Cet article est reproduit du compte public WeChat "Youerhut", écrit par Youerhut. Pour réimprimer cet article, veuillez contacter le compte public Youerhut.
Bonjour à tous, je m'appelle Peter~
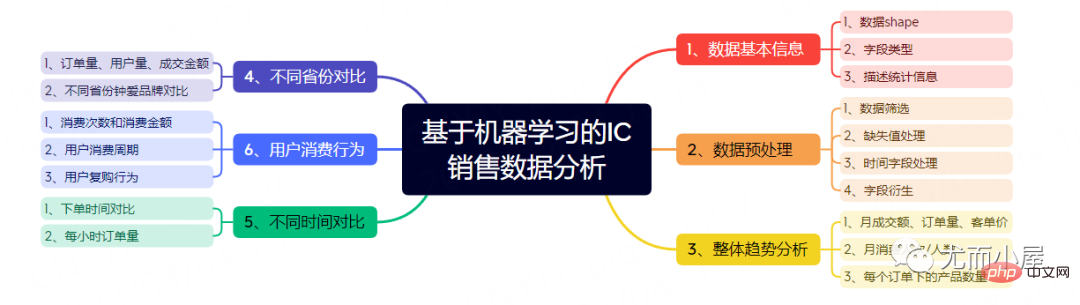
J'ai récemment obtenu des données de commerce électronique de produits électroniques IC et je procéderai plus tard à l'analyse et à l'exploration de données sur 3 sujets :
Phase 1 : Basée sur pandas, numpy, matplotlib , seaborn , plotly et autres bibliothèques
Deuxième étape : analyse du portrait d'utilisateur basée sur un algorithme de clustering d'apprentissage automatique et un modèle RFM
Troisième étape : exploration de corrélation de marque, de produit et de catégorie de produit basée sur un algorithme de règles d'association
Cet article est le premier étape. Le contenu principal comprend :
Prétraitement des données
Exploration des données EDA
Analyse comparative multi-angle
Bibliothèque d'importation
Dans [1]:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import time
import os
from datetime import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
#设置中文编码和负号的正常显示
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
import plotly_express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import missingno as ms
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler Copier après la connexion
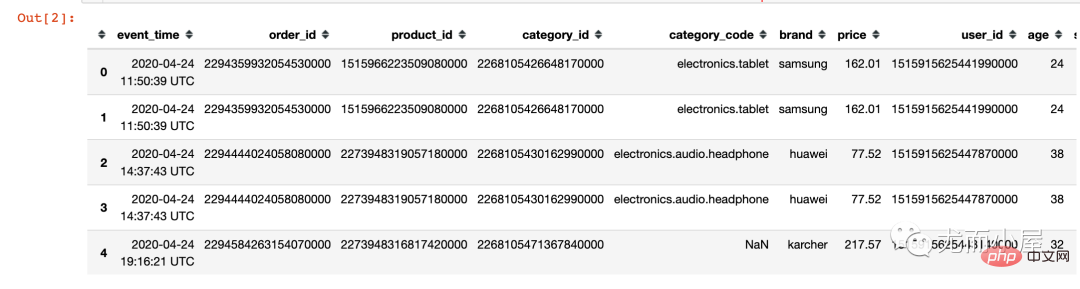
Informations de base sur les données Lire. data df = pd.read_csv(
"ic_sale.csv",
encoding="utf-8",# 指定编码
cnotallow={"order_id":str,"product_id":str,"category_id":str,"user_id":str} # 指定字段类型
)
df.head() Copier après la connexion
Le rôle du paramètre converters : les multiples champs d'identification dans les données sont tous des nombres, qui sont traités comme des nombres dans le fichier csv ou excel (exprimés en notation scientifique, ce sont essentiellement des "chaînes" "Les informations ne le sont pas) ; avoir une quelconque signification. Vous devez spécifier le type lors de la lecture.
