Framework Fork/Join et méthode d'appel en Java
Qu'est-ce que ForkJoin ?
ForkJoin Littéralement, Fork signifie bifurcation, et Join signifie combinaison. Nous pouvons le comprendre comme diviser les grandes tâches en petites tâches pour le calcul et la solution, et enfin diviser les petites tâches en Les résultats sont combinés. pour trouver la solution à la grande tâche. Ces petites tâches fissurées peuvent être confiées à différents threads pour le calcul. Ceci est similaire à l'informatique distribuée hors ligne MapReduce dans le Big Data. L'une des applications les plus classiques de ForkJoin est Stream en Java8. Nous savons que Stream est divisé en flux série et flux parallèle. ParallelStream s'appuie sur ForkJoin pour réaliser un traitement parallèle. de.
Jetons un coup d'œil aux noyaux ForkJoinTask et ForkJoinPool. ForkJoinTask和ForkJoinPool。
ForkJoinTask 任务
ForkJoinTask本身的依赖关系并不复杂,它与异步任务计算FutureTask一样均实现了Future接口
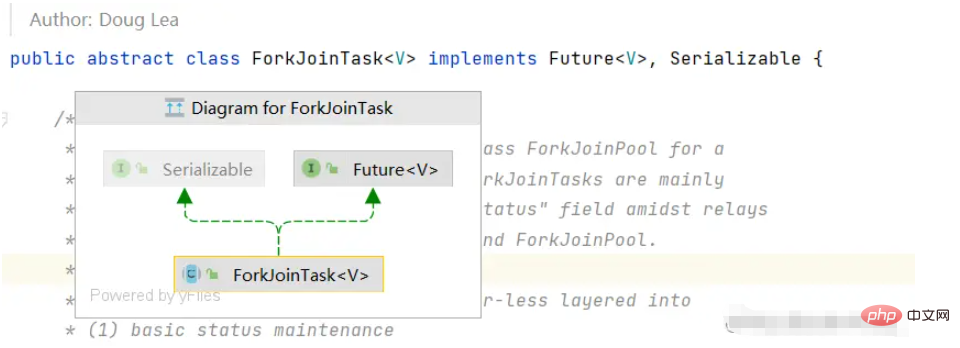
下面我们就ForkJoinTask的核心源码来研究一下,该任务是如何通过分治法进行计算。
ForkJoinTask最核心的莫过于fork()和join()方法了。
fork()
判断当前线程是不是ForkJoinWorkerThread线程
是 直接将当前线程push到工作队列中
否 调用ForkJoinPool 的externalPush方法
在ForkJoinPool构建了一个静态的common对象,这里调用的就是common的externalPush()
join()
调用doJoin()方法,等待线程执行完成
public final ForkJoinTask<V> fork() {
Thread t;
if ((t = Thread.currentThread()) instanceof ForkJoinWorkerThread)
((ForkJoinWorkerThread)t).workQueue.push(this);
else
ForkJoinPool.common.externalPush(this);
return this;
}
public final V join() {
int s;
if ((s = doJoin() & DONE_MASK) != NORMAL)
reportException(s);
return getRawResult();
}
private int doJoin() {
int s; Thread t; ForkJoinWorkerThread wt; ForkJoinPool.WorkQueue w;
return (s = status) < 0 ? s :
((t = Thread.currentThread()) instanceof ForkJoinWorkerThread) ?
(w = (wt = (ForkJoinWorkerThread)t).workQueue).
