 développement back-end
développement back-end
 Tutoriel Python
Tutoriel Python
 Comment utiliser le module xlrd/xlwt/xlutils pour le traitement des données Python Excel
Comment utiliser le module xlrd/xlwt/xlutils pour le traitement des données Python Excel
Comment utiliser le module xlrd/xlwt/xlutils pour le traitement des données Python Excel
Le traitement conventionnel des données Excel implique des opérations de lecture/écriture/objet de fichier sur des fichiers de données Excel.
La logique métier spécifique au traitement des données est implémentée via la bibliothèque python non standard correspondante xlrd/xlwt/xlutils.
Dans le traitement complexe des données commerciales Excel, les trois frères jouent un rôle indispensable. Aujourd'hui, notre contenu porte sur la façon d'utiliser les trois modules de xlrd/xlwt/xlutils pour implémenter le traitement des données.
1. Description du module
La meilleure chose à propos de l'utilisation de ces trois modules pour traiter des données Excel est qu'ils ont les mêmes concepts de traitement de données correspondant aux objets de fichier Excel, ce qui peut mieux faciliter notre compréhension des objets de données.
Tout d'abord, ces trois modules sont des bibliothèques non standards de python, et vous pouvez choisir pip pour les installer.
pip install xlrd pip install xlwt pip install xlutils
Ce qui suit est le contenu des données sources que nous avons préparé pour démontrer le processus de traitement des données, juste à des fins de test.
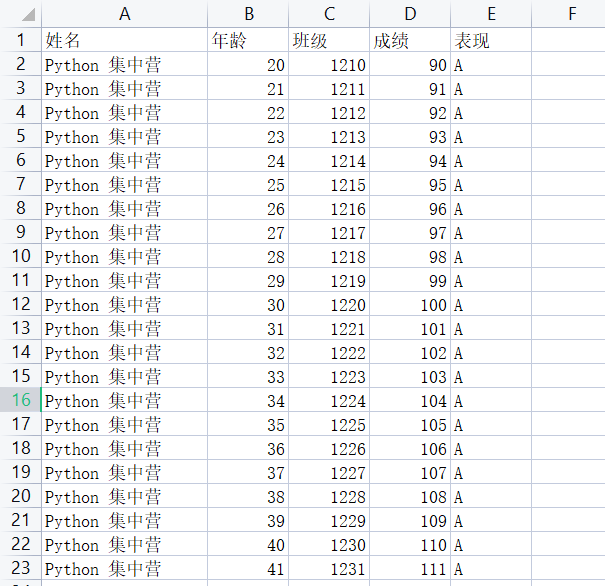
xlrd : utilisé pour lire les fichiers de données Excel, mettre les objets de données renvoyés en mémoire, puis interroger les informations pertinentes des objets du fichier de données.
xlwt : utilisé pour générer de nouveaux objets de fichier de données en mémoire et les écrire dans le fichier de données Excel une fois le traitement terminé.
xlutils : Sa fonction principale est de copier de nouveaux objets fichiers et d'effectuer des opérations de traitement de données dans de nouveaux objets de données.
Importez les trois modules xlrd/xlwt/xlutils dans le bloc de code à développer pour assurer le support.
# Importing the xlrd module. import xlrd as read # Importing the xlwt module. import xlwt as write # Copying the contents of the original workbook into a new workbook. from xlutils.copy import copy
2.
# Opening the workbook and assigning it to the variable `work_book`.
work_book = read.open_workbook('D:/test-data-work/test.xls')
# Assigning the sheet named 'Sheet1' to the variable `sheet`.
sheet = work_book.sheet_by_name('Sheet1')