Informations de base Après la lecture, vérifiez les informations de base des données :
In [3]:
# 1、数据shape
df.shape Copier après la connexion
Out[3]:
(564169, 11) Copier après la connexion
In [4]:
# 2、数据字段类型
df.dtypes Copier après la connexion
Out [4 ]:
event_timeobject
order_idobject
product_idobject
category_id object
category_code object
brand object
pricefloat64
user_id object
ageint64
sex object
local object
dtype: object Copier après la connexion
In [5]:
Les statistiques descriptives concernent les champs numériques :
# 3、数据描述统计信息
df.describe() Copier après la connexion
Out[5]:
price
âge
compte
564169.000000
564169.000000
moyenne
208.269324
33.184388
std
304.559875
10.122088
min
0.000000
16.000000
25%
23.130000
24.000000
50%
87.940000
33.000000
75%
277.750000
42.000000
max
18328.680000
50.000000
In [6]:
# 4、总共多少个不同客户
df["user_id"].nunique() Copier après la connexion
Out[6]:
6908 Copier après la connexion
In [7]:
# 5、总共多少个不同品牌
df["brand"].nunique() Copier après la connexion
Out[7]:
868 Copier après la connexion
In [8]:
# 6、总共多少个订单
df["order_id"].nunique() Copier après la connexion
Out[8]:
234232 Copier après la connexion
In [9]:
# 7、总共多少个产品
df["product_id"].nunique() Copier après la connexion
Out[9]:
3756 Copier après la connexion
数据预处理 数据筛选 从描述统计信息中发现price字段的最小值是0,应该是没有成交的数据;我们选择price大于0的信息:
In [10]:
df = df[df["price"] > 0] Copier après la connexion
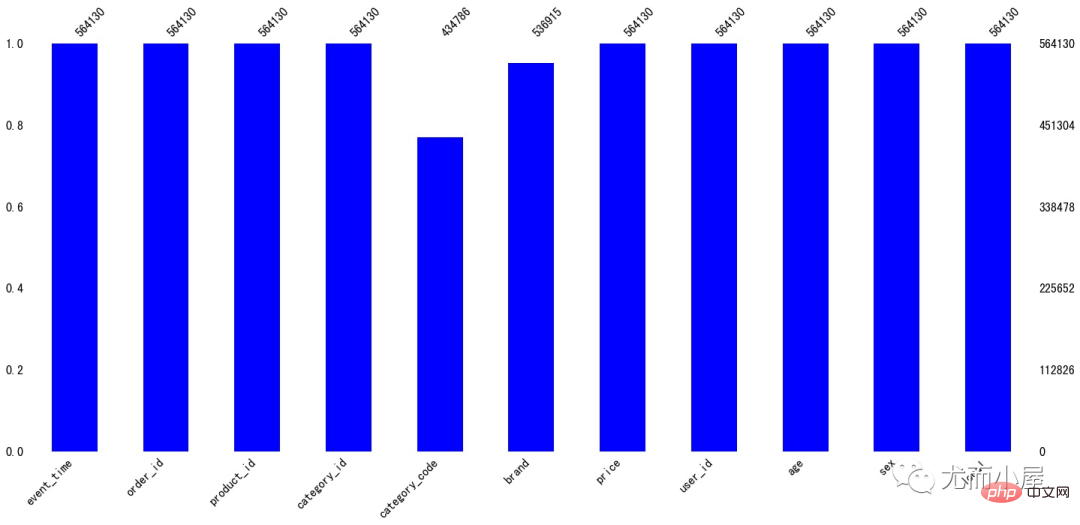
缺失值处理 缺失值情况 In [11]:
df.isnull().sum() Copier après la connexion
Out[11]:
event_time0
order_id0
product_id0
category_id 0
category_code129344
brand 27215
price 0
user_id 0
age 0
sex 0
local 0
dtype: int64 Copier après la connexion
可以看到缺失值体现在字段:
In [12]:
ms.bar(df,color="blue")# 缺失值可视化
plt.show() Copier après la connexion
缺失值填充 In [13]:
df.fillna("missing",inplace=True) Copier après la connexion
In [14]:
df.isnull().sum()# 填充之后无缺失值 Copier après la connexion
Out[14]:
event_time 0
order_id 0
product_id 0
category_id0
category_code0
brand0
price0
user_id0
age0
sex0
local0
dtype: int64 Copier après la connexion
时间字段处理 字段类型转化 读进来的数据中时间字段是object类型,需要将其转成时间格式的类型
In [15]:
df["event_time"][:5] # 处理前 Copier après la connexion
Out[15]:
02020-04-24 11:50:39 UTC
12020-04-24 11:50:39 UTC
22020-04-24 14:37:43 UTC
32020-04-24 14:37:43 UTC
42020-04-24 19:16:21 UTC
Name: event_time, dtype: object Copier après la connexion
In [16]:
# 去掉最后的UTC
df["event_time"] = df["event_time"].apply(lambda x: x[:19]) Copier après la connexion
In [17]:
# 时间数据类型转化:字符类型---->指定时间格式
df['event_time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['event_time'], format="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") Copier après la connexion
字段衍生 In [18]:
# 提取多个时间相关字段
df['month']=df['event_time'].dt.month
