Comment utiliser le module de threading en python
Explication détaillée du module threading en python. Threading fournit une API de niveau supérieur à celle du module thread pour fournir la concurrence des threads. Ces threads s'exécutent simultanément et partagent la mémoire.
Regardons l'utilisation spécifique du module threading :
1 L'utilisation de Thread
La fonction cible peut instancier un objet Thread, chaque Thread L'objet représente un thread et peut être démarré via la méthode start().
Voici une comparaison entre l'utilisation de la concurrence multi-thread et la non-application de la concurrence multi-thread :
La première est l'opération sans utiliser le multi-threading :
# 🎜🎜 #Le code est le suivant :#!/usr/bin/python
#compare for multi threads
import time
def worker():
print"worker"
time.sleep(1)
return
if__name__ =="__main__":
for i in xrange(5):
worker()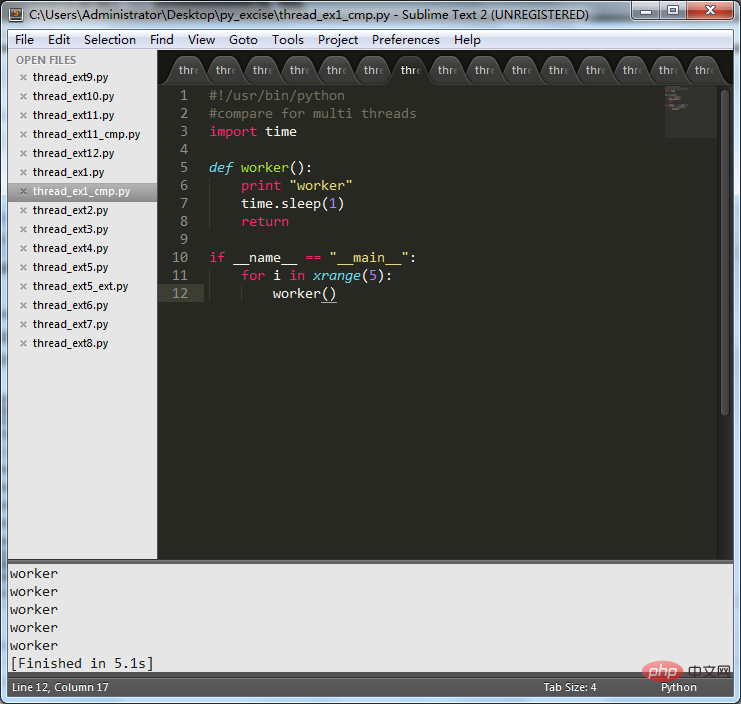
Le code est le suivant :
#!/usr/bin/python
import threading
import time
defworker():
print"worker"
time.sleep(1)
return
fori in xrange(5):
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.start()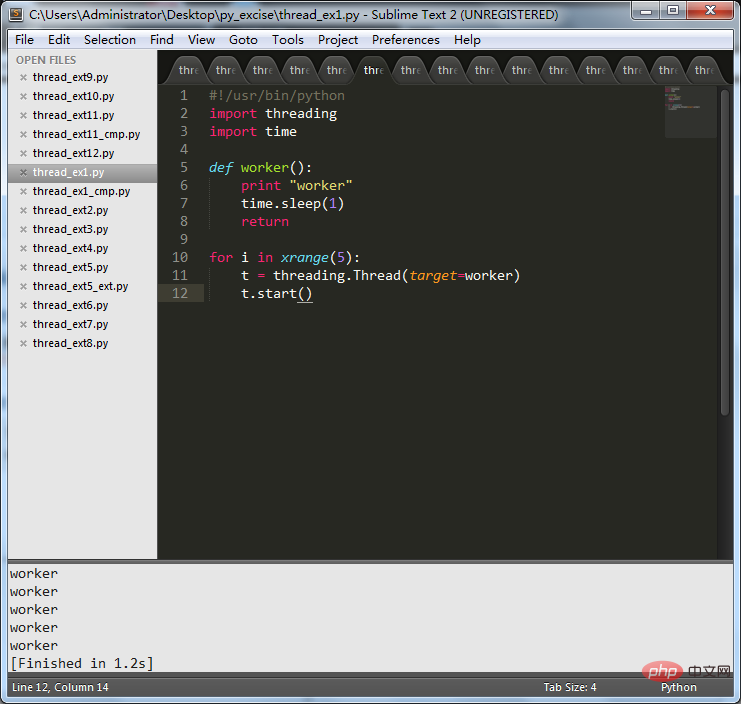
#!/usr/bin/python
#current's number of threads
import threading
import time
defworker():
print"test"
time.sleep(1)
for i in xrange(5):
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.start()
print"current has %d threads" % (threading.activeCount() -1)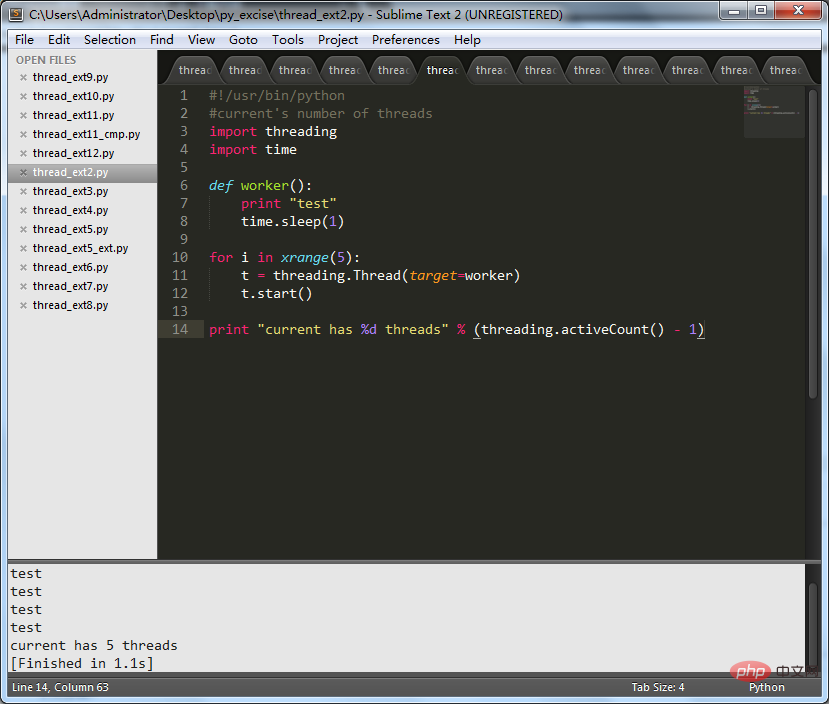
#!/usr/bin/python
#test the variable threading.enumerate()
import threading
import time
defworker():
print"test"
time.sleep(2)
threads=[]
for i in xrange(5):
