 Java
Java
 javaDidacticiel
javaDidacticiel
 Comment SpringBoot implémente le décryptage automatique de l'interface RAS+AES
Comment SpringBoot implémente le décryptage automatique de l'interface RAS+AES
Comment SpringBoot implémente le décryptage automatique de l'interface RAS+AES
1. Parlez d'un accident
La sécurité des interfaces est un cliché
Je l'ai fait avant le Nouvel An chinois Un mini-jeu H5 sur les combats d'avions. En mode infini, les points de l'utilisateur doivent être sauvegardés. Parce que le corps est utilisé pour transmettre des paramètres, les paramètres sont visibles, pour des raisons de sécurité de l'interface. le front-end que les paramètres à passer sont : user Les points en mode illimité + "un nombre sur lequel nous nous sommes mis d'accord" + la somme des identifiants utilisateur sont cryptés en Base64. La requête est envoyée au serveur et je la décrypte pour obtenir les points de l'utilisateur en mode illimité ; que le score de la liste de classement des points du mode infini était erroné : Base64加密,请求到服务器我再解密,出用户无限模式的积分;如下:
{
"integral": "MTExMTM0NzY5NQ==",
}可是过年的时候,运营突然找我说无限模式积分排行榜分数不对:
这就很诡异了,第二名才一万多分,第一名就40多万分!!!!
一开始我以为是我解密有问题,反复看了好几变,可就两三行代码不可能有问题的!!!
没办法我去翻了好久的日志,才发现这个用户把我接口参数给改了。。。。
他把Base64接口参数改了
事已至此,我也不能怪用户,谁让我把人家想得太简单,接口安全也没到位
所以年后上班第一件是就是把接口加密的工作搞起来
目前常用的加密方式就对称性加密和非对称性加密,加密解密的操作的肯定是大家知道的,最重要的使用什么加密解密方式,制定什么样的加密策略;考虑到我技术水平和接口的速度,采用的是RAS非对称加密和AES对称加密一起用!!!!
二、RSA和AES基础知识
1、非对称加密和对称加密
非对称加密
非对称加密算法是一种密钥的保密方法。 非对称加密算法需要两个密钥:公开密钥(publickey:简称公钥)和私有密钥(privatekey:简称私钥)。公钥和私钥是成对出现的,使用公钥加密数据后,只有对应的私钥才能进行解密。由于使用两个不同的密钥进行加密和解密,因此这种算法被称为非对称加密算法。
对称加密
加密秘钥和解密秘钥是一样,当你的密钥被别人知道后,就没有秘密可言了
AES 是对称加密算法,优点:加密速度快;缺点:如果秘钥丢失,就容易解密密文,安全性相对比较差
RSA 是非对称加密算法 , 优点:安全 ;缺点:加密速度慢
2、RSA基础知识
RSA——非对称加密,会产生公钥和私钥,公钥在客户端,私钥在服务端。公钥用于加密,私钥用于解密。
大概的流程:
客户端向服务器发送消息: 客户端用公钥加密信息,发送给服务端,服务端再用私钥机密
服务器向客户端发送消息:服务端用私钥加密信息,发送给客户端,客户端再用公钥机密
当然中间要保障密钥的安全,还有很多为了保障数据安全的操作,比如数字签名,证书签名等等,在这我们就先不说了;
RSA加密解密算法支持三种填充模式,
分别是ENCRYPTION_OAEP、ENCRYPTION_PKCS1、ENCRYPTION_NONE
- Au début, j'ai pensé qu'il y avait un problème avec mon décryptage, je l'ai lu plusieurs fois, mais il ne pouvait pas y avoir de problème avec seulement deux ou trois lignes de code ! ! !
Pas question, j'ai longuement parcouru les logs et j'ai découvert que cet utilisateur avait modifié mes paramètres d'interface. . . .
