
Méthodes pour obtenir le type des variables JavaScript : 1. Utilisez l'opérateur typeof, syntaxe "typeof variable" ; 2. Utilisez la méthode "$.type()" de jQuery 3. Obtenez le type via le constructeur.

L'environnement d'exploitation de ce tutoriel : système windows7, version javascript1.8.5&&jquery1.10.0, ordinateur Dell G3.
En JavaScript, comment obtenir avec précision le nom de type d'une variable est une question fréquemment posée.
Mais souvent, le nom exact de la variable ne peut pas être obtenu, ou la méthode dans jQuery doit être utilisée Ici, j'utilise typeof, jQuery. .type et Les trois méthodes d'utilisation des constructeurs pour obtenir des types de variables sont présentées en détail.
J'espère que cela pourra vous aider.
Au premier coup d'œil en voyant la question, certains étudiants peuvent penser au type d'opérateur.
En langage JavaScript, il est donné d'utiliser l'opérateur typeof pour obtenir le nom du type de base (Notez qu'il ne s'agit pas d'un type de base)
C'est toute l'utilisation de typeof
.01-typeof.htm
console.log('typeof of 10 ~~~~' +typeof 10);
console.log('typeof of "a" ~~~~' +typeof 'a');
console.log('typeof of true ~~~~' +typeof true);
console.log('typeof of {} ~~~~' +typeof {});
console.log('typeof of /123/ ~~~~' +typeof /123/);
console.log('typeof of function(){} ~~~~' +typeof function(){});
console.log('typeof of undefined ~~~~' +typeof undefined);
console.log('typeof of null ~~~~' +typeof null);Ceci est le résultat
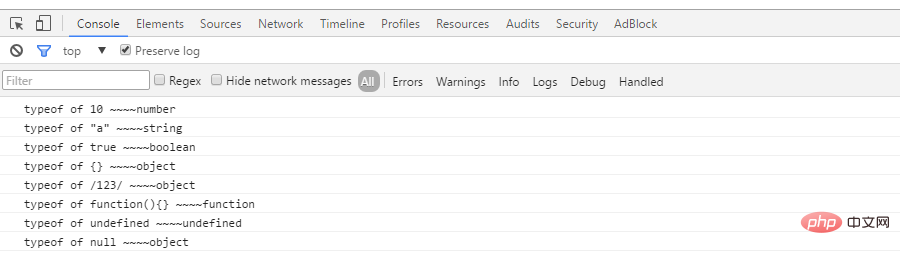
Selon les résultats imprimés ci-dessus, nous résumons les points suivants à noter
typeof (type de référence) À l'exception des fonctions, elles sont toutes des « objets » , tel que typeof /123/
typeof null est 'objet'
typeof undefined est 'indéfini', généralement, si vous utilisez deux signes égaux, null == undefined est vrai. L'usage courant de la conversion
. à un nombre est "10" -0, si la conversion échoue, Renvoyant NaN, en raison d'une caractéristique de NaN : NaN != NaN, donc la manière courante de juger si la conversion est réussie est : (Ceci c'est aussi ce que j'ai trouvé en me référant au code source de jQuery. Lire 100 fois le code source de jQuery n'est pas une exagération)( "10x" - 0) == ("10x" - 0); le résultat est faux !("10x" - 0) == ("10x" - 0); // 结果为假!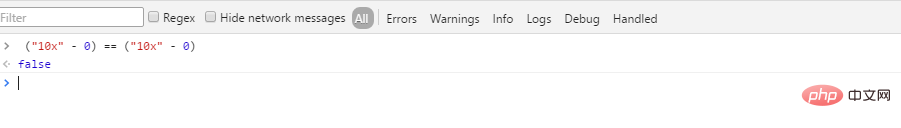
现在看看jQuery是怎么做的
// 先申明一个对象,目的是用来做映射
var class2type = {};
// 申明一个core_toString() 的方法,得到最原始的toString() 方法,因为在很多对象中,toStrintg() 已经被重写
var core_toString() = class2type.toString;// 这里为 toStrintg() 后的结果和类型名做一个映射,申明一个core_toString() 后的结果,而值就是类型名
jQuery.each("Boolean Number String Function Array Date RegExp Object Error".split(" "), function(i, name) {
class2type[ "[object " + name + "]" ] = name.toLowerCase();
});因为 Object.prototype.toString() 方法调用结果如下
var core_toString = {}.toString;
console.log( core_toString.call(1) );
console.log( core_toString.call("11") );
console.log( core_toString.call(/123/) );
console.log( core_toString.call({}) );
console.log( core_toString.call(function(){}) );
console.log( core_toString.call([]) );
console.log( core_toString.call(true) );
console.log( core_toString.call(new Date()) );
console.log( core_toString.call(new Error() ));
console.log( core_toString.call(null) );
console.log( core_toString.call(undefined) );
console.log( String(null) );
console.log( String(undefined) );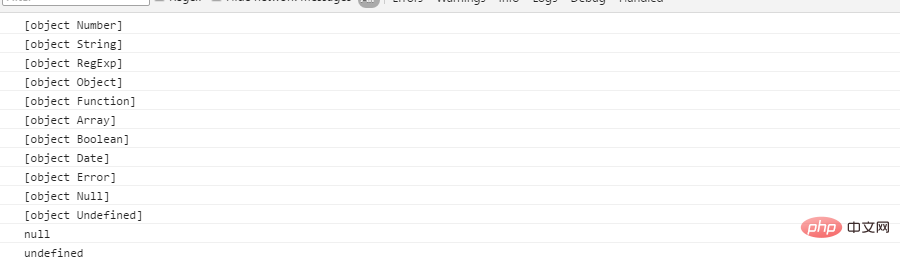
上面的打印结果与
class2type[ "[object " + name + "]" ] = name.toLowerCase();
不谋而合!
