 interface Web
interface Web
 Tutoriel H5
Tutoriel H5
 Comment dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas sur un canevas HTML5 (avec code)
Comment dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas sur un canevas HTML5 (avec code)
Comment dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas sur un canevas HTML5 (avec code)
Cet article vous expliquera comment utiliser le canevas HTML5 pour dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas. Il a une certaine valeur de référence. Les amis dans le besoin peuvent s'y référer. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile.
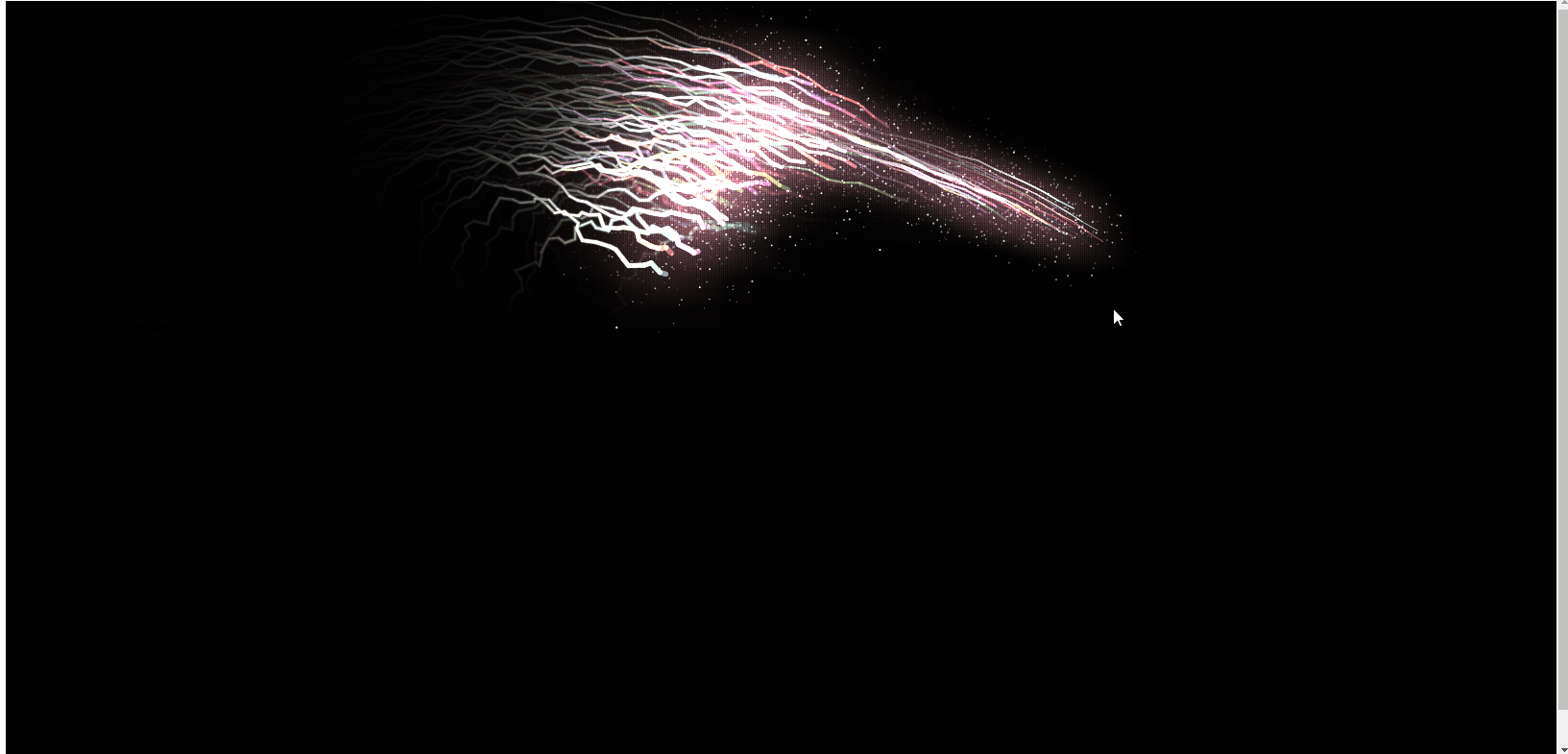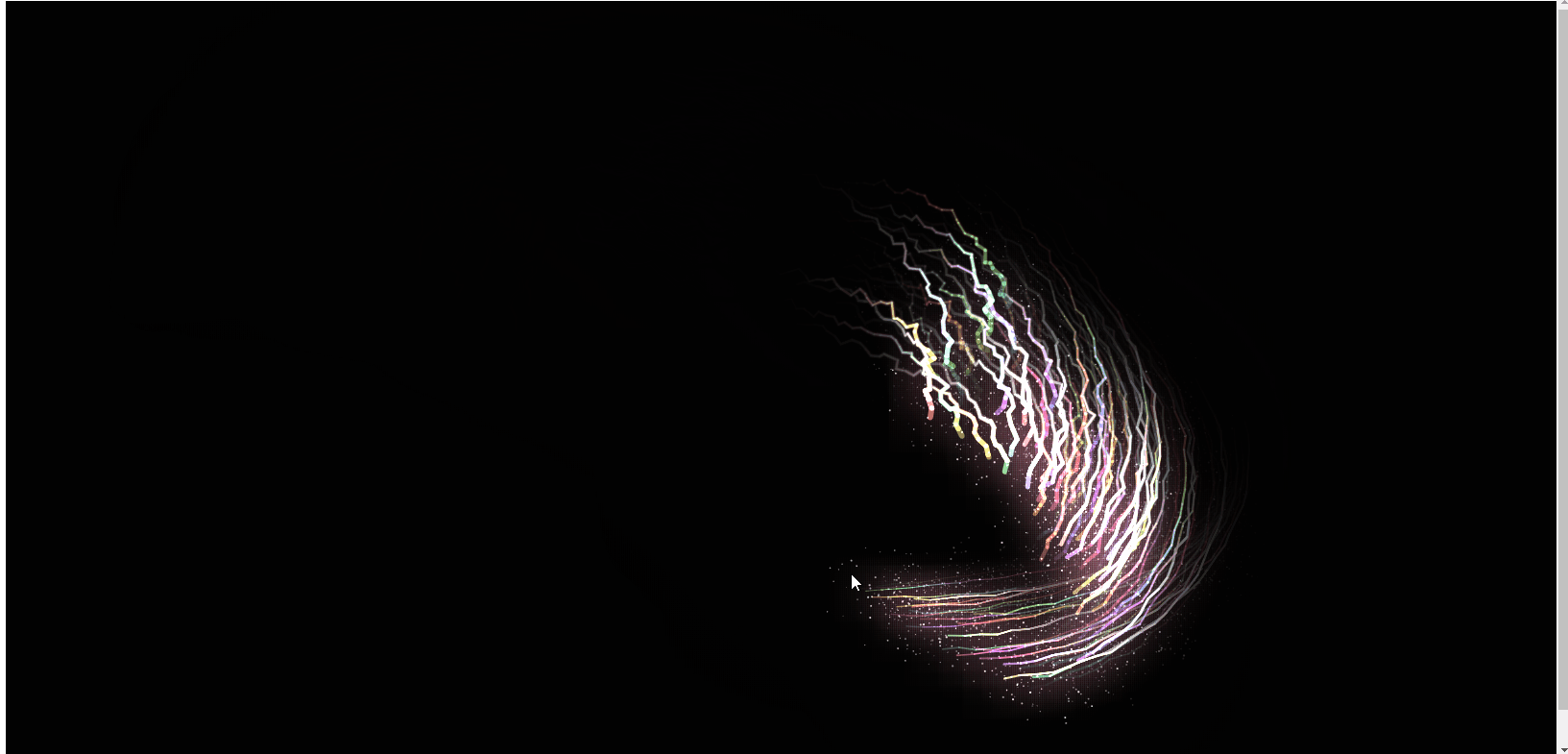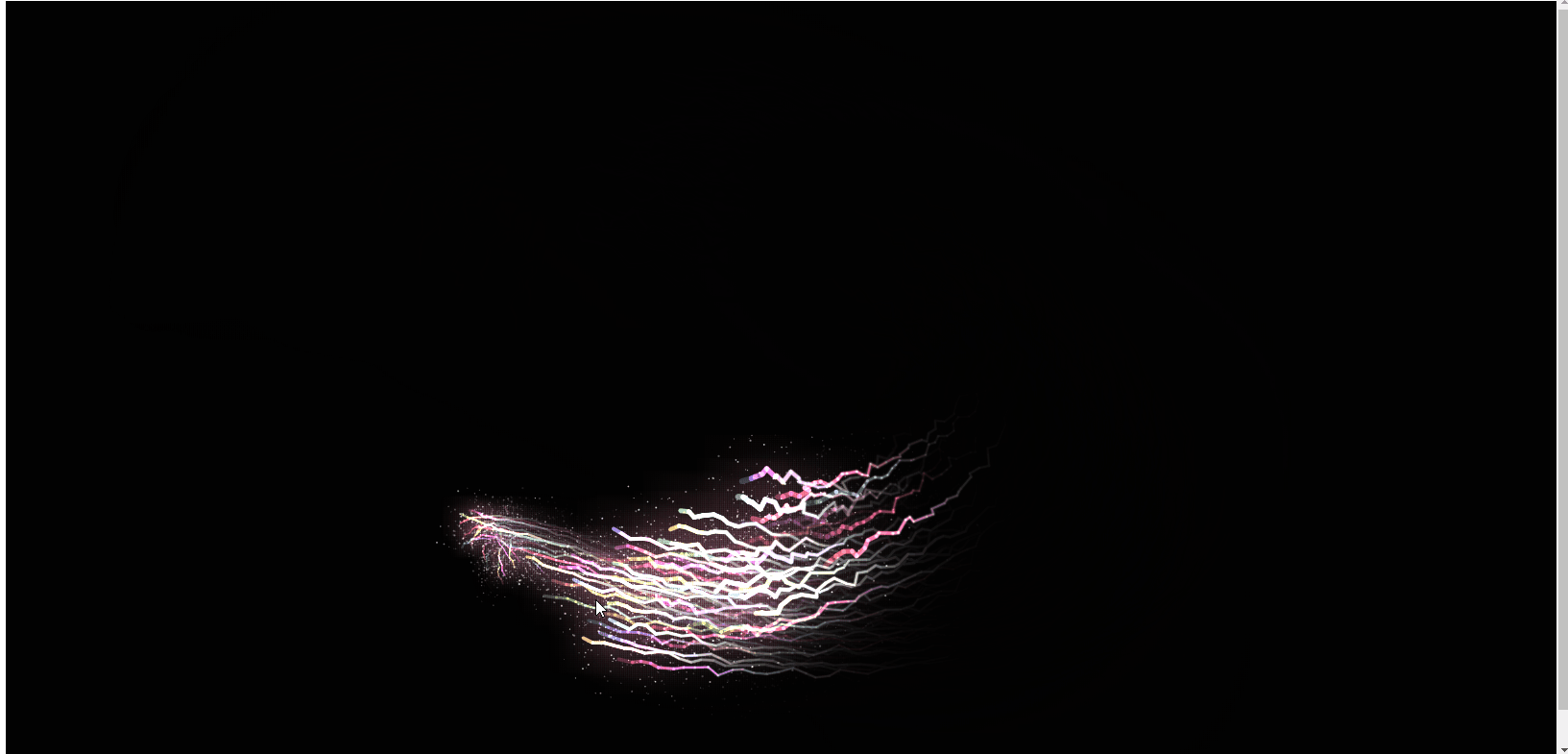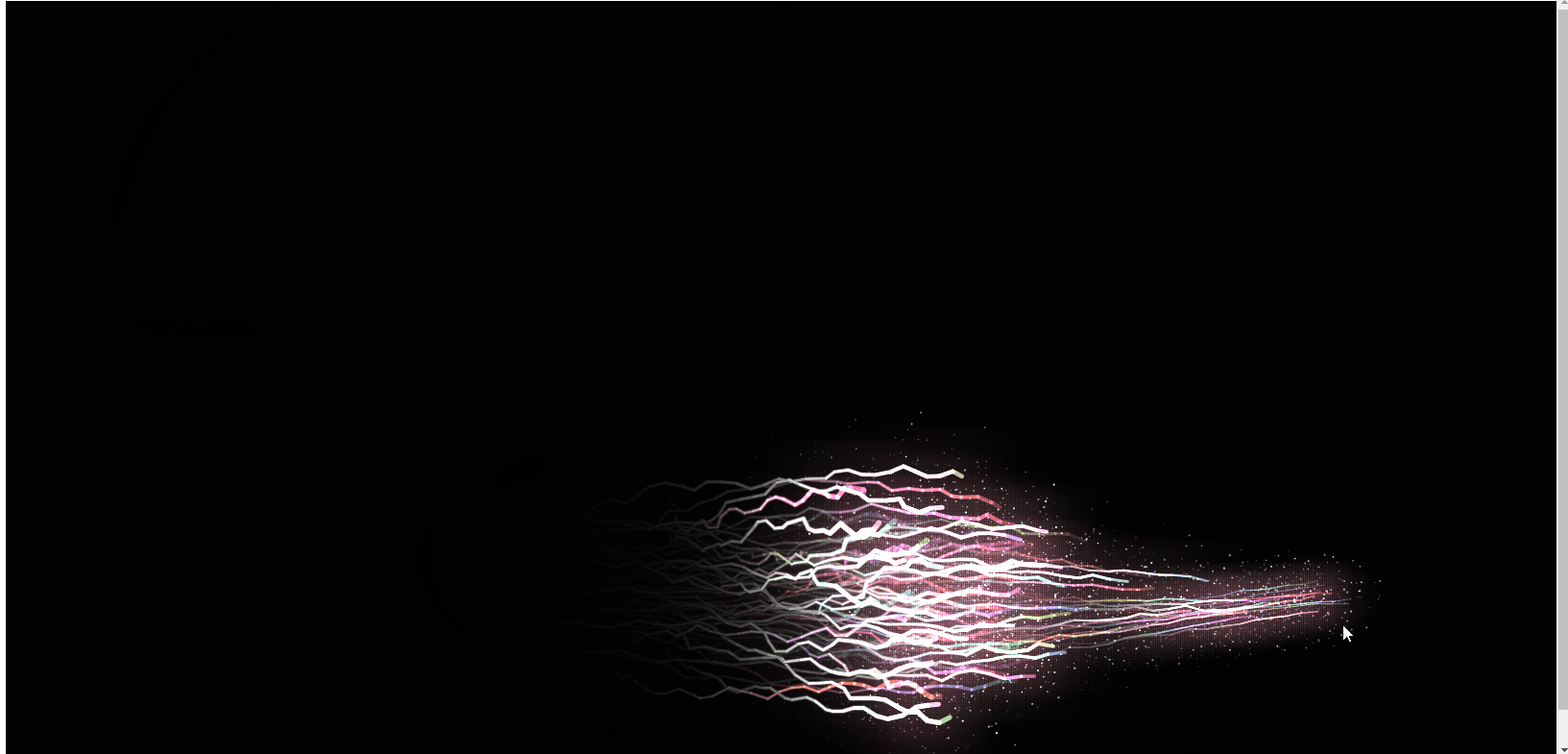
Ce qui précède est le rendu, et le code js est directement joint ci-dessous. J'espère qu'il sera utile à tout le monde ! !
// UTILconst PI = Math.PI,
TWO_PI = Math.PI * 2;const Util = {};Util.timeStamp = function() {
return window.performance.now();};Util.random = function(min, max) {
return min + Math.random() * (max - min);};Util.map = function(a, b, c, d, e) {
return (a - b) / (c - b) * (e - d) + d;};Util.lerp = function(value1, value2, amount) {
return value1 + (value2 - value1) * amount;};Util.clamp = function(value, min, max) {
return Math.max(min, Math.min(max, value));};// Vectorclass Vector {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x || 0;
this.y = y || 0;
}
set(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
reset() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
fromAngle(angle) {
let x = Math.cos(angle),
y = Math.sin(angle);
return new Vector(x, y);
}
add(vector) {
this.x += vector.x;
this.y += vector.y;
}
sub(vector) {
this.x -= vector.x;
this.y -= vector.y;
}
mult(scalar) {
this.x *= scalar;
this.y *= scalar;
}
p(scalar) {
this.x /= scalar;
this.y /= scalar;
}
dot(vector) {
return vector.x * this.x + vector.y * this.y;
}
limit(limit_value) {
if (this.mag() > limit_value) this.setMag(limit_value);
}
mag() {
return Math.hypot(this.x, this.y);
}
setMag(new_mag) {
if (this.mag() > 0) {
this.normalize();
} else {
this.x = 1;
this.y = 0;
}
this.mult(new_mag);
}
normalize() {
let mag = this.mag();
if (mag > 0) {
this.x /= mag;
this.y /= mag;
}
}
heading() {
return Math.atan2(this.y, this.x);
}
setHeading(angle) {
let mag = this.mag();
this.x = Math.cos(angle) * mag;
this.y = Math.sin(angle) * mag;
}
dist(vector) {
return new Vector(this.x - vector.x, this.y - vector.y).mag();
}
angle(vector) {
return Math.atan2(vector.y - this.y, vector.x - this.x);
}
copy() {
return new Vector(this.x, this.y);
}}// Init canvaslet canvas = document.createElement("canvas"),
ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"),
H = (canvas.height = window.innerHeight),
W = (canvas.width = window.innerWidth);document.body.appendChild(canvas);// Mouselet mouse = {
x: W/2,
y: H/2};canvas.onmousemove = function(event) {
mouse.x = event.clientX - canvas.offsetLeft;
mouse.y = event.clientY - canvas.offsetTop;};document.body.onresize = function(event){
H = (canvas.height = window.innerHeight);
W = (canvas.width = window.innerWidth);}// Let's goclass Arrow {
constructor(x, y, target) {
this.position = new Vector(x, y);
this.velocity = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
this.acceleration = new Vector(0, 0);
this.target = target;
this.travelled_distance = 0;
this.min_size = 1;
this.max_size = 6;
this.size = Util.random(this.min_size, this.max_size);
this.zone = this.size * 4;
this.topSpeed = Util.map(this.size,this.min_size,this.max_size,40,10);
let tailLength = Math.floor(Util.map(this.size, this.min_size, this.max_size, 4, 16));
this.tail = [];
for (let i = 0; i < tailLength; i++) {
this.tail.push({
x: this.position.x,
y: this.position.y });
}
this.wiggle_speed = Util.map(this.size, this.min_size, this.max_size, 2 , 1.2);
this.blink_offset = Util.random(0, 100);
this.alpha = Util.random(0.1,1)
}
render() {
this.update();
this.draw();
}
update() {
let old_position = this.position.copy();
// Focus on target
let t = new Vector(this.target.x, this.target.y),
angle = this.position.angle(t);
let d_f_target = t.dist(this.position);
let f = new Vector().fromAngle(angle);
f.setMag(Util.map(Util.clamp(d_f_target,0,400), 0, 400, 0, this.topSpeed * 0.1));
this.addForce(f);
// Update position and velocity
this.velocity.add(this.acceleration);
if(d_f_target < 800){
this.velocity.limit(Util.map(Util.clamp(d_f_target,0,800), 0, 800, this.topSpeed*0.4, this.topSpeed));
}else{
this.velocity.limit(this.topSpeed);
}
this.position.add(this.velocity);
// Reset acceleration for the next loop
this.acceleration.mult(0);
this.travelled_distance += old_position.dist(this.position);
let wiggle =
Math.sin(frame * this.wiggle_speed) *
Util.map(this.velocity.mag(), 0, this.topSpeed, 0, this.size);
let w_a = this.velocity.heading() + Math.PI / 2;
let w_x = this.position.x + Math.cos(w_a) * wiggle,
w_y = this.position.y + Math.sin(w_a) * wiggle;
this.travelled_distance = 0;
let from = this.tail.length - 1,
to = 0;
let n = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
n.setMag(Math.random()*this.size);
var tail = { x: w_x+ n.x, y: w_y + n.y};
this.tail.splice(from, 1);
this.tail.splice(to, 0, tail);
}
draw() {
let energy = Util.map(this.velocity.mag(),0,this.topSpeed,0.1,1);
let color =
"hsl("+Math.sin((frame + this.blink_offset) * 0.1) * 360+",50%,"+
Util.map(this.velocity.mag(),0,this.topSpeed,40,100) * this.alpha
+"%)";
ctx.globalAlpha = this.alpha;
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