Il a modifié les paramètres de l'interfaceBase64 - Maintenant que l'on en est là, je ne peux pas blâmer l'utilisateur qui m'a fait réfléchir. des autres aussi tout simplement ? La sécurité de l'interface n'est pas en place
Donc la première chose à faire quand j'arrive au travail après la nouvelle année est de commencer les travaux de cryptage de l'interface
Les méthodes de cryptage actuellement couramment utilisées sont le cryptage symétrique et le cryptage asymétrique. Les opérations de cryptage, de cryptage et de décryptage doivent être connues de tous. Le plus important est de savoir quelle méthode de cryptage et de décryptage utiliser et quelle stratégie de cryptage formuler compte tenu de mon niveau technique et de la rapidité. de l'interface, j'utilise le cryptage asymétrique RAS et le cryptage symétrique AES. Utilisez-les ensemble ! ! ! ! - 2. Connaissance de base de RSA et AES
1 Cryptage asymétrique et cryptage symétrique
Cryptage asymétrique# 🎜. 🎜# L'algorithme de cryptage asymétrique est une méthode clé secrète. L'algorithme de chiffrement asymétrique nécessite deux clés : une clé publique (publickey : appelée clé publique) et une clé privée (privatekey : appelée clé privée). Les clés publiques et les clés privées apparaissent par paires. Après avoir utilisé la clé publique pour chiffrer les données, seule la clé privée correspondante peut les déchiffrer. Puisque deux clés différentes sont utilisées pour le cryptage et le déchiffrement, cet algorithme est appelé algorithme de cryptage asymétrique.
Cryptage symétrique
- La clé de cryptage et la clé de déchiffrement sont les mêmes. Lorsque votre clé est connue des autres, il n'y a pas de secret. Yan Li
- AES est un algorithme de cryptage symétrique , avantages : cryptage rapide inconvénients : si la clé secrète est perdue, il est facile de déchiffrer le texte chiffré, et la sécurité ; est relativement médiocre#🎜 🎜#
RSA est un algorithme de cryptage asymétrique
, avantages : sécurité inconvénients : vitesse de cryptage lente
2. h4>
- Le client envoie un message au serveur : Le client crypte les informations avec la clé publique et l'envoie au serveur, et le serveur utilise la clé privée pour le garder secret Le serveur envoie un message au client : le serveur crypte le message avec la clé privée et l'envoie au client, et le client utilise la clé publique pour garder c'est secret
- Bien sûr il y a une étape intermédiaire Pour assurer la sécurité des clés, il existe de nombreuses opérations pour assurer la sécurité des données, comme les signatures numériques, les signatures de certificat, etc. N'entrez pas dans les détails ici ; Algorithme de cryptage et de décryptage RSA Prend en charge trois modes de remplissage
- , respectivement