这是jQuery.type 的核心方法
type: function( obj ) {
if ( obj == null ) {
return String( obj );
}
// Support: Safari <= 5.1 (functionish RegExp)
return typeof obj === "object" || typeof obj === "function" ?
class2type[ core_toString.call(obj) ] || "object" :
typeof obj;
},注意,为什么把 null 或者 undefined 单独讨论呢,因为 在一些版本浏览器中
console.log(core_toString.call(null)); console.log(core_toString.call(undefined));Copier après la connexion这是会报错的!
如果是对象类型,另:由于 在一些低版本的浏览器中,typeof /123/ 会返回的是 "function" 而不是 "object",所以这里要判断是否是函数,要明白 这里的 typeof obj === function
Utilisez la méthode $.type()
Maintenant, voyez comment jQuery le fait
typeof obj === "object" || typeof obj === "function" ?
class2type[ core_toString.call(obj) ]class2type[ core_toString.call(obj) ] || "object" : // 这是防止一些未知情况的,如果未取到,就返回object
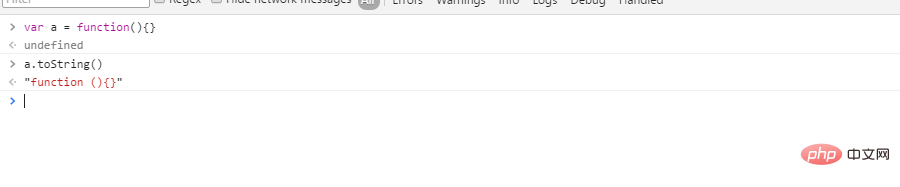
Parce que Object.prototype.toStr ing( ) Le résultat de l'appel de méthode est le suivantL'impression ci-dessus Le résultat coïncide avecfunction Person(){ this.name = 'pawn'; } var p = Person.toString();Copier après la connexion
function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person); function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
Person.protype = {
XX: ... ,
xx: ... ,
...
}Remarquez pourquoi null ou undefined sont discutés séparément, car dans certaines versions de navigateurs
Person.protype = {
construction: Person,
XX: ... ,
xx: ... ,
...
}typeof obj === function ici, ce n'est pas discuté pour les fonctions, car la fonction elle-même peut obtenir le type via typeof. jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
constructor: jQuery,
init: function( selector, context, rootjQuery ) {
var match, elem; var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
if(typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'fucntion'){
...
}else{
// 如果不是引用类型,那么就是基本类型
return typeof obj
}
} Mais jQuery.type
Mais jQuery.type a un gros défaut
Il s'agit d'un type personnalisé
function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
var p = new Person();
console.log(p.constructor);C'est également le cas. un gros défaut !
Ensuite, nous obtenons le type précis via le constructeur
var regex = /function\s(.+?)\(/
function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
var p = new Person();
var c = p.constructor
var regex = /function\s(.+?)\(/;
console.log('|' + regex.exec(c)[1] + '|');var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
if(typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'function'){
var constructor = obj.constructor;
if(constructor && constructor.name){
return constructor.name;
}
var regex = /function\s(.+?)\(/;
return regex.exec(c)[1];
}else{
// 如果不是引用类型,那么就是基本;类型
return typeof obj;
}
};var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
if(typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'function'){
return obj.constructor && obj.constructor.name.toLowerCase() ||
/function\s(.+?)\(/.exec(obj.constructor)[1].toLowerCase();
}else{
// 如果不是引用类型,那么就是基本类型
return typeof obj;
}
};var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
return typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'function' ?
obj.constructor && obj.constructor.name && obj.constructor.name.toLowerCase() ||
/function\s(.+?)\(/.exec(obj.constructor)[1].toLowerCase():
typeof obj;
};也就是,如果调用一个函数的toString() 方法.那么就会打印这个函数的函数体.
