Implémentation des tâches périodiques de THINKPHP

THINKPHP的cron计划任务的实现,利用THINKPHP自带的cli,加上数据库执行记录(记录任务的报错,成功)。
在服务器cron定时任务在网站目录(不是网站根目录)执行php cron.php,网站根目录为Public。
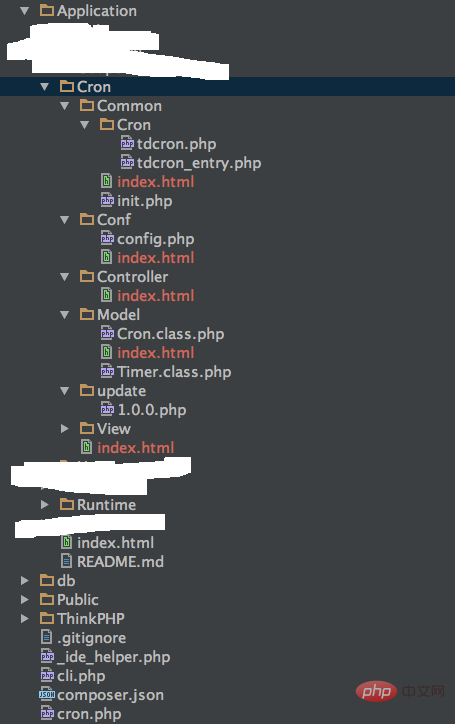
写一个cli的入口文件
cli.php
<?php define('MODE_NAME', 'cli'); // 检测PHP环境 if(version_compare(PHP_VERSION,'5.3.0','<')) die('require PHP > 5.3.0 !'); define('APP_DEBUG', true); // 定义应用目录 define('APP_PATH', __DIR__ . '/Application/'); // 引入ThinkPHP入口文件 require __DIR__ . '/ThinkPHP/ThinkPHP.php';
写一个执行文件
cron.php
define('AUTO_CRON', true); include __DIR__ . '/cli.php';
数据库设计
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `cron`; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `cron` ( `cron_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `expression` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `class` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `method` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `type` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `status` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', `updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', `run_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, `ms` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `error` text COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`cron_id`), KEY `name` (`name`,`created_at`), KEY `cron_status_index` (`status`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci AUTO_INCREMENT=1 ;
配置文件
<?php
return array(
'version' => '1.0.0',
'beastalkd' => array(
'process_untreated_queue' => array(
'expression' => '* * * * *',
'class' => 'Statistics\Model\PheanstalkModel',
'method' => 'processUntreatedQueue'
)
)
);执行文件 init.php
/写个hook程序执行init.php
<?php
use Think\Log, Think\Db, Cron\Model\Cron;
$Model = new \Think\Model();
$Has = !$Model->query("SHOW TABLES LIKE 'cron'")?false:true;
if(defined("AUTO_CRON") && $Has){
class CronCommand
{
protected $_initializedJobs;
protected $_jobs;
protected $_now;
public function __construct()
{
$this->_now = strtotime(date('Y-n-j H:i'));
import("Cron.Common.Cron.tdcron_entry",'','.php');
import("Cron.Common.Cron.tdcron",'','.php');
}
/**
* 这里是放要执行的代码
*/
public function fire()
{
restore_error_handler();
restore_exception_handler();
$this->_initializedJobs = array();
$jobs = M('cron')->where("status = 'initialized'")->select();
/**
* @var $cron Cron
* 已存在 cron
*/
if($jobs) {
$cron = new Cron();
foreach ($jobs as $data) {
$cron->setData($data)->isNew(false);
$this->_initializedJobs[$data['name']] = $cron;
}
}
/**
* 新 cron
*/
foreach ($this->getCronJobs() as $name => $cronJob) {
if (isset($cronJob['expression'])) {
$expression = $cronJob['expression'];
} else {
Log::write('Cron expression is required for cron job "' . $name . '"',Log::WARN);
continue;
}
if ($this->_now != tdCron::getNextOccurrence($expression, $this->_now)) continue;
$cronJob['name'] = $name;
$cron = isset($this->_initializedJobs[$name]) ? $this->_initializedJobs[$name] : $this->_initializedJobs[$name] = new Cron();
$cron->initialize($cronJob);
}
/* @var $cron Cron 处理*/
foreach ($this->_initializedJobs as $cron) {
$cron->run();
}
}
/**
* Get All Defined Cron Jobs
* 获取配置
* @return array
*/
public function getCronJobs()
{
if ($this->_jobs === null) {
$this->_jobs = C('beastalkd');
}
return $this->_jobs;
}
}
$command = new CronCommand();
$command->fire();
}cron 模型
<?php
namespace Cron\Model;
use Common\Model;
use Think\Log;
/**
* Class Cron
* @method string getClass()
* @method string getMethod()
* @method string getName()
* @method string getType()
* @package Cron\Model
*/
class Cron extends Model{
const STATUS_COMPLETED = 'completed';
const STATUS_FAILED = 'failed';
const STATUS_INITIALIZED = 'initialized';
const STATUS_RUNNING = 'running';
protected $name = 'cron';