ENCRYPTION_OAEP,ENCRYPTION_PKCS1,ENCRYPTION_NONE, le remplissage RSA est afin d'avoir la même longueur que la clé publique. - #🎜🎜#ENCRYPTION_OAEP est le mode de remplissage de cryptage asymétrique optimal et le mode de remplissage recommandé le plus récent et le plus sécurisé pour le cryptage RSA et le déchiffrement RSA. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#ENCRYPTION_PKCS1 : mode de remplissage aléatoire des données, le résultat de chaque cryptage est différent, c'est le plus largement utilisé pour le cryptage RSA et RSA mode de remplissage de décryptage. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#ENCRYPTION_NONE : Pas de mode de remplissage, qui est un mode de remplissage qui utilise moins de remplissage pour le cryptage RSA et le déchiffrement RSA. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Mode de remplissage de cryptage couramment utilisé par RSA#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜# RSA/None/PKCS1Padding#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Point de connaissance : #🎜🎜## 🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#L'implémentation RSA par défaut en Java est RSA/None/PKCS1Padding#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Lors de la création d'une paire de clés RSA, la longueur est la meilleur choix Un multiple entier de 2048, une longueur de 1024 n'est plus très sécuritaire #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜# Généralement, une paire de clés secrètes est créée par le serveur, la clé privée est enregistrée sur le serveur, et la clé publique est distribuée au Terminal client#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#DER est le format binaire de la clé RSA, et PEM est le format de caractères dans lequel DER est transcodé en Base64 Le DER étant un format binaire, il n'est pas facile à lire et à comprendre. De manière générale, les clés sont stockées au format PEM#🎜🎜#
/**
* 生成密钥对
* @param keyLength 密钥长度
* @return KeyPair
*/
public static KeyPair getKeyPair(int keyLength) {
try {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); //默认:RSA/None/PKCS1Padding
keyPairGenerator.initialize(keyLength);
return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("生成密钥对时遇到异常" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 获取公钥
*/
public static byte[] getPublicKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPublicKey rsaPublicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
return rsaPublicKey.getEncoded();
}
/**
* 获取私钥
*/
public static byte[] getPrivateKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
return rsaPrivateKey.getEncoded();
}3、AES基础知识
AES 简介 AES加密解密算法是一种可逆的对称加密算法,这类算法在加密和AES解密时使用相同的密钥,或是使用两个可以简单地相互推算的密钥,一般用于服务端对服务端之间对数据进行加密解密。它是一种为了替代原先DES、3DES而建立的高级加密标准(Advanced Encryption Standard)。作为可逆且对称的块加密,AES加密算法的速度比公钥加密等加密算法快很多,在很多场合都需要AES对称加密,但是要求加密端和解密端双方都使用相同的密钥是AES算法的主要缺点之一。
