 interface Web
interface Web
 js tutoriel
js tutoriel
 Implémentation Javascript d'exemples de développement de graphiques statistiques dynamiques_compétences Javascript
Implémentation Javascript d'exemples de développement de graphiques statistiques dynamiques_compétences Javascript
Implémentation Javascript d'exemples de développement de graphiques statistiques dynamiques_compétences Javascript
L'exemple de cet article décrit le code d'implémentation de graphiques statistiques dynamiques en JavaScript. Partagez-le avec tout le monde pour votre référence. Les détails sont les suivants :
La capture d'écran de l'effet en cours d'exécution est la suivante :
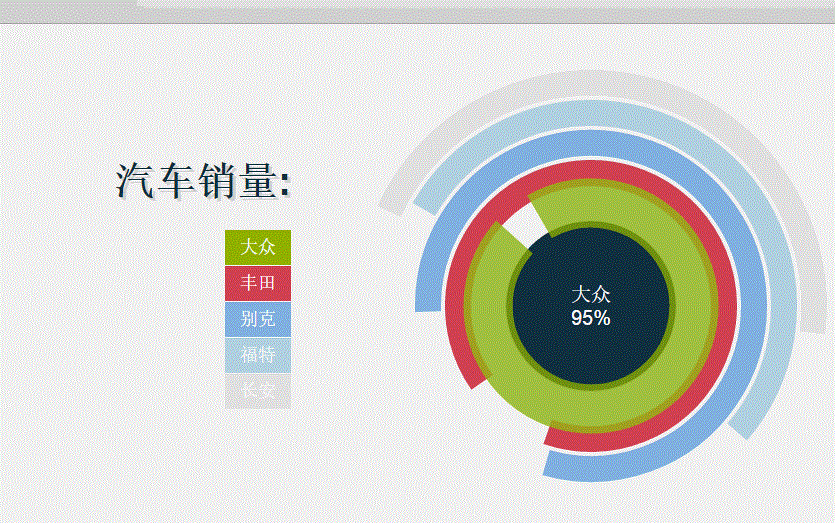
Le code spécifique est le suivant
code html :
<div id="content">
<div class="legend">
<h1>汽车销量:</h1>
<div class="skills">
<ul>
<li class="jq">大众</li>
<li class="css">丰田</li>
<li class="html">别克</li>
<li class="php">福特</li>
<li class="sql">长安</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div id="diagram"></div>
</div>
<div class="get">
<div class="arc">
<span class="text">大众</span>
<input type="hidden" class="percent" value="95" />
<input type="hidden" class="color" value="#97BE0D" />
</div>
<div class="arc">
<span class="text">丰田</span>
<input type="hidden" class="percent" value="90" />
<input type="hidden" class="color" value="#D84F5F" />
</div>
<div class="arc">
<span class="text">别克</span>
<input type="hidden" class="percent" value="80" />
<input type="hidden" class="color" value="#88B8E6" />
</div>
<div class="arc">
<span class="text">福特</span>
<input type="hidden" class="percent" value="53" />
<input type="hidden" class="color" value="#BEDBE9" />
</div>
<div class="arc">
<span class="text">长安</span>
<input type="hidden" class="percent" value="45" />
<input type="hidden" class="color" value="#EDEBEE" />
</div>
</div>
code css :
#content {
position:absolute;
top:50%;
left:50%;
margin:-340px 0 0 -450px;
width:900px;
height:600px;
}
.legend {
float:left;
width:250px;
margin-top:140px;
}
#content h1 {
font-family:'Cabin Sketch', arial, serif;
text-shadow:3px 3px 0 #ddd;
color:#193340;
font-size:40px;
margin-bottom:40px;
text-align:right;
}
.skills {
float:left;
clear:both;
width:100%;
}
.skills ul,
.skills li {
display:block;
list-style:none;
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.skills li {
float:right;
clear:both;
padding:0 15px;
height:35px;
line-height:35px;
color:#fff;
margin-bottom:1px;
font-size:18px;
}
code js :
var o = {
init: function () {
this.diagram();
},
random: function (l, u) {
return Math.floor((Math.random() * (u - l + 1)) + l);
},
diagram: function () {
var r = Raphael('diagram', 600, 600),
rad = 73;
r.circle(300, 300, 85).attr({ stroke: 'none', fill: '#193340' });
var title = r.text(300, 300, 'loading...').attr({
font: '20px Arial',
fill: '#fff'
}).toFront();
r.customAttributes.arc = function (value, color, rad) {
var v = 3.6 * value,
alpha = v == 360 ? 359.99 : v,
random = o.random(91, 240),
a = (random - alpha) * Math.PI / 180,
b = random * Math.PI / 180,
sx = 300 + rad * Math.cos(b),
