
Nous devons d'abord télécharger le package Seata-server

Décompressez ce package zip dans un fichier non-. Annuaire chinois, sa structure de répertoire est la suivante :

Modifier le fichierregistre.conf dans le répertoire conf :
Le contenu est le suivant :
registry {
# tc服务的注册中心类,这里选择nacos,也可以是eureka、zookeeper等
type = "nacos"
nacos {
# seata tc 服务注册到 nacos的服务名称,可以自定义
application = "seata-tc-server"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8848"
group = "DEFAULT_GROUP"
namespace = ""
cluster = "SH"
username = "nacos"
password = "nacos"
}
}
config {
# 读取tc服务端的配置文件的方式,这里是从nacos配置中心读取,这样如果tc是集群,可以共享配置
type = "nacos"
# 配置nacos地址等信息
nacos {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8848"
namespace = ""
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
username = "nacos"
password = "nacos"
dataId = "seataServer.properties"
}
}Attention particulière, afin de permettre aux clusters de services tc de partager des configurations, nous avons choisi nacos comme centre de configuration unifié. Par conséquent, le fichier de configuration du serveurseataServer.properties doit être configuré dans nacos.
Le format est le suivant :
Le contenu de la configuration est le suivant :
# 数据存储方式,db代表数据库 store.mode=db store.db.datasource=druid store.db.dbType=mysql store.db.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver store.db.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata?useUnicode=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true store.db.user=root store.db.password=123 store.db.minConn=5 store.db.maxConn=30 store.db.globalTable=global_table store.db.branchTable=branch_table store.db.queryLimit=100 store.db.lockTable=lock_table store.db.maxWait=5000 # 事务、日志等配置 server.recovery.committingRetryPeriod=1000 server.recovery.asynCommittingRetryPeriod=1000 server.recovery.rollbackingRetryPeriod=1000 server.recovery.timeoutRetryPeriod=1000 server.maxCommitRetryTimeout=-1 server.maxRollbackRetryTimeout=-1 server.rollbackRetryTimeoutUnlockEnable=false server.undo.logSaveDays=7 server.undo.logDeletePeriod=86400000 # 客户端与服务端传输方式 transport.serialization=seata transport.compressor=none # 关闭metrics功能,提高性能 metrics.enabled=false metrics.registryType=compact metrics.exporterList=prometheus metrics.exporterPrometheusPort=9898
L'adresse de la base de données, le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe doivent être modifiés par vos propres informations de base de données.
Remarque spéciale : lorsque le service tc gère des transactions distribuées, il doit enregistrer les données liées aux transactions dans la base de données. Vous devez créer ces tables à l'avance.
Créez une nouvelle base de données nommée Seata et exécutez le fichier SQL fourni dans le matériel de pré-cours :
Ces tables enregistrent principalement les transactions globales, les transactions de branche et les informations de verrouillage global :
SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; -- ---------------------------- -- 分支事务表 -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `branch_table`; CREATE TABLE `branch_table` ( `branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `xid` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL, `transaction_id` bigint(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `resource_group_id` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `resource_id` varchar(256) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `branch_type` varchar(8) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `status` tinyint(4) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `client_id` varchar(64) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `application_data` varchar(2000) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `gmt_create` datetime(6) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `gmt_modified` datetime(6) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`branch_id`) USING BTREE, INDEX `idx_xid`(`xid`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact; -- ---------------------------- -- 全局事务表 -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `global_table`; CREATE TABLE `global_table` ( `xid` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL, `transaction_id` bigint(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `status` tinyint(4) NOT NULL, `application_id` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `transaction_service_group` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `transaction_name` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `timeout` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `begin_time` bigint(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `application_data` varchar(2000) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `gmt_create` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL, `gmt_modified` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`xid`) USING BTREE, INDEX `idx_gmt_modified_status`(`gmt_modified`, `status`) USING BTREE, INDEX `idx_transaction_id`(`transaction_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
Entrez le répertoire bin, exécutez Seata-server.bat dedans :
Après un démarrage réussi, Seata-server aurait dû être enregistré auprès du centre d'enregistrement Nacos.