AES加密解密
AES加密需要:明文 + 密钥+ 偏移量(IV)+密码模式(算法/模式/填充) AES解密需要:密文 + 密钥+ 偏移量(IV)+密码模式(算法/模式/填充)
AES的算法模式一般为 AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding 或 AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding
AES常见的工作模式:
电码本模式(ECB)
密码分组链接模式(CBC)
计算器模式(CTR)
密码反馈模式(CFB)
输出反馈模式(OFB)
除了ECB无须设置初始化向量IV而不安全之外,其它AES工作模式都必须设置向量IV,其中GCM工作模式较为特殊。
AES填充模式
块密码只能对确定长度的数据块进行处理,而消息的长度通常是可变的,因此需要选择填充模式。
填充区别:在ECB、CBC工作模式下最后一块要在加密前进行填充,其它不用选择填充模式;填充模式:AES支持的填充模式为PKCS7和NONE不填充。其中PKCS7标准是主流加密算法都遵循的数据填充算法。AES标准规定的区块长度为固定值128Bit,对应的字节长度为16位,这明显和PKCS5标准规定使用的固定值8位不符,虽然有些框架特殊处理后可以通用PKCS5,但是从长远和兼容性考虑,推荐PKCS7。
AES密钥KEY和初始化向量IV
初始化向量IV可以有效提升安全性,但是在实际的使用场景中,它不能像密钥KEY那样直接保存在配置文件或固定写死在代码中,一般正确的处理方式为:在加密端将IV设置为一个16位的随机值,然后和加密文本一起返给解密端即可。
密钥KEY:AES标准规定区块长度只有一个值,固定为128Bit,对应的字节为16位。AES算法规定密钥长度只有三个值,128Bit、192Bit、256Bit,对应的字节为16位、24位和32位,其中密钥KEY不能公开传输,用于加密解密数据;初始化向量IV:该字段可以公开,用于将加密随机化。同样的明文被多次加密也会产生不同的密文,避免了较慢的重新产生密钥的过程,初始化向量与密钥相比有不同的安全性需求,因此IV通常无须保密。然而在大多数情况中,不应当在使用同一密钥的情况下两次使用同一个IV,一般推荐初始化向量IV为16位的随机值。
三、加密策略
RAS、AES加密解密的操作都是一样,如果有效的结合到一起才能达到更好的加密效果很重要;
上面说到:
AES 是对称加密算法,优点:加密速度快;缺点:如果秘钥丢失,就容易解密密文,安全性相对比较差
RSA 是非对称加密算法 , 优点:安全 ;缺点:加密速度慢
1、主要思路:
那么我们就结合2个加密算法的优点来操作:
1、因为接口传递的参数有多有少,当接口传递的参数过多时,使用RSA加密会导致加密速度慢,所以我们使用AES加密加密接口参数
2、因为AES的密钥key和偏移量VI都是固定的所以可以使用RSA加密
3、客户端将AES加密后的密文和RSA加密后的密文,传递给服务器即可。
2、涉及工具类:
util包下:
ActivityRSAUtilAES256UtilRequestDecryptionUtil
3、加密策略
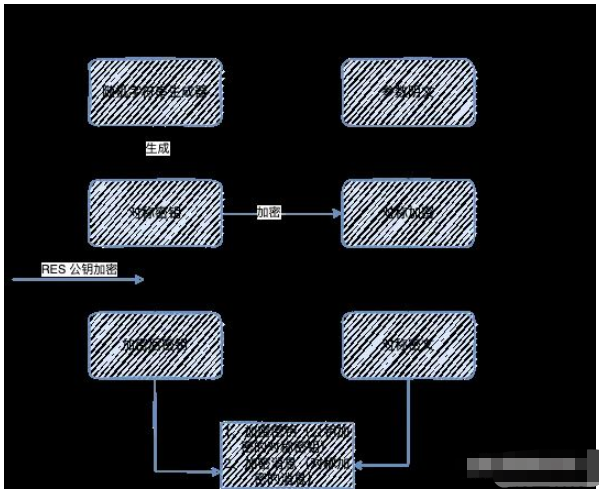
4、交互方式
前端:
1、客户端随机生成2个16为的AES密钥和AES偏移量
2、使用AES加密算法加密真实传递参数,得到参数密文“asy”
3、将AES密钥、AES偏移量和当前时间戳,格式如下:
key:密钥
keyVI:偏移量
time:请求时间,用户判断是否重复请求
{
"key":"0t7FtCDKofbEVpSZS",
"keyVI":"0t7WESMofbEVpSZS",
"time":211213232323323
}
//转成JSON字符串4、AES信息密钥信息,再使用RSA公钥加密,得到AES密钥的密文“sym”
5、将“sym”和“asy”作为body参数,调用接口
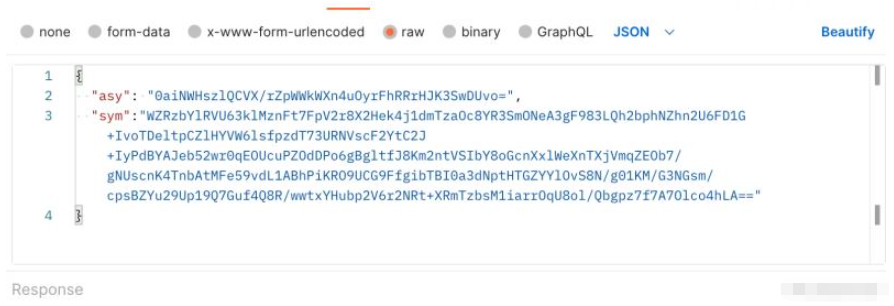
后端:
1、在接口接收参数中,多增加2个字段接收加密后的“sym”和“asy” (名字可以自己定,能接收到就行)
2、使用RequestDecryptionUtil.getRequestDecryption()方法解密,返回解密后的真实传递参数
四、服务器自动解密
因为不是每个接口都需求加密解密,我们可以自定义一个注解,将需要解密的接口上加一个这个注解,
1、自定义解密注解:@RequestRSA
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestRSA {
}2、创建一个aop切片
1、AOP判断controller接收到请求是否带有@RequestRSA注解
2、如果带有注解,通过ProceedingJoinPoint类getArgs()方法获取请求的body参数,
3、将body参数,传为JSONObject类,获取到"asy"和"sym"属性,再调用RequestDecryptionUtil解密获取接口传递的真实参数
4、获取接口入参的类
5、将获取解密后的真实参数,封装到接口入参的类中
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import app.activity.common.interceptor.RequestRSA;
import app.activity.util.RequestDecryptionUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-08 16:41
* @copyright 请求验证RSA & AES 统一验证切面
**/
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(2)
@Slf4j
public class RequestRSAAspect {
/**
* 1> 获取请求参数
* 2> 获取被请求接口的入参类型
* 3> 判断是否为get请求 是则跳过AES解密判断
* 4> 请求参数解密->封装到接口的入参
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * app.activity.controller.*.*(..))")