df['day'] = df['event_time'].dt.day
df['dayofweek']=df['event_time'].dt.dayofweek
df['hour']=df['event_time'].dt.hour Copier après la connexion
In [19]:
df["event_time"][:5] # 处理后 Copier après la connexion
Out[19]:
0 2020-04-24 11:50:39
1 2020-04-24 11:50:39
2 2020-04-24 14:37:43
3 2020-04-24 14:37:43
4 2020-04-24 19:16:21
Name: event_time, dtype: datetime64[ns] Copier après la connexion
可以看到字段类型已经发生了变化
整体趋势分析 分析1:每月成交金额多少? In [20]:
amount_by_month = df.groupby("month")["price"].sum().reset_index()
amount_by_month Copier après la connexion
Out[20]:
month
price
0
1
1953358.17
1
2
2267809.88
2
3
2897486.26
3
4
1704422.41
4
5
7768637.79
5
6
7691244.33
6
7
16354029.27
7
8
27982605.44
8
9
17152310.57
9
10
19765680.76In [21]:
fig = px.scatter(amount_by_month,x="month",y="price",size="price",color="price")
fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交金额")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
可以看到:
8月份是整个销售的顶峰 下半年的整体销售会好于下半年 分析2:月订单量如何变化? In [22]:
order_by_month = df.groupby("month")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
order_by_month Copier après la connexion
Out[22]:
month
order_id
0
1
10353
1
2
11461
2
3
12080
3
4
9001
4
5
30460
5
6
2897 8
6
7
57659
7
8
73897
8
9
345
9
10
14
10
11
6
In [23]:
fig = px.line(order_by_month,x="month",y="order_id")
fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交订单量")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
关于订单量:
从1到8月份是一个逐渐上升的趋势;尤其是4到8月份;可能是五一假期或者暑假、开学季引起的 9、10月份订单量陡降:开学之后销量下降快 分析3:月消费人数/人次如何变化? In [24]:
# nunique:对每个user_id进行去重:消费人数
# count:统计user_id 的次数;消费人次(存在一人多次购买)
people_by_month = df.groupby("month")["user_id"].agg(["nunique","count"]).reset_index()
people_by_month Copier après la connexion
Out[24]:
month
nunique
count
0
1
1388
15575
1
2
1508
17990
2
3
1597
18687
3
4
1525
11867
4
5
3168
40332
5
6
3966
41355
6
7
5159
76415
7
8
6213
100006
8
9
5497
70496
9
10
4597
104075
10
11
3 134
67332
In [25]:
fig = px.line(people_by_month,x="month",y="nunique")
fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交人数")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
fig = px.line(people_by_month,x="month",y="count")
fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交人次")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
分析4:每月订单价多少? In [27]:
amount_by_month# 每月成交金额 Copier après la connexion
Out[27]:
month
price
0
1
1953358.17
1
2
2267809.88
2
3
2897486.26
3
4
1704422.41
4
5
7768637.79
5
6
7691244.33
6
7
16354029.27
7
8
27982605.44
8
9
17152310.57
9
10
19765680.76In [28]:
order_by_month# 每月订单数 Copier après la connexion
Out[28]:
month
order_id
0
1
10353
1
2
11461
2
3
12080
3
4
9001
4
5
30460
5
6
2897 8
6
7
57659
7
8
73897
8
9
345
9
10
14
10
11
6
In [29]:
amount_by_userid = pd.merge(amount_by_month,order_by_month)