tryUnpush(this) && (s = doExec()) < 0 ? s :
wt.pool.awaitJoin(w, this, 0L) :
externalAwaitDone();
}
// 获取结果的方法由子类实现
public abstract V getRawResult(); RecursiveTask 是ForkJoinTask的一个子类主要对获取结果的方法进行了实现,通过泛型约束结果。我们如果需要自己创建任务,仍需要实现RecursiveTask,并去编写最为核心的计算方法compute()。
public abstract class RecursiveTask<V> extends ForkJoinTask<V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5232453952276485270L;
V result;
protected abstract V compute();
public final V getRawResult() {
return result;
}
protected final void setRawResult(V value) {
result = value;
}
protected final boolean exec() {
result = compute();
return true;
}
}ForkJoinPool 线程池
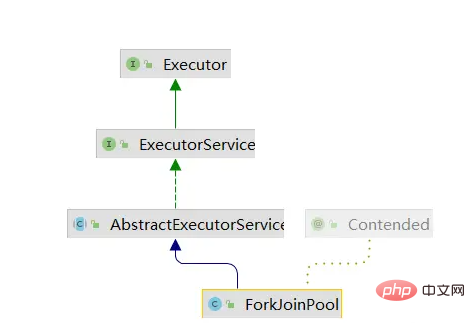
ForkJoinTask 中许多功能都依赖于ForkJoinPool线程池,所以说ForkJoinTask运行离不开ForkJoinPool,ForkJoinPool与ThreadPoolExecutor有许多相似之处,他是专门用来执行ForkJoinTask任务的线程池,我之前也有文章对线程池技术进行了介绍,感兴趣的可以进行阅读——从java源码分析线程池(池化技术)的实现原理
ForkJoinPool与ThreadPoolExecutor的继承关系几乎是相同的,他们相当于兄弟关系。
工作窃取算法
ForkJoinPool中采取工作窃取算法,如果每次fork子任务如果都去创建新线程去处理的话,对系统资源的开销是巨大的,所以必须采取线程池。一般的线程池只有一个任务队列,但是对于ForkJoinPool来说,由于同一个任务Fork出的各个子任务是平行关系,为了提高效率,减少线程的竞争,需要将这些平行的任务放到不同的队列中,由于线程处理不同任务的速度不同,这样就可能存在某个线程先执行完了自己队列中的任务,这时为了提升效率,就可以让该线程去“窃取”其它任务队列中的任务,这就是所谓的“工作窃取算法”。
对于一般的队列来说,入队元素都是在队尾,出队元素在队首,要满足“工作窃取”的需求,任务队列应该支持从“队尾”出队元素,这样可以减少与其它工作线程的冲突(因为其它工作线程会从队首获取自己任务队列中的任务),这时就需要使用双端阻塞队列来解决。
构造方法
首先我们来看ForkJoinPool线程池的构造方法,他为我们提供了三种形式的构造,其中最为复杂的是四个入参的构造,下面我们看一下它四个入参都代表什么?
int parallelism 可并行级别(不代表最多存在的线程数量)
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory 线程创建工厂
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler 异常捕获处理器
boolean asyncMode 先进先出的工作模式 或者 后进先出的工作模式
public ForkJoinPool() {
this(Math.min(MAX_CAP, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()),
defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory, null, false);
}
public ForkJoinPool(int parallelism) {
this(parallelism, defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory, null, false);
}
public ForkJoinPool(int parallelism,
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory,
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler,
boolean asyncMode) {
this(checkParallelism(parallelism),
checkFactory(factory),
handler,
asyncMode ? FIFO_QUEUE : LIFO_QUEUE,
"ForkJoinPool-" + nextPoolId() + "-worker-");
checkPermission();
}提交方法
下面我们看一下提交任务的方法:
externalPush
 🎜🎜Étudions le code source principal de ForkJoinTask et comment la tâche est calculée via la méthode diviser pour régner. 🎜🎜Le cœur de ForkJoinTask est constitué des méthodes fork() et join(). 🎜🎜fork()🎜
🎜🎜Étudions le code source principal de ForkJoinTask et comment la tâche est calculée via la méthode diviser pour régner. 🎜🎜Le cœur de ForkJoinTask est constitué des méthodes fork() et join(). 🎜🎜fork()🎜- 🎜Détermine si le thread actuel est un thread ForkJoinWorkerThread🎜
- 🎜 consiste à pousser directement le thread actuel dans la file d'attente de travail 🎜
- 🎜 s'il faut appeler la méthode externalPush de ForkJoinPool 🎜 🎜🎜🎜 est intégré à
- 🎜Appelez la méthode doJoin() et attendez la fin de l'exécution du thread🎜 🎜
- 🎜niveau de parallélisme int (ne représente pas le nombre maximum de threads existants)🎜
- 🎜ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory usine de création de threads d'usine🎜
- 🎜Gestionnaire de capture d'exceptions du gestionnaire UncaughtExceptionHandler🎜
- 🎜mode de travail booléen asyncMode premier entré, premier sorti ou mode de travail dernier entré, premier sorti🎜 🎜
ForkJoinPool Un objet commun statique est appelé ici la classe externalPush()🎜🎜join()🎜 public ForkJoinTask<?> submit(Runnable task) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
ForkJoinTask<?> job;
if (task instanceof ForkJoinTask<?>) // avoid re-wrap
job = (ForkJoinTask<?>) task;
else
job = new ForkJoinTask.AdaptedRunnableAction(task);
externalPush(job);
return job;
}
final void externalPush(ForkJoinTask<?> task) {
WorkQueue[] ws; WorkQueue q; int m;
int r = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
int rs = runState;
if ((ws = workQueues) != null && (m = (ws.length - 1)) >= 0 &&