public void requestRAS() {
}
@Around("requestRAS()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//=======AOP解密切面通知=======
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method methods = methodSignature.getMethod();
RequestRSA annotation = methods.getAnnotation(RequestRSA.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(annotation)){
//获取请求的body参数
Object data = getParameter(methods, joinPoint.getArgs());
String body = JSONObject.toJSONString(data);
//获取asy和sym的值
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(body);
String asy = jsonObject.get("asy").toString();
String sym = jsonObject.get("sym").toString();
//调用RequestDecryptionUtil方法解密,获取解密后的真实参数
JSONObject decryption = RequestDecryptionUtil.getRequestDecryption(sym, asy);
//获取接口入参的类
String typeName = joinPoint.getArgs()[0].getClass().getTypeName();
System.out.println("参数值类型:"+ typeName);
Class<?> aClass = joinPoint.getArgs()[0].getClass();
//将获取解密后的真实参数,封装到接口入参的类中
Object o = JSONObject.parseObject(decryption.toJSONString(), aClass);
Object[] as = {o};
return joinPoint.proceed(as);
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
/**
* 根据方法和传入的参数获取请求参数 获取的是接口的入参
*/
private Object getParameter(Method method, Object[] args) {
List<Object> argList = new ArrayList<>();
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
//将RequestBody注解修饰的参数作为请求参数
RequestBody requestBody = parameters[i].getAnnotation(RequestBody.class);
if (requestBody != null) {
argList.add(args[i]);
}
}
if (argList.size() == 0) {
return null;
} else if (argList.size() == 1) {
return argList.get(0);
} else {
return argList;
}
}
}3、RequestDecryptionUtil 解密类
1、使用privateKey私钥对”sym“解密获取到客户端加密的AES密钥,偏移量、时间等信息
{
"key":"0t7FtSMofbEVpSZS",
"keyVI":"0t7FtSMofbEVpSZS",
"time":211213232323323
}2、获取当前时间戳,与time比较是否超过一分钟(6000毫秒),超过就抛出“Request timed out, please try again”异常
3、没有超时,将获取的到AES密钥和偏移量,再对“asy”解密获取接口传递的真实参数
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import app.activity.common.rsa.RSADecodeData;
import app.common.exception.ServiceException;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-09 17:43
* @copyright
**/
public class RequestDecryptionUtil {
private final static String publicKey = "RSA生成的公钥";
private final static String privateKey = "RSA生成的私钥";
private final static Integer timeout = 60000;
/**
*
* @param sym RSA 密文
* @param asy AES 密文
* @param clazz 接口入参类
* @return Object
*/
public static <T> Object getRequestDecryption(String sym, String asy, Class<T> clazz){
//验证密钥
try {
//解密RSA
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = ActivityRSAUtil.getRSAPrivateKeyByString(privateKey);
String RSAJson = ActivityRSAUtil.privateDecrypt(sym, rsaPrivateKey);
RSADecodeData rsaDecodeData = JSONObject.parseObject(RSAJson, RSADecodeData.class);
boolean isTimeout = Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData) && Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData.getTime()) && System.currentTimeMillis() - rsaDecodeData.getTime() < timeout;
if (!isTimeout){
throw new ServiceException("Request timed out, please try again."); //请求超时
}
//解密AES
String AESJson = AES256Util.decode(rsaDecodeData.getKey(),asy,rsaDecodeData.getKeyVI());
System.out.println("AESJson: "+AESJson);
return JSONObject.parseObject(AESJson,clazz);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("RSA decryption Exception: " +e.getMessage());
}
}
public static JSONObject getRequestDecryption(String sym, String asy){
//验证密钥
try {
//解密RSA
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = ActivityRSAUtil.getRSAPrivateKeyByString(privateKey);
String RSAJson = ActivityRSAUtil.privateDecrypt(sym, rsaPrivateKey);
RSADecodeData rsaDecodeData = JSONObject.parseObject(RSAJson, RSADecodeData.class);
boolean isTimeout = Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData) && Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData.getTime()) && System.currentTimeMillis() - rsaDecodeData.getTime() < timeout;
if (!isTimeout){
throw new ServiceException("Request timed out, please try again."); //请求超时
}
//解密AES
String AESJson = AES256Util.decode(rsaDecodeData.getKey(),asy,rsaDecodeData.getKeyVI());
System.out.println("AESJson: "+AESJson);
return JSONObject.parseObject(AESJson);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("RSA decryption Exception: " +e.getMessage());
}
}
}4、ActivityRSAUtil 工具类
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-07 16:54
* @copyright
**/
public class ActivityRSAUtil {
/**
* 字符集
*/
public static String CHARSET = "UTF-8";
/**
* 生成密钥对
* @param keyLength 密钥长度
* @return KeyPair
*/
public static KeyPair getKeyPair(int keyLength) {
try {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); //默认:RSA/None/PKCS1Padding
keyPairGenerator.initialize(keyLength);
return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("生成密钥对时遇到异常" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 获取公钥
*/
public static byte[] getPublicKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPublicKey rsaPublicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
return rsaPublicKey.getEncoded();
}
/**
* 获取私钥
*/
public static byte[] getPrivateKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
return rsaPrivateKey.getEncoded();
}
/**
* 公钥字符串转PublicKey实例
* @param publicKey 公钥字符串
* @return PublicKey