# `row = sheet.nrows` is assigning the number of rows in the sheet to the variable `row`.
row = sheet.nrows
# `col = sheet.ncols` is assigning the number of columns in the sheet to the variable `col`.
col = sheet.ncols
print('Sheet1工作表有:{0}行,{1}列'.format(str(row), str(col)))
# Sheet1工作表有:23行,5列3, traitement xlwt
for a in sheet.get_rows():
print(a)
# [text:'姓名', text:'年龄', text:'班级', text:'成绩', text:'表现']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:20.0, number:1210.0, number:90.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:21.0, number:1211.0, number:91.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:22.0, number:1212.0, number:92.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:23.0, number:1213.0, number:93.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:24.0, number:1214.0, number:94.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:25.0, number:1215.0, number:95.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:26.0, number:1216.0, number:96.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:27.0, number:1217.0, number:97.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:28.0, number:1218.0, number:98.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:29.0, number:1219.0, number:99.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:30.0, number:1220.0, number:100.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:31.0, number:1221.0, number:101.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:32.0, number:1222.0, number:102.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:33.0, number:1223.0, number:103.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:34.0, number:1224.0, number:104.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:35.0, number:1225.0, number:105.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:36.0, number:1226.0, number:106.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:37.0, number:1227.0, number:107.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:38.0, number:1228.0, number:108.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:39.0, number:1229.0, number:109.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:40.0, number:1230.0, number:110.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:41.0, number:1231.0, number:111.0, text:'A']
for b in range(row):
print(sheet.row_values(b))
# ['姓名', '年龄', '班级', '成绩', '表现']
# ['Python 集中营', 20.0, 1210.0, 90.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 21.0, 1211.0, 91.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 22.0, 1212.0, 92.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 23.0, 1213.0, 93.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 24.0, 1214.0, 94.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 25.0, 1215.0, 95.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 26.0, 1216.0, 96.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 27.0, 1217.0, 97.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 28.0, 1218.0, 98.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 29.0, 1219.0, 99.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 30.0, 1220.0, 100.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 31.0, 1221.0, 101.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 32.0, 1222.0, 102.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 33.0, 1223.0, 103.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 34.0, 1224.0, 104.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 35.0, 1225.0, 105.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 36.0, 1226.0, 106.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 37.0, 1227.0, 107.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 38.0, 1228.0, 108.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 39.0, 1229.0, 109.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 40.0, 1230.0, 110.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 41.0, 1231.0, 111.0, 'A']
for c in range(col):
print(sheet.col_values(c))
# ['姓名', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营']
# ['年龄', 20.0, 21.0, 22.0, 23.0, 24.0, 25.0, 26.0, 27.0, 28.0, 29.0, 30.0, 31.0, 32.0, 33.0, 34.0, 35.0, 36.0, 37.0, 38.0, 39.0, 40.0, 41.0]
# ['班级', 1210.0, 1211.0, 1212.0, 1213.0, 1214.0, 1215.0, 1216.0, 1217.0, 1218.0, 1219.0, 1220.0, 1221.0, 1222.0, 1223.0, 1224.0, 1225.0, 1226.0, 1227.0, 1228.0, 1229.0, 1230.0, 1231.0]
# ['成绩', 90.0, 91.0, 92.0, 93.0, 94.0, 95.0, 96.0, 97.0, 98.0, 99.0, 100.0, 101.0, 102.0, 103.0, 104.0, 105.0, 106.0, 107.0, 108.0, 109.0, 110.0, 111.0]
# ['表现', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A']4, traitement xlutils
# Creating a new workbook.
work_book_2 = write.Workbook()
# Creating a new sheet named 'Sheet4' in the workbook.
sheet_2 = work_book_2.add_sheet('Sheet4')
list = [
['姓名', '年龄', '班级', '成绩'],
['张三', '20', '1210', '89'],
['李四', '21', '1211', '90'],
['王五', '22', '1212', '91'],
]
for row_index in range(4):
for col_index in range(4):
sheet_2.write(row_index, col_index, list[row_index][col_index])
col_index += 1
row_index += 1
# Saving the workbook to the specified location.
work_book_2.save('D:/test-data-work/test2.xls')Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 MySQL doit-il payer
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL doit-il payer
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL a une version communautaire gratuite et une version d'entreprise payante. La version communautaire peut être utilisée et modifiée gratuitement, mais le support est limité et convient aux applications avec des exigences de stabilité faibles et des capacités techniques solides. L'Enterprise Edition fournit une prise en charge commerciale complète pour les applications qui nécessitent une base de données stable, fiable et haute performance et disposées à payer pour le soutien. Les facteurs pris en compte lors du choix d'une version comprennent la criticité des applications, la budgétisation et les compétences techniques. Il n'y a pas d'option parfaite, seulement l'option la plus appropriée, et vous devez choisir soigneusement en fonction de la situation spécifique.
 Comment utiliser MySQL après l'installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Comment utiliser MySQL après l'installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
L'article présente le fonctionnement de la base de données MySQL. Tout d'abord, vous devez installer un client MySQL, tel que MySQLWorkBench ou le client de ligne de commande. 1. Utilisez la commande MySQL-UROot-P pour vous connecter au serveur et connecter avec le mot de passe du compte racine; 2. Utilisez Createdatabase pour créer une base de données et utilisez Sélectionner une base de données; 3. Utilisez CreateTable pour créer une table, définissez des champs et des types de données; 4. Utilisez InsertInto pour insérer des données, remettre en question les données, mettre à jour les données par mise à jour et supprimer les données par Supprimer. Ce n'est qu'en maîtrisant ces étapes, en apprenant à faire face à des problèmes courants et à l'optimisation des performances de la base de données que vous pouvez utiliser efficacement MySQL.
