
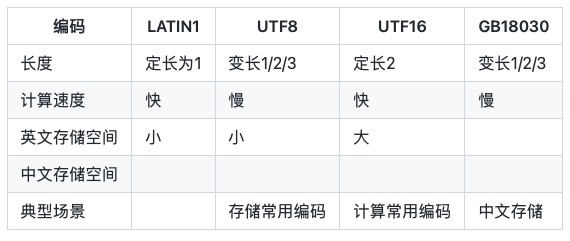
Les encodages de chaînes courants sont :
LATIN1 ne peut enregistrer que les caractères ASCII, également connus sous le nom d'ISO-8859-1.
UTF-8 est un codage d'octets de longueur variable qui utilise 1, 2 ou 3 octets pour représenter un caractère. Étant donné que la représentation du chinois nécessite généralement 3 octets, l'encodage de la scène chinoise UTF-8 nécessite généralement plus d'espace et l'alternative est GBK/GB2312/GB18030.
UTF-16 2 octets, un caractère doit être représenté par 2 octets, également connu sous le nom d'UCS-2 (2-byte Universal Character Set). Selon la distinction entre les grandes et les petites extrémités, UTF-16 a deux formes, UTF-16BE et UTF-16LE. L'UTF-16 par défaut fait référence à UTF-16BE. char en langage Java est un encodage UTF-16LE.
GB18030 adopte un codage d'octets de longueur variable et chaque caractère est représenté par 1, 2 ou 3 octets. Semblable à UTF8, l’utilisation de 2 caractères pour représenter le chinois peut économiser des octets, mais cette méthode n’est pas universelle au niveau international.
Pour faciliter le calcul, les chaînes en mémoire utilisent généralement des caractères à largeur fixe. Les caractères en langage Java et les caractères en .NET utilisent UTF-16. Les premiers Windows-NT ne prenaient en charge que l'UTF-16.
La conversion entre UTF-16 et UTF-8 est plus compliquée et a généralement des performances médiocres.
Ce qui suit est une implémentation de la conversion de l'encodage UTF-16 en UTF-8. On peut voir que l'algorithme est relativement complexe, donc les performances sont médiocres. Cette opération ne peut pas être optimisée à l'aide de l'API vectorielle.
static int encodeUTF8(char[] utf16, int off, int len, byte[] dest, int dp) {
int sl = off + len, last_offset = sl - 1;
while (off < sl) {
char c = utf16[off++];
if (c < 0x80) {
// Have at most seven bits
dest[dp++] = (byte) c;
} else if (c < 0x800) {
// 2 dest, 11 bits
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0xc0 | (c >> 6));
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f));
} else if (c >= '\uD800' && c < '\uE000') {
int uc;
if (c < '\uDC00') {
if (off > last_offset) {
dest[dp++] = (byte) '?';
return dp;
}
char d = utf16[off];
if (d >= '\uDC00' && d < '\uE000') {
uc = (c << 10) + d + 0xfca02400;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("encodeUTF8 error", new MalformedInputException(1));
}
} else {
uc = c;
}
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0xf0 | ((uc >> 18)));
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((uc >> 12) & 0x3f));
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((uc >> 6) & 0x3f));
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (uc & 0x3f));
off++; // 2 utf16
} else {
// 3 dest, 16 bits
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0xe0 | ((c >> 12)));
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3f));
dest[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f));
}
}
return dp;
}Étant donné que char en Java est codé en UTF-16LE, si vous devez convertir char[] en octet codé UTF-16LE[], vous pouvez utiliser la méthode sun.misc.Unsafe#copyMemory pour copier rapidement. Par exemple :
static int writeUtf16LE(char[] chars, int off, int len, byte[] dest, final int dp) {
UNSAFE.copyMemory(chars
, CHAR_ARRAY_BASE_OFFSET + off * 2
, dest
, BYTE_ARRAY_BASE_OFFSET + dp
, len * 2
);
dp += len * 2;
return dp;
}Étant donné que différentes versions du JDK implémentent différentes méthodes de traitement de chaînes, les performances seront différentes. Après JDK 9, String peut également utiliser le codage LATIN1 en interne, bien que char utilise toujours le codage UTF-16.
static class String {
final char[] value;
final int offset;
final int count;
}Avant Java 6, l'objet String généré par la méthode String.subString et l'objet String d'origine partagent une valeur char[], ce qui entraînera le char[] de la chaîne renvoyée par la méthode subString à référencer et ne peut pas être recyclée par GC. De nombreuses bibliothèques évitent d'utiliser la méthode subString pour éviter les problèmes dans JDK 6 et versions antérieures.