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for item in threading.enumerate():
print item
print for item in threads:
print item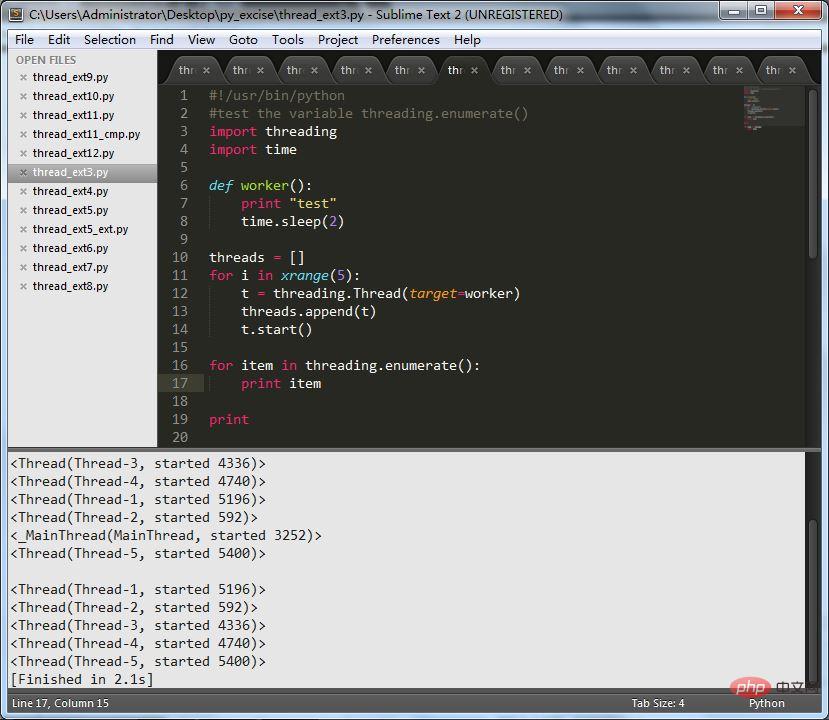
#!/usr/bin/python
#create a daemon
import threading
import time
def worker():
time.sleep(3)
print"worker"
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
print"haha"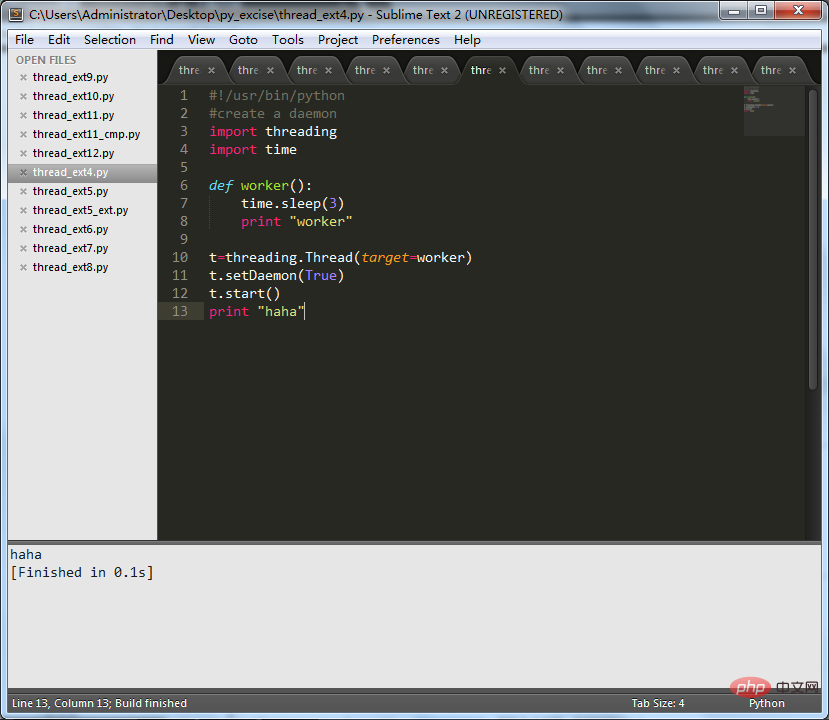
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Quelle est la raison pour laquelle PS continue de montrer le chargement?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
Quelle est la raison pour laquelle PS continue de montrer le chargement?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
Les problèmes de «chargement» PS sont causés par des problèmes d'accès aux ressources ou de traitement: la vitesse de lecture du disque dur est lente ou mauvaise: utilisez Crystaldiskinfo pour vérifier la santé du disque dur et remplacer le disque dur problématique. Mémoire insuffisante: améliorez la mémoire pour répondre aux besoins de PS pour les images à haute résolution et le traitement complexe de couche. Les pilotes de la carte graphique sont obsolètes ou corrompues: mettez à jour les pilotes pour optimiser la communication entre le PS et la carte graphique. Les chemins de fichier sont trop longs ou les noms de fichiers ont des caractères spéciaux: utilisez des chemins courts et évitez les caractères spéciaux. Problème du PS: réinstaller ou réparer le programme d'installation PS.
 Comment résoudre le problème du chargement lorsque PS est démarré?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