protected $tableName = 'cron';
protected $pk = 'cron_id';
protected $_originalData = array();
/**
* 保存配置信息CLASS
*/
protected static $_cron_classes = array();
/**
* @param $class
* @return mixed 获取配置的 CLASS
*/
public function getSingleton($class)
{
isset(static::$_cron_classes[$class]) or static::$_cron_classes[$class] = new $class;
return static::$_cron_classes[$class];
}
/**
* @param $cronJob
* @return $this
* 初始化 任务状态
*/
public function initialize($cronJob)
{
foreach ($cronJob as $k => $v) {
$this->setData($k, $v);
}
$now = date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
$this->setData('status',self::STATUS_INITIALIZED)->setData('created_at',$now)->setData('updated_at',$now)->save();
return $this;
}
/**
* @return $this run 命令
*/
public function run()
{
$this->setData('run_at',date('Y-m-d H:i:s'))->setData('status',self::STATUS_RUNNING)->save();
Timer::start();
try {
$class = $this->getData('class');
$method = $this->getData('method');
if (!class_exists($class)) throw new \Exception(sprintf('Class "%s" not found!', $class));
if (!method_exists($class, $method)) throw new \Exception(sprintf('Method "%s::%s()" not found!', $class, $method));
$callback = array($this->getSingleton($class), $method);
//new CLASS 使用操作方法
// 执行配置里的 Statistics\Model\PheanstalkModel类 的 processUntreatedQueue 操作
call_user_func($callback);
Timer::stop();
$this->setData('ms',round(Timer::diff() * 1000))->setData('status',self::STATUS_COMPLETED)->save();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
Timer::stop();
$this->setData('ms',round(Timer::diff() * 1000))
->setData('status',self::STATUS_FAILED)
->setData('error',$e->getMessage() . "\nParams:\n" . var_export($this->getDbFields(), true))->save();
Log::write($e->getMessage() . "\n" . $e->getTraceAsString(),Log::ERR);
}
return $this;
}
}Common\Model 模型
<?php
namespace Common;
use Think\Model as ThinkModel;
/**
* Class Model
* @package Common
*
* @property \Think\Db\Driver\Mysql $db DB instance
*/
abstract class Model extends ThinkModel {
protected $_isNew = true;
protected $_jsonFields = array();
protected $_originalData = array();
protected function _after_find(&$result, $options) {
foreach ($this->_jsonFields as $field) {
is_string($_data = fnGet($result, $field)) and $result[$field] = json_decode($_data, true);
}
$this->_originalData = $result;
$this->_isNew = !$result;
parent::_after_find($result, $options);
}
protected function _after_save($result) {
}
protected function _before_find() {
$this->_originalData = array();
}
protected function _facade($data) {
foreach ($this->_jsonFields as $field) {
is_array($_data = fnGet($data, $field)) and $data[$field] = json_encode($_data);
}
return parent::_facade($data);
}
public function find($options = array()) {
$this->_before_find();
return parent::find($options);
}
public function getData($key = null) {
return $key === null ? $this->data : $this->__get($key);
}
public function getOptions() {
return $this->options;
}
public function getOriginalData($key = null) {
return $key === null ? $this->_originalData : fnGet($this->_originalData, $key);
}
/**
* Get or set isNew flag
*
* @param bool $flag
*
* @return bool
*/
public function isNew($flag = null) {
if ($flag !== null) $this->_isNew = (bool)$flag;
return $this->_isNew;
}
public function save($data = '', $options = array()) {
if ($this->_isNew) {
$oldData = $this->data;
$result = $this->add($data, $options);
$this->data = $oldData;
if ($result && $this->pk && is_string($this->pk)) {
$this->setData($this->pk, $result);
}
$this->_isNew = false;
} else {
$oldData = $this->data;
$result = parent::save($data, $options);
$this->data = $oldData;
}
$this->_after_save($result);
return $result;
}
public function setData($key, $value = null) {
is_array($key) ?
