a cinq au total. Le premier paramètre représente le type de dégradé (type), qui peut être linéaire (dégradé linéaire) ou radial (dégradé radial). Le deuxième paramètre et le troisième paramètre sont tous deux une paire de valeurs, représentant respectivement le point de départ et le point final du dégradé. Cette paire de valeurs peut être exprimée sous forme de coordonnées ou de valeurs clés, telles que haut gauche (coin supérieur gauche) et bas gauche (coin inférieur gauche). Les quatrième et cinquième paramètres sont respectivement deux fonctions d'arrêt de couleur. La fonction color-stop accepte deux paramètres. Le premier représente la position du dégradé, 0 est le point de départ, 0,5 est le point médian et 1 est le point final ; Comme le montre l'image :


Regardons d'abord un exemple d'écriture à l'ancienne :
Copiez le code
Le code est le suivant :
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,center top,center bottom,from(#ccc), to(#000));
L'effet est le suivant :

Alors jetons un coup d'œil à la nouvelle façon d'écrire :
-webkit-linear-gradient(top,#ccc,#000);
Je ne publierai plus cet effet. Tout le monde comprendra à. un coup d'œil dans le navigateur pour savoir s'il s'agit de résultats cohérents. En comparant attentivement, les méthodes d'apprentissage des deux sous Mozilla et Webkit sont fondamentalement les mêmes, à l'exception de la différence de préfixes. Bien sûr, ce serait mieux pour nous si un jour elles pouvaient être unifiées en un seul, donc il n'y en a pas. il faut s'en occuper. Cela nous fera grandement gagner du temps de développement.
3. Application du dégradé linéaire dans Opera
Syntaxe :
Copier le code
Le code est le suivant :
-o-linear-gradient([<point> || <angle>,]? <stop>, <stop> [, <stop>]); /* Opera 11.10+ */
参数:-o-linear-gradient 有三个参数。第一个参数表示线性渐变的方向,top 是从上到下、left 是从左到右,如果定义成 left top,那就是从左上角到右下角。第二个和第三个参数分别是起点颜色和终点颜色。你还可以在它们之间插入更多的参数,表示多种颜色的渐变。(注:Opera 支持的版本有限,本例测试都是在 Opera11.1 版本下,后面不在提示),如图所示:
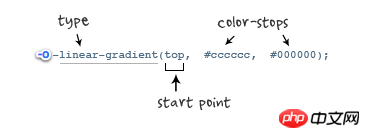
示例代码:
background: -o-linear-gradient(top,#ccc, #000);
效果如图所示:

四、线性渐变在 Trident (IE) 下的应用
语法:
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(GradientType=0, startColorstr=#1471da, endColorstr=#1C85FB);/*IE<9>*/ -ms-filter: "progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient (GradientType=0, startColorstr=#1471da, endColorstr=#1C85FB)";/*IE8+*/
IE依靠滤镜实现渐变。startColorstr表示起点的颜色,endColorstr 表示终点颜色。GradientType 表示渐变类型,0 为缺省值,表示垂直渐变,1 表示水平渐变。如图所示:

上面我们主要介绍了线性渐变在上述四大核心模块下的实现方法,接着我们主要针对线性渐变在 Mozilla、Webkit、Opera 三大模块下实现各种不同线性渐变实例:
从上面的语法中我们可以很清楚的知道,要创建一个线性渐变,我们需要创建一个起点和一个渐变方向(或角度),定义一个起始色:
-moz-linear-gradient( [<point> || <angle>,]? <stop>, <stop> [, <stop>]* ) -webkit-linear-gradient( [<point> || <angle>,]? <stop>, <stop> [, <stop>]* ) -o-linear-gradient( [<point> || <angle>,]? <stop>, <stop> [, <stop>]* )
具体应用如下:
background:-moz-linear-gradient(left,#ace,#f96);/*Mozilla*/ background:-webkit-gradient(linear,0 50%,100% 50%,from(#ace),to(#f96));/*Old gradient for webkit*/ background:-webkit-linear-gradient(left,#ace,#f96);/*new gradient for Webkit*/ background:-o-linear-gradient(left,#ace,#f96); /*Opera11*/
效果如下:

起始点(Starting Point)的工作方式类似于 background position。您可以设置水平和垂直位置为百分比,或以像素为单位,或在水平方向上可以使用left/center/right,在垂直方向上可以使用top/center/bottom。位置起始于左上角。如果你不指定水平或垂直位置,它将默认为center。其工作方式主要包含:Top → Bottom、Left → Right、bottom → top、right → left等,接着我们主要一种一种来看其实现的效果:
1、开始于center(水平方向)和top(垂直方向)也就是Top → Bottom:
/* Firefox 3.6+ */ background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #ace, #f96); /* Safari 4-5, Chrome 1-9 */ /* -webkit-gradient(, [, ]?, [, ]? [, ]*) */ background: -webkit-gradient(linear,top,from(#ace),to(#f96)); /* Safari 5.1+, Chrome 10+ */ background: -webkit-linear-gradient(top, #ace, #f96); /* Opera 11.10+ */ background: -o-linear-gradient(top, #ace, #f96);
效果:

2、始于left(水平方向)和center(垂直方向)也是就Left → Right:
/* Firefox 3.6+ */ background: -moz-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96); /* Safari 5.1+, Chrome 10+ */ background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96); /* Opera 11.10+ */ background: -o-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96);
效果如下:

3、起始于left(水平方向)和top(垂直方向):
background: -moz-linear-gradient(left top, #ace, #f96); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left top, #ace, #f96); background: -o-linear-gradient(left top, #ace, #f96);
效果如下:

4、Linear Gradient (with Even Stops):
/* Firefox 3.6+ */ background: -moz-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96, #ace, #f96, #ace); /* Safari 4-5, Chrome 1-9 */ background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, right top, from(#ace), color-stop(0.25, #f96), color-stop(0.5, #ace), color-stop(0.75, #f96), to(#ace)); /* Safari 5.1+, Chrome 10+ */ background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96, #ace, #f96, #ace); /* Opera 11.10+ */ background: -o-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96, #ace, #f96, #ace);
效果如下:

5、with Specified Arbitrary Stops:
/* Firefox 3.6+ */ background: -moz-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96 5%, #ace, #f96 95%, #ace); /* Safari 4-5, Chrome 1-9 */ background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, right top, from(#ace), color-stop(0.05, #f96), color-stop(0.5, #ace), color-stop(0.95, #f96), to(#ace)); /* Safari 5.1+, Chrome 10+ */ background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96 5%, #ace, #f96 95%, #ace); /* Opera 11.10+ */ background: -o-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96 5%, #ace, #f96 95%, #ace);
效果如下:

6、角度(Angle):
正如上面看到的示例,如果您不指定一个角度,它会根据起始位置自动定义。如果你想更多的控制渐变的方向,您不妨设置角度试试。例如,下面的两个渐变具有相同的起点left center,但是加上一个30度的角度。
没有角度的示例代码:
background: -moz-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left,#ace,#f96); background: -o-linear-gradient(left, #ace, #f96);
加上30度的角度代码:
background: -moz-linear-gradient(left 30deg, #ace, #f96); background: -webkit-gradient(linear, 0 0, 100% 100%, from(#ace),to(#f96)); background: -o-linear-gradient(30deg, #ace, #f96);
效果图如下:


当指定的角度,请记住,它是一个由水平线与渐变线产生的的角度,逆时针方向。因此,使用0deg将产生一个左到右横向梯度,而90度将创建一个从底部到顶部的垂直渐变。我来看看你核心代码:
background: -moz-linear-gradient(<angle>, #ace, #f96); background: -webkit-gradient(<type>,<angle>, from(#ace), to(#f96)); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(<angle>, #ace, #f96); background: -o-linear-gradient(<angle>, #ace, #f96);
我们来看看各角度的区别:
.deg0 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(0deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,0 50%,100% 50%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(0deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(0deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg45 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(45deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,0 100%,100% 0%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(45deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(45deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg90 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(90deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,50% 100%,50% 0%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(90deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(90deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg135 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(135deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,100% 100%,0 0,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(135deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(135deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg180 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(180deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,100% 50%,0 50%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(180deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(180deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg225 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(225deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,100% 0%,0 100%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(225deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(225deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg270 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(270deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,50% 0%,50% 100%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(270deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(270deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg315 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(315deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,0% 0%,100% 100%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(315deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(315deg, #ace, #f96);
}
.deg360 {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(360deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear,0 50%,100% 50%,from(#ace),to(#f96));
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(360deg, #ace, #f96);
background: -o-linear-gradient(360deg, #ace, #f96);
}效果如下:

除了起始位置和角度,你应该指定起止颜色。起止颜色是沿着渐变线,将会在指定位置(以百分比或长度设定)含有指定颜色的点。色彩的起止数是无限的。如果您使用一个百分比位置,0%代表起点和100%是终点,但区域外的值可以被用来达到预期的效果。 这也是通过CSS3 Gradient制作渐变的一个关键所在,其直接影响了你的设计效果,像我们这里的示例都不是完美的效果,只是为了能给大家展示一个渐变的效果,大家就这样先用着吧。我们接着看一下不同的起址色的示例:
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #ace, #f96 80%, #f96); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(top,#ace,#f96 80%,#f96); background: -o-linear-gradient(top, #ace, #f96 80%, #f96);
效果如下:

如果没有指定位置,颜色会均匀分布。如下面的示例:
background: -moz-linear-gradient(left, red, #f96, yellow, green, #ace); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left,red,#f96,yellow,green,#ace); background: -o-linear-gradient(left, red, #f96, yellow, green, #ace);
效果如下