Comment résoudre le problème du chargement lorsque PS est démarré?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
Un PS est coincé sur le "chargement" lors du démarrage peut être causé par diverses raisons: désactiver les plugins corrompus ou conflictuels. Supprimer ou renommer un fichier de configuration corrompu. Fermez des programmes inutiles ou améliorez la mémoire pour éviter une mémoire insuffisante. Passez à un entraînement à semi-conducteurs pour accélérer la lecture du disque dur. Réinstaller PS pour réparer les fichiers système corrompus ou les problèmes de package d'installation. Afficher les informations d'erreur pendant le processus de démarrage de l'analyse du journal d'erreur.
 Comment résoudre le problème du chargement lorsque le PS ouvre le fichier?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
Comment résoudre le problème du chargement lorsque le PS ouvre le fichier?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
Le bégaiement "Chargement" se produit lors de l'ouverture d'un fichier sur PS. Les raisons peuvent inclure: un fichier trop grand ou corrompu, une mémoire insuffisante, une vitesse du disque dur lente, des problèmes de pilote de carte graphique, des conflits de version PS ou du plug-in. Les solutions sont: vérifier la taille et l'intégrité du fichier, augmenter la mémoire, mettre à niveau le disque dur, mettre à jour le pilote de carte graphique, désinstaller ou désactiver les plug-ins suspects et réinstaller PS. Ce problème peut être résolu efficacement en vérifiant progressivement et en faisant bon usage des paramètres de performances PS et en développant de bonnes habitudes de gestion des fichiers.