$this->data = $key :
$this->data[$key] = $value;
return $this;
}
}Timer.class.php
<?php
namespace Cron\Model;
class Timer
{
protected static $_start = array(0, 0);
protected static $_stop = array(0, 0);
public static function diff($start = null, $stop = null)
{
$start and self::start($start);
$stop and self::stop($stop);
return (self::$_stop[0] - self::$_start[0]) + (self::$_stop[1] - self::$_start[1]);
}
public static function start($microtime = null)
{
$microtime or $microtime = microtime();
self::$_start = explode(' ', $microtime);
}
public static function stop($microtime = null)
{
$microtime or $microtime = microtime();
self::$_stop = explode(' ', $microtime);
}
}tdcron.php
<?php
define('IDX_MINUTE', 0);
define('IDX_HOUR', 1);
define('IDX_DAY', 2);
define('IDX_MONTH', 3);
define('IDX_WEEKDAY', 4);
define('IDX_YEAR', 5);
/*
* tdCron v0.0.1 beta - CRON-Parser for PHP
*
* Copyright (c) 2010 Christian Land / tagdocs.de
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and
* associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction,
* including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense,
* and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so,
* subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial
* portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN
* NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE
* SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
*
* @author Christian Land <devel@tagdocs.de>
* @package tdCron
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2010, Christian Land / tagdocs.de
* @version v0.0.1 beta
*/
class tdCron
{
/**
* Parsed cron-expressions cache.
* @var mixed
*/
static private $pcron = array();
/**
* getNextOccurrence() uses a cron-expression to calculate the time and date at which a cronjob
* should be executed the next time. If a reference-time is passed, the next time and date
* after that time is calculated.
*
* @access public
* @param string $expression cron-expression to use
* @param int $timestamp optional reference-time
* @return int
* @throws Exception
*/
static public function getNextOccurrence($expression, $timestamp = null)
{
try {
// Convert timestamp to array
$next = self::getTimestamp($timestamp);
// Calculate date/time
$next_time = self::calculateDateTime($expression, $next);
} catch (Exception $e) {
throw $e;
}
// return calculated time
return $next_time;
}
/**
* getLastOccurrence() does pretty much the same as getNextOccurrence(). The only difference
* is, that it doesn't calculate the next but the last time a cronjob should have been executed.
*
* @access public
* @param string $expression cron-expression to use
* @param int $timestamp optional reference-time
* @return int
* @throws Exception
*/
static public function getLastOccurrence($expression, $timestamp = null)
{
try {
// Convert timestamp to array
$last = self::getTimestamp($timestamp);
// Calculate date/time
$last_time = self::calculateDateTime($expression, $last, false);
} catch (Exception $e) {
throw $e;
}
// return calculated time
return $last_time;
}
/**
* calculateDateTime() is the function where all the magic happens :-)
*
* It calculates the time and date at which the next/last call of a cronjob is/was due.
*
* @access private
* @param mixed $expression cron-expression
* @param mixed $rtime reference-time
* @param bool $next true = nextOccurence, false = lastOccurence
* @return int
* @throws Exception
*/
static private function calculateDateTime($expression, $rtime, $next = true)
{
// Initialize vars
$calc_date = true;
// Parse cron-expression (if neccessary)
$cron = self::getExpression($expression, !$next);
// OK, lets see if the day/month/weekday of the reference-date exist in our
// $cron-array.
if (!in_array($rtime[IDX_DAY], $cron[IDX_DAY]) || !in_array($rtime[IDX_MONTH], $cron[IDX_MONTH]) || !in_array($rtime[IDX_WEEKDAY], $cron[IDX_WEEKDAY])) {
// OK, things are easy. The day/month/weekday of the reference time
// can't be found in the $cron-array. This means that no matter what
// happens, we WILL end up at at a different date than that of our
// reference-time. And in this case, the lastOccurrence will ALWAYS
// happen at the latest possible time of the day and the nextOccurrence
// at the earliest possible time.
//
// In both cases, the time can be found in the first elements of the
// hour/minute cron-arrays.
$rtime[IDX_HOUR] = reset($cron[IDX_HOUR]);
$rtime[IDX_MINUTE] = reset($cron[IDX_MINUTE]);
} else {
// OK, things are getting a little bit more complicated...
