Comment implémenter le déploiement à chaud de Nginx
Fermez le pare-feu pour que le service Nginx soit accessible localement via le navigateur. Nginx服务。
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
信号量
查看信号量:
[root@localhost ~]# kill -l 1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP 6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1 11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM 16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP 21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ 26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR 31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3 38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8 43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13 48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12 53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7 58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2 63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX
有64种信号量,以下是几种常用的信号量:
SIGINT、SIGTERM:快速关闭。SIGQUIT:从容关闭(优雅的关闭进程,即等请求结束后再关闭)。SIGHUP:平滑重启,重新加载配置文件 (平滑重启,修改配置文件之后不用重启服务器)。SIGUSR1:重新读取日志文件,在切割日志文件时用途较大。SIGUSR2:平滑升级可执行程序 ,nginx升级时候用。SIGWINCH:从容关闭工作进程。
Nginx热部署
Nginx是一个多进程的高性能反向代理服务器,包含一个master进程和多个worker进程(worker进程的数量可以通过nginx.conf配置文件中的worker_processes参数进行设置,默认1个),这样可以充分利用多核处理器。
默认1个worker进程。

并且master进程和worker进程是父子进程关系。
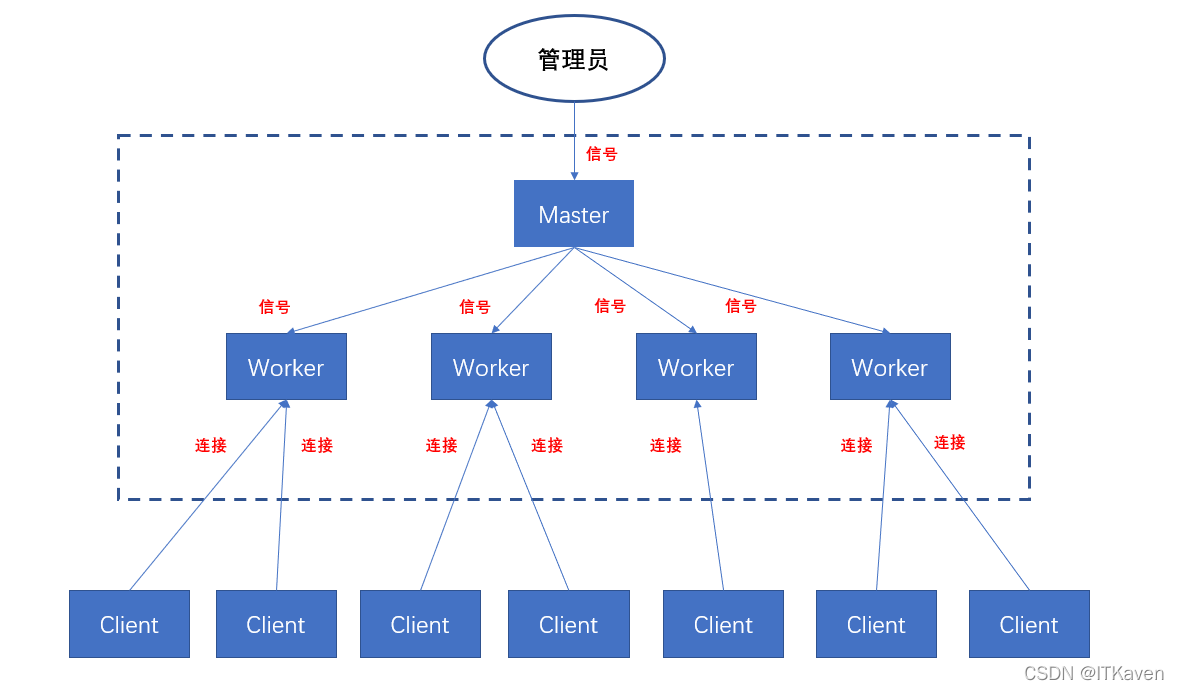
Nginx工作模式为多进程,Nginx在启动之后会有一个master进程和多个worker进程(默认1个),多个worker子进程将监听master父进程监听的端口(参考父子进程的关系),并行处理请求。master父进程主要用来管理worker子进程(管理真正提供服务的worker进程,向worker进程发送信号,监控worker进程的运行状态,当worker进程异常退出后,会重新启动新的worker进程),读取并验证配置信息,master进程不会对用户请求提供服务,而用户请求是由worker进程进行处理。
Nginx是通过信号量来控制,比如停止和重启Nginx。信号量是进程间通信的一种机制,master主进程控制多个worker子进程,也是通过信号量。
现在来演示Nginx是怎么实现热部署的,博主通过修改Nginx的配置文件来模拟Nginx的升级(先copy一份副本)。
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/ [root@localhost conf]# ll 总用量 68 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1077 12月 20 20:24 fastcgi.conf -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1077 12月 20 20:24 fastcgi.conf.default -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1007 12月 20 20:24 fastcgi_params -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1007 12月 20 20:24 fastcgi_params.default -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2837 12月 20 20:24 koi-utf -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2223 12月 20 20:24 koi-win -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5231 12月 20 20:24 mime.types -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5231 12月 20 20:24 mime.types.default -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2656 12月 20 21:26 nginx.conf -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2656 12月 20 20:24 nginx.conf.default -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 636 12月 20 20:24 scgi_params -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 636 12月 20 20:24 scgi_params.default -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 664 12月 20 20:24 uwsgi_params -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 664 12月 20 20:24 uwsgi_params.default -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3610 12月 20 20:24 win-utf [root@localhost conf]# cp nginx.conf nginx_old.conf [root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
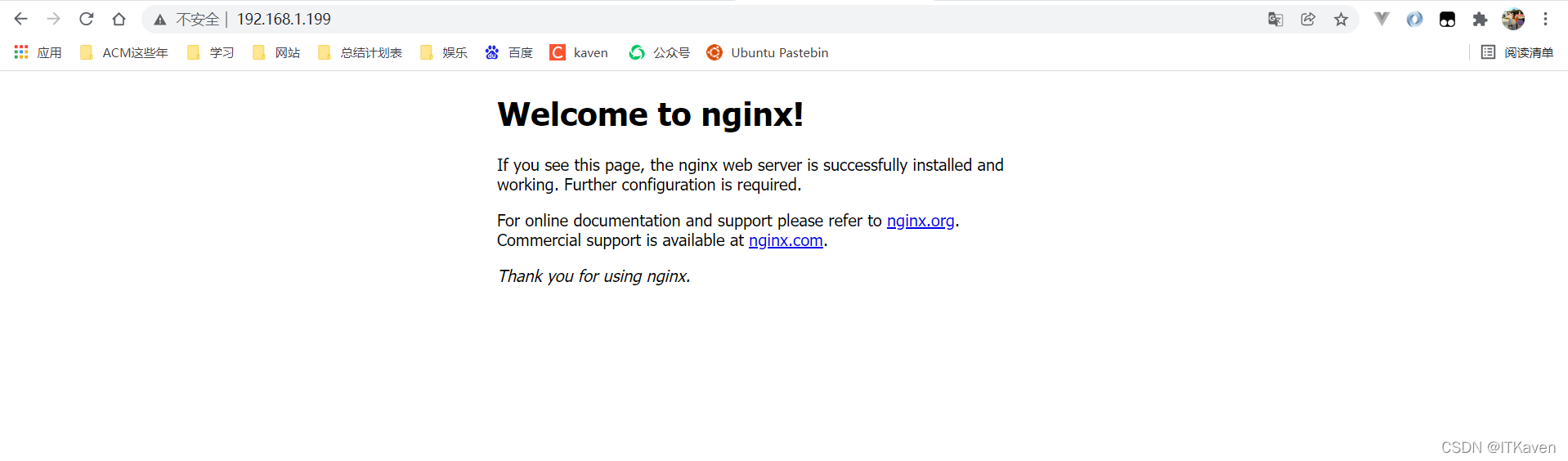
由于还没有给Nginx进行热部署,现在访问http://192.168.1.199/还是原来的Nginx页面。
查看Nginx的进程:
[root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 14964 1 0 22:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 14965 14964 0 22:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15016 1521 0 23:07 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