static class String {
final char[] value;
}Après le JDK 7, les champs offset et count sont supprimés des chaînes, et value.length est le nombre d'origine. Cela évite le problème du référencement de subString par un grand char[] et facilite l'optimisation. En conséquence, les performances des opérations de chaîne dans JDK7/8 sont grandement améliorées par rapport à Java 6.
static class String {
final byte code;
final byte[] value;
static final byte LATIN1 = 0;
static final byte UTF16 = 1;
}Après le JDK 9, le type de valeur passe de char[] à byte[], et un code de champ est ajouté si les caractères sont tous des caractères ASCII, utilisez value pour. utilisez le codage LATIN. Si des caractères non-ASCII sont présents, ils sont codés en UTF16. Cette méthode de codage mixte permet aux scènes anglaises d'occuper moins de mémoire. L'inconvénient est que les performances de l'API String de Java 9 peuvent ne pas être aussi bonnes que celles du JDK 8. En particulier, lorsque char[] est passé pour construire une chaîne, elle sera compressée en octet codé en latin[], qui peut diminuer de 10 % dans certains scénarios.
Afin de réaliser l'immuabilité des chaînes, lors de la construction d'une chaîne, il y aura un processus de copie. Si vous souhaitez augmenter le coût de construction d'une chaîne, vous devez éviter une telle copie. .
Par exemple, ce qui suit est l'implémentation d'un constructeur de String dans JDK8
public final class String {
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
}Dans JDK8, il existe un constructeur qui ne copie pas, mais cette méthode n'est pas publique. Vous devez utiliser une astuce pour implémenter MethodHandles.Lookup. & Réflexion de liaison LambdaMetafactory Pour appeler, il y a du code introduisant cette technique plus loin dans l'article.
public final class String {
String(char[] value, boolean share) {
// assert share : "unshared not supported";
this.value = value;
}
}Il existe trois façons de construire rapidement des caractères :
Utilisez MethodHandles.Lookup et LambdaMetafactory pour lier la réflexion
Utilisez les méthodes associées de JavaLangAccess
Utilisez Unsafe pour construire directement
1 et 2 Les performances sont similaires, 3 est légèrement plus lente, mais ils sont tous deux plus rapides que l'utilisation directe d'une nouvelle chaîne. Les données du JDK8 utilisant le test JMH sont les suivantes : , n 193 ; 6,754 ops/ms
StringCreateBenchmark.langAccess thrpt 5 784029,186 ± 2734,300 ops/msStringCreateBenchmark.unsafe thrpt 5 761176.319 ± 11914.549 ops/msStringCreateBenchmark.newString thrpt 5 140883.533 ± 2217.773 ops/ms
Après JDK 9, la construction directe peut obtenir de meilleurs résultats pour les scènes qui sont toutes des caractères ASCII.4.1 基于MethodHandles.Lookup & LambdaMetafactory绑定反射的快速构造字符串的方法
4.1.1 JDK8快速构造字符串
public static BiFunction<char[], Boolean, String> getStringCreatorJDK8() throws Throwable { Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); MethodHandles lookup = constructor.newInstance( String.class , -1 // Lookup.TRUSTED ); MethodHandles.Lookup caller = lookup.in(String.class); MethodHandle handle = caller.findConstructor( String.class, MethodType.methodType(void.class, char[].class, boolean.class) ); CallSite callSite = LambdaMetafactory.metafactory( caller , "apply" , MethodType.methodType(BiFunction.class) , handle.type().generic() , handle , handle.type() ); return (BiFunction) callSite.getTarget().invokeExact(); }Copier après la connexion4.1.2 JDK 11快速构造字符串的方法
public static ToIntFunction<String> getStringCode11() throws Throwable { Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); MethodHandles.Lookup lookup = constructor.newInstance( String.class , -1 // Lookup.TRUSTED ); MethodHandles.Lookup caller = lookup.in(String.class); MethodHandle handle = caller.findVirtual( String.class, "coder", MethodType.methodType(byte.class) ); CallSite callSite = LambdaMetafactory.metafactory( caller , "applyAsInt" , MethodType.methodType(ToIntFunction.class) , MethodType.methodType(int.class, Object.class) , handle , handle.type() ); return (ToIntFunction<String>) callSite.getTarget().invokeExact(); }Copier après la connexionif (JDKUtils.JVM_VERSION == 11) { Function<byte[], String> stringCreator = JDKUtils.getStringCreatorJDK11(); byte[] bytes = new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c'}; String apply = stringCreator.apply(bytes); assertEquals("abc", apply); }Copier après la connexion4.1.3 JDK 17快速构造字符串的方法