$nhour = self::findValue($rtime[IDX_HOUR], $cron[IDX_HOUR], $next);
// Meh. Such a cruel world. Something has gone awry. Lets see HOW awry it went.
if ($nhour === false) {
// Ah, the hour-part went wrong. Thats easy. Wrong hour means that no
// matter what we do we'll end up at a different date. Thus we can use
// some simple operations to make things look pretty ;-)
//
// As alreasy mentioned before -> different date means earliest/latest
// time:
$rtime[IDX_HOUR] = reset($cron[IDX_HOUR]);
$rtime[IDX_MINUTE] = reset($cron[IDX_MINUTE]);
// Now all we have to do is add/subtract a day to get a new reference time
// to use later to find the right date. The following line probably looks
// a little odd but thats the easiest way of adding/substracting a day without
// screwing up the date. Just trust me on that one ;-)
$rtime = explode(',', strftime('%M,%H,%d,%m,%w,%Y', mktime($rtime[IDX_HOUR], $rtime[IDX_MINUTE], 0, $rtime[IDX_MONTH], $rtime[IDX_DAY], $rtime[IDX_YEAR]) + ((($next) ? 1 : -1) * 86400)));
} else {
// OK, there is a higher/lower hour available. Check the minutes-part.
$nminute = self::findValue($rtime[IDX_MINUTE], $cron[IDX_MINUTE], $next);
if ($nminute === false) {
// No matching minute-value found... lets see what happens if we substract/add an hour
$nhour = self::findValue($rtime[IDX_HOUR] + (($next) ? 1 : -1), $cron[IDX_HOUR], $next);
if ($nhour === false) {
// No more hours available... add/substract a day... you know what happens ;-)
$nminute = reset($cron[IDX_MINUTE]);
$nhour = reset($cron[IDX_HOUR]);
$rtime = explode(',', strftime('%M,%H,%d,%m,%w,%Y', mktime($nhour, $nminute, 0, $rtime[IDX_MONTH], $rtime[IDX_DAY], $rtime[IDX_YEAR]) + ((($next) ? 1 : -1) * 86400)));
} else {
// OK, there was another hour. Set the right minutes-value
$rtime[IDX_HOUR] = $nhour;
$rtime[IDX_MINUTE] = (($next) ? reset($cron[IDX_MINUTE]) : end($cron[IDX_MINUTE]));
$calc_date = false;
}
} else {
// OK, there is a matching minute... reset minutes if hour has changed
if ($nhour <> $rtime[IDX_HOUR]) {
$nminute = reset($cron[IDX_MINUTE]);
}
// Set time
$rtime[IDX_HOUR] = $nhour;
$rtime[IDX_MINUTE] = $nminute;
$calc_date = false;
}
}
}
// If we have to calculate the date... we'll do so
if ($calc_date) {
if (in_array($rtime[IDX_DAY], $cron[IDX_DAY]) && in_array($rtime[IDX_MONTH], $cron[IDX_MONTH]) && in_array($rtime[IDX_WEEKDAY], $cron[IDX_WEEKDAY])) {
return mktime($rtime[1], $rtime[0], 0, $rtime[3], $rtime[2], $rtime[5]);
} else {
// OK, some searching necessary...
$cdate = mktime(0, 0, 0, $rtime[IDX_MONTH], $rtime[IDX_DAY], $rtime[IDX_YEAR]);
// OK, these three nested loops are responsible for finding the date...
//
// The class has 2 limitations/bugs right now:
//
// -> it doesn't work for dates in 2036 or later!
// -> it will most likely fail if you search for a Feburary, 29th with a given weekday
// (this does happen because the class only searches in the next/last 10 years! And
// while it usually takes less than 10 years for a "normal" date to iterate through
// all weekdays, it can take 20+ years for Feb, 29th to iterate through all weekdays!
for ($nyear = $rtime[IDX_YEAR]; (($next) ? ($nyear <= $rtime[IDX_YEAR] + 10) : ($nyear >= $rtime[IDX_YEAR] - 10)); $nyear = $nyear + (($next) ? 1 : -1)) {
foreach ($cron[IDX_MONTH] as $nmonth) {
foreach ($cron[IDX_DAY] as $nday) {
if (checkdate($nmonth, $nday, $nyear)) {
$ndate = mktime(0, 0, 1, $nmonth, $nday, $nyear);
if (($next) ? ($ndate >= $cdate) : ($ndate <= $cdate)) {
$dow = date('w', $ndate);
// The date is "OK" - lets see if the weekday matches, too...
if (in_array($dow, $cron[IDX_WEEKDAY])) {
// WIN! :-) We found a valid date...