(q = ws[m & r & SQMASK]) != null && r != 0 && rs > 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 0, 1)) {
ForkJoinTask<?>[] a; int am, n, s;
if ((a = q.array) != null &&
(am = a.length - 1) > (n = (s = q.top) - q.base)) {
int j = ((am & s) << ASHIFT) + ABASE;
U.putOrderedObject(a, j, task);
U.putOrderedInt(q, QTOP, s + 1);
U.putOrderedInt(q, QLOCK, 0);
if (n <= 1)
signalWork(ws, q);
return;
}
U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 1, 0);
}
externalSubmit(task);
}
private void externalSubmit(ForkJoinTask<?> task) {
int r; // initialize caller's probe
if ((r = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit();
r = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
}
for (;;) {
WorkQueue[] ws; WorkQueue q; int rs, m, k;
boolean move = false;
if ((rs = runState) < 0) {
tryTerminate(false, false); // help terminate
throw new RejectedExecutionException();
}
else if ((rs & STARTED) == 0 || // initialize
((ws = workQueues) == null || (m = ws.length - 1) < 0)) {
int ns = 0;
rs = lockRunState();
try {
if ((rs & STARTED) == 0) {
U.compareAndSwapObject(this, STEALCOUNTER, null,
new AtomicLong());
// create workQueues array with size a power of two
int p = config & SMASK; // ensure at least 2 slots
int n = (p > 1) ? p - 1 : 1;
n |= n >>> 1; n |= n >>> 2; n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8; n |= n >>> 16; n = (n + 1) << 1;
workQueues = new WorkQueue[n];
ns = STARTED;
}
} finally {
unlockRunState(rs, (rs & ~RSLOCK) | ns);
}
}
else if ((q = ws[k = r & m & SQMASK]) != null) {
if (q.qlock == 0 && U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 0, 1)) {
ForkJoinTask<?>[] a = q.array;
int s = q.top;
boolean submitted = false; // initial submission or resizing
try { // locked version of push
if ((a != null && a.length > s + 1 - q.base) ||
(a = q.growArray()) != null) {
int j = (((a.length - 1) & s) << ASHIFT) + ABASE;
U.putOrderedObject(a, j, task);
U.putOrderedInt(q, QTOP, s + 1);
submitted = true;
}
} finally {
U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 1, 0);
}
if (submitted) {
signalWork(ws, q);
return;
}
}
move = true; // move on failure
}
else if (((rs = runState) & RSLOCK) == 0) { // create new queue
q = new WorkQueue(this, null);
q.hint = r;
q.config = k | SHARED_QUEUE;
q.scanState = INACTIVE;
rs = lockRunState(); // publish index
if (rs > 0 && (ws = workQueues) != null &&
k < ws.length && ws[k] == null)
ws[k] = q; // else terminated
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
}
else
move = true; // move if busy
if (move)
r = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(r);
}
} final void signalWork(WorkQueue[] ws, WorkQueue q) {
long c; int sp, i; WorkQueue v; Thread p;
while ((c = ctl) < 0L) { // too few active
if ((sp = (int)c) == 0) { // no idle workers
if ((c & ADD_WORKER) != 0L) // too few workers
tryAddWorker(c);
break;
}
if (ws == null) // unstarted/terminated
break;
if (ws.length <= (i = sp & SMASK)) // terminated
break;
if ((v = ws[i]) == null) // terminating
break;
int vs = (sp + SS_SEQ) & ~INACTIVE; // next scanState
int d = sp - v.scanState; // screen CAS
long nc = (UC_MASK & (c + AC_UNIT)) | (SP_MASK & v.stackPred);
if (d == 0 && U.compareAndSwapLong(this, CTL, c, nc)) {
v.scanState = vs; // activate v
if ((p = v.parker) != null)
U.unpark(p);
break;
}
if (q != null && q.base == q.top) // no more work
break;
}
}
private void tryAddWorker(long c) {
boolean add = false;
do {
long nc = ((AC_MASK & (c + AC_UNIT)) |
(TC_MASK & (c + TC_UNIT)));
if (ctl == c) {
int rs, stop; // check if terminating
if ((stop = (rs = lockRunState()) & STOP) == 0)
add = U.compareAndSwapLong(this, CTL, c, nc);
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
if (stop != 0)
break;
if (add) {
createWorker();
break;
}
}
} while (((c = ctl) & ADD_WORKER) != 0L && (int)c == 0);
}
private boolean createWorker() {
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory fac = factory;
Throwable ex = null;
ForkJoinWorkerThread wt = null;
try {
if (fac != null && (wt = fac.newThread(this)) != null) {
wt.start();
return true;
}
} catch (Throwable rex) {
ex = rex;
}