给master进程发送SIGUSR2信号,让Nginx平滑升级可执行程序。可以看到Nginx重新启动了一组master进程和worker进程,而新master进程是旧master进程的子进程(通过父子进程的继承关系,新master进程可以很方便地继承旧master进程的相关资源)。
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGUSR2 14964 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 14964 1 0 22:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 14965 14964 0 22:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15019 14964 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15020 15019 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15022 1521 0 23:19 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
并且Nginx在日志目录中存储了新旧pid文件(保存了新旧master进程的ID)。
[root@localhost conf]# ll ../logs 总用量 16 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2729 12月 20 23:20 access.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 708 12月 20 23:18 error.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 12月 20 23:18 nginx.pid -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 12月 20 22:25 nginx.pid.oldbin [root@localhost conf]# cat ../logs/nginx.pid 15019 [root@localhost conf]# cat ../logs/nginx.pid.oldbin 14964
给旧master进程发送SIGWINCH信号,让旧master进程关闭旧worker进程。
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGWINCH 14964 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 14964 1 0 22:25 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx root 15019 14964 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15020 15019 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15030 1521 0 23:27 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
现在访问http://192.168.1.199/,会响应404。
而访问http://192.168.1.199/nacos,会访问到Nacos
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGQUIT 14964 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 15019 1 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15020 15019 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15034 1521 0 23:31 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
 # 🎜🎜#
# 🎜🎜#Sémaphore
Afficher les sémaphores :[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGHUP 15084 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 15084 1 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx root 15106 15084 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15107 15106 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process nobody 15131 15084 0 00:02 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15141 1521 0 00:09 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
 Il existe
Il existe 64 types de sémaphores. Voici plusieurs sémaphores couramment utilisés. : SIGINT,SIGTERM: Fermez rapidement. #🎜🎜#- #🎜🎜#
SIGQUIT: Arrêtez-vous correctement (fermez le processus correctement, c'est-à-dire attendez que la demande soit terminée, puis arrêtez-vous). #🎜🎜# - #🎜🎜#
SIGHUP: Redémarrage en douceur, rechargez le fichier de configuration (redémarrage en douceur, pas besoin de redémarrer le serveur après modification du fichier de configuration). #🎜🎜# - #🎜🎜#
SIGUSR1: Relisez le fichier journal, ce qui est plus utile lors de la découpe du fichier journal. #🎜🎜# - #🎜🎜#
SIGUSR2: Mise à niveau fluide des programmes exécutables, utilisée lors de la mise à niveau denginx. #🎜🎜# - #🎜🎜#
SIGWINCH: Arrêtez le processus de travail en douceur. #🎜🎜#
Déploiement à chaud de Nginx
#🎜🎜#Nginx est un serveur proxy inverse multi-processus et hautes performances, comprenant un < code >master et plusieurs processus worker (le nombre de processus worker peut être transmis via dans le <code>nginx.conf</code) > fichier de configuration Définissez le paramètre worker_processes, la valeur par défaut est 1), afin que les processeurs multicœurs puissent être pleinement utilisés. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜# # 🎜 🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#La valeur par défaut est
