

Tout d'abord, parlons du principe.
Cette méthode peut également garantir que la page entière n'a toujours que 2 balises img, sans avoir à créer tous les nœuds img. Le point clé est de remplacer le src de l'img invisible à chaque fois. 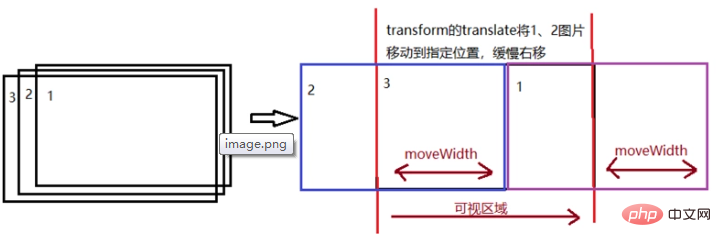
Implémentation de l'animation
Cela complète une animation en mouvement.
<header> <p> <img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banner1.jpg" class="lazy" alt="Native JS utilise la transformation pour obtenir un effet de défilement infini de la bannière" > <img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banner2.jpg" class="lazy" alt="Native JS utilise la transformation pour obtenir un effet de défilement infini de la bannière" > <img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banner3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="Native JS utilise la transformation pour obtenir un effet de défilement infini de la bannière" > <img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banner4.jpg" class="lazy" alt="Native JS utilise la transformation pour obtenir un effet de défilement infini de la bannière" > </p> <p> </p> <p>1</p> <p>2</p> <p>3</p> <p>4</p> <p> </p> <p></p> <p> </p> <p></p> </header>
var timeout = null;
window.onload = function () {
var oLeft = document.querySelector('.left');
var oRight = document.querySelector('.right');
var oButton = document.querySelector('.buttons');
var oButtons = document.querySelectorAll('.buttons p');
var oImgs = document.querySelectorAll('.box img');
var imgWidth = oImgs[0].width;
var gIndex = 0;
begainAnimate();
// 绑定左右点击事件
oLeft.onclick = function () {
clearTimeout(timeout);
leftMove();
begainAnimate();
};
oRight.onclick = function () {
clearTimeout(timeout);
rightMove();
begainAnimate();
};
// 绑定数字序号事件
oButton.onclick = function (event) {
clearTimeout(timeout);
var targetEl = event.target;
var nextIndex = (+targetEl.innerText) - 1;
console.log(nextIndex);
rightMove(nextIndex);
begainAnimate();
}
// 默认初始动画朝右边
function begainAnimate() {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(function () {
rightMove();
begainAnimate();
}, 3000);
}
// 向左移动动画
function leftMove() {
var nextIndex = (gIndex - 1 = oImgs.length) ? 0 : gIndex + 1;
}
animateSteps(nextIndex, 50);
}
// 一次动画
function animateSteps(nextIndex, timestamp) {
var currentImg = oImgs[gIndex];
var nextImg = oImgs[nextIndex];
nextImg.style.zIndex = 10;
var step = 0;
requestAnimationFrame(goStep);
// 走一帧的动画,移动timestamp
function goStep() {
var moveWidth = timestamp * step++;
if (Math.abs(moveWidth) 0 ? (moveWidth - imgWidth) : (imgWidth + moveWidth)}px)`;
requestAnimationFrame(goStep);
} else {
currentImg.style.zIndex = 1;
currentImg.style.transform = `translate(0px)`;
nextImg.style.transform = `translate(0px)`;
oButtons[gIndex].setAttribute('class', '');
oButtons[nextIndex].setAttribute('class', 'active');
gIndex = nextIndex;
}
}
}
}
window.onclose = function () {
clearTimeout(timeout);
}<style>
/* 首先设置图片box的区域,将图片重叠在一起 */
header {
width: 100%;
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
}
.box {
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
}
.box img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: absolute;
transform: translateX(0);
z-index: 1;
}
.box img:first-child {
z-index: 10;
}
/* 数字序列按钮 */
.buttons {
position: absolute;
right: 10%;
bottom: 5%;
display: flex;
z-index: 100;
}
.buttons p {
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: #aaa;
border: 1px solid #aaa;
text-align: center;
margin: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
opacity: .7;
border-radius: 15px;
line-height: 30px;
}
.buttons p.active {
background-color: white;
}
/* 左右切换按钮 */
.left,
.right {
position: absolute;
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
background-color: #ccc;
z-index: 100;
top: 110px;
border-radius: 40px;
opacity: .5;
cursor: pointer;
}
.left {
left: 2%;
}
.right {
right: 2%;
}
.left .arrow {
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
border-left: solid 5px #666;
border-top: solid 5px #666;
transform: translate(-5px, 25px) rotate(-45deg) translate(25px, 25px);
}
.right .arrow {
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
border-left: solid 5px #666;
border-top: solid 5px #666;
transform: translate(50px, 25px) rotate(135deg) translate(25px, 25px);
}
</style>Tutoriel recommandé : "tutoriel js"
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!