deregisterWorker(wt, ex);
return false;
}
final void deregisterWorker(ForkJoinWorkerThread wt, Throwable ex) {
WorkQueue w = null;
if (wt != null && (w = wt.workQueue) != null) {
WorkQueue[] ws; // remove index from array
int idx = w.config & SMASK;
int rs = lockRunState();
if ((ws = workQueues) != null && ws.length > idx && ws[idx] == w)
ws[idx] = null;
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
}
long c; // decrement counts
do {} while (!U.compareAndSwapLong
(this, CTL, c = ctl, ((AC_MASK & (c - AC_UNIT)) |
(TC_MASK & (c - TC_UNIT)) |
(SP_MASK & c))));
if (w != null) {
w.qlock = -1; // ensure set
w.transferStealCount(this);
w.cancelAll(); // cancel remaining tasks
}
for (;;) { // possibly replace
WorkQueue[] ws; int m, sp;
if (tryTerminate(false, false) || w == null || w.array == null ||
(runState & STOP) != 0 || (ws = workQueues) == null ||
(m = ws.length - 1) < 0) // already terminating
break;
if ((sp = (int)(c = ctl)) != 0) { // wake up replacement
if (tryRelease(c, ws[sp & m], AC_UNIT))
break;
}
else if (ex != null && (c & ADD_WORKER) != 0L) {
tryAddWorker(c); // create replacement
break;
}
else // don't need replacement
break;
}
if (ex == null) // help clean on way out
ForkJoinTask.helpExpungeStaleExceptions();
else // rethrow
ForkJoinTask.rethrow(ex);
}
public static interface ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory {
public ForkJoinWorkerThread newThread(ForkJoinPool pool);
}
static final class DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory
implements ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory {
public final ForkJoinWorkerThread newThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
return new ForkJoinWorkerThread(pool);
}
}
protected ForkJoinWorkerThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
// Use a placeholder until a useful name can be set in registerWorker
super("aForkJoinWorkerThread");
this.pool = pool;
this.workQueue = pool.registerWorker(this);
}
final WorkQueue registerWorker(ForkJoinWorkerThread wt) {
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler;
wt.setDaemon(true); // configure thread
if ((handler = ueh) != null)
wt.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(handler);
WorkQueue w = new WorkQueue(this, wt);
int i = 0; // assign a pool index
int mode = config & MODE_MASK;
int rs = lockRunState();
try {
WorkQueue[] ws; int n; // skip if no array
if ((ws = workQueues) != null && (n = ws.length) > 0) {
int s = indexSeed += SEED_INCREMENT; // unlikely to collide
int m = n - 1;
i = ((s << 1) | 1) & m; // odd-numbered indices
if (ws[i] != null) { // collision
int probes = 0; // step by approx half n
int step = (n <= 4) ? 2 : ((n >>> 1) & EVENMASK) + 2;
while (ws[i = (i + step) & m] != null) {
if (++probes >= n) {
workQueues = ws = Arrays.copyOf(ws, n <<= 1);
m = n - 1;
probes = 0;
}
}
}
w.hint = s; // use as random seed
w.config = i | mode;
w.scanState = i; // publication fence
ws[i] = w;
}
} finally {
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
}
wt.setName(workerNamePrefix.concat(Integer.toString(i >>> 1)));
return w;
} 🎜
🎜Algorithme de vol de travail
🎜ForkJoinPool utilise un algorithme de vol de travail si un nouveau thread est créé pour chaque sous-tâche fork, la surcharge sur les ressources système sera énorme, un pool de threads doit donc être utilisé. Un pool de threads général n'a qu'une seule file d'attente de tâches, mais pour ForkJoinPool, puisque les sous-tâches exécutées par la même tâche sont parallèles, afin d'améliorer l'efficacité et de réduire la concurrence des threads, ces tâches parallèles doivent être placées dans des files d'attente différentes, car les threads. traiter différentes tâches à des vitesses différentes, il peut y avoir un thread qui a fini d'exécuter les tâches dans sa propre file d'attente en premier. À ce stade, afin d'améliorer l'efficacité, le thread peut être autorisé à « voler ». d'autres tâches dans la file d'attente, c'est ce qu'on appelle "Algorithme de vol de travail". 🎜🎜Pour les files d'attente générales, les éléments entrant dans la file d'attente sont à la fin de la file d'attente et les éléments quittant la file d'attente sont au début. Pour répondre aux besoins de « vol de travail », la file d'attente des tâches doit prendre en charge le retrait des éléments de la file d'attente. tail", qui peut réduire les conflits avec d'autres threads de travail (car les autres threads de travail obtiendront des tâches dans leurs propres files d'attente de tâches à partir de la tête de la file d'attente) doivent être résolus en utilisant une file d'attente de blocage à double extrémité. 🎜Méthode de construction
