

Tout d'abord, jetons un coup d'œil à notre objectif : insérer par lots 10 000 éléments de données dans la base de données mysql
Environnement d'exploitation : le code Mysql et Java s'exécutent tous deux sur mon ordinateur Windows local (processeur i7, 4 cœurs, 16 Go de mémoire en cours d'exécution, système d'exploitation 64 bits
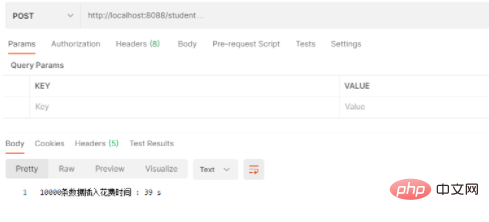
1. Exécution JPA monothread
Code omis, prend environ 39S
2. Exécution multithread JPA
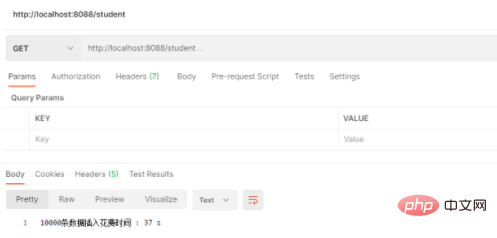
Cela prend environ 37S, ce qui n'est pas beaucoup plus rapide que prévu
( Partage de vidéos d'apprentissage gratuit :Tutoriel vidéo Java)
Raison : Le multithreading ne fait qu'améliorer considérablement le temps nécessaire au programme pour traiter les données, mais n'augmente pas le temps d'insertion dans la base de données. Au contraire, dans le cadre de JPA ici, le multi-threading Cela signifie que plusieurs connexions consomment plus de performances de base de données
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import com.example.demo.service.StudentServiceInterface;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.xml.bind.ValidationException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentServiceInterface studentServiceInterface;
// 来使主线程等待线程池中的线程执行完毕
private CountDownLatch threadsSignal;
// 每个线程处理的数据量
private static final int count = 1000;
// 我的电脑为4核 线程池大小设置为2N+1
private static ExecutorService execPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(9);
/**
* 多线程保存
*
* @return
* @throws ValidationException
*/
@GetMapping()
public String saveStudentEnableThread() throws ValidationException {
Long begin = new Date().getTime();
// 需要插入数据库的数据
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("张三");
student.setAge(10);
list.add(student);
}
try {
if (list.size() <= count) {
threadsSignal = new CountDownLatch(1);
execPool.submit(new InsertDate(list));
} else {
List<List<Student>> lists = dealData(list, count);
threadsSignal = new CountDownLatch(lists.size());
for (List<Student> students : lists) {
execPool.submit(new InsertDate(students));
}
}
threadsSignal.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString() + " 错误所在行数:" + e.getStackTrace()[0].getLineNumber());
}
// 结束时间
Long end = new Date().getTime();
return "10000条数据插入花费时间 : " + (end - begin) / 1000 + " s";
}
/**
* 数据组装
* 把每个线程要处理的数据 再组成一个List
* 我这边就是把10000条数据 组成 10个1000条的集合
*
* @param target 数据源
* @param size 每个线程处理的数量
* @return
*/
public static List<List<Student>> dealData(List<Student> target, int size) {
List<List<Student>> threadList = new ArrayList<List<Student>>();
// 获取被拆分的数组个数
int arrSize = target.size() % size == 0 ? target.size() / size : target.size() / size + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < arrSize; i++) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
//把指定索引数据放入到list中
for (int j = i * size; j <= size * (i + 1) - 1; j++) {
if (j <= target.size() - 1) {
students.add(target.get(j));
}
}
threadList.add(students);
}
return threadList;
}
/**
* 内部类,开启线程批量保存数据
*/
class InsertDate extends Thread {
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
public InsertDate(List<Student> students) {
list = students;
}
public void run() {
try {
// 与数据库交互
studentServiceInterface.save(list);
threadsSignal.countDown();
} catch (ValidationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}3 Insertion JDBC traditionnelle
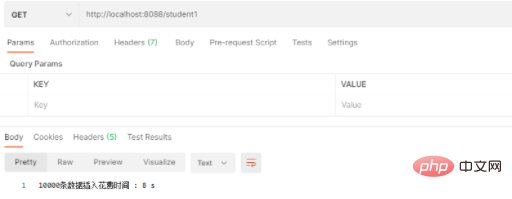
. prend environ 8S, par rapport aux deux premiers. La méthode est beaucoup plus rapide. Le code est le suivant :
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.xml.bind.ValidationException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.util.Date;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student1")
public class StudentController1 {
@GetMapping()
public String saveStudentEnableThread() throws ValidationException {
// 开始时间
Long begin = new Date().getTime();
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01?characterEncoding=utf8&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true", "admin", "123456");//获取连接
if (connection != null) {
System.out.println("获取连接成功");
} else {
System.out.println("获取连接失败");
}
//这里必须设置为false,我们手动批量提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//这里需要注意,SQL语句的格式必须是预处理的这种,就是values(?,?,...,?),否则批处理不起作用
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement("insert into student(id,`name`,age) values(?,?,?)");
// 塞数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
statement.setInt(1, i+1);
statement.setString(2, "张三");
statement.setInt(3, 10);
//将要执行的SQL语句先添加进去,不执行
statement.addBatch();
}
// 提交要执行的批处理,防止 JDBC 执行事务处理
statement.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
// 关闭相关连接
statement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 结束时间
Long end = new Date().getTime();
// 耗时
System.out.println("10000条数据插入花费时间 : " + (end - begin) / 1000 + " s");
return "10000条数据插入花费时间 : " + (end - begin) / 1000 + " s";
}
}4 Enfin, vérifiez si les données ont été stockées avec succès dans la base de données. Il y a 30 000 éléments au total. et aucune donnée n'est perdue
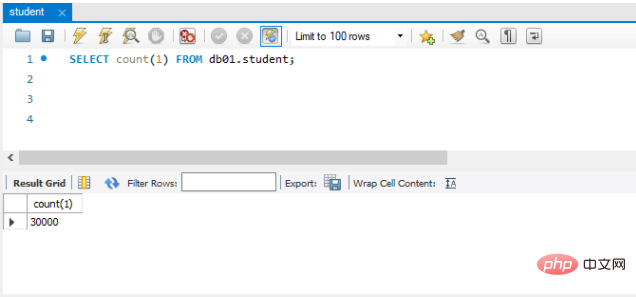
Terminé !
Recommandations associées : Tutoriel d'introduction à Java
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!