 interface Web
interface Web
 js tutoriel
js tutoriel
 Parlons de la façon d'utiliser angulaire Material pour créer des tableaux statistiques
Parlons de la façon d'utiliser angulaire Material pour créer des tableaux statistiques
Parlons de la façon d'utiliser angulaire Material pour créer des tableaux statistiques
Comment utiliser angulaire Material pour réaliser des tableaux statistiques ? L'article suivant vous présentera comment utiliser le matériel angular pour créer des tableaux statistiques. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile !

Utilisez Angular Material pour créer des tableaux statistiques
Installez Angular Material, le kit de développement de composants (CDK) et la bibliothèque d'animation angulaire, et exécutez le schéma de code
ng add @angular/material
Le schéma de table créera un composant qui peut Créez un matériau angulaire avec des sources de données triables et de pagination prédéfinies. [Tutoriels associés recommandés : "tutoriel angulaire"]
ng generate @angular/material:table texe1
Ensuite, apportez des modifications en fonction de cela.
Le fichier html de ce composant
<div class="mat-elevation-z8">
<table mat-table class="full-width-table" matSort aria-label="Elements">
<!-- Id Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="id">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header>序号</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.id}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- Name Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="name">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header> 岩土名</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.name}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- num1 Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="num1">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header> 期望数量</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.num1}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- num2 Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="num2">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header> 当前数量</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.num2}}</td>
</ng-container>
<tr mat-header-row *matHeaderRowDef="displayedColumns"></tr>
<tr mat-row *matRowDef="let row; columns: displayedColumns;"></tr>
</table>
<!-- 控制表格数据的显示长度 -->
<mat-paginator #paginator
[length]="dataSource?.data?.length"
[pageIndex]="0"
[pageSize]="10"
[pageSizeOptions]="[5, 10, 17]"
aria-label="Select page">
</mat-paginator>
</div>Le fichier texe1-datasource.ts de ce composant
import { DataSource } from '@angular/cdk/collections';
import { MatPaginator } from '@angular/material/paginator';
import { MatSort } from '@angular/material/sort';
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { Observable, of as observableOf, merge } from 'rxjs';
// TODO: Replace this with your own data model type
export interface Texe1Item {
name: string;
id: number;
num1: number;
num2: number;
}
// TODO: replace this with real data from your application
const EXAMPLE_DATA: Texe1Item[] = [
{id: 1, name: '粉质粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 2, name: '淤泥质粉质粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 3, name: '粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 4, name: '粘质粉土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 5, name: '淤泥质粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 6, name: '圆砾(角砾)', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 7, name: '中砂', num1:1000, num2:1000,},
{id: 8, name: '有机质土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 9, name: '泥炭质土A', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 10, name: '泥炭质土B', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 11, name: '砂质粉土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 12, name: '粉砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 13, name: '细砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 14, name: '粗砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 15, name: '砾砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 16, name: '卵石(碎石)', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 17, name: '漂石(块石)', num1:1000, num2:100,},
];
/**
* Data source for the Texe1 view. This class should
* encapsulate all logic for fetching and manipulating the displayed data
* (including sorting, pagination, and filtering).
*/
export class Texe1DataSource extends DataSource<Texe1Item> {
data: Texe1Item[] = EXAMPLE_DATA;
paginator: MatPaginator | undefined;
sort: MatSort | undefined;
constructor() {
super();
}
/**
* Connect this data source to the table. The table will only update when
* the returned stream emits new items.
* @returns A stream of the items to be rendered.
*/
connect(): Observable<Texe1Item[]> {
if (this.paginator && this.sort) {
// Combine everything that affects the rendered data into one update
// stream for the data-table to consume.
return merge(observableOf(this.data), this.paginator.page, this.sort.sortChange)
.pipe(map(() => {
return this.getPagedData(this.getSortedData([...this.data ]));
}));
} else {
throw Error('Please set the paginator and sort on the data source before connecting.');
}
}
/**
* Called when the table is being destroyed. Use this function, to clean up
* any open connections or free any held resources that were set up during connect.
*/
disconnect(): void {}
/**
* Paginate the data (client-side). If you're using server-side pagination,
* this would be replaced by requesting the appropriate data from the server.
*/
private getPagedData(data: Texe1Item[]): Texe1Item[] {
if (this.paginator) {
const startIndex = this.paginator.pageIndex * this.paginator.pageSize;
return data.splice(startIndex, this.paginator.pageSize);
} else {
return data;
}
}
/**
* Sort the data (client-side). If you're using server-side sorting,
* this would be replaced by requesting the appropriate data from the server.