* @throws Exception e
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(String publicKey) throws Exception {
byte[] publicKeyBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKey.getBytes());
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
}
/**
* 私钥字符串转PrivateKey实例
* @param privateKey 私钥字符串
* @return PrivateKey
* @throws Exception e
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String privateKey) throws Exception {
byte[] privateKeyBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKey.getBytes());
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
}
/**
* 获取公钥字符串
* @param keyPair KeyPair
* @return 公钥字符串
*/
public static String getPublicKeyString(KeyPair keyPair){
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic(); // 得到公钥
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64(publicKey.getEncoded()));
}
/**
* 获取私钥字符串
* @param keyPair KeyPair
* @return 私钥字符串
*/
public static String getPrivateKeyString(KeyPair keyPair){
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); // 得到私钥
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64((privateKey.getEncoded())));
}
/**
* 公钥加密
* @param data 明文
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return 密文
*/
public static String publicEncrypt(String data, RSAPublicKey publicKey) {
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] bytes = rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, data.getBytes(CHARSET), publicKey.getModulus().bitLength());
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64(bytes));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("加密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常"+ e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 私钥解密
* @param data 密文
* @param privateKey 私钥
* @return 明文
*/
public static String privateDecrypt(String data, RSAPrivateKey privateKey) {
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return new String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, Base64.getDecoder().decode(data), privateKey.getModulus().bitLength()), CHARSET);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("privateKey解密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常"+ e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 私钥加密
* @param content 明文
* @param privateKey 私钥
* @return 密文
*/
public static String encryptByPrivateKey(String content, RSAPrivateKey privateKey){
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] bytes = rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,content.getBytes(CHARSET), privateKey.getModulus().bitLength());
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64(bytes));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("privateKey加密字符串[" + content + "]时遇到异常" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 公钥解密
* @param content 密文
* @param publicKey 私钥
* @return 明文
*/
public static String decryByPublicKey(String content, RSAPublicKey publicKey){
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return new String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, Base64.getDecoder().decode(content), publicKey.getModulus().bitLength()), CHARSET);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("publicKey解密字符串[" + content + "]时遇到异常" +e.getMessage());
}
}
public static RSAPublicKey getRSAPublicKeyByString(String publicKey){
try {
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKey));
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return (RSAPublicKey)keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("String转PublicKey出错" + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static RSAPrivateKey getRSAPrivateKeyByString(String privateKey){
try {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8EncodedKeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKey));
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return (RSAPrivateKey)keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8EncodedKeySpec);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("String转PrivateKey出错" + e.getMessage());
}
}
//rsa切割解码 , ENCRYPT_MODE,加密数据 ,DECRYPT_MODE,解密数据
private static byte[] rsaSplitCodec(Cipher cipher, int opmode, byte[] datas, int keySize) {
int maxBlock = 0; //最大块
if (opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE) {
maxBlock = keySize / 8;
} else {
maxBlock = keySize / 8 - 11;
}
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int offSet = 0;
byte[] buff;
int i = 0;
try {
while (datas.length > offSet) {
if (datas.length - offSet > maxBlock) {
//可以调用以下的doFinal()方法完成加密或解密数据:
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, maxBlock);
} else {
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, datas.length - offSet);
}
out.write(buff, 0, buff.length);
i++;
offSet = i * maxBlock;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("加解密阀值为[" + maxBlock + "]的数据时发生异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
byte[] resultDatas = out.toByteArray();
IOUtils.closeQuietly(out);
return resultDatas;
}
}5、AES256Util 工具类
import org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.Security;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-07 16:14
* @copyright
**/
public class AES256Util {
private static final String AES = "AES";
/**
* 初始向量IV, 初始向量IV的长度规定为128位16个字节, 初始向量的来源为随机生成.