🎜Tout d'abord, regardons la méthode de construction du pool de threads ForkJoinPool. Elle nous propose trois formes de construction, dont la plus complexe est la construction de quatre paramètres d'entrée. regardez-le ci-dessous. Que représentent les quatre ginsengs ? 🎜package com.zhj.interview;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
public class Test16 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
int[] bigArr = new int[10000000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
bigArr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 10000000);
}
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
MyForkJoinTask task = new MyForkJoinTask(bigArr);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
forkJoinPool.submit(task).get();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end-start));
}
}
class MyForkJoinTask extends RecursiveTask<int[]> {
private int source[];
public MyForkJoinTask(int source[]) {
if (source == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("参数有误!!!");
}
this.source = source;
}
@Override
protected int[] compute() {
int l = source.length;
if (l < 2) {
return Arrays.copyOf(source, l);
}
if (l == 2) {
if (source[0] > source[1]) {
int[] tar = new int[2];
tar[0] = source[1];
tar[1] = source[0];
return tar;
} else {
return Arrays.copyOf(source, l);
}
}
if (l > 2) {
int mid = l / 2;
MyForkJoinTask task1 = new MyForkJoinTask(Arrays.copyOf(source, mid));
task1.fork();
MyForkJoinTask task2 = new MyForkJoinTask(Arrays.copyOfRange(source, mid, l));
task2.fork();
int[] res1 = task1.join();
int[] res2 = task2.join();
int tar[] = merge(res1, res2);
return tar;
}
return null;
}
// 合并数组
private int[] merge(int[] res1, int[] res2) {
int l1 = res1.length;
int l2 = res2.length;
int l = l1 + l2;
int tar[] = new int[l];
for (int i = 0, i1 = 0, i2 = 0; i < l; i++) {
int v1 = i1 >= l1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : res1[i1];
int v2 = i2 >= l2 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : res2[i2];
// 如果条件成立,说明应该取数组array1中的值
if(v1 < v2) {
tar[i] = v1;
i1++;
} else {
tar[i] = v2;
i2++;
}
}
return tar;
}
}Méthode de soumission
🎜Jetons un coup d'œil à la méthode de soumission des tâches : 🎜🎜externalPush Cette méthode nous est très familière. C'est exactement lors du forking If. le thread actuel n'est pas ForkJoinWorkerThread, la nouvelle tâche soumise l'est également. La tâche sera effectuée via cette méthode. On peut voir que fork consiste à créer une nouvelle sous-tâche à soumettre. 🎜externalSubmit是最为核心的一个方法,它可以首次向池提交第一个任务,并执行二次初始化。它还可以检测外部线程的首次提交,并创建一个新的共享队列。
signalWork(ws, q)是发送工作信号,让工作队列进行运转。
public ForkJoinTask<?> submit(Runnable task) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
ForkJoinTask<?> job;
if (task instanceof ForkJoinTask<?>) // avoid re-wrap
job = (ForkJoinTask<?>) task;
else
job = new ForkJoinTask.AdaptedRunnableAction(task);
externalPush(job);
return job;
}
final void externalPush(ForkJoinTask<?> task) {
WorkQueue[] ws; WorkQueue q; int m;
int r = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
int rs = runState;
if ((ws = workQueues) != null && (m = (ws.length - 1)) >= 0 &&
(q = ws[m & r & SQMASK]) != null && r != 0 && rs > 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 0, 1)) {
ForkJoinTask<?>[] a; int am, n, s;
if ((a = q.array) != null &&
(am = a.length - 1) > (n = (s = q.top) - q.base)) {
int j = ((am & s) << ASHIFT) + ABASE;
U.putOrderedObject(a, j, task);
U.putOrderedInt(q, QTOP, s + 1);