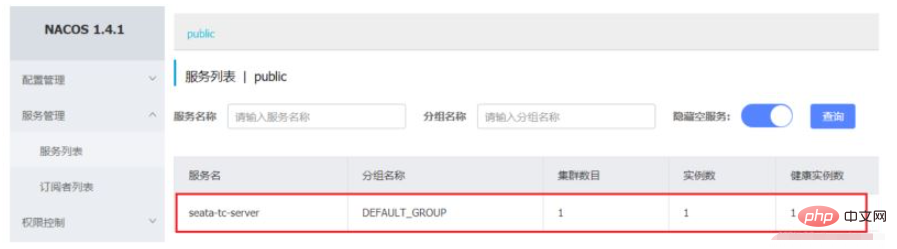
Ouvrez le navigateur, visitez l'adresse nacos : http://localhost:8848, puis entrez dans la page de la liste des services. Vous pouvez voir les informations du serveur Seata-tc :
Tout d'abord, nous devons introduire les dépendances Seata dans le microservice :
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!--版本较低,1.3.0,因此排除-->
<exclusion>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--seata starter 采用1.4.2版本-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${seata.version}</version>
</dependency>Vous devez modifier le fichier application.yml et ajouter quelques configurations :
seata:
registry: # TC服务注册中心的配置,微服务根据这些信息去注册中心获取tc服务地址
# 参考tc服务自己的registry.conf中的配置
type: nacos
nacos: # tc
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
namespace: ""
group: DEFAULT_GROUP
application: seata-tc-server # tc服务在nacos中的服务名称
cluster: SH
tx-service-group: seata-demo # 事务组,根据这个获取tc服务的cluster名称
service:
vgroup-mapping: # 事务组与TC服务cluster的映射关系
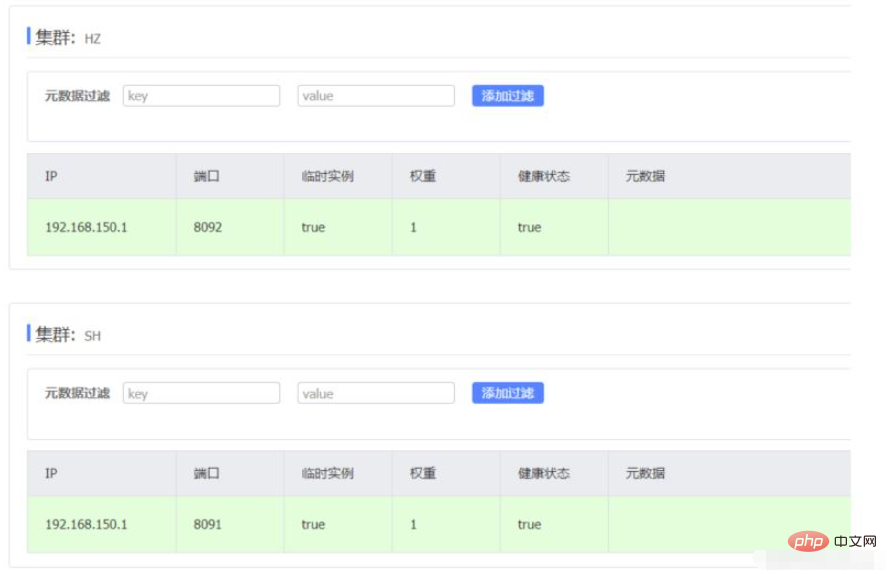
seata-demo: SHPrévoyez de démarrer deux nœuds de service Seata TC :
| Nom du nœud | Adresse IP | Numéro de port | Nom du cluster |
|---|---|---|---|
| seata | 127.0.0.1 | 8091 | SH |
| seata2 | 127.0.0.1 | 8 092 | HZ |
Nous avons commencé avant un service Seata, le port est 8091 et le nom du cluster est SH.