7、渐变上应用透明度(Transparency):
透明渐变对于制作一些特殊的效果是相当有用的,例如,当堆叠多个背景时。这里是两个背景的结合:一张图片,一个白色到透明的线性渐变。我们来看一个官网的示例吧:
background: -moz-linear-gradient(right, rgba(255,255,255,0), rgba(255,255,255,1)),url(http://demos.hacks.mozilla.org/openweb/resources/images/patterns/flowers-pattern.jpg); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(right, rgba(255,255,255,0), rgba(255,255,255,1)),url(http://demos.hacks.mozilla.org/openweb/resources/images/patterns/flowers-pattern.jpg); background: -o-linear-gradient(right, rgba(255,255,255,0), rgba(255,255,255,1)),url(http://demos.hacks.mozilla.org/openweb/resources/images/patterns/flowers-pattern.jpg);
接着看看效果吧

是不是很神奇呀。如果想体会的话,快点动手跟我一起做吧。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
CSS3中nth-child与nth-of-type的区别以及使用技巧
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment utiliser les liens magnétiques
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
Comment utiliser les liens magnétiques
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
Le lien magnétique est une méthode de lien pour télécharger des ressources, qui est plus pratique et efficace que les méthodes de téléchargement traditionnelles. Les liens magnétiques vous permettent de télécharger des ressources de manière peer-to-peer sans recourir à un serveur intermédiaire. Cet article explique comment utiliser les liens magnétiques et à quoi il faut prêter attention. 1. Qu'est-ce qu'un lien magnétique ? Un lien magnétique est une méthode de téléchargement basée sur le protocole P2P (Peer-to-Peer). Grâce à des liens magnétiques, les utilisateurs peuvent se connecter directement à l'éditeur de la ressource pour finaliser le partage et le téléchargement des ressources. Par rapport aux méthodes de téléchargement traditionnelles, magnétique
 Comment utiliser les fichiers mdf et mds
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Comment utiliser les fichiers mdf et mds
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Comment utiliser les fichiers mdf et mds Grâce aux progrès continus de la technologie informatique, nous pouvons stocker et partager des données de différentes manières. Dans le domaine des médias numériques, nous rencontrons souvent des formats de fichiers particuliers. Dans cet article, nous discuterons d'un format de fichier courant - les fichiers mdf et mds, et présenterons comment les utiliser. Tout d’abord, nous devons comprendre la signification des fichiers mdf et mds. mdf est l'extension du fichier image CD/DVD et le fichier mds est le fichier de métadonnées du fichier mdf.
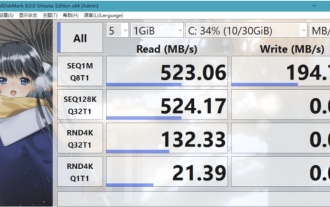 Quel logiciel est CrystalDiskmark ? -Comment utiliser crystaldiskmark ?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
Quel logiciel est CrystalDiskmark ? -Comment utiliser crystaldiskmark ?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark est un petit outil de référence pour disques durs qui mesure rapidement les vitesses de lecture/écriture séquentielles et aléatoires. Ensuite, laissez l'éditeur vous présenter CrystalDiskMark et comment utiliser crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction à CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark est un outil de test de performances de disque largement utilisé pour évaluer la vitesse et les performances de lecture et d'écriture des disques durs mécaniques et des disques SSD (SSD). ). Performances d’E/S aléatoires. Il s'agit d'une application Windows gratuite qui fournit une interface conviviale et divers modes de test pour évaluer différents aspects des performances du disque dur. Elle est largement utilisée dans les revues de matériel.
 Comment télécharger foobar2000 ? -Comment utiliser foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
Comment télécharger foobar2000 ? -Comment utiliser foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 est un logiciel qui peut écouter des ressources musicales à tout moment. Il vous offre toutes sortes de musique avec une qualité sonore sans perte. La version améliorée du lecteur de musique vous permet d'obtenir une expérience musicale plus complète et plus confortable. lire l'audio avancé sur l'ordinateur. L'appareil est transplanté sur le téléphone mobile pour offrir une expérience de lecture de musique plus pratique et efficace. La conception de l'interface est simple, claire et facile à utiliser. opérations pour démarrer rapidement. Il prend également en charge une variété de skins et de thèmes, personnalisez les paramètres en fonction de vos propres préférences et créez un lecteur de musique exclusif prenant en charge la lecture de plusieurs formats audio. Il prend également en charge la fonction de gain audio pour régler le volume. selon vos propres conditions auditives pour éviter les dommages auditifs causés par un volume excessif. Ensuite, laisse-moi t'aider