U.putOrderedInt(q, QLOCK, 0);
if (n <= 1)
signalWork(ws, q);
return;
}
U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 1, 0);
}
externalSubmit(task);
}
private void externalSubmit(ForkJoinTask<?> task) {
int r; // initialize caller's probe
if ((r = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit();
r = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
}
for (;;) {
WorkQueue[] ws; WorkQueue q; int rs, m, k;
boolean move = false;
if ((rs = runState) < 0) {
tryTerminate(false, false); // help terminate
throw new RejectedExecutionException();
}
else if ((rs & STARTED) == 0 || // initialize
((ws = workQueues) == null || (m = ws.length - 1) < 0)) {
int ns = 0;
rs = lockRunState();
try {
if ((rs & STARTED) == 0) {
U.compareAndSwapObject(this, STEALCOUNTER, null,
new AtomicLong());
// create workQueues array with size a power of two
int p = config & SMASK; // ensure at least 2 slots
int n = (p > 1) ? p - 1 : 1;
n |= n >>> 1; n |= n >>> 2; n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8; n |= n >>> 16; n = (n + 1) << 1;
workQueues = new WorkQueue[n];
ns = STARTED;
}
} finally {
unlockRunState(rs, (rs & ~RSLOCK) | ns);
}
}
else if ((q = ws[k = r & m & SQMASK]) != null) {
if (q.qlock == 0 && U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 0, 1)) {
ForkJoinTask<?>[] a = q.array;
int s = q.top;
boolean submitted = false; // initial submission or resizing
try { // locked version of push
if ((a != null && a.length > s + 1 - q.base) ||
(a = q.growArray()) != null) {
int j = (((a.length - 1) & s) << ASHIFT) + ABASE;
U.putOrderedObject(a, j, task);
U.putOrderedInt(q, QTOP, s + 1);
submitted = true;
}
} finally {
U.compareAndSwapInt(q, QLOCK, 1, 0);
}
if (submitted) {
signalWork(ws, q);
return;
}
}
move = true; // move on failure
}
else if (((rs = runState) & RSLOCK) == 0) { // create new queue
q = new WorkQueue(this, null);
q.hint = r;
q.config = k | SHARED_QUEUE;
q.scanState = INACTIVE;
rs = lockRunState(); // publish index
if (rs > 0 && (ws = workQueues) != null &&
k < ws.length && ws[k] == null)
ws[k] = q; // else terminated
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
}
else
move = true; // move if busy
if (move)
r = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(r);
}
}创建工人(线程)
提交任务后,通过signalWork(ws, q)方法,发送工作信号,当符合没有执行完毕,且没有出现异常的条件下,循环执行任务,根据控制变量尝试添加工人(线程),通过线程工厂,生成线程,并且启动线程,也控制着工人(线程)的下岗。
final void signalWork(WorkQueue[] ws, WorkQueue q) {
long c; int sp, i; WorkQueue v; Thread p;
while ((c = ctl) < 0L) { // too few active
if ((sp = (int)c) == 0) { // no idle workers
if ((c & ADD_WORKER) != 0L) // too few workers
tryAddWorker(c);
break;
}
if (ws == null) // unstarted/terminated
break;
if (ws.length <= (i = sp & SMASK)) // terminated
break;
if ((v = ws[i]) == null) // terminating
break;
int vs = (sp + SS_SEQ) & ~INACTIVE; // next scanState
int d = sp - v.scanState; // screen CAS
long nc = (UC_MASK & (c + AC_UNIT)) | (SP_MASK & v.stackPred);
if (d == 0 && U.compareAndSwapLong(this, CTL, c, nc)) {
v.scanState = vs; // activate v
if ((p = v.parker) != null)
U.unpark(p);
break;
}
if (q != null && q.base == q.top) // no more work
break;
}
}
private void tryAddWorker(long c) {
boolean add = false;
do {
long nc = ((AC_MASK & (c + AC_UNIT)) |
(TC_MASK & (c + TC_UNIT)));
if (ctl == c) {
int rs, stop; // check if terminating
if ((stop = (rs = lockRunState()) & STOP) == 0)
add = U.compareAndSwapLong(this, CTL, c, nc);
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
if (stop != 0)
break;
if (add) {
createWorker();
break;
}
}
} while (((c = ctl) & ADD_WORKER) != 0L && (int)c == 0);
}
private boolean createWorker() {
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory fac = factory;
Throwable ex = null;
ForkJoinWorkerThread wt = null;
try {
if (fac != null && (wt = fac.newThread(this)) != null) {
wt.start();
return true;
}
} catch (Throwable rex) {
ex = rex;
}
deregisterWorker(wt, ex);
return false;
}
final void deregisterWorker(ForkJoinWorkerThread wt, Throwable ex) {
WorkQueue w = null;
if (wt != null && (w = wt.workQueue) != null) {
WorkQueue[] ws; // remove index from array
int idx = w.config & SMASK;
int rs = lockRunState();
if ((ws = workQueues) != null && ws.length > idx && ws[idx] == w)
ws[idx] = null;
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
}
long c; // decrement counts
do {} while (!U.compareAndSwapLong
(this, CTL, c = ctl, ((AC_MASK & (c - AC_UNIT)) |
(TC_MASK & (c - TC_UNIT)) |
(SP_MASK & c))));
if (w != null) {
w.qlock = -1; // ensure set
w.transferStealCount(this);
w.cancelAll(); // cancel remaining tasks
}
for (;;) { // possibly replace
WorkQueue[] ws; int m, sp;
if (tryTerminate(false, false) || w == null || w.array == null ||
(runState & STOP) != 0 || (ws = workQueues) == null ||
(m = ws.length - 1) < 0) // already terminating
break;
if ((sp = (int)(c = ctl)) != 0) { // wake up replacement
if (tryRelease(c, ws[sp & m], AC_UNIT))
break;
}
else if (ex != null && (c & ADD_WORKER) != 0L) {
tryAddWorker(c); // create replacement
break;
}
else // don't need replacement
break;
}
if (ex == null) // help clean on way out
ForkJoinTask.helpExpungeStaleExceptions();
else // rethrow
ForkJoinTask.rethrow(ex);
}
public static interface ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory {
public ForkJoinWorkerThread newThread(ForkJoinPool pool);
}
static final class DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory
implements ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory {
public final ForkJoinWorkerThread newThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
return new ForkJoinWorkerThread(pool);
}
}
protected ForkJoinWorkerThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
// Use a placeholder until a useful name can be set in registerWorker
super("aForkJoinWorkerThread");
this.pool = pool;
this.workQueue = pool.registerWorker(this);
}
final WorkQueue registerWorker(ForkJoinWorkerThread wt) {
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler;
wt.setDaemon(true); // configure thread
if ((handler = ueh) != null)
wt.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(handler);
WorkQueue w = new WorkQueue(this, wt);
int i = 0; // assign a pool index
int mode = config & MODE_MASK;
int rs = lockRunState();
try {
WorkQueue[] ws; int n; // skip if no array
if ((ws = workQueues) != null && (n = ws.length) > 0) {
int s = indexSeed += SEED_INCREMENT; // unlikely to collide
int m = n - 1;
i = ((s << 1) | 1) & m; // odd-numbered indices
if (ws[i] != null) { // collision
int probes = 0; // step by approx half n
int step = (n <= 4) ? 2 : ((n >>> 1) & EVENMASK) + 2;
while (ws[i = (i + step) & m] != null) {
if (++probes >= n) {
workQueues = ws = Arrays.copyOf(ws, n <<= 1);
m = n - 1;
probes = 0;
}
}
}
w.hint = s; // use as random seed
w.config = i | mode;
w.scanState = i; // publication fence
ws[i] = w;
}
} finally {
unlockRunState(rs, rs & ~RSLOCK);
}
wt.setName(workerNamePrefix.concat(Integer.toString(i >>> 1)));
return w;
}例:ForkJoinTask实现归并排序
这里我们就用经典的归并排序为例,构建一个我们自己的ForkJoinTask,按照归并排序的思路,重写其核心的compute()方法,通过ForkJoinPool.submit(task)提交任务,通过get()同步获取任务执行结果。
package com.zhj.interview;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
public class Test16 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
int[] bigArr = new int[10000000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
bigArr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 10000000);
}
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
MyForkJoinTask task = new MyForkJoinTask(bigArr);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
forkJoinPool.submit(task).get();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end-start));
}
}
class MyForkJoinTask extends RecursiveTask<int[]> {
private int source[];
public MyForkJoinTask(int source[]) {
if (source == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("参数有误!!!");
}
this.source = source;
}
@Override
protected int[] compute() {
int l = source.length;
if (l < 2) {
return Arrays.copyOf(source, l);
}
if (l == 2) {
if (source[0] > source[1]) {
int[] tar = new int[2];
tar[0] = source[1];
tar[1] = source[0];
return tar;
} else {