 Comment utiliser MySQL après l'installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Comment utiliser MySQL après l'installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
L'article présente le fonctionnement de la base de données MySQL. Tout d'abord, vous devez installer un client MySQL, tel que MySQLWorkBench ou le client de ligne de commande. 1. Utilisez la commande MySQL-UROot-P pour vous connecter au serveur et connecter avec le mot de passe du compte racine; 2. Utilisez Createdatabase pour créer une base de données et utilisez Sélectionner une base de données; 3. Utilisez CreateTable pour créer une table, définissez des champs et des types de données; 4. Utilisez InsertInto pour insérer des données, remettre en question les données, mettre à jour les données par mise à jour et supprimer les données par Supprimer. Ce n'est qu'en maîtrisant ces étapes, en apprenant à faire face à des problèmes courants et à l'optimisation des performances de la base de données que vous pouvez utiliser efficacement MySQL.
 Comment les plumes PS contrôlent-elles la douceur de la transition?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Comment les plumes PS contrôlent-elles la douceur de la transition?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
La clé du contrôle des plumes est de comprendre sa nature progressive. Le PS lui-même ne fournit pas la possibilité de contrôler directement la courbe de gradient, mais vous pouvez ajuster de manière flexible le rayon et la douceur du gradient par plusieurs plumes, des masques correspondants et des sélections fines pour obtenir un effet de transition naturel.
 MySQL doit-il payer
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL doit-il payer
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL a une version communautaire gratuite et une version d'entreprise payante. La version communautaire peut être utilisée et modifiée gratuitement, mais le support est limité et convient aux applications avec des exigences de stabilité faibles et des capacités techniques solides. L'Enterprise Edition fournit une prise en charge commerciale complète pour les applications qui nécessitent une base de données stable, fiable et haute performance et disposées à payer pour le soutien. Les facteurs pris en compte lors du choix d'une version comprennent la criticité des applications, la budgétisation et les compétences techniques. Il n'y a pas d'option parfaite, seulement l'option la plus appropriée, et vous devez choisir soigneusement en fonction de la situation spécifique.
 Comment optimiser les performances de la base de données après l'installation de MySQL
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
Comment optimiser les performances de la base de données après l'installation de MySQL
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
L'optimisation des performances MySQL doit commencer à partir de trois aspects: configuration d'installation, indexation et optimisation des requêtes, surveillance et réglage. 1. Après l'installation, vous devez ajuster le fichier my.cnf en fonction de la configuration du serveur, tel que le paramètre innodb_buffer_pool_size, et fermer query_cache_size; 2. Créez un index approprié pour éviter les index excessifs et optimiser les instructions de requête, telles que l'utilisation de la commande Explication pour analyser le plan d'exécution; 3. Utilisez le propre outil de surveillance de MySQL (ShowProcessList, Showstatus) pour surveiller la santé de la base de données, et sauvegarde régulièrement et organisez la base de données. Ce n'est qu'en optimisant en continu ces étapes que les performances de la base de données MySQL peuvent être améliorées.
 Que dois-je faire si la carte PS est dans l'interface de chargement?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Que dois-je faire si la carte PS est dans l'interface de chargement?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
L'interface de chargement de la carte PS peut être causée par le logiciel lui-même (corruption de fichiers ou conflit de plug-in), l'environnement système (corruption du pilote ou des fichiers système en raison), ou matériel (corruption du disque dur ou défaillance du bâton de mémoire). Vérifiez d'abord si les ressources informatiques sont suffisantes, fermez le programme d'arrière-plan et publiez la mémoire et les ressources CPU. Correction de l'installation de PS ou vérifiez les problèmes de compatibilité pour les plug-ins. Mettre à jour ou tomber la version PS. Vérifiez le pilote de la carte graphique et mettez-le à jour et exécutez la vérification du fichier système. Si vous résumez les problèmes ci-dessus, vous pouvez essayer la détection du disque dur et les tests de mémoire.






