
Cet article présente principalement en détail l'implémentation de l'algorithme de réseau neuronal (BP) et une application simple en Python. Il a une certaine valeur de référence. Les amis intéressés peuvent s'y référer
Les exemples de cet article sont partagés avec. vous. Le code spécifique pour implémenter des algorithmes et des applications de réseau neuronal en Python est fourni pour votre référence. Le contenu spécifique est le suivant
Tout d'abord, utilisez Python pour implémenter un algorithme de réseau neuronal simple :
import numpy as np
# 定义tanh函数
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
# tanh函数的导数
def tan_deriv(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x) * np.tan(x)
# sigmoid函数
def logistic(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# sigmoid函数的导数
def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x) * (1 - logistic(x))
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, layers, activation='tanh'):
"""
神经网络算法构造函数
:param layers: 神经元层数
:param activation: 使用的函数(默认tanh函数)
:return:none
"""
if activation == 'logistic':
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tan_deriv
# 权重列表
self.weights = []
# 初始化权重(随机)
for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1):
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1)) - 1) * 0.25)
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1])) - 1) * 0.25)
def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
"""
训练神经网络
:param X: 数据集(通常是二维)
:param y: 分类标记
:param learning_rate: 学习率(默认0.2)
:param epochs: 训练次数(最大循环次数,默认10000)
:return: none
"""
# 确保数据集是二维的
X = np.atleast_2d(X)
temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1] + 1])
temp[:, 0: -1] = X
X = temp
y = np.array(y)
for k in range(epochs):
# 随机抽取X的一行
i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0])
# 用随机抽取的这一组数据对神经网络更新
a = [X[i]]
# 正向更新
for l in range(len(self.weights)):
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l])))
error = y[i] - a[-1]
deltas = [error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])]
# 反向更新
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1):
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T) * self.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse()
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta)
def predict(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0] + 1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l]))
return a
Utilisez votre propre algorithme de réseau neuronal défini pour implémenter quelques fonctions simples :
Petit cas :
X : Y
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
from NN.NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork import numpy as np nn = NeuralNetwork([2, 2, 1], 'tanh') temp = [[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]] X = np.array(temp) y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0]) nn.fit(X, y) for i in temp: print(i, nn.predict(i))
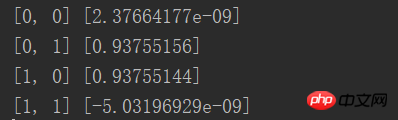
Les résultats sont essentiellement Mécanisme, illimité Proche de 0 ou infiniment proche de 1
Deuxième exemple : Identifier des nombres en images
Importer des données :
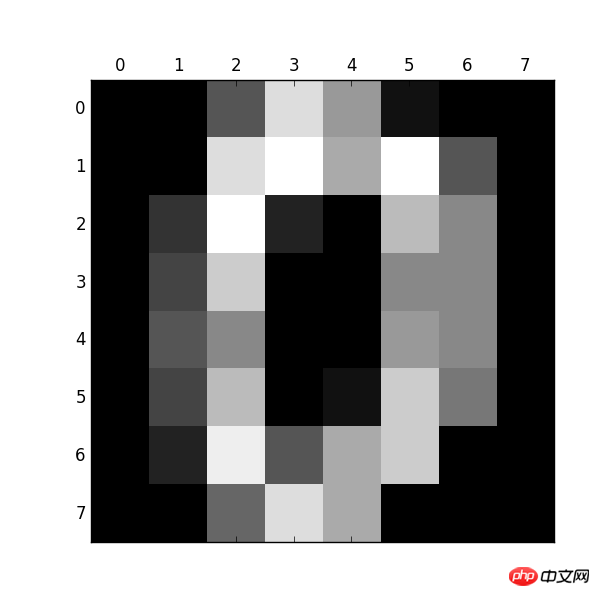
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits import pylab as pl digits = load_digits() print(digits.data.shape) pl.gray() pl.matshow(digits.images[0]) pl.show()
Observez ci-dessous : Taille : (1797, 64)
Numéro 0
Le code suivant est à identifier eux :
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from NN.NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
# 加载数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.data
y = digits.target
# 处理数据,使得数据处于0,1之间,满足神经网络算法的要求
X -= X.min()
X /= X.max()
# 层数:
# 输出层10个数字
# 输入层64因为图片是8*8的,64像素
# 隐藏层假设100
nn = NeuralNetwork([64, 100, 10], 'logistic')
# 分隔训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
# 转化成sklearn需要的二维数据类型
labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train)
labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test)
print("start fitting")
# 训练3000次
nn.fit(X_train, labels_train, epochs=3000)
predictions = []
for i in range(X_test.shape[0]):
o = nn.predict(X_test[i])
# np.argmax:第几个数对应最大概率值
predictions.append(np.argmax(o))
# 打印预测相关信息
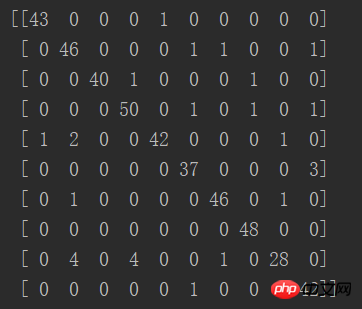
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions))
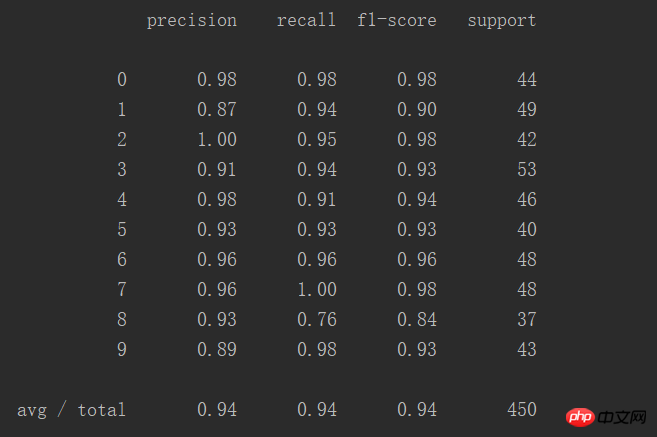
print(classification_report(y_test, predictions))Résultat :
La diagonale de la matrice représente le nombre de prédictions correctes, et on constate que la bonne le taux est multiple
Ce tableau montre la précision de la prédiction de manière plus intuitive :
Un total de 450 cas, le succès le taux est de 94 %
Recommandations associées :
Implémentation de l'algorithme Python KNN et méthode simple de reconnaissance des nombres
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!