# 🎜 🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#La valeur par défaut est 1 worker processus. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜# #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Et le processus
#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Et le processus master et le processus worker ont une relation de processus parent-enfant. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜# #🎜🎜##🎜🎜#
#🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Nginx fonctionne en mode multi-processus. Après le démarrage de Nginx, il y aura un maître processus et plusieurs processus worker (par défaut 1), plusieurs processus enfants worker écouteront le port surveillé par le master</code > processus parent (faisant référence à la relation entre les processus parent et enfant), les demandes sont traitées en parallèle. Le processus parent <code>master est principalement utilisé pour gérer le processus enfant worker (gérer le processus worker qui fournit réellement des services, au worker Processus Envoie un signal et surveille l'état d'exécution du processus worker Lorsque le processus worker se termine anormalement, un nouveau processus worker. sera redémarré), lisez et vérifiez les informations de configuration. Le processus master ne répondra pas aux demandes des utilisateurs, mais les demandes des utilisateurs sont traitées par le processus worker. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Nginx est contrôlé via des sémaphores, tels que l'arrêt et le redémarrage de Nginx. Les sémaphores sont un mécanisme de communication inter-processus. Le processus principal master contrôle plusieurs sous-processus worker via des sémaphores. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜# #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Montrons maintenant comment
#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Montrons maintenant comment Nginx implémente le déploiement à chaud. Le blogueur le simule en modifiant le fichier de configuration de Nginx< Mise à niveau de Code>Nginx (copier une copie en premier). #🎜🎜#[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGQUIT 15106 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 15084 1 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15131 15084 0 00:02 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15159 1521 0 00:25 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
 # 🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Puisque
# 🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Puisque Nginx n'a pas encore été déployé à chaud, visiter http://192.168.1.199/ est toujours le Nginx< d'origine /code> >page. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/168491854217364.png" class="lazy" alt="Comment implémenter le déploiement à chaud de Nginx " />#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Voir le processus <code>Nginx : #🎜🎜#[root@localhost conf]# cp -f nginx_old.conf nginx.conf cp:是否覆盖"nginx.conf"? y
SIGUSR2 au <code>maître</code > processus Signal permet à Nginx de mettre à jour en douceur le programme exécutable. Vous pouvez voir que Nginx a redémarré un ensemble de processus master et de processus worker, et que le nouveau processus master est l'ancien processus master. Le processus enfant du processus code>master (grâce à la relation d'héritage entre les processus parent et enfant, le nouveau processus master peut facilement hériter des ressources associées de l'ancien processus master). #🎜🎜#[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGHUP 15084