$rtime = explode(',', strftime('%M,%H,%d,%m,%w,%Y', mktime($rtime[IDX_HOUR], $rtime[IDX_MINUTE], 0, $nmonth, $nday, $nyear)));
return mktime($rtime[1], $rtime[0], 0, $rtime[3], $rtime[2], $rtime[5]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
throw new Exception('Failed to find date, No matching date found in a 10 years range!', 10004);
}
return mktime($rtime[1], $rtime[0], 0, $rtime[3], $rtime[2], $rtime[5]);
}
/**
* getTimestamp() converts an unix-timestamp to an array. The returned array contains the following values:
*
* [0] -> minute
* [1] -> hour
* [2] -> day
* [3] -> month
* [4] -> weekday
* [5] -> year
*
* The array is used by various functions.
*
* @access private
* @param int $timestamp If none is given, the current time is used
* @return mixed
*/
static private function getTimestamp($timestamp = null)
{
if (is_null($timestamp)) {
$arr = explode(',', strftime('%M,%H,%d,%m,%w,%Y', time()));
} else {
$arr = explode(',', strftime('%M,%H,%d,%m,%w,%Y', $timestamp));
}
// Remove leading zeros (or we'll get in trouble ;-)
foreach ($arr as $key => $value) {
$arr[$key] = (int)ltrim($value, '0');
}
return $arr;
}
/**
* findValue() checks if the given value exists in an array. If it does not exist, the next
* higher/lower value is returned (depending on $next). If no higher/lower value exists,
* false is returned.
*
* @access public
* @param int $value
* @param mixed $data
* @param bool $next
* @return mixed
*/
static private function findValue($value, $data, $next = true)
{
if (in_array($value, $data)) {
return (int)$value;
} else {
if (($next) ? ($value <= end($data)) : ($value >= end($data))) {
foreach ($data as $curval) {
if (($next) ? ($value <= (int)$curval) : ($curval <= $value)) {
return (int)$curval;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* getExpression() returns a parsed cron-expression. Parsed cron-expressions are cached to reduce
* unneccessary calls of the parser.
*
* @access public
* @param string $expression
* @param bool $reverse
* @return mixed
* @throws Exception
*/
static private function getExpression($expression, $reverse = false)
{
// First of all we cleanup the expression and remove all duplicate tabs/spaces/etc.
// For example "* * * * *" would be converted to "* * * * *", etc.
$expression = preg_replace('/(\s+)/', ' ', strtolower(trim($expression)));
// Lets see if we've already parsed that expression
if (!isset(self::$pcron[$expression])) {
// Nope - parse it!
try {
self::$pcron[$expression] = tdCronEntry::parse($expression);
self::$pcron['reverse'][$expression] = self::arrayReverse(self::$pcron[$expression]);
} catch (Exception $e) {
throw $e;
}
}
return ($reverse ? self::$pcron['reverse'][$expression] : self::$pcron[$expression]);
}
/**
* arrayReverse() reverses all sub-arrays of our cron array. The reversed values are used for calculations
* that are run when getLastOccurence() is called.
*
* @access public
* @param mixed $cron
* @return mixed
*/
static private function arrayReverse($cron)
{
foreach ($cron as $key => $value) {
$cron[$key] = array_reverse($value);
}
return $cron;
}
}tdcron_entry.php
<?php /** * tinyCronEntry is part of tdCron. Its a class to parse Cron-Expressions like "1-45 1,2,3 1-30/5 January,February Mon,Tue" * and convert it to an easily useable format. * * The parser is quite powerful and understands pretty much everything you will ever find in a Cron-Expression. * * A Cron-Expression consists of 5 segments: * * <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> * .---------------- minute (0 - 59) * | .------------- hour (0 - 23) * | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31) * | | | .------- month (1 - 12) * | | | | .----- day of week (0 - 6) * | | | | | * * * * * * *
* 1,2,3,4,5 * 1-5 * 10-20/* * Jan,Feb,Oct * Monday-Friday * 1-10,15,20,40-50/2 *
推荐教程:《TP5》
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment exécuter le projet thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
Comment exécuter le projet thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
Pour exécuter le projet ThinkPHP, vous devez : installer Composer ; utiliser Composer pour créer le projet ; entrer dans le répertoire du projet et exécuter php bin/console serve ; visiter http://localhost:8000 pour afficher la page d'accueil.
