
Différence : 1. db2 utilise "créer une table a comme b" pour créer une table similaire, oracle utilise "créer une table a en sélectionnant * à partir de b" ; 2. db2 utilise la conversion de type varchar, oracle utilise la fonction "to_char" pour convertir.

L'environnement d'exploitation de ce tutoriel : système Windows 10, version Oracle 11g, ordinateur Dell G3.
Oracle : create table a as select * from b; DB2 : create table a like b; (8版本有效,9版本无效) create table new_a as select col1,col2... from a definition only
Oracle : truncate table a; DB2 : alter table a active not logged initially with empty table;
Oracle : select * from a where rownum <strong></strong>5. Les méthodes de conversion de valeurs nulles sont différentes
Oracle : select sysdate from dual; DB2 : select current timestamp from sysibm.sysdummy1;
Oracle : select col1,col2,nvl(col3,'0') from tablename; (判断col3字段是否为空,不为空就输出原来的数值,为空就输出0) DB2 : select col1,col2,value(col3,'0') from tablename; (mysql和Db2可以使用Coalesce(col3,'0')函数来实现上述功能)
这个函数主要用来进行空值处理,其参数格式如下: COALESCE ( expression,value1,value2……,valuen) COALESCE()函数的第一个参数expression为待检测的表达式,而其后的参数个数不定。 COALESCE()函数将会返回包括expression在内的所有参数中的第一个非空表达式。 如果expression不为空值则返回expression; 否则判断value1是否是空值,如果value1不为空值则返回value1; 否则判断value2是否是空值,如果value2不为空值则返回value2; ……以此类推, 如果所有的表达式都为空值,则返回NULL。
oracle : select to_char(sysdate,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS') from dual; DB2 : select varchar(current timestamp) from sysibm.sysdummy1;
8. requête (requête hiérarchique)
Oracle数据类型改变函数:to_char()、to_date()、to_number()等;
如果仅仅取年,月,日等,可以用
to_char(sysdate, 'YYYY'),
to_char('MM') ,
to_char('DD')取得。
只取年月日TRUNC(SYSDATE)。
取时分秒TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'HH24:MI:SS')。
DB2数据类型改变函数:char()、varchar()、int()、date()、time()等;
取得年,月,日等的写法:
YEAR(current timestamp),
MONTH(current timestamp),
DAY(current timestamp),
HOUR(current timestamp),
MINUTE(current timestamp),
SECOND(current timestamp),
MICROSECOND(current timestamp),
只取年月日可以用
DATE(current timestamp),
取时分秒
TIME(current timestamp)。
Char()是定长字符串(1-255),varchar()为非定长字符串(1-32672)日期,
时间形态变为字符形态:
char(current date),
char(current time)
将字符串转换成日期或时间形态:
TIMESTAMP('2002-10-2012:00:00'),
DATE('2002-10-20'),
DATE('10/20/2002'),
TIME('12:00:00')Oracle:
select to_number('123') from dual;
select cast('123' as integer) from dual;
DB2 :
select cast('123' as integer) from sysibm.sysdummy1;
select cast(current time as char(8)) from sysibm.sysdummy1;Oracle: 直接用子查询 Db2:WITH语句 WITH a1 AS(SELECT max(id) AS aa1 FROM test )SELECT id ,aa1 FROM test ,a1
Comme le montre l'image ci-dessus, commencez par petit-enfant pour interroger tous ses nœuds parents. Définissez d'abord le point de départ de la table virtuelle, qui est la quatrième ligne à gauche dans l'ordre, son parent est fils = ; enfant dans la ligne précédente, c'est-à-dire VT.parent + 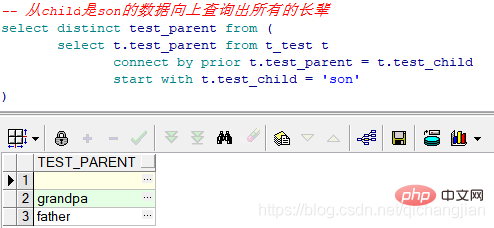 10 Il existe des différences dans les types de données
10 Il existe des différences dans les types de données
Oracle递归查询:CONNECT BY PRIOR ... START WITH ... DB2 递归查询:DB2较难理解,要WITH一个虚拟表
//从child是son的数据向上查询出所有的长辈select distinct test_parent from ( select t.test_parent from t_test t connect by prior t.test_parent = t.test_child start with t.test_child = 'son' )
12.decode method
// Db2递归查询写法with par_test(test_child,test_parent) as( select test_child,test_parent from t_test where child='grandchild' -- 设置递归起点 union all select t.test_child,t.test_parent from par_test pt,t_test t where pt.test_parent = t.test_child ----递归的方向为从子向父)select distinct test_parent from par_test
 Tutoriel recommandé : "
Tutoriel recommandé : "Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!