
CREATE TABLE `employees` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名', `age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '年龄', `position` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '职位', `hire_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '入职时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_name_age_position` (`name`,`age`,`position`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工记录表'; INSERT INTO employees(name,age,position,hire_time) VALUES('LiLei',22,'manager',NOW()); INSERT INTO employees(name,age,position,hire_time) VALUES('HanMeimei', 23,'dev',NOW()); INSERT INTO employees(name,age,position,hire_time) VALUES('Lucy',23,'dev',NOW()); ‐‐ 插入一些示例数据 drop procedure if exists insert_emp; delimiter ;; create procedure insert_emp() begin declare i int; set i=1; while(i<=100000)do insert into employees(name,age,position) values(CONCAT('zhuge',i),i,'dev'); set i=i+1; end while; end;; delimiter ; call insert_emp();
Comme ci-dessus, il existe une table employés, avec un index de clé primaire et un index conjoint (nom, âge, poste), employees 表,有主键索引和 (name, age, position ) 联合索引, 看下面的查询示例:
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

结论:联合索引第一个字段就用范围查找不会走索引,mysql内部可能觉得第一个字段就用范围,结果集应该很大,回表效率不高,还不如就全表扫描
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees force index(idx_name_age_position) WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

结论:虽然使用了强制走索引让联合索引第一个字段范围查找也走索引,扫描的行rows看上去也少了点,但是最终查找效率不一定比全表扫描高,因为回表效率不高, 一般不会使用这个手段,除非有证据能证明强制走索引后效率大幅度提高
EXPLAIN SELECT name,age,position FROM employees WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

将 select * 修改为 select name, age, posiion , 只选择索引中已经存在的列,可以不用回表,所以会利用索引
在表数据量比较大的情况会走索引,数据量不多的情况下会选择全表扫描,示例如下:
in 查询
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name in ('LiLei','HanMeimei','Lucy') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

用到全部索引 or 查询
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE (name = 'LiLei' or name = 'HanMeimei') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

用到全部索引
下面新建一张 employees_copy 表,结构和 employee 一样,但数据只有三条, 再执行上面两个查询
in 查询
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees_copy WHERE name in ('LiLei','HanMeimei','Lucy') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

全表扫描
or查询
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees_copy WHERE (name = 'LiLei' or name = 'HanMeimei') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

全表扫描
大表
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name like 'LiLei%' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

小表
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees_copy WHERE name like 'LiLei%' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';

可以看到,无论表的数据量大小,都会利用索引,为什么呢?
其实 like 用到了索引下推的优化
对于辅助联合索引,正常情况下按照最左前缀原则, SELECT * from employees where name like 'LiLei%' and age = 22 and position = 'dev' 这种情况下只会走name字段的索引,因为根据name字段过滤完,得到的索引行里的age和position是无序的,无法很好的利用索引。
在MySQL5.6之前的版本,这个查询只能在联合索引里匹配到名字是 'LiLei' 开头的索引,然后拿这些索引对应的主键逐个回表,到主键索引上找出相应的记录,再比对age和position这两个字段的值是否符合。
MySQL 5.6引入了索引下推优化,可以在索引遍历过程中,对索引中包含的所有字段先做判断,过滤掉不符合条件的记录之后再回表,可以有效的减少回表次数。使用了索引下推优化后,上面那个查询在联合索引里匹配到名字是 'LiLei' 开头的索引之后,同时还会在索引里过滤age和position这两个字段,拿着过滤完剩下的索引对应的主键id再回表查整行数据。
索引下推会减少回表次数,对于innodb引擎的表索引下推只能用于二级索引,innodb的主键索引(聚簇索引)树叶子节点上保存的是全行数据,所以这个时候索引下推并不会起到减少查询全行数据的效果。
估计应该是Mysql认为范围查找过滤的结果集过大,like KK%Regardez l'exemple de requête suivant :
mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; --开启trace mysql> select * from employees where name > 'a' order by position; mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;

Conclusion : utilisez une recherche par plage pour le premier champ de l'index conjoint et ne parcourez pas l'index. MySQL peut penser en interne que utilisez une plage pour le premier champ
. L'ensemble de résultats doit être très volumineux et l'efficacité du retour de la table n'est pas élevée. Il est préférable de scanner la table entière 🎜🎜Indexation forcée🎜{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": { //第一阶段:SQL准备阶段,格式化sql
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `employees`.`id` AS `id`,`employees`.`name` AS `name`,`employees`.`age` AS `age`,`employees`.`position` AS `position`,`employees`.`hire_time` AS `hire_time` from `employees` where (`employees`.`name` > 'a') order by `employees`.`position`"
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_preparation */
},
{
"join_optimization": { //第二阶段:SQL优化阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"condition_processing": { //条件处理
"condition": "WHERE",
"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')",
"steps": [
{
"transformation": "equality_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
},
{
"transformation": "constant_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
},
{
"transformation": "trivial_condition_removal",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
}
] /* steps */
} /* condition_processing */
},
{
"substitute_generated_columns": {
} /* substitute_generated_columns */
},
{
"table_dependencies": [ //表依赖详情
{
"table": "`employees`",
"row_may_be_null": false,
"map_bit": 0,
"depends_on_map_bits": [
] /* depends_on_map_bits */
}
] /* table_dependencies */
},
{
"ref_optimizer_key_uses": [
] /* ref_optimizer_key_uses */
},
{
"rows_estimation": [ //预估表的访问成本
{
"table": "`employees`",
"range_analysis": {
"table_scan": { //全表扫描情况
"rows": 10123, //扫描行数
"cost": 2054.7 //查询成本
} /* table_scan */,
"potential_range_indexes": [ //查询可能使用的索引
{
"index": "PRIMARY", //主键索引
"usable": false,
"cause": "not_applicable"
},
{
"index": "idx_name_age_position", //辅助索引
"usable": true,
"key_parts": [
"name",
"age",
"position",
"id"
] /* key_parts */
}
] /* potential_range_indexes */,
"setup_range_conditions": [
] /* setup_range_conditions */,
"group_index_range": {
"chosen": false,
"cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct"
} /* group_index_range */,
"analyzing_range_alternatives": { //分析各个索引使用成本
"range_scan_alternatives": [
{
"index": "idx_name_age_position",
"ranges": [
"a < name" //索引使用范围
] /* ranges */,
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": false, //使用该索引获取的记录是否按照主键排序
"using_mrr": false,
"index_only": false, //是否使用覆盖索引
"rows": 5061, //索引扫描行数
"cost": 6074.2, //索引使用成本
"chosen": false, //是否选择该索引
"cause": "cost"
}
] /* range_scan_alternatives */,
"analyzing_roworder_intersect": {
"usable": false,
"cause": "too_few_roworder_scans"
} /* analyzing_roworder_intersect */
} /* analyzing_range_alternatives */
} /* range_analysis */
}
] /* rows_estimation */
},
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
] /* plan_prefix */,
"table": "`employees`",
"best_access_path": { //最优访问路径
"considered_access_paths": [ //最终选择的访问路径
{
"rows_to_scan": 10123,
"access_type": "scan", //访问类型:为scan,全表扫描
"resulting_rows": 10123,
"cost": 2052.6,
"chosen": true, //确定选择
"use_tmp_table": true
}
] /* considered_access_paths */
} /* best_access_path */,
"condition_filtering_pct": 100,
"rows_for_plan": 10123,
"cost_for_plan": 2052.6,
"sort_cost": 10123,
"new_cost_for_plan": 12176,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_execution_plans */
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')",
"attached_conditions_computation": [
] /* attached_conditions_computation */,
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`employees`",
"attached": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
}
] /* attached_conditions_summary */
} /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */
},
{
"clause_processing": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"original_clause": "`employees`.`position`",
"items": [
{
"item": "`employees`.`position`"
}
] /* items */,
"resulting_clause_is_simple": true,
"resulting_clause": "`employees`.`position`"
} /* clause_processing */
},
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"steps": [
] /* steps */,
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`employees`",
"index_provides_order": false,
"order_direction": "undefined",
"index": "unknown",
"plan_changed": false
} /* index_order_summary */
} /* reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering */
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`employees`"
}
] /* refine_plan */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_optimization */
},
{
"join_execution": { //第三阶段:SQL执行阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
] /* steps */
} /* join_execution */
}
] /* steps */
}
// 结论:全表扫描的成本低于索引扫描,所以mysql最终选择全表扫描 🎜🎜 Conclusion : bien que l'indexation forcée soit utilisée pour que la première recherche de plage de champs de l'index conjoint utilise également l'index, et que les lignes analysées semblent être moindres, la L'efficacité de la recherche finale n'est pas nécessairement supérieure à l'analyse complète de la table, car l'efficacité du retour de la table n'est pas élevée, cette méthode n'est généralement pas utilisée à moins qu'il soit prouvé que l'efficacité est grandement améliorée après l'indexation forcée🎜🎜Optimisation de l'index de couverture🎜
🎜🎜 Conclusion : bien que l'indexation forcée soit utilisée pour que la première recherche de plage de champs de l'index conjoint utilise également l'index, et que les lignes analysées semblent être moindres, la L'efficacité de la recherche finale n'est pas nécessairement supérieure à l'analyse complète de la table, car l'efficacité du retour de la table n'est pas élevée, cette méthode n'est généralement pas utilisée à moins qu'il soit prouvé que l'efficacité est grandement améliorée après l'indexation forcée🎜🎜Optimisation de l'index de couverture🎜mysql> select * from employees where name > 'zzz' order by position; mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE; # 查看trace字段可知索引扫描的成本低于全表扫描,所以mysql最终选择索引扫描 mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; //关闭trace
 🎜🎜 Modifier
🎜🎜 Modifier select *</ code> pour <code>sélectionner le nom, l'âge, la position et sélectionner uniquement l'index. Les colonnes qui existent déjà dans la table n'ont pas besoin d'être renvoyées à la table, donc l'index sera utilisé🎜🎜dans et/ou être utilisé lorsque l'index est utilisé🎜🎜🎜Lorsque la quantité de données dans la table est relativement importante, l'index sera utilisé lorsque la quantité de données est faible, l'analyse complète de la table sera sélectionnée, les exemples sont les suivants. : 🎜🎜🎜🎜in query🎜🎜select * from employees limit 10000,10;
 🎜🎜utilisez tous les index 🎜ou requête🎜🎜
🎜🎜utilisez tous les index 🎜ou requête🎜🎜select * from employees where id > 90000 limit 5;
 🎜🎜Utilisez tous les index🎜🎜Créez une nouvelle table employés_copie ci-dessous. La structure est la même que celle de l'employé, mais il n'y a que trois éléments de données. Ensuite, exécutez les deux requêtes ci-dessus🎜🎜🎜dans la requête🎜🎜
🎜🎜Utilisez tous les index🎜🎜Créez une nouvelle table employés_copie ci-dessous. La structure est la même que celle de l'employé, mais il n'y a que trois éléments de données. Ensuite, exécutez les deux requêtes ci-dessus🎜🎜🎜dans la requête🎜🎜EXPLAIN select * from employees ORDER BY name limit 90000,5;
select * from employees e inner join (select id from employees order by name limit 90000,5) ed on e.id = ed.id;
 🎜🎜Analyse complète de la table🎜🎜 J'aime xx% utilise généralement l'indexation, cela n'a rien à voir avec la quantité de données🎜🎜Grande table🎜
🎜🎜Analyse complète de la table🎜🎜 J'aime xx% utilise généralement l'indexation, cela n'a rien à voir avec la quantité de données🎜🎜Grande table🎜CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_a` (`a`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
create table t2 like t1;
-- 插入一些示例数据
-- 往t1表插入1万行记录
drop procedure if exists insert_t1;
delimiter ;;
create procedure insert_t1()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=10000)do
insert into t1(a,b) values(i,i);
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call insert_t1();
-- 往t2表插入100行记录
drop procedure if exists insert_t2;
delimiter ;;
create procedure insert_t2()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=100)do
insert into t2(a,b) values(i,i);
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call insert_t2(); 🎜🎜Petite table🎜
🎜🎜Petite table🎜EXPLAIN select * from t1 inner join t2 on t1.a= t2.a;
 🎜🎜Vous pouvez voir que quelle que soit la taille des données dans le tableau, l'index sera utilisé. Pourquoi ? 🎜🎜En fait, comme utilise l'optimisation du pushdown d'index🎜🎜Pushdown d'index🎜🎜Pour l'index articulaire auxiliaire, dans des circonstances normales, selon le principe du préfixe le plus à gauche,
🎜🎜Vous pouvez voir que quelle que soit la taille des données dans le tableau, l'index sera utilisé. Pourquoi ? 🎜🎜En fait, comme utilise l'optimisation du pushdown d'index🎜🎜Pushdown d'index🎜🎜Pour l'index articulaire auxiliaire, dans des circonstances normales, selon le principe du préfixe le plus à gauche, SELECT * des employés dont le nom est comme 'LiLei%' et age = 22 et position = 'dev' Dans ce cas, seul l'index du champ nom sera utilisé, car après filtrage selon le champ nom, l'âge et la position dans la ligne d'index obtenue sont dans le désordre , et l'index ne peut pas être bien utilisé. 🎜🎜Dans les versions antérieures à MySQL5.6, cette requête ne peut faire correspondre que les index commençant par 'LiLei' dans l'index conjoint, puis renvoyer les clés primaires correspondant à ces index à la table une par une, pour l'index de clé primaire Recherchez l'enregistrement correspondant, puis comparez les valeurs des deux champs age et position pour voir si elles correspondent. 🎜