*/
private getSortedData(data: Texe1Item[]): Texe1Item[] {
if (!this.sort || !this.sort.active || this.sort.direction === '') {
return data;
}
return data.sort((a, b) => {
const isAsc = this.sort?.direction === 'asc';
switch (this.sort?.active) {
case 'name': return compare(a.name, b.name, isAsc);
case 'id': return compare(+a.id, +b.id, isAsc);
default: return 0;
}
});
}
}
/** Simple sort comparator for example ID/Name columns (for client-side sorting). */
function compare(a: string | number, b: string | number, isAsc: boolean): number {
return (a < b ? -1 : 1) * (isAsc ? 1 : -1);
}Le fichier texe1.component.ts de ce composant
import { AfterViewInit, Component, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { MatPaginator } from '@angular/material/paginator';
import { MatSort } from '@angular/material/sort';
import { MatTable } from '@angular/material/table';
import { Texe1DataSource, Texe1Item } from './texe1-datasource';
@Component({
selector: 'app-texe1',
templateUrl: './texe1.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./texe1.component.css']
})
export class Texe1Component implements AfterViewInit {
@ViewChild(MatPaginator) paginator!: MatPaginator;
@ViewChild(MatSort) sort!: MatSort;
@ViewChild(MatTable) table!: MatTable<Texe1Item>;
dataSource: Texe1DataSource;
/** Columns displayed in the table. Columns IDs can be added, removed, or reordered. */
displayedColumns = ['id', 'name','num1','num2'];
constructor() {
this.dataSource = new Texe1DataSource();
}
ngAfterViewInit(): void {
this.dataSource.sort = this.sort;
this.dataSource.paginator = this.paginator;
this.table.dataSource = this.dataSource;
}
}Enfin, il est affiché dans le fichier app.component.html .
<app-texe1></app-texe1>
Rendu : 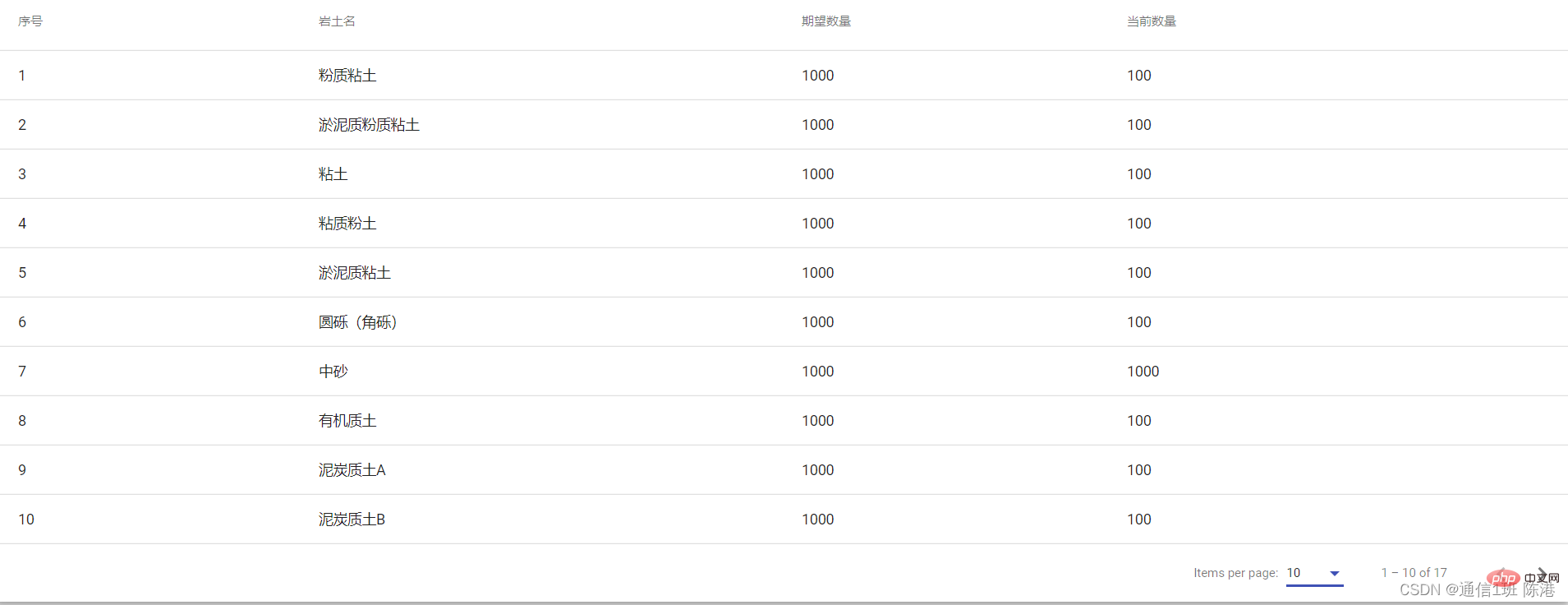
Pour plus de connaissances liées à la programmation, veuillez visiter : Vidéo de programmation ! !