在JDK 17中,MethodHandles.Lookup使用Reflection.registerFieldsToFilter对lookupClass和allowedModes做了保护,网上搜索到的通过修改allowedModes的办法是不可用的。
在JDK 17中,要通过配置JVM启动参数才能使用MethodHandlers。如下:
--add-opens java.base/java.lang.invoke=ALL-UNNAMEDCopier après la connexionpublic static BiFunction<byte[], Charset, String> getStringCreatorJDK17() throws Throwable { Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Class.class, int.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); MethodHandles.Lookup lookup = constructor.newInstance( String.class , null , -1 // Lookup.TRUSTED ); MethodHandles.Lookup caller = lookup.in(String.class); MethodHandle handle = caller.findStatic( String.class, "newStringNoRepl1", MethodType.methodType(String.class, byte[].class, Charset.class) ); CallSite callSite = LambdaMetafactory.metafactory( caller , "apply" , MethodType.methodType(BiFunction.class) , handle.type().generic() , handle , handle.type() ); return (BiFunction<byte[], Charset, String>) callSite.getTarget().invokeExact(); }Copier après la connexionif (JDKUtils.JVM_VERSION == 17) { BiFunction<byte[], Charset, String> stringCreator = JDKUtils.getStringCreatorJDK17(); byte[] bytes = new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c'}; String apply = stringCreator.apply(bytes, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII); assertEquals("abc", apply); }Copier après la connexion4.2 基于JavaLangAccess快速构造
通过SharedSecrets提供的JavaLangAccess,也可以不拷贝构造字符串,但是这个比较麻烦,JDK 8/11/17的API都不一样,对一套代码兼容不同的JDK版本不方便,不建议使用。
JavaLangAccess javaLangAccess = SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess(); javaLangAccess.newStringNoRepl(b, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);Copier après la connexion4.3 基于Unsafe实现快速构造字符串
public static final Unsafe UNSAFE; static { Unsafe unsafe = null; try { Field theUnsafeField = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); theUnsafeField.setAccessible(true); unsafe = (Unsafe) theUnsafeField.get(null); } catch (Throwable ignored) {} UNSAFE = unsafe; } //////////////////////////////////////////// Object str = UNSAFE.allocateInstance(String.class); UNSAFE.putObject(str, valueOffset, chars);Copier après la connexion注意:在JDK 9之后,实现是不同,比如:
Object str = UNSAFE.allocateInstance(String.class); UNSAFE.putByte(str, coderOffset, (byte) 0); UNSAFE.putObject(str, valueOffset, (byte[]) bytes);Copier après la connexion4.4 快速构建字符串的技巧应用:
如下的方法格式化日期为字符串,性能就会非常好。
public String formatYYYYMMDD(Calendar calendar) throws Throwable { int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR); int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1; int dayOfMonth = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); byte y0 = (byte) (year / 1000 + '0'); byte y1 = (byte) ((year / 100) % 10 + '0'); byte y2 = (byte) ((year / 10) % 10 + '0'); byte y3 = (byte) (year % 10 + '0'); byte m0 = (byte) (month / 10 + '0'); byte m1 = (byte) (month % 10 + '0'); byte d0 = (byte) (dayOfMonth / 10 + '0'); byte d1 = (byte) (dayOfMonth % 10 + '0'); if (JDKUtils.JVM_VERSION >= 9) { byte[] bytes = new byte[] {y0, y1, y2, y3, m0, m1, d0, d1}; if (JDKUtils.JVM_VERSION == 17) { return JDKUtils.getStringCreatorJDK17().apply(bytes, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII); } if (JDKUtils.JVM_VERSION <= 11) { return JDKUtils.getStringCreatorJDK11().apply(bytes); } return new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII); } char[] chars = new char[]{ (char) y0, (char) y1, (char) y2, (char) y3, (char) m0, (char) m1, (char) d0, (char) d1 }; if (JDKUtils.JVM_VERSION == 8) { return JDKUtils.getStringCreatorJDK8().apply(chars, true); } return new String(chars); }Copier après la connexion5.快速遍历字符串的办法