amount_by_userid Copier après la connexion
Out[29]:
month
price
order_id
0
1
1953358.17
10353
1
2
2267809.88
11461
2
3
2897486.26
12080
3
4
1704422.41
9001
4
5
7768 637.79
30460
5
6
7691244.33
28978
6
7
16354029.27
57659
7
8
27982605.44
73897
8
9
17152310.57
345
9
10
19765680.76
14
10
11
11961511.52
6
In [30]:
amount_by_userid["average"] = amount_by_userid["price"] / amount_by_userid["order_id"]
amount_by_userid Copier après la connexion
fig = px.line(amount_by_userid,x="month",y="average")
fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月客单价")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
从上面的折线图可以看出来:
1到8月份月订单量基本持平;可能是有很多批量的订单;通过量大带来利润:量的路线 9到10月份:月单价急剧上升;订单量少,但是金额;可能存在大额消费的用户:质的路线 分析5:每个订单包含多少产品 In [32]:
product_by_order = df.groupby("order_id")["product_id"].count().reset_index().sort_values("product_id",ascending=False)
product_by_order.head(10) Copier après la connexion
Out[32]:
order_id
product_id
234208
2388440981134640000
15021
234210
2388440981134660000
14891
234211
2388440981134670000
14845
234212
2388440981134680000
14765
234202
2388440981134580000
14587
234205
2388 440981134610000
14571
234207
2388440981134630000
14443
234204
2388440981134600000
14416
234206
2388440981134620000
14414
234203
2388440981134590000
14194
In [33]:
fig = px.bar(product_by_order[:20],
x="order_id",
y="product_id",
text="product_id"
)
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
一个订单下包含的产品数量是不同;上万的订单可能是小型的ic元器件产品。
不同省份对比 分析6:订单量、用户量和成交金额对比 不同省份下的订单量、用户量和成交金额对比
In [34]:
local = df.groupby("local").agg({"order_id":"nunique","user_id":"nunique","price":sum}).reset_index()
local.head() Copier après la connexion
Out[34]:
local
order_id
user_id
price
0
上海
39354
5680
19837942.20
1
北京
38118
5702
19137748.75
2
Sichuan
13396
3589
6770891.28
3
Tianjin
13058
3497
In [35]:
df1 = local.sort_values("order_id",ascending=True)# 订单量升序
df1 Copier après la connexion
Out[35]:
local
order_id
user_id
price
6
浙江
12790
3485
6522657.59
8
湖北
12810
3488
5993820.57
3
天津
13058
3497
6433736.85
10
Chongqing
13058
3496
6479488.14
7
Hainan
13076
3587
6968674.41
2
Sichuan
13396
3589
6770891.28
9
1
0Shanghai
39354
5680
19837942.20
4
Guangdong
51471
6085
26013770.86
In [36]:
fig = px.pie(df1, names="local",labels="local",values="price")
fig.update_traces(
textpositinotallow="inside",
textinfo="percent+label"
)
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
无疑:广东省No.1
每个省份的订单量对比:
fig = px.bar(df1,x="order_id",y="local",orientatinotallow="h")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
# 整体的可视化效果
fig = px.scatter_3d(local,
x="order_id",
y="user_id",
z="price",
color="order_id",
hover_name="local"
)
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
通过3D散点图我们发现:广东省真的是一骑绝尘!