sy = 300 - rad * Math.sin(b),
x = 300 + rad * Math.cos(a),
y = 300 - rad * Math.sin(a),
path = [['M', sx, sy], ['A', rad, rad, 0, +(alpha > 180), 1, x, y]];
return { path: path, stroke: color }
}
$('.get').find('.arc').each(function (i) {
var t = $(this),
color = t.find('.color').val(),
value = t.find('.percent').val(),
text = t.find('.text').text();
rad += 30;
var z = r.path().attr({ arc: [value, color, rad], 'stroke-width': 26 });
z.mouseover(function () {
this.animate({ 'stroke-width': 50, opacity: .75 }, 1000, 'elastic');
if (Raphael.type != 'VML') //solves IE problem
this.toFront();
title.animate({ opacity: 0 }, 500, '>', function () {
this.attr({ text: text + '\n' + value + '%' }).animate({ opacity: 1 }, 500, '<');
});
}).mouseout(function () {
this.animate({ 'stroke-width': 26, opacity: 1 }, 1000, 'elastic');
});
});
}
}
$(function () { o.init(); });J'espère que cet article sera utile à tous ceux qui apprennent la programmation JavaScript.

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Interface ECharts et Java : Comment implémenter rapidement des graphiques statistiques tels que des graphiques linéaires, des graphiques à barres, des diagrammes circulaires, etc.
Dec 17, 2023 pm 10:37 PM
Interface ECharts et Java : Comment implémenter rapidement des graphiques statistiques tels que des graphiques linéaires, des graphiques à barres, des diagrammes circulaires, etc.
Dec 17, 2023 pm 10:37 PM
Interface ECharts et Java : comment implémenter rapidement des graphiques statistiques tels que des graphiques linéaires, des graphiques à barres et des diagrammes circulaires, nécessitant des exemples de code spécifiques. Avec l'avènement de l'ère Internet, l'analyse des données est devenue de plus en plus importante. Les graphiques statistiques sont une méthode d'affichage très intuitive et puissante. Les graphiques peuvent afficher les données plus clairement, permettant aux utilisateurs de mieux comprendre la connotation et les modèles des données. Dans le développement Java, nous pouvons utiliser les interfaces ECharts et Java pour afficher rapidement divers graphiques statistiques. ECharts est un logiciel développé par Baidu
 Comment mettre en œuvre un système de reconnaissance vocale en ligne à l'aide de WebSocket et JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
Comment mettre en œuvre un système de reconnaissance vocale en ligne à l'aide de WebSocket et JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
Comment utiliser WebSocket et JavaScript pour mettre en œuvre un système de reconnaissance vocale en ligne Introduction : Avec le développement continu de la technologie, la technologie de reconnaissance vocale est devenue une partie importante du domaine de l'intelligence artificielle. Le système de reconnaissance vocale en ligne basé sur WebSocket et JavaScript présente les caractéristiques d'une faible latence, d'un temps réel et d'une multiplateforme, et est devenu une solution largement utilisée. Cet article explique comment utiliser WebSocket et JavaScript pour implémenter un système de reconnaissance vocale en ligne.