*/
/**
* 加密解密算法/加密模式/填充方式
*/
private static final String CIPHER_ALGORITHM = "AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding";
private static final Base64.Encoder base64Encoder = java.util.Base64.getEncoder();
private static final Base64.Decoder base64Decoder = java.util.Base64.getDecoder();
//通过在运行环境中设置以下属性启用AES-256支持
static {
Security.setProperty("crypto.policy", "unlimited");
}
/*
* 解决java不支持AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding模式解密
*/
static {
Security.addProvider(new BouncyCastleProvider());
}
/**
* AES加密
*/
public static String encode(String key, String content,String keyVI) {
try {
javax.crypto.SecretKey secretKey = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), AES);
javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = javax.crypto.Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(javax.crypto.Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(keyVI.getBytes()));
// 获取加密内容的字节数组(这里要设置为utf-8)不然内容中如果有中文和英文混合中文就会解密为乱码
byte[] byteEncode = content.getBytes(java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 根据密码器的初始化方式加密
byte[] byteAES = cipher.doFinal(byteEncode);
// 将加密后的数据转换为字符串
return base64Encoder.encodeToString(byteAES);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* AES解密
*/
public static String decode(String key, String content,String keyVI) {
try {
javax.crypto.SecretKey secretKey = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), AES);
javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = javax.crypto.Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(javax.crypto.Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(keyVI.getBytes()));
// 将加密并编码后的内容解码成字节数组
byte[] byteContent = base64Decoder.decode(content);
// 解密
byte[] byteDecode = cipher.doFinal(byteContent);
return new String(byteDecode, java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* AES加密ECB模式PKCS7Padding填充方式
* @param str 字符串
* @param key 密钥
* @return 加密字符串
* @throws Exception 异常信息
*/
public static String aes256ECBPkcs7PaddingEncrypt(String str, String key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS7Padding");
byte[] keyBytes = key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, AES));
byte[] doFinal = cipher.doFinal(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(doFinal));
}
/**
* AES解密ECB模式PKCS7Padding填充方式
* @param str 字符串
* @param key 密钥
* @return 解密字符串
* @throws Exception 异常信息
*/
public static String aes256ECBPkcs7PaddingDecrypt(String str, String key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS7Padding");
byte[] keyBytes = key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, AES));
byte[] doFinal = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(str));
return new String(doFinal);
}
}Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment Springboot intègre Jasypt pour implémenter le chiffrement des fichiers de configuration
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Comment Springboot intègre Jasypt pour implémenter le chiffrement des fichiers de configuration
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Introduction à Jasypt Jasypt est une bibliothèque Java qui permet à un développeur d'ajouter des fonctionnalités de chiffrement de base à son projet avec un minimum d'effort et ne nécessite pas une compréhension approfondie du fonctionnement du chiffrement. Haute sécurité pour le chiffrement unidirectionnel et bidirectionnel. technologie de cryptage basée sur des normes. Cryptez les mots de passe, le texte, les chiffres, les binaires... Convient pour l'intégration dans des applications basées sur Spring, API ouverte, pour une utilisation avec n'importe quel fournisseur JCE... Ajoutez la dépendance suivante : com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2 1.1. Les avantages de Jasypt protègent la sécurité de notre système. Même en cas de fuite du code, la source de données peut être garantie.
 Comment SpringBoot intègre Redisson pour implémenter la file d'attente différée
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Comment SpringBoot intègre Redisson pour implémenter la file d'attente différée
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Scénario d'utilisation 1. La commande a été passée avec succès mais le paiement n'a pas été effectué dans les 30 minutes. Le paiement a expiré et la commande a été automatiquement annulée 2. La commande a été signée et aucune évaluation n'a été effectuée pendant 7 jours après la signature. Si la commande expire et n'est pas évaluée, le système donne par défaut une note positive. 3. La commande est passée avec succès. Si le commerçant ne reçoit pas la commande pendant 5 minutes, la commande est annulée. 4. Le délai de livraison expire et. un rappel par SMS est envoyé... Pour les scénarios avec des délais longs et de faibles performances en temps réel, nous pouvons utiliser la planification des tâches pour effectuer un traitement d'interrogation régulier. Par exemple : xxl-job Aujourd'hui, nous allons choisir
 Comment utiliser Redis pour implémenter des verrous distribués dans SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Comment utiliser Redis pour implémenter des verrous distribués dans SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