无论JDK什么版本,String.charAt都是一个较大的开销,JIT的优化效果并不好,无法消除参数index范围检测的开销,不如直接操作String里面的value数组。
public final class String { private final char value[]; public char charAt(int index) { if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) { throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); } return value[index]; } }Copier après la connexion在JDK 9之后的版本,charAt开销更大
public final class String { private final byte[] value; private final byte coder; public char charAt(int index) { if (isLatin1()) { return StringLatin1.charAt(value, index); } else { return StringUTF16.charAt(value, index); } } }Copier après la connexion5.1 获取String.value的方法
获取String.value的方法有如下:
使用Field反射
使用Unsafe
Unsafe和Field反射在JDK 8 JMH的比较数据如下:
Benchmark Mode Cnt Score Error Units
StringGetValueBenchmark.reflect thrpt 5 438374.685 ± 1032.028 ops/ms
StringGetValueBenchmark.unsafe thrpt 5 1302654.150 ± 59169.706 ops/ms5.1.1 使用反射获取String.value
static Field valueField; static { try { valueField = String.class.getDeclaredField("value"); valueField.setAccessible(true); } catch (NoSuchFieldException ignored) {} } //////////////////////////////////////////// char[] chars = (char[]) valueField.get(str);Copier après la connexion5.1.2 使用Unsafe获取String.value
static long valueFieldOffset; static { try { Field valueField = String.class.getDeclaredField("value"); valueFieldOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(valueField); } catch (NoSuchFieldException ignored) {} } //////////////////////////////////////////// char[] chars = (char[]) UNSAFE.getObject(str, valueFieldOffset);Copier après la connexionstatic long valueFieldOffset; static long coderFieldOffset; static { try { Field valueField = String.class.getDeclaredField("value"); valueFieldOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(valueField); Field coderField = String.class.getDeclaredField("coder"); coderFieldOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(coderField); } catch (NoSuchFieldException ignored) {} } //////////////////////////////////////////// byte coder = UNSAFE.getObject(str, coderFieldOffset); byte[] bytes = (byte[]) UNSAFE.getObject(str, valueFieldOffset);Copier après la connexion6.更快的encodeUTF8方法
当能直接获取到String.value时,就可以直接对其做encodeUTF8操作,会比String.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)性能好很多。
6.1 JDK8高性能encodeUTF8的方法
public static int encodeUTF8(char[] src, int offset, int len, byte[] dst, int dp) { int sl = offset + len; int dlASCII = dp + Math.min(len, dst.length); // ASCII only optimized loop while (dp < dlASCII && src[offset] < '\u0080') { dst[dp++] = (byte) src[offset++]; } while (offset < sl) { char c = src[offset++]; if (c < 0x80) { // Have at most seven bits dst[dp++] = (byte) c; } else if (c < 0x800) { // 2 bytes, 11 bits dst[dp++] = (byte) (0xc0 | (c >> 6)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f)); } else if (c >= '\uD800' && c < ('\uDFFF' + 1)) { //Character.isSurrogate(c) but 1.7 final int uc; int ip = offset - 1; if (c >= '\uD800' && c < ('\uDBFF' + 1)) { // Character.isHighSurrogate(c) if (sl - ip < 2) { uc = -1; } else { char d = src[ip + 1]; // d >= '\uDC00' && d < ('\uDFFF' + 1) if (d >= '\uDC00' && d < ('\uDFFF' + 1)) { // Character.isLowSurrogate(d) uc = ((c << 10) + d) + (0x010000 - ('\uD800' << 10) - '\uDC00'); // Character.toCodePoint(c, d) } else { dst[dp++] = (byte) '?'; continue; } } } else { // if (c >= '\uDC00' && c < ('\uDFFF' + 1)) { // Character.isLowSurrogate(c) dst[dp++] = (byte) '?'; continue; } else { uc = c; } } if (uc < 0) { dst[dp++] = (byte) '?'; } else { dst[dp++] = (byte) (0xf0 | ((uc >> 18))); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((uc >> 12) & 0x3f)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((uc >> 6) & 0x3f)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (uc & 0x3f)); offset++; // 2 chars } } else { // 3 bytes, 16 bits dst[dp++] = (byte) (0xe0 | ((c >> 12))); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3f)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f)); } } return dp; }Copier après la connexion使用encodeUTF8方法举例