 Comment utiliser NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
Comment utiliser NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, en tant qu'adresse e-mail largement utilisée par les internautes chinois, a toujours gagné la confiance des utilisateurs grâce à ses services stables et efficaces. NetEase Mailbox Master est un logiciel de messagerie spécialement créé pour les utilisateurs de téléphones mobiles. Il simplifie grandement le processus d'envoi et de réception d'e-mails et rend le traitement de nos e-mails plus pratique. Alors comment utiliser NetEase Mailbox Master, et quelles sont ses fonctions spécifiques Ci-dessous, l'éditeur de ce site vous donnera une introduction détaillée, en espérant vous aider ! Tout d’abord, vous pouvez rechercher et télécharger l’application NetEase Mailbox Master dans la boutique d’applications mobiles. Recherchez « NetEase Mailbox Master » dans l'App Store ou Baidu Mobile Assistant, puis suivez les instructions pour l'installer. Une fois le téléchargement et l'installation terminés, nous ouvrons le compte de messagerie NetEase et nous connectons. L'interface de connexion est la suivante
 Comment utiliser l'application Baidu Netdisk
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Comment utiliser l'application Baidu Netdisk
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Le stockage cloud est devenu aujourd’hui un élément indispensable de notre vie quotidienne et de notre travail. En tant que l'un des principaux services de stockage cloud en Chine, Baidu Netdisk a gagné la faveur d'un grand nombre d'utilisateurs grâce à ses puissantes fonctions de stockage, sa vitesse de transmission efficace et son expérience de fonctionnement pratique. Et que vous souhaitiez sauvegarder des fichiers importants, partager des informations, regarder des vidéos en ligne ou écouter de la musique, Baidu Cloud Disk peut répondre à vos besoins. Cependant, de nombreux utilisateurs peuvent ne pas comprendre l'utilisation spécifique de l'application Baidu Netdisk, ce didacticiel vous présentera donc en détail comment utiliser l'application Baidu Netdisk. Si vous êtes toujours confus, veuillez suivre cet article pour en savoir plus ! Comment utiliser Baidu Cloud Network Disk : 1. Installation Tout d'abord, lors du téléchargement et de l'installation du logiciel Baidu Cloud, veuillez sélectionner l'option d'installation personnalisée.
 Tutoriel BTCC : Comment lier et utiliser le portefeuille MetaMask sur l'échange BTCC ?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
Tutoriel BTCC : Comment lier et utiliser le portefeuille MetaMask sur l'échange BTCC ?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (également appelé Little Fox Wallet en chinois) est un logiciel de portefeuille de cryptage gratuit et bien accueilli. Actuellement, BTCC prend en charge la liaison au portefeuille MetaMask. Après la liaison, vous pouvez utiliser le portefeuille MetaMask pour vous connecter rapidement, stocker de la valeur, acheter des pièces, etc., et vous pouvez également obtenir un bonus d'essai de 20 USDT pour la première liaison. Dans le didacticiel du portefeuille BTCCMetaMask, nous présenterons en détail comment enregistrer et utiliser MetaMask, ainsi que comment lier et utiliser le portefeuille Little Fox dans BTCC. Qu'est-ce que le portefeuille MetaMask ? Avec plus de 30 millions d’utilisateurs, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet est aujourd’hui l’un des portefeuilles de crypto-monnaie les plus populaires. Son utilisation est gratuite et peut être installée sur le réseau en tant qu'extension
 Comment utiliser Xiaoai Speaker Comment connecter Xiaoai Speaker à un téléphone mobile
Feb 22, 2024 pm 05:19 PM
Comment utiliser Xiaoai Speaker Comment connecter Xiaoai Speaker à un téléphone mobile
Feb 22, 2024 pm 05:19 PM
Après avoir appuyé longuement sur le bouton play de l'enceinte, connectez-vous au wifi dans le logiciel pour l'utiliser. Tutoriel Modèle applicable : Xiaomi 12 Système : EMUI11.0 Version : Xiaoai Classmate 2.4.21 Analyse 1 Trouvez d'abord le bouton de lecture du haut-parleur et maintenez-le enfoncé pour accéder au mode de distribution réseau. 2 Connectez-vous à votre compte Xiaomi dans le logiciel Xiaoai Speaker sur votre téléphone et cliquez pour ajouter un nouveau haut-parleur Xiaoai. 3. Après avoir entré le nom et le mot de passe du wifi, vous pouvez appeler Xiao Ai pour l'utiliser. Supplément : quelles sont les fonctions de Xiaoai Speaker ? 1 Xiaoai Speaker a des fonctions système, des fonctions sociales, des fonctions de divertissement, des fonctions de connaissances, des fonctions de vie, une maison intelligente et des plans de formation. Résumé/Remarques : L'application Xiao Ai doit être installée à l'avance sur votre téléphone mobile pour une connexion et une utilisation faciles.