Nginx stocke les anciens et les nouveaux fichiers pid dans le répertoire des journaux (enregistre le de l'ancien et du nouveau <code> processus maître >ID). #🎜🎜#rrreee#🎜🎜#Envoyez le signal SIGWINCH à l'ancien processus maître et laissez l'ancien processus maître fermer l'ancien travailleur code>processus. #🎜🎜#rrreee#🎜🎜# Maintenant, visitez http://192.168.1.199/ et il répondra avec 404. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜# #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Lorsque vous visitez
#🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#Lorsque vous visitez http://192.168.1.199/nacos, vous accéderez au service Nacos. #🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜##🎜🎜#如果升级版本没有问题,就可以给旧master进程发送SIGQUIT信号,让旧master进程关闭,这样就只剩下新master进程和新worker进程,实现了Nginx的热部署。
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGQUIT 14964 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 15019 1 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15020 15019 0 23:18 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15034 1521 0 23:31 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
如果升级版本有问题,需要回滚到之前的版本,就可以给旧master进程发送SIGHUP信号,因为博主重新进行了测试,所以进程号都变了,但很显然旧master进程重新创建了旧worker进程,并且进行版本升级的master和worker进程没有被关闭。
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGHUP 15084 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 15084 1 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx root 15106 15084 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15107 15106 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process nobody 15131 15084 0 00:02 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15141 1521 0 00:09 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
给新master进程发送SIGQUIT信号,让新master进程关闭,这样就只剩下旧master进程和新创建的旧worker进程,实现了回滚。
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGQUIT 15106 [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep nginx root 15084 1 0 12月20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process ./nginx nobody 15131 15084 0 00:02 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 15159 1521 0 00:25 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
回滚成功。
还需要对版本回滚(即博主这里的配置文件回滚,不然下次重启就会出问题)。
[root@localhost conf]# cp -f nginx_old.conf nginx.conf cp:是否覆盖"nginx.conf"? y
为什么给旧master进程发送SIGHUP信号,旧master进程重新创建的worker进程没有重新读取配置文件?下面是官方的说明:
Send the HUP signal to the old master process. The old master process will start new worker processes without re-reading the configuration. After that, all new processes can be shut down gracefully, by sending the QUIT signal to the new master process.
向旧
master进程发送SIGHUP信号。旧master进程将启动新worker进程,而无需重新读取配置。之后,通过向新master进程发送SIGQUIT信号,所有新进程都可以正常关闭。
如果不存在新进程的情况下(只有一组master、worker进程),修改配置文件,再向master进程发送SIGHUP信号,看是否会重新加载配置文件。
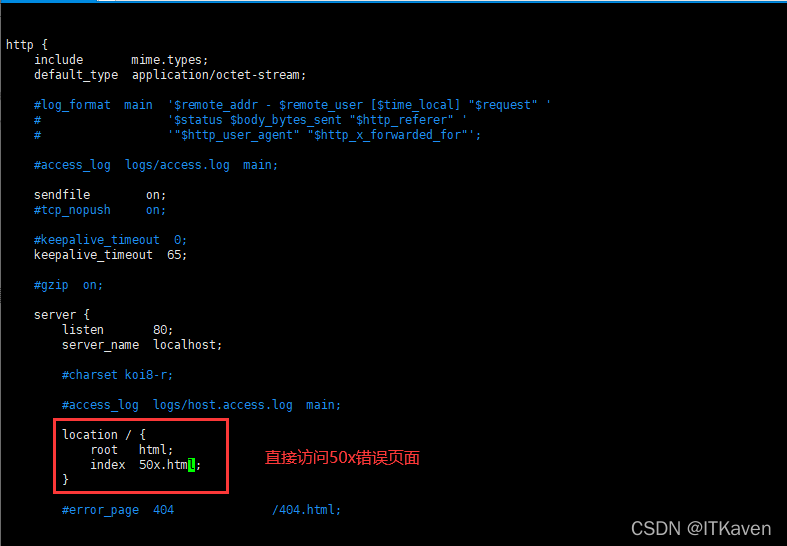
[root@localhost conf]# kill -s SIGHUP 15084
很显然配置文件被重新加载了,由于博主还没有看源码,只能猜测Nginx的实现(如果说错了,请大家评论补充),Nginx应该是根据当前是否在进行热部署(存在新master进程),来决定SIGHUP信号是否需要重新加载配置文件。
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment configurer le nom de domaine du serveur cloud dans nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Comment configurer le nom de domaine du serveur cloud dans nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Comment configurer un nom de domaine NGINX sur un serveur cloud: Créez un enregistrement A pointant vers l'adresse IP publique du serveur cloud. Ajoutez des blocs d'hôtes virtuels dans le fichier de configuration Nginx, en spécifiant le port d'écoute, le nom de domaine et le répertoire racine du site Web. Redémarrez Nginx pour appliquer les modifications. Accéder à la configuration du test de nom de domaine. Autres notes: Installez le certificat SSL pour activer HTTPS, assurez-vous que le pare-feu autorise le trafic Port 80 et attendez que la résolution DNS prenne effet.