订单量多;订单金额也大:主打搞钱 除去北上广,湖南和江苏的用户群是最多的,有前景 分析7:不同省份的客户钟爱哪些品牌? In [39]:
local_brand = df.groupby(["local","brand"]).size().to_frame().reset_index()
local_brand.columns = ["local","brand","number"]# 修改字段名
local_brand Copier après la connexion
# 根据local和number进行排序
local_brand.sort_values(["local","number"],ascending=[True,False],inplace=True,ignore_index=True)
local_brand = local_brand[local_brand["brand"] != "missing"]
# 每个local下面最受欢迎的前3个品牌
local_brand = local_brand.groupby("local").head(3)
local_brand Copier après la connexion
fig = px.bar(local_brand,
x="brand",
y="number",
color="number",
facet_col="local")
fig.update_layout(height=500,width=1000)
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
看来大家都很喜欢: samsung 、apple、ava
不同时间对比 分析8:下单时间对比 In [43]:
df.columns Copier après la connexion
Out[43]:
Index(['event_time', 'order_id', 'product_id', 'category_id', 'category_code',
'brand', 'price', 'user_id', 'age', 'sex', 'local', 'month', 'day',
'dayofweek', 'hour'],
dtype='object') Copier après la connexion
In [44]:
df2 = df.groupby("dayofweek")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
df2 Copier après la connexion
Out[44]:
dayofweek
order_id
0
0
35690
1
1
34256
2
2
31249
3
3
3155 5
4
4
33010
5
5
34772
6
6
33922
In [45]:
plt.figure(figsize=(12,7))
df2["order_id"].plot.bar()
plt.xticks(range(7),['周一','周二','周三','周四','周五','周六','周日'],rotatinotallow=0)
plt.xlabel('星期')
plt.ylabel('订单量')
plt.title('订单数随星期变化')
plt.show() Copier après la connexion
分析9:每小时订单量 In [46]:
df3 = df.groupby("hour")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
df3.head(10) Copier après la connexion
Out[46]:
hour
order_id
0
0
2865
1
1
2711
2
2
3981
3
3
6968
4
4
12176
5
5
16411
6
6
18667
7
7
20034
8
8
20261
9
9
20507
In [47]:
plt.figure(figsize=(14,8))
df3["order_id"].plot()
plt.xlabel('小时')
plt.ylabel('订单数量')
plt.title('订单随小时数变化')
plt.grid()
plt.show() Copier après la connexion
用户都喜欢在上午8、9、10点下单;可能是刚开始上班工作,大家更积极
不同用户消费行为分析 分析10:消费次数和消费金额 In [48]:
df4 = df.groupby("user_id").agg({"order_id":"nunique", "price":sum})
fig = px.scatter(df4,
x="order_id",
y="price",
color="price",
size="price")
fig.show() Copier après la connexion
分析11:用户消费周期 In [50]:
# 用户消费周期
# shift函数:移动一个单位
purchase_time=df.groupby('user_id').apply(lambda x: x['event_time'] - x['event_time'].shift()).dt.days
purchase_time Copier après la connexion
Out[50]:
user_id
151591562543995000096014NaN
1515915625440030000374760 NaN
48492735.0
1515915625440050000463812 NaN
473430 1.0
...
1515915625514880000564132 0.0
564143 0.0
564164 0.0
1515915625514890000564158 NaN
564165 0.0
Name: event_time, Length: 564130, dtype: float64 Copier après la connexion
In [51]:
purchase_time[purchase_time>0].describe() Copier après la connexion
Out[51]:
count120629.000000
mean 35.494500
std 663.803583
min 1.000000
25% 2.000000
50% 4.000000
75%12.000000
max 18466.000000
Name: event_time, dtype: float64 Copier après la connexion
说明:
至少消费两次的用户的消费周期是4天 有75%的客户消费周期在12天 分析12:用户复购行为 In [52]:
pivoted_counts = df.pivot_table(index='user_id',
columns='month',
values='order_id',
aggfunc='nunique').fillna(0)
pivoted_counts Copier après la connexion
Out[52]:
pivoted_counts_map.sum() / pivoted_counts_map.count()
# 结果
month
1 0.406340
2 0.439655
3 0.474640
4 0.700328
5 0.829861
6 0.792990
7 0.891452
8 0.920328
9 0.781153
100.609963
110.419592
dtype: float64 Copier après la connexion
(pivoted_counts_map.sum()/pivoted_counts_map.count()).plot(figsize=(12,6))
plt.xticks(range(11),columns_month)
plt.title('复购率')
plt.show() Copier après la connexion
复购的高峰期在4、6、9月份
10月份开始,销售开始冷淡;复购急降
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Déclaration de ce site Web
Le contenu de cet article est volontairement contribué par les internautes et les droits d'auteur appartiennent à l'auteur original. Ce site n'assume aucune responsabilité légale correspondante. Si vous trouvez un contenu suspecté de plagiat ou de contrefaçon, veuillez contacter admin@php.cn
Derniers articles par auteur
2024-10-13 13:32:21
2024-10-12 11:58:51
2024-10-11 20:06:51
2024-10-11 18:59:31
2024-10-11 18:30:51
2024-10-11 15:51:51
2024-10-11 15:42:10
2024-10-11 14:41:20
2024-10-11 14:08:31
2024-10-11 13:42:21
Recommandations populaires
Tutoriels populaires
Plus>
Recommandations populaires
Derniers téléchargements
Plus>