Maintenant, copiez le répertoire Seata et nommez-le Seata2
Modifiez le contenu de Seata2/conf/registry.conf comme suit :
registry {
# tc服务的注册中心类,这里选择nacos,也可以是eureka、zookeeper等
type = "nacos"
nacos {
# seata tc 服务注册到 nacos的服务名称,可以自定义
application = "seata-tc-server"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8848"
group = "DEFAULT_GROUP"
namespace = ""
cluster = "HZ"
username = "nacos"
password = "nacos"
}
}
config {
# 读取tc服务端的配置文件的方式,这里是从nacos配置中心读取,这样如果tc是集群,可以共享配置
type = "nacos"
# 配置nacos地址等信息
nacos {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8848"
namespace = ""
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
username = "nacos"
password = "nacos"
dataId = "seataServer.properties"
}
}Entrez le répertoire Seata2/bin, puis exécutez la commande :
seata-server.bat -p 8092
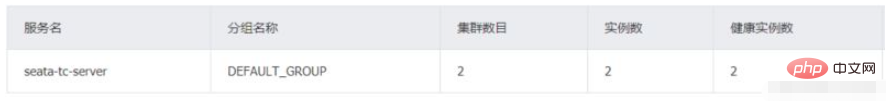
Ouvrez le nacos console et vérifiez la liste des services :
Cliquez pour plus de détails :
Ensuite, nous devons configurer la relation de mappage entre tx-service-group et le cluster vers la configuration nacos centre.
Créez une nouvelle configuration :
Le contenu de la configuration est le suivant :
# 事务组映射关系 service.vgroupMapping.seata-demo=SH service.enableDegrade=false service.disableGlobalTransaction=false # 与TC服务的通信配置 transport.type=TCP transport.server=NIO transport.heartbeat=true transport.enableClientBatchSendRequest=false transport.threadFactory.bossThreadPrefix=NettyBoss transport.threadFactory.workerThreadPrefix=NettyServerNIOWorker transport.threadFactory.serverExecutorThreadPrefix=NettyServerBizHandler transport.threadFactory.shareBossWorker=false transport.threadFactory.clientSelectorThreadPrefix=NettyClientSelector transport.threadFactory.clientSelectorThreadSize=1 transport.threadFactory.clientWorkerThreadPrefix=NettyClientWorkerThread transport.threadFactory.bossThreadSize=1 transport.threadFactory.workerThreadSize=default transport.shutdown.wait=3 # RM配置 client.rm.asyncCommitBufferLimit=10000 client.rm.lock.retryInterval=10 client.rm.lock.retryTimes=30 client.rm.lock.retryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict=true client.rm.reportRetryCount=5 client.rm.tableMetaCheckEnable=false client.rm.tableMetaCheckerInterval=60000 client.rm.sqlParserType=druid client.rm.reportSuccessEnable=false client.rm.sagaBranchRegisterEnable=false # TM配置 client.tm.commitRetryCount=5 client.tm.rollbackRetryCount=5 client.tm.defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout=60000 client.tm.degradeCheck=false client.tm.degradeCheckAllowTimes=10 client.tm.degradeCheckPeriod=2000 # undo日志配置 client.undo.dataValidation=true client.undo.logSerialization=jackson client.undo.onlyCareUpdateColumns=true client.undo.logTable=undo_log client.undo.compress.enable=true client.undo.compress.type=zip client.undo.compress.threshold=64k client.log.exceptionRate=100
Ensuite, vous devez modifier le fichier application.yml de chaque microservice pour autoriser le microservice pour lire nacos Le fichier client.properties dans :
seata:
config:
type: nacos
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
username: nacos
password: nacos
group: SEATA_GROUP
data-id: client.propertiesRedémarrez le microservice. Maintenant, si le microservice est connecté au cluster SH de tc ou au cluster HZ de tc, il est déterminé par client.properties de nacos.
lient.log.exceptionRate=100
## 3.微服务读取nacos配置
接下来,需要修改每一个微服务的application.yml文件,让微服务读取nacos中的client.properties文件:
```yaml
seata:
config:
type: nacos
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
username: nacos
password: nacos
group: SEATA_GROUP
data-id: client.propertiesRedémarrez le microservice. Désormais, le fait que le microservice soit connecté au cluster SH de tc ou au cluster HZ de tc est déterminé par client.properties de nacos.
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!