 Comment vérifier la version nginx
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Comment vérifier la version nginx
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Les méthodes qui peuvent interroger la version Nginx sont: utilisez la commande nginx -v; Afficher la directive de version dans le fichier nginx.conf; Ouvrez la page d'erreur Nginx et affichez le titre de la page.
 Comment démarrer le serveur Nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Comment démarrer le serveur Nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Le démarrage d'un serveur Nginx nécessite différentes étapes en fonction des différents systèmes d'exploitation: Système Linux / Unix: Installez le package NGINX (par exemple, en utilisant Apt-Get ou Yum). Utilisez SystemCTL pour démarrer un service NGINX (par exemple, sudo systemctl start nginx). Système Windows: téléchargez et installez les fichiers binaires Windows. Démarrer Nginx à l'aide de l'exécutable Nginx.exe (par exemple, nginx.exe -c conf \ nginx.conf). Peu importe le système d'exploitation que vous utilisez, vous pouvez accéder au serveur IP
 Comment vérifier si Nginx est démarré
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Comment vérifier si Nginx est démarré
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Comment confirmer si Nginx est démarré: 1. Utilisez la ligne de commande: SystemCTl Status Nginx (Linux / Unix), netStat -ano | Findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Vérifiez si le port 80 est ouvert; 3. Vérifiez le message de démarrage NGINX dans le journal système; 4. Utilisez des outils tiers, tels que Nagios, Zabbix et Icinga.
 Comment vérifier le nom du conteneur Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Comment vérifier le nom du conteneur Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Vous pouvez interroger le nom du conteneur Docker en suivant les étapes: répertorier tous les conteneurs (Docker PS). Filtrez la liste des conteneurs (à l'aide de la commande grep). Obtient le nom du conteneur (situé dans la colonne "Noms").
 Comment exécuter nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
Comment exécuter nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
Pour faire en sorte que Nginx exécute Apache, vous devez: 1. Installez Nginx et Apache; 2. Configurer l'agent Nginx; 3. Démarrer Nginx et Apache; 4. Testez la configuration pour vous assurer que vous pouvez voir le contenu Apache après avoir accédé au nom de domaine. De plus, vous devez faire attention à d'autres questions telles que la correspondance du numéro de port, la configuration de l'hôte virtuel et les paramètres SSL / TLS.
 Comment créer un miroir dans Docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Comment créer un miroir dans Docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Étapes pour créer une image docker: écrivez un dockerfile qui contient les instructions de construction. Créez l'image dans le terminal, en utilisant la commande docker build. Marquez l'image et attribuez des noms et des balises à l'aide de la commande docker tag.
 Comment démarrer un conteneur par Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Comment démarrer un conteneur par Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Étapes de démarrage du conteneur Docker: Tirez l'image du conteneur: Exécutez "Docker Pull [Mirror Name]". Créer un conteneur: utilisez "Docker Create [Options] [Mirror Name] [Commandes et paramètres]". Démarrez le conteneur: exécutez "docker start [nom de conteneur ou id]". Vérifiez l'état du conteneur: vérifiez que le conteneur s'exécute avec "Docker PS".