return Arrays.copyOf(source, l);
}
}
if (l > 2) {
int mid = l / 2;
MyForkJoinTask task1 = new MyForkJoinTask(Arrays.copyOf(source, mid));
task1.fork();
MyForkJoinTask task2 = new MyForkJoinTask(Arrays.copyOfRange(source, mid, l));
task2.fork();
int[] res1 = task1.join();
int[] res2 = task2.join();
int tar[] = merge(res1, res2);
return tar;
}
return null;
}
// 合并数组
private int[] merge(int[] res1, int[] res2) {
int l1 = res1.length;
int l2 = res2.length;
int l = l1 + l2;
int tar[] = new int[l];
for (int i = 0, i1 = 0, i2 = 0; i < l; i++) {
int v1 = i1 >= l1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : res1[i1];
int v2 = i2 >= l2 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : res2[i2];
// 如果条件成立,说明应该取数组array1中的值
if(v1 < v2) {
tar[i] = v1;
i1++;
} else {
tar[i] = v2;
i2++;
}
}
return tar;
}
}ForkJoin计算流程
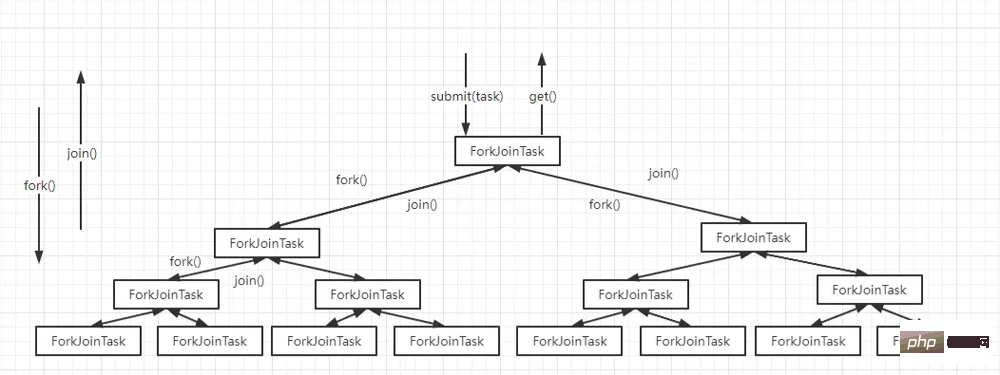
通过ForkJoinPool提交任务,获取结果流程如下,拆分子任务不一定是二分的形式,可参照MapReduce的模式,也可以按照具体需求进行灵活的设计。
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Racine carrée en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Racine carrée en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide de la racine carrée en Java. Nous discutons ici du fonctionnement de Square Root en Java avec un exemple et son implémentation de code respectivement.
 Nombre parfait en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Nombre parfait en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide du nombre parfait en Java. Nous discutons ici de la définition, comment vérifier le nombre parfait en Java ?, des exemples d'implémentation de code.
 Générateur de nombres aléatoires en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Générateur de nombres aléatoires en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide du générateur de nombres aléatoires en Java. Nous discutons ici des fonctions en Java avec des exemples et de deux générateurs différents avec d'autres exemples.
 Weka en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide de Weka en Java. Nous discutons ici de l'introduction, de la façon d'utiliser Weka Java, du type de plate-forme et des avantages avec des exemples.
 Numéro de Smith en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Numéro de Smith en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide du nombre de Smith en Java. Nous discutons ici de la définition, comment vérifier le numéro Smith en Java ? exemple avec implémentation de code.
 Questions d'entretien chez Java Spring
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Questions d'entretien chez Java Spring
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Dans cet article, nous avons conservé les questions d'entretien Java Spring les plus posées avec leurs réponses détaillées. Pour que vous puissiez réussir l'interview.
 Break or Return of Java 8 Stream Forach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or Return of Java 8 Stream Forach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 présente l'API Stream, fournissant un moyen puissant et expressif de traiter les collections de données. Cependant, une question courante lors de l'utilisation du flux est: comment se casser ou revenir d'une opération FOREAK? Les boucles traditionnelles permettent une interruption ou un retour précoce, mais la méthode Foreach de Stream ne prend pas directement en charge cette méthode. Cet article expliquera les raisons et explorera des méthodes alternatives pour la mise en œuvre de terminaison prématurée dans les systèmes de traitement de flux. Lire plus approfondie: Améliorations de l'API Java Stream Comprendre le flux Forach La méthode foreach est une opération terminale qui effectue une opération sur chaque élément du flux. Son intention de conception est
 Horodatage à ce jour en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Horodatage à ce jour en Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide de TimeStamp to Date en Java. Ici, nous discutons également de l'introduction et de la façon de convertir l'horodatage en date en Java avec des exemples.