 WebSocket et JavaScript : technologies clés pour mettre en œuvre des systèmes de surveillance en temps réel
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket et JavaScript : technologies clés pour mettre en œuvre des systèmes de surveillance en temps réel
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket et JavaScript : technologies clés pour réaliser des systèmes de surveillance en temps réel Introduction : Avec le développement rapide de la technologie Internet, les systèmes de surveillance en temps réel ont été largement utilisés dans divers domaines. L'une des technologies clés pour réaliser une surveillance en temps réel est la combinaison de WebSocket et de JavaScript. Cet article présentera l'application de WebSocket et JavaScript dans les systèmes de surveillance en temps réel, donnera des exemples de code et expliquera leurs principes de mise en œuvre en détail. 1. Technologie WebSocket
 Comment utiliser JavaScript et WebSocket pour mettre en œuvre un système de commande en ligne en temps réel
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Comment utiliser JavaScript et WebSocket pour mettre en œuvre un système de commande en ligne en temps réel
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction à l'utilisation de JavaScript et de WebSocket pour mettre en œuvre un système de commande en ligne en temps réel : avec la popularité d'Internet et les progrès de la technologie, de plus en plus de restaurants ont commencé à proposer des services de commande en ligne. Afin de mettre en œuvre un système de commande en ligne en temps réel, nous pouvons utiliser les technologies JavaScript et WebSocket. WebSocket est un protocole de communication full-duplex basé sur le protocole TCP, qui peut réaliser une communication bidirectionnelle en temps réel entre le client et le serveur. Dans le système de commande en ligne en temps réel, lorsque l'utilisateur sélectionne des plats et passe une commande
 Comment mettre en œuvre un système de réservation en ligne à l'aide de WebSocket et JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
Comment mettre en œuvre un système de réservation en ligne à l'aide de WebSocket et JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
Comment utiliser WebSocket et JavaScript pour mettre en œuvre un système de réservation en ligne. À l'ère numérique d'aujourd'hui, de plus en plus d'entreprises et de services doivent fournir des fonctions de réservation en ligne. Il est crucial de mettre en place un système de réservation en ligne efficace et en temps réel. Cet article explique comment utiliser WebSocket et JavaScript pour implémenter un système de réservation en ligne et fournit des exemples de code spécifiques. 1. Qu'est-ce que WebSocket ? WebSocket est une méthode full-duplex sur une seule connexion TCP.
 ECharts et interface Java : un guide de démarrage pour la mise en œuvre de différents types de graphiques statistiques
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
ECharts et interface Java : un guide de démarrage pour la mise en œuvre de différents types de graphiques statistiques
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
ECharts et interface Java : un guide de démarrage pour la mise en œuvre de divers types de graphiques statistiques Introduction : Avec l'application généralisée de la visualisation de données dans divers secteurs et domaines, diverses bibliothèques de graphiques se sont également développées rapidement. ECharts est une puissante bibliothèque de visualisation open source développée et maintenue par Baidu. Elle propose des types de graphiques riches et des capacités de personnalisation flexibles. Cet article explique comment utiliser ECharts via l'interface Java pour implémenter différents types de graphiques statistiques. Préparation Avant de commencer, nous devons nous assurer que l'environnement de développement Java a été installé.
 JavaScript et WebSocket : créer un système efficace de prévisions météorologiques en temps réel
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript et WebSocket : créer un système efficace de prévisions météorologiques en temps réel
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript et WebSocket : Construire un système efficace de prévisions météorologiques en temps réel Introduction : Aujourd'hui, la précision des prévisions météorologiques revêt une grande importance pour la vie quotidienne et la prise de décision. À mesure que la technologie évolue, nous pouvons fournir des prévisions météorologiques plus précises et plus fiables en obtenant des données météorologiques en temps réel. Dans cet article, nous apprendrons comment utiliser la technologie JavaScript et WebSocket pour créer un système efficace de prévisions météorologiques en temps réel. Cet article démontrera le processus de mise en œuvre à travers des exemples de code spécifiques. Nous
 Tutoriel JavaScript simple : Comment obtenir le code d'état HTTP
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Tutoriel JavaScript simple : Comment obtenir le code d'état HTTP
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Tutoriel JavaScript : Comment obtenir le code d'état HTTP, des exemples de code spécifiques sont requis Préface : Dans le développement Web, l'interaction des données avec le serveur est souvent impliquée. Lors de la communication avec le serveur, nous devons souvent obtenir le code d'état HTTP renvoyé pour déterminer si l'opération a réussi et effectuer le traitement correspondant en fonction de différents codes d'état. Cet article vous apprendra comment utiliser JavaScript pour obtenir des codes d'état HTTP et fournira quelques exemples de codes pratiques. Utilisation de XMLHttpRequest