 Il existe plusieurs versions de thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
Il existe plusieurs versions de thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
ThinkPHP dispose de plusieurs versions conçues pour différentes versions de PHP. Les versions majeures incluent 3.2, 5.0, 5.1 et 6.0, tandis que les versions mineures sont utilisées pour corriger les bogues et fournir de nouvelles fonctionnalités. La dernière version stable est ThinkPHP 6.0.16. Lorsque vous choisissez une version, tenez compte de la version PHP, des exigences en matière de fonctionnalités et du support de la communauté. Il est recommandé d'utiliser la dernière version stable pour de meilleures performances et une meilleure assistance.
 Comment exécuter thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Comment exécuter thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Étapes pour exécuter ThinkPHP Framework localement : Téléchargez et décompressez ThinkPHP Framework dans un répertoire local. Créez un hôte virtuel (facultatif) pointant vers le répertoire racine ThinkPHP. Configurez les paramètres de connexion à la base de données. Démarrez le serveur Web. Initialisez l'application ThinkPHP. Accédez à l'URL de l'application ThinkPHP et exécutez-la.
 Lequel est le meilleur, Laravel ou thinkphp ?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Lequel est le meilleur, Laravel ou thinkphp ?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Comparaison des performances des frameworks Laravel et ThinkPHP : ThinkPHP fonctionne généralement mieux que Laravel, en se concentrant sur l'optimisation et la mise en cache. Laravel fonctionne bien, mais pour les applications complexes, ThinkPHP peut être mieux adapté.
 Suggestions de développement : Comment utiliser le framework ThinkPHP pour implémenter des tâches asynchrones
Nov 22, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
Suggestions de développement : Comment utiliser le framework ThinkPHP pour implémenter des tâches asynchrones
Nov 22, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
"Suggestions de développement : comment utiliser le framework ThinkPHP pour implémenter des tâches asynchrones" Avec le développement rapide de la technologie Internet, les applications Web ont des exigences de plus en plus élevées pour gérer un grand nombre de requêtes simultanées et une logique métier complexe. Afin d'améliorer les performances du système et l'expérience utilisateur, les développeurs envisagent souvent d'utiliser des tâches asynchrones pour effectuer certaines opérations chronophages, telles que l'envoi d'e-mails, le traitement des téléchargements de fichiers, la génération de rapports, etc. Dans le domaine de PHP, le framework ThinkPHP, en tant que framework de développement populaire, offre des moyens pratiques d'implémenter des tâches asynchrones.
 Comment installer thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Comment installer thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Étapes d'installation de ThinkPHP : Préparez les environnements PHP, Composer et MySQL. Créez des projets à l'aide de Composer. Installez le framework ThinkPHP et ses dépendances. Configurez la connexion à la base de données. Générez le code de l'application. Lancez l'application et visitez http://localhost:8000.
 Quelles sont les performances de thinkphp ?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
Quelles sont les performances de thinkphp ?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
ThinkPHP est un framework PHP hautes performances présentant des avantages tels que le mécanisme de mise en cache, l'optimisation du code, le traitement parallèle et l'optimisation des bases de données. Les tests de performances officiels montrent qu'il peut gérer plus de 10 000 requêtes par seconde et qu'il est largement utilisé dans les sites Web à grande échelle et les systèmes d'entreprise tels que JD.com et Ctrip dans les applications réelles.
 Service RPC basé sur ThinkPHP6 et Swoole pour implémenter la fonction de transfert de fichiers
Oct 12, 2023 pm 12:06 PM
Service RPC basé sur ThinkPHP6 et Swoole pour implémenter la fonction de transfert de fichiers
Oct 12, 2023 pm 12:06 PM
Le service RPC basé sur ThinkPHP6 et Swoole implémente la fonction de transfert de fichiers Introduction : Avec le développement d'Internet, le transfert de fichiers est devenu de plus en plus important dans notre travail quotidien. Afin d'améliorer l'efficacité et la sécurité du transfert de fichiers, cet article présentera la méthode d'implémentation spécifique de la fonction de transfert de fichiers basée sur le service RPC basé sur ThinkPHP6 et Swoole. Nous utiliserons ThinkPHP6 comme framework Web et utiliserons la fonction RPC de Swoole pour réaliser le transfert de fichiers entre serveurs. 1. Norme environnementale