char[] chars = UNSAFE.getObject(str, valueFieldOffset); // ensureCapacity(chars.length * 3) byte[] bytes = ...; // int bytesLength = IOUtils.encodeUTF8(chars, 0, chars.length, bytes, bytesOffset);Copier après la connexion这样encodeUTF8操作,不会有多余的arrayCopy操作,性能会得到提升。
6.1.1 性能测试比较
测试代码
public class EncodeUTF8Benchmark { static String STR = "01234567890ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWZYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwzyz一二三四五六七八九十"; static byte[] out; static long valueFieldOffset; static { out = new byte[STR.length() * 3]; try { Field valueField = String.class.getDeclaredField("value"); valueFieldOffset = UnsafeUtils.UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(valueField); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Benchmark public void unsafeEncodeUTF8() throws Exception { char[] chars = (char[]) UnsafeUtils.UNSAFE.getObject(STR, valueFieldOffset); int len = IOUtils.encodeUTF8(chars, 0, chars.length, out, 0); } @Benchmark public void getBytesUTF8() throws Exception { byte[] bytes = STR.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.arraycopy(bytes, 0, out, 0, bytes.length); } public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException { Options options = new OptionsBuilder() .include(EncodeUTF8Benchmark.class.getName()) .mode(Mode.Throughput) .timeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) .forks(1) .build(); new Runner(options).run(); } }Copier après la connexion测试结果
EncodeUTF8Benchmark.getBytesUTF8 thrpt 5 20690.960 ± 5431.442 ops/ms
EncodeUTF8Benchmark.unsafeEncodeUTF8 thrpt 5 34508.606 ± 55.510 ops/ms从结果来看,通过unsafe + 直接调用encodeUTF8方法, 编码的所需要开销是newStringUTF8的58%。
6.2 JDK9/11/17高性能encodeUTF8的方法
public static int encodeUTF8(byte[] src, int offset, int len, byte[] dst, int dp) { int sl = offset + len; while (offset < sl) { byte b0 = src[offset++]; byte b1 = src[offset++]; if (b1 == 0 && b0 >= 0) { dst[dp++] = b0; } else { char c = (char)(((b0 & 0xff) << 0) | ((b1 & 0xff) << 8)); if (c < 0x800) { // 2 bytes, 11 bits dst[dp++] = (byte) (0xc0 | (c >> 6)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f)); } else if (c >= '\uD800' && c < ('\uDFFF' + 1)) { //Character.isSurrogate(c) but 1.7 final int uc; int ip = offset - 1; if (c >= '\uD800' && c < ('\uDBFF' + 1)) { // Character.isHighSurrogate(c) if (sl - ip < 2) { uc = -1; } else { b0 = src[ip + 1]; b1 = src[ip + 2]; char d = (char) (((b0 & 0xff) << 0) | ((b1 & 0xff) << 8)); // d >= '\uDC00' && d < ('\uDFFF' + 1) if (d >= '\uDC00' && d < ('\uDFFF' + 1)) { // Character.isLowSurrogate(d) uc = ((c << 10) + d) + (0x010000 - ('\uD800' << 10) - '\uDC00'); // Character.toCodePoint(c, d) } else { return -1; } } } else { // if (c >= '\uDC00' && c < ('\uDFFF' + 1)) { // Character.isLowSurrogate(c) return -1; } else { uc = c; } } if (uc < 0) { dst[dp++] = (byte) '?'; } else { dst[dp++] = (byte) (0xf0 | ((uc >> 18))); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((uc >> 12) & 0x3f)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((uc >> 6) & 0x3f)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (uc & 0x3f)); offset++; // 2 chars } } else { // 3 bytes, 16 bits dst[dp++] = (byte) (0xe0 | ((c >> 12))); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3f)); dst[dp++] = (byte) (0x80 | (c & 0x3f)); } } } return dp; }Copier après la connexion使用encodeUTF8方法举例
byte coder = UNSAFE.getObject(str, coderFieldOffset); byte[] value = UNSAFE.getObject(str, coderFieldOffset); if (coder == 0) { // ascii arraycopy } else { // ensureCapacity(chars.length * 3) byte[] bytes = ...; // int bytesLength = IOUtils.encodeUTF8(value, 0, value.length, bytes, bytesOffset); }Copier après la connexion这样encodeUTF8操作,不会有多余的arrayCopy操作,性能会得到提升。
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!