好了,经过上面两个步骤,你明白我要做什么了吗?
如何通过构造函数来获得变量的类型?
var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
if(typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'fucntion'){
...
}else{
// 如果不是引用类型,那么就是基本类型
return typeof obj
}
} function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
var p = new Person();
console.log(p.constructor);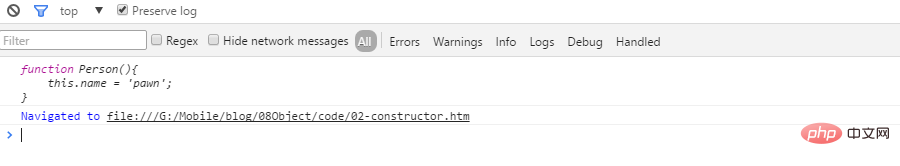
现在要做的事 : 如何将Person 提取出来呢?
毋庸置疑,字符串切割那一套肯定可以办到,但是太 low 啦!
这里,我使用正则将Person提取出来
var regex = /function\s(.+?)\(/
function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
var p = new Person();
var c = p.constructor
var regex = /function\s(.+?)\(/;
console.log('|' + regex.exec(c)[1] + '|');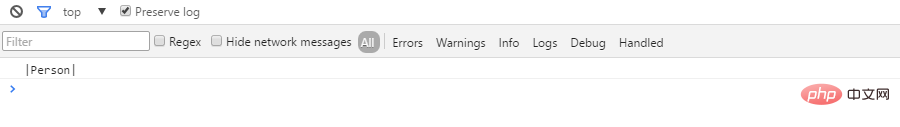
其实,除了上面的正则,每个函数还有一个name属性,返回函数名,但是ie8 是不支持的.
因此上面的代码可以写为:
var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
if(typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'function'){
var constructor = obj.constructor;
if(constructor && constructor.name){
return constructor.name;
}
var regex = /function\s(.+?)\(/;
return regex.exec(c)[1];
}else{
// 如果不是引用类型,那么就是基本;类型
return typeof obj;
}
};但是上面的代码太丑啦,将其简化
var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
if(typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'function'){
return obj.constructor && obj.constructor.name.toLowerCase() ||
/function\s(.+?)\(/.exec(obj.constructor)[1].toLowerCase();
}else{
// 如果不是引用类型,那么就是基本类型
return typeof obj;
}
};还是比较麻烦,继续简化
var getType = function(obj){
if(obj == null){
return String(obj);
}
return typeof obj === 'object' || typeof obj === 'function' ?
obj.constructor && obj.constructor.name && obj.constructor.name.toLowerCase() ||
/function\s(.+?)\(/.exec(obj.constructor)[1].toLowerCase():
typeof obj;
};好了,已经全部弄完了,写个代码测试一下:
function Person(){
this.name = 'pawn';
}
var p = new Person();
console.log(getType(p));
console.log(getType(1));
console.log(getType("a"));
console.log(getType(false));
console.log(getType(/123/));
console.log(getType({}));
console.log(getType(function(){}));
console.log(getType(new Date()));
console.log(getType(new Error()));
console.log(getType( null));
console.log(getType( undefined));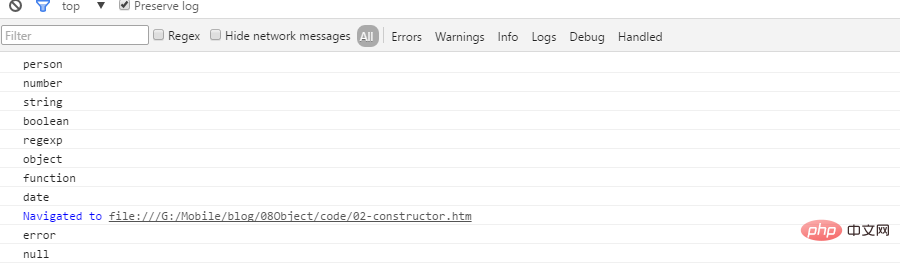
【推荐学习:javascript高级教程】
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!