1. Redis implémente le principe du verrouillage distribué et pourquoi les verrous distribués sont nécessaires. Avant de parler de verrous distribués, il est nécessaire d'expliquer pourquoi les verrous distribués sont nécessaires. Le contraire des verrous distribués est le verrouillage autonome. Lorsque nous écrivons des programmes multithreads, nous évitons les problèmes de données causés par l'utilisation d'une variable partagée en même temps. Nous utilisons généralement un verrou pour exclure mutuellement les variables partagées afin de garantir l'exactitude de celles-ci. les variables partagées. Son champ d’utilisation est dans le même processus. S’il existe plusieurs processus qui doivent exploiter une ressource partagée en même temps, comment peuvent-ils s’exclure mutuellement ? Les applications métier d'aujourd'hui sont généralement une architecture de microservices, ce qui signifie également qu'une application déploiera plusieurs processus si plusieurs processus doivent modifier la même ligne d'enregistrements dans MySQL, afin d'éviter les données sales causées par des opérations dans le désordre, les besoins de distribution. à introduire à ce moment-là. Le style est verrouillé. Vous voulez marquer des points
 Comment résoudre le problème selon lequel Springboot ne peut pas accéder au fichier après l'avoir lu dans un package jar
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Comment résoudre le problème selon lequel Springboot ne peut pas accéder au fichier après l'avoir lu dans un package jar
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot lit le fichier, mais ne peut pas accéder au dernier développement après l'avoir empaqueté dans un package jar. Il existe une situation dans laquelle Springboot ne peut pas lire le fichier après l'avoir empaqueté dans un package jar. La raison en est qu'après l'empaquetage, le chemin virtuel du fichier. n’est pas valide et n’est accessible que via le flux Read. Le fichier se trouve sous les ressources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Comment implémenter Springboot+Mybatis-plus sans utiliser d'instructions SQL pour ajouter plusieurs tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Comment implémenter Springboot+Mybatis-plus sans utiliser d'instructions SQL pour ajouter plusieurs tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Lorsque Springboot+Mybatis-plus n'utilise pas d'instructions SQL pour effectuer des opérations d'ajout de plusieurs tables, les problèmes que j'ai rencontrés sont décomposés en simulant la réflexion dans l'environnement de test : Créez un objet BrandDTO avec des paramètres pour simuler le passage des paramètres en arrière-plan. qu'il est extrêmement difficile d'effectuer des opérations multi-tables dans Mybatis-plus. Si vous n'utilisez pas d'outils tels que Mybatis-plus-join, vous pouvez uniquement configurer le fichier Mapper.xml correspondant et configurer le ResultMap malodorant et long, puis. écrivez l'instruction SQL correspondante Bien que cette méthode semble lourde, elle est très flexible et nous permet de
 Comparaison et analyse des différences entre SpringBoot et SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparaison et analyse des différences entre SpringBoot et SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot et SpringMVC sont tous deux des frameworks couramment utilisés dans le développement Java, mais il existe des différences évidentes entre eux. Cet article explorera les fonctionnalités et les utilisations de ces deux frameworks et comparera leurs différences. Tout d’abord, découvrons SpringBoot. SpringBoot a été développé par l'équipe Pivotal pour simplifier la création et le déploiement d'applications basées sur le framework Spring. Il fournit un moyen rapide et léger de créer des fichiers exécutables autonomes.
 Comment SpringBoot personnalise Redis pour implémenter la sérialisation du cache
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
Comment SpringBoot personnalise Redis pour implémenter la sérialisation du cache
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. Personnalisez RedisTemplate1.1, mécanisme de sérialisation par défaut RedisAPI. L'implémentation du cache Redis basée sur l'API utilise le modèle RedisTemplate pour les opérations de mise en cache des données. Ici, ouvrez la classe RedisTemplate et affichez les informations sur le code source de la classe. Déclarer la clé, diverses méthodes de sérialisation de la valeur, la valeur initiale est vide @NullableprivateRedisSe
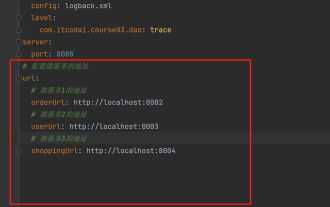 Comment obtenir la valeur dans application.yml au Springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
Comment obtenir la valeur dans application.yml au Springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
Dans les projets, certaines informations de configuration sont souvent nécessaires. Ces informations peuvent avoir des configurations différentes dans l'environnement de test et dans l'environnement de production, et peuvent devoir être modifiées ultérieurement en fonction des conditions commerciales réelles. Nous ne pouvons pas coder en dur ces configurations dans le code. Il est préférable de les écrire dans le fichier de configuration. Par exemple, vous pouvez écrire ces informations dans le fichier application.yml. Alors, comment obtenir ou utiliser cette adresse dans le code ? Il existe 2 méthodes. Méthode 1 : Nous pouvons obtenir la valeur correspondant à la clé dans le fichier de configuration (application.yml) via le ${key} annoté avec @Value. Cette méthode convient aux situations où il y a relativement peu de microservices. Méthode 2 : En réalité. projets, Quand les affaires sont compliquées, la logique