 MySQL a-t-il besoin d'Internet
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
MySQL a-t-il besoin d'Internet
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
MySQL peut s'exécuter sans connexions réseau pour le stockage et la gestion des données de base. Cependant, la connexion réseau est requise pour l'interaction avec d'autres systèmes, l'accès à distance ou l'utilisation de fonctionnalités avancées telles que la réplication et le clustering. De plus, les mesures de sécurité (telles que les pare-feu), l'optimisation des performances (choisissez la bonne connexion réseau) et la sauvegarde des données sont essentielles pour se connecter à Internet.
 Comment optimiser les performances MySQL pour les applications de haute charge?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
Comment optimiser les performances MySQL pour les applications de haute charge?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
Guide d'optimisation des performances de la base de données MySQL dans les applications à forte intensité de ressources, la base de données MySQL joue un rôle crucial et est responsable de la gestion des transactions massives. Cependant, à mesure que l'échelle de l'application se développe, les goulots d'étranglement des performances de la base de données deviennent souvent une contrainte. Cet article explorera une série de stratégies efficaces d'optimisation des performances MySQL pour garantir que votre application reste efficace et réactive dans des charges élevées. Nous combinerons des cas réels pour expliquer les technologies clés approfondies telles que l'indexation, l'optimisation des requêtes, la conception de la base de données et la mise en cache. 1. La conception de l'architecture de la base de données et l'architecture optimisée de la base de données sont la pierre angulaire de l'optimisation des performances MySQL. Voici quelques principes de base: sélectionner le bon type de données et sélectionner le plus petit type de données qui répond aux besoins peut non seulement économiser un espace de stockage, mais également améliorer la vitesse de traitement des données.
 HaDIDB: une base de données légère et évolutive horizontalement dans Python
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
HaDIDB: une base de données légère et évolutive horizontalement dans Python
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
HaDIDB: Une base de données Python évolutive de haut niveau légère HaDIDB (HaDIDB) est une base de données légère écrite en Python, avec un niveau élevé d'évolutivité. Installez HaDIDB à l'aide de l'installation PIP: PiPinStallHaDIDB User Management Créer un utilisateur: CreateUser () pour créer un nouvel utilisateur. La méthode Authentication () authentifie l'identité de l'utilisateur. FromHadidb.OperationMportUserUser_OBJ = User ("Admin", "Admin") User_OBJ.
 Méthode de Navicat pour afficher le mot de passe de la base de données MongoDB
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
Méthode de Navicat pour afficher le mot de passe de la base de données MongoDB
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
Il est impossible de visualiser le mot de passe MongoDB directement via NAVICAT car il est stocké sous forme de valeurs de hachage. Comment récupérer les mots de passe perdus: 1. Réinitialiser les mots de passe; 2. Vérifiez les fichiers de configuration (peut contenir des valeurs de hachage); 3. Vérifiez les codes (May Code Hardcode).
 MySQL Workbench peut-il se connecter à MariaDB
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
MySQL Workbench peut-il se connecter à MariaDB
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
MySQL Workbench peut se connecter à MARIADB, à condition que la configuration soit correcte. Sélectionnez d'abord "MariADB" comme type de connecteur. Dans la configuration de la connexion, définissez correctement l'hôte, le port, l'utilisateur, le mot de passe et la base de données. Lorsque vous testez la connexion, vérifiez que le service MARIADB est démarré, si le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe sont corrects, si le numéro de port est correct, si le pare-feu autorise les connexions et si la base de données existe. Dans une utilisation avancée, utilisez la technologie de mise en commun des connexions pour optimiser les performances. Les erreurs courantes incluent des autorisations insuffisantes, des problèmes de connexion réseau, etc. Lors des erreurs de débogage, analysez soigneusement les informations d'erreur et utilisez des outils de débogage. L'optimisation de la configuration du réseau peut améliorer les performances
 MySQL a-t-il besoin d'un serveur
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
MySQL a-t-il besoin d'un serveur
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
Pour les environnements de production, un serveur est généralement nécessaire pour exécuter MySQL, pour des raisons, notamment les performances, la fiabilité, la sécurité et l'évolutivité. Les serveurs ont généralement un matériel plus puissant, des configurations redondantes et des mesures de sécurité plus strictes. Pour les petites applications à faible charge, MySQL peut être exécutée sur des machines locales, mais la consommation de ressources, les risques de sécurité et les coûts de maintenance doivent être soigneusement pris en considération. Pour une plus grande fiabilité et sécurité, MySQL doit être déployé sur le cloud ou d'autres serveurs. Le choix de la configuration du serveur approprié nécessite une évaluation en fonction de la charge d'application et du volume de données.





