Que dois-je faire si nginx n'analyse pas php ?
La solution pour nginx qui n'analyse pas php : installez d'abord php-fpm ; puis modifiez le fichier de configuration nginx nginx.conf et enfin redémarrez nginx et php-fpm ;

L'environnement d'exploitation de cet article : système Linux5.9.8, version PHP5.3.3, ordinateur DELL G3
Solution à l'environnement lnmp, nginx ne peut pas analyser le fichier php
Environnement lnmp, nginx ne peut pas analyser le fichier php fichier, HTML est une analyse normale.
Lorsque nginx ne peut pas analyser php, il affiche 404 Not Found
Installation en un clic de l'environnement lnmp, y compris nginx.
Installez d'abord php-fpm,
yum install php-fpm service php-fpm start #启动 php-fpm
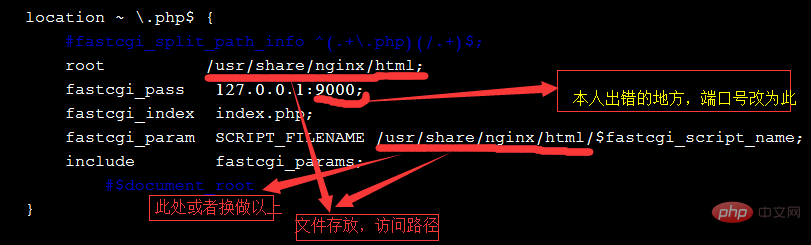
Puis modifiez le fichier de configuration nginx nginx.conf pour identifier php
vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf,如下把之前的#给去掉就可以了,顺手改一下fastcgi_param
location ~ \.php$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/share/nginx/html/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
Enfin, redémarrez nginx et php-fpm.
service nginx restart service php-fpm restart
Cela montrera le succès.
La pièce jointe est mon fichier de configuration nginx nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
autoindex
on;
#fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
server {
listen 80;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name localhost;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#error_page 404 = /404.html;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location ~ \.php$ {
#fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/share/nginx/html/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
#$document_root
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
rtmp {
server {
listen 1937; #鐩戝惉鐨勭鍙?
chunk_size 4000;
application hls { #rtmp鎺ㄦ祦璇锋眰璺緞
live on;
hls on;
hls_path /usr/share/nginx/html/hls;
hls_fragment 5s;
}
}
}Apprentissage recommandé : "Tutoriel vidéo PHP"
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Guide d'installation et de mise à niveau de PHP 8.4 pour Ubuntu et Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Guide d'installation et de mise à niveau de PHP 8.4 pour Ubuntu et Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 apporte plusieurs nouvelles fonctionnalités, améliorations de sécurité et de performances avec une bonne quantité de dépréciations et de suppressions de fonctionnalités. Ce guide explique comment installer PHP 8.4 ou mettre à niveau vers PHP 8.4 sur Ubuntu, Debian ou leurs dérivés. Bien qu'il soit possible de compiler PHP à partir des sources, son installation à partir d'un référentiel APT comme expliqué ci-dessous est souvent plus rapide et plus sécurisée car ces référentiels fourniront les dernières corrections de bogues et mises à jour de sécurité à l'avenir.
 Comment configurer Visual Studio Code (VS Code) pour le développement PHP
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Comment configurer Visual Studio Code (VS Code) pour le développement PHP
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code, également connu sous le nom de VS Code, est un éditeur de code source gratuit – ou environnement de développement intégré (IDE) – disponible pour tous les principaux systèmes d'exploitation. Avec une large collection d'extensions pour de nombreux langages de programmation, VS Code peut être c
 Comment analysez-vous et traitez-vous HTML / XML dans PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Comment analysez-vous et traitez-vous HTML / XML dans PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Ce tutoriel montre comment traiter efficacement les documents XML à l'aide de PHP. XML (Language de balisage extensible) est un langage de balisage basé sur le texte polyvalent conçu à la fois pour la lisibilité humaine et l'analyse de la machine. Il est couramment utilisé pour le stockage de données et
 Programme PHP pour compter les voyelles dans une chaîne
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Programme PHP pour compter les voyelles dans une chaîne
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Une chaîne est une séquence de caractères, y compris des lettres, des nombres et des symboles. Ce tutoriel apprendra à calculer le nombre de voyelles dans une chaîne donnée en PHP en utilisant différentes méthodes. Les voyelles en anglais sont a, e, i, o, u, et elles peuvent être en majuscules ou en minuscules. Qu'est-ce qu'une voyelle? Les voyelles sont des caractères alphabétiques qui représentent une prononciation spécifique. Il y a cinq voyelles en anglais, y compris les majuscules et les minuscules: a, e, i, o, u Exemple 1 Entrée: String = "TutorialSpoint" Sortie: 6 expliquer Les voyelles dans la chaîne "TutorialSpoint" sont u, o, i, a, o, i. Il y a 6 yuans au total
 7 fonctions PHP que je regrette de ne pas connaître auparavant
Nov 13, 2024 am 09:42 AM
7 fonctions PHP que je regrette de ne pas connaître auparavant
Nov 13, 2024 am 09:42 AM
Si vous êtes un développeur PHP expérimenté, vous aurez peut-être le sentiment d'y être déjà allé et de l'avoir déjà fait. Vous avez développé un nombre important d'applications, débogué des millions de lignes de code et peaufiné de nombreux scripts pour réaliser des opérations.
 Expliquez les jetons Web JSON (JWT) et leur cas d'utilisation dans les API PHP.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Expliquez les jetons Web JSON (JWT) et leur cas d'utilisation dans les API PHP.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT est une norme ouverte basée sur JSON, utilisée pour transmettre en toute sécurité des informations entre les parties, principalement pour l'authentification de l'identité et l'échange d'informations. 1. JWT se compose de trois parties: en-tête, charge utile et signature. 2. Le principe de travail de JWT comprend trois étapes: la génération de JWT, la vérification de la charge utile JWT et l'analyse. 3. Lorsque vous utilisez JWT pour l'authentification en PHP, JWT peut être généré et vérifié, et les informations sur le rôle et l'autorisation des utilisateurs peuvent être incluses dans l'utilisation avancée. 4. Les erreurs courantes incluent une défaillance de vérification de signature, l'expiration des jetons et la charge utile surdimensionnée. Les compétences de débogage incluent l'utilisation des outils de débogage et de l'exploitation forestière. 5. L'optimisation des performances et les meilleures pratiques incluent l'utilisation des algorithmes de signature appropriés, la définition des périodes de validité raisonnablement,
 Expliquez la liaison statique tardive en PHP (statique: :).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Expliquez la liaison statique tardive en PHP (statique: :).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Liaison statique (statique: :) implémente la liaison statique tardive (LSB) dans PHP, permettant à des classes d'appel d'être référencées dans des contextes statiques plutôt que de définir des classes. 1) Le processus d'analyse est effectué au moment de l'exécution, 2) Recherchez la classe d'appel dans la relation de succession, 3) il peut apporter des frais généraux de performance.
 L'accès au fichier du site WordPress est restreint: pourquoi mon fichier .txt n'est-il pas accessible via le nom de domaine?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
L'accès au fichier du site WordPress est restreint: pourquoi mon fichier .txt n'est-il pas accessible via le nom de domaine?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
L'accès au fichier du site WordPress est restreint: dépannage de la raison pour laquelle le fichier .txt ne peut pas être accessible récemment. Certains utilisateurs ont rencontré un problème lors de la configuration du nom de domaine commercial du programme MINI: � ...