for (let i = 0; i < this.tail.length - 1; i++) {
let t = this.tail[i],
next_t = this.tail[i + 1];
ctx.lineWidth = Util.map(i, 0, this.tail.length - 1, this.size, 1);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(t.x, t.y);
ctx.lineTo(next_t.x, next_t.y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.stroke();
}
let gradient_size = 140 * energy;var grd = ctx.createRadialGradient(
this.position.x,this.position.y , 5,
this.position.x,this.position.y, gradient_size);grd.addColorStop(0, "rgba(255,255,255,0.01)");grd.addColorStop(0.1, "rgba(255,120,200,0.02)");grd.addColorStop(0.9, "rgba(255,255,120,0)");grd.addColorStop(1, "rgba(0,0,0,0)");// Fill with gradientctx.fillStyle = grd;ctx.fillRect(this.position.x - gradient_size / 2 ,this.position.y - gradient_size / 2 , gradient_size, gradient_size);
ctx.globalAlpha = energy+0.2;
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
for(let i = 0; i < 4; i++){
let n = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
n.setMag(Math.random()*energy*100);
n.add(this.position);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(n.x,n.y,Math.random(),0,TWO_PI)
ctx.fill();
}
}
addForce(vector) {
this.acceleration.add(vector);
}
avoid(others) {
others.forEach(other => {
if (other !== this) {
let dist = this.position.dist(other.position),
max_dist = this.zone + other.size;
if (max_dist - dist >= 0) {
let angle = other.position.angle(this.position);
let force = new Vector().fromAngle(angle);
force.setMag(Util.map(dist, 0, max_dist, 2, 0));
this.addForce(force);
}
}
});
}}let arrows = [];for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
arrows.push(new Arrow(W / 2, H / 2, mouse));}let frame = 0;ctx.strokeStyle = "white";function loop() {
ctx.fillStyle="black";
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "source-over";
ctx.globalAlpha = 0.2;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, W, H);
ctx.globalAlpha = 1;
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "lighter";
arrows.forEach(a => {
a.avoid(arrows);
});
arrows.forEach(a => {
a.render();
});
frame += 1;
requestAnimationFrame(loop);}ctx.lineCap = "round";ctx.lineJoin = "round";loop();Apprentissage recommandé : Tutoriel vidéo HTML5
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Bordure de tableau en HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Bordure de tableau en HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide de la bordure de tableau en HTML. Nous discutons ici de plusieurs façons de définir une bordure de tableau avec des exemples de bordure de tableau en HTML.
 Marge gauche HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Marge gauche HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide de la marge HTML gauche. Nous discutons ici d'un bref aperçu de la marge gauche HTML et de ses exemples ainsi que de son implémentation de code.
 Tableau imbriqué en HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Tableau imbriqué en HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Ceci est un guide des tableaux imbriqués en HTML. Nous discutons ici de la façon de créer un tableau dans le tableau ainsi que des exemples respectifs.
 Disposition du tableau HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Disposition du tableau HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide de mise en page des tableaux HTML. Nous discutons ici des valeurs de la mise en page des tableaux HTML ainsi que des exemples et des résultats en détail.
 Espace réservé d'entrée HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Espace réservé d'entrée HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide de l'espace réservé de saisie HTML. Nous discutons ici des exemples d'espace réservé d'entrée HTML ainsi que des codes et des sorties.
 Liste ordonnée HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Liste ordonnée HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide de la liste ordonnée HTML. Ici, nous discutons également de l'introduction de la liste et des types HTML ordonnés ainsi que de leur exemple respectivement.
 Déplacer du texte en HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Déplacer du texte en HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide pour déplacer du texte en HTML. Nous discutons ici d'une introduction, du fonctionnement des balises de sélection avec la syntaxe et des exemples à implémenter.
 Bouton HTML onclick
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Bouton HTML onclick
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide du bouton HTML onclick. Nous discutons ici de leur introduction, de leur fonctionnement, des exemples et de l'événement onclick dans divers événements respectivement.