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment installer Angular sur Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Comment installer Angular sur Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Angular.js est une plateforme JavaScript librement accessible pour créer des applications dynamiques. Il vous permet d'exprimer rapidement et clairement divers aspects de votre application en étendant la syntaxe HTML en tant que langage de modèle. Angular.js fournit une gamme d'outils pour vous aider à écrire, mettre à jour et tester votre code. De plus, il offre de nombreuses fonctionnalités telles que le routage et la gestion des formulaires. Ce guide expliquera comment installer Angular sur Ubuntu24. Tout d’abord, vous devez installer Node.js. Node.js est un environnement d'exécution JavaScript basé sur le moteur ChromeV8 qui vous permet d'exécuter du code JavaScript côté serveur. Être à Ub
 L'apprentissage angulaire parle de composants autonomes (Standalone Component)
Dec 19, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
L'apprentissage angulaire parle de composants autonomes (Standalone Component)
Dec 19, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Cet article vous amènera à continuer à apprendre Angular et à comprendre brièvement le composant autonome (Standalone Component) dans Angular. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile !
 Explication détaillée du gestionnaire d'état d'apprentissage angulaire NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
Explication détaillée du gestionnaire d'état d'apprentissage angulaire NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
Cet article vous donnera une compréhension approfondie du gestionnaire d'état NgRx d'Angular et vous présentera comment utiliser NgRx. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile !
 Une brève analyse de la façon d'utiliser monaco-editor en angulaire
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
Une brève analyse de la façon d'utiliser monaco-editor en angulaire
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
Comment utiliser monaco-editor en angulaire ? L'article suivant enregistre l'utilisation de monaco-editor dans angulaire qui a été utilisé dans une entreprise récente. J'espère qu'il sera utile à tout le monde !
 Un article explorant le rendu côté serveur (SSR) dans Angular
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Un article explorant le rendu côté serveur (SSR) dans Angular
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Connaissez-vous Angular Universel ? Cela peut aider le site Web à fournir un meilleur support SEO !
 Angular + NG-ZORRO développent rapidement un système backend
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
Angular + NG-ZORRO développent rapidement un système backend
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
Cet article partagera avec vous une expérience pratique d'Angular et apprendra comment développer rapidement un système backend en utilisant Angualr combiné avec ng-zorro. J'espère que cela sera utile à tout le monde !
 Comment utiliser PHP et Angular pour le développement front-end
May 11, 2023 pm 04:04 PM
Comment utiliser PHP et Angular pour le développement front-end
May 11, 2023 pm 04:04 PM
Avec le développement rapide d'Internet, la technologie de développement front-end s'améliore et se répète constamment. PHP et Angular sont deux technologies largement utilisées dans le développement front-end. PHP est un langage de script côté serveur capable de gérer des tâches telles que le traitement des formulaires, la génération de pages dynamiques et la gestion des autorisations d'accès. Angular est un framework JavaScript qui peut être utilisé pour développer des applications monopage et créer des applications Web composées de composants. Cet article explique comment utiliser PHP et Angular pour le développement front-end et comment les combiner.
 Composants angulaires et leurs propriétés d'affichage : comprendre les valeurs par défaut non bloquantes
Mar 15, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Composants angulaires et leurs propriétés d'affichage : comprendre les valeurs par défaut non bloquantes
Mar 15, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Le comportement d'affichage par défaut des composants du framework Angular ne concerne pas les éléments au niveau du bloc. Ce choix de conception favorise l'encapsulation des styles de composants et encourage les développeurs à définir consciemment la manière dont chaque composant est affiché. En définissant explicitement l'affichage des propriétés CSS, l'affichage des composants angulaires peut être entièrement contrôlé pour obtenir la mise en page et la réactivité souhaitées.





