Quel est le cycle de vie du Bean dans le code source SpringBoot ?
La méthode de saisie est SpringApplication#run()
1.SpringApplication#run()SpringApplication#run()
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}2.SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}3.SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof SmartFactoryBean<?> smartFactoryBean && smartFactoryBean.isEagerInit()) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
// 此处就是初始化bean的方法
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 此处就是解决循环依赖的代码
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton) {
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
smartInitialize.end();
}
}
}解决循环依赖的代码如下:
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 尝试从缓存中获取成品的目标对象,如果存在,则直接返回
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果缓存中不存在目标对象,则判断当前对象是否已经处于创建过程中,在前面的讲解中,第一次尝试获取A对象
// 的实例之后,就会将A对象标记为正在创建中,因而最后再尝试获取A对象的时候,这里的if判断就会为true
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 这里的singletonFactories是一个Map,其key是bean的名称,而值是一个ObjectFactory类型的
// 对象,这里对于A和B而言,调用图其getObject()方法返回的就是A和B对象的实例,无论是否是半成品
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 获取目标对象的实例
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}一级缓存,singletonObjects 单例缓存,存储已经实例化的单例bean。
二级缓存,earlySingletonObjects 提前暴露的单例缓存,这里存储的bean是刚刚构造完成,但还会通过属性注入bean。
三级缓存,singletonFactories 生产单例的工厂缓存,存储工厂。
解决原理如下:
在第一层中,先去获取 A 的 Bean,发现没有就准备去创建一个,然后将 A 的代理工厂放入“三级缓存”(这个 A 其实是一个半成品,还没有对里面的属性进行注入),但是 A 依赖 B 的创建,就必须先去创建 B;
在第二层中,准备创建 B,发现 B 又依赖 A,需要先去创建 A,去创建 A,因为第一层已经创建了 A 的代理工厂,直接从“三级缓存”中拿到 A 的代理工厂,获取 A 的代理对象,放入“二级缓存”,并清除“三级缓存”;
有了 A 的代理对象,对 A 的依赖完美解决(这里的 A 仍然是个半成品),B 初始化成功。在 B 初始化成功,完成 A 对象的属性注入,然后再填充 A 的其它属性,以及 A 的其它步骤(包括 AOP),完成对 A 完整的初始化功能(这里的 A 才是完整的 Bean)。
将 A 放入“一级缓存”。
4.SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>AbstractBeanFactory#getBean() => AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean()=>AbstractBeanFactory#createBean()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class // which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition. Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// 1.调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessBeforeInstantiation
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 跟进doCreateBean()
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry. throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}SpringApplication#run()=> = > SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 2.创建bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.markAsPostProcessed();
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 跟进populateBean()
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 跟进initializeBean()
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException bce && beanName.equals(bce.getBeanName())) {
throw bce;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}SpringApplication#run()=> ) => SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory #preInstantiateSingletons () < /code><p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
if (bw.getWrappedClass().isRecord()) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to a record");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for records since they are immutable.
return;
}
}
// 3.调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessAfterInstantiation
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
if (hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 4.注入属性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copier après la connexion</div></div><br/>Le code pour résoudre la dépendance circulaire est le suivant :</p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 5.设置Aware接口的属性
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 5.调用BeanPostProcessor的初始化前置方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 6.调用init-method方法,进行初始化操作
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 7. 调用BeanPostProcessor的初始化后置方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copier après la connexion</div></div><ul class=" list-paddingleft-2">
<li><p>Le cache de premier niveau, singletonObjects singleton cache, stocke le singleton instancié haricots. </p></li>
<li><p>Cache de niveau 2, cache singleton earlySingletonObjects exposé à l'avance. Les beans stockés ici viennent d'être construits, mais les beans seront également injectés via des attributs. <br></p></li>
<li>Cache de niveau 3, cache d'usine singletonFactories pour la production singleton, usine de stockage. <p></p>
</li>
</ul>Le principe de la solution est le suivant : <p></p>
<ul class=" list-paddingleft-2">
<li>Dans la première couche, récupérez d'abord le Bean de A, et si vous trouvez il n'est pas disponible, préparez-vous à en créer un, puis placez l'usine proxy de A dans le "cache à trois niveaux" (ce A est en fait un produit semi-fini, et les attributs à l'intérieur n'ont pas encore été injectés), mais si A dépend de la création de B, vous devez d'abord créer B ; <p> li></p>
</li>
<li>Dans la deuxième couche, préparez-vous à créer B et constatez que B dépend de A. Vous devez d'abord créer A, car le premier La couche a déjà créé la fabrique de proxy de A, directement à partir du « cache à trois niveaux » « Obtenez la fabrique de proxy de A, récupérez l'objet proxy de A, placez-le dans le « cache de deuxième niveau » et effacez le « cache de troisième niveau » ; <p> </p>
</li>
<li>Avec l'objet proxy de A, la dépendance de A est parfaitement résolue (A ici est encore un produit semi-fini) et B est initialisé avec succès. Une fois que B est initialisé avec succès, l'injection de propriétés de l'objet A est terminée, puis d'autres propriétés de A sont remplies, ainsi que d'autres étapes de A (y compris AOP), pour compléter la fonction d'initialisation complète de A (A ici est le Bean complet). <p></p>
</li>
<li>Mettez A dans le "cache de niveau un". <p></p>
</li>
</ul>4.<code>SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext #refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>AbstractBeanFactory#getBean() => RésuméBeanFactory#createBean ()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()🎜🎜Cycle de vie du bean : 🎜🎜1. Appelez InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessBeforeInstantiation🎜Suivi de doCreateBean()🎜rrreee 🎜2.Créer un exemple de bean 🎜🎜Ortymez un peuple PopulateBean () 🎜 SOINS UP INITISTIONNEMENT Méthode BeanPostProcessor 🎜🎜7. Tout d'abord ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(), puis appelez la méthode init-method pour effectuer l'opération d'initialisation 🎜🎜8. Appelez la post-méthode d'initialisation de BeanPostProcessor 🎜rrreee.Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)

Sujets chauds
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 Comment Springboot intègre Jasypt pour implémenter le chiffrement des fichiers de configuration
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Comment Springboot intègre Jasypt pour implémenter le chiffrement des fichiers de configuration
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Introduction à Jasypt Jasypt est une bibliothèque Java qui permet à un développeur d'ajouter des fonctionnalités de chiffrement de base à son projet avec un minimum d'effort et ne nécessite pas une compréhension approfondie du fonctionnement du chiffrement. Haute sécurité pour le chiffrement unidirectionnel et bidirectionnel. technologie de cryptage basée sur des normes. Cryptez les mots de passe, le texte, les chiffres, les binaires... Convient pour l'intégration dans des applications basées sur Spring, API ouverte, pour une utilisation avec n'importe quel fournisseur JCE... Ajoutez la dépendance suivante : com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2 1.1. Les avantages de Jasypt protègent la sécurité de notre système. Même en cas de fuite du code, la source de données peut être garantie.
 Comment SpringBoot intègre Redisson pour implémenter la file d'attente différée
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Comment SpringBoot intègre Redisson pour implémenter la file d'attente différée
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Scénario d'utilisation 1. La commande a été passée avec succès mais le paiement n'a pas été effectué dans les 30 minutes. Le paiement a expiré et la commande a été automatiquement annulée 2. La commande a été signée et aucune évaluation n'a été effectuée pendant 7 jours après la signature. Si la commande expire et n'est pas évaluée, le système donne par défaut une note positive. 3. La commande est passée avec succès. Si le commerçant ne reçoit pas la commande pendant 5 minutes, la commande est annulée. 4. Le délai de livraison expire et. un rappel par SMS est envoyé... Pour les scénarios avec des délais longs et de faibles performances en temps réel, nous pouvons utiliser la planification des tâches pour effectuer un traitement d'interrogation régulier. Par exemple : xxl-job Aujourd'hui, nous allons choisir
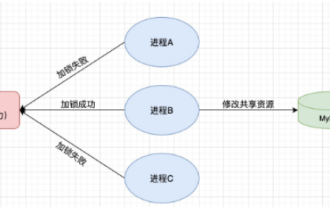 Comment utiliser Redis pour implémenter des verrous distribués dans SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Comment utiliser Redis pour implémenter des verrous distribués dans SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
1. Redis implémente le principe du verrouillage distribué et pourquoi les verrous distribués sont nécessaires. Avant de parler de verrous distribués, il est nécessaire d'expliquer pourquoi les verrous distribués sont nécessaires. Le contraire des verrous distribués est le verrouillage autonome. Lorsque nous écrivons des programmes multithreads, nous évitons les problèmes de données causés par l'utilisation d'une variable partagée en même temps. Nous utilisons généralement un verrou pour exclure mutuellement les variables partagées afin de garantir l'exactitude de celles-ci. les variables partagées. Son champ d’utilisation est dans le même processus. S’il existe plusieurs processus qui doivent exploiter une ressource partagée en même temps, comment peuvent-ils s’exclure mutuellement ? Les applications métier d'aujourd'hui sont généralement une architecture de microservices, ce qui signifie également qu'une application déploiera plusieurs processus si plusieurs processus doivent modifier la même ligne d'enregistrements dans MySQL, afin d'éviter les données sales causées par des opérations dans le désordre, les besoins de distribution. à introduire à ce moment-là. Le style est verrouillé. Vous voulez marquer des points
 Comment résoudre le problème selon lequel Springboot ne peut pas accéder au fichier après l'avoir lu dans un package jar
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Comment résoudre le problème selon lequel Springboot ne peut pas accéder au fichier après l'avoir lu dans un package jar
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot lit le fichier, mais ne peut pas accéder au dernier développement après l'avoir empaqueté dans un package jar. Il existe une situation dans laquelle Springboot ne peut pas lire le fichier après l'avoir empaqueté dans un package jar. La raison en est qu'après l'empaquetage, le chemin virtuel du fichier. n’est pas valide et n’est accessible que via le flux Read. Le fichier se trouve sous les ressources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Comment implémenter Springboot+Mybatis-plus sans utiliser d'instructions SQL pour ajouter plusieurs tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Comment implémenter Springboot+Mybatis-plus sans utiliser d'instructions SQL pour ajouter plusieurs tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Lorsque Springboot+Mybatis-plus n'utilise pas d'instructions SQL pour effectuer des opérations d'ajout de plusieurs tables, les problèmes que j'ai rencontrés sont décomposés en simulant la réflexion dans l'environnement de test : Créez un objet BrandDTO avec des paramètres pour simuler le passage des paramètres en arrière-plan. qu'il est extrêmement difficile d'effectuer des opérations multi-tables dans Mybatis-plus. Si vous n'utilisez pas d'outils tels que Mybatis-plus-join, vous pouvez uniquement configurer le fichier Mapper.xml correspondant et configurer le ResultMap malodorant et long, puis. écrivez l'instruction SQL correspondante Bien que cette méthode semble lourde, elle est très flexible et nous permet de
 Comparaison et analyse des différences entre SpringBoot et SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparaison et analyse des différences entre SpringBoot et SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot et SpringMVC sont tous deux des frameworks couramment utilisés dans le développement Java, mais il existe des différences évidentes entre eux. Cet article explorera les fonctionnalités et les utilisations de ces deux frameworks et comparera leurs différences. Tout d’abord, découvrons SpringBoot. SpringBoot a été développé par l'équipe Pivotal pour simplifier la création et le déploiement d'applications basées sur le framework Spring. Il fournit un moyen rapide et léger de créer des fichiers exécutables autonomes.
 Comment SpringBoot personnalise Redis pour implémenter la sérialisation du cache
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
Comment SpringBoot personnalise Redis pour implémenter la sérialisation du cache
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. Personnalisez RedisTemplate1.1, mécanisme de sérialisation par défaut RedisAPI. L'implémentation du cache Redis basée sur l'API utilise le modèle RedisTemplate pour les opérations de mise en cache des données. Ici, ouvrez la classe RedisTemplate et affichez les informations sur le code source de la classe. Déclarer la clé, diverses méthodes de sérialisation de la valeur, la valeur initiale est vide @NullableprivateRedisSe
 Tutoriel pratique de développement SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
Tutoriel pratique de développement SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
Cet article écrira un exemple détaillé pour parler du développement réel de dubbo+nacos+Spring Boot. Cet article ne couvrira pas trop de connaissances théoriques, mais écrira l'exemple le plus simple pour illustrer comment dubbo peut être intégré à nacos pour créer rapidement un environnement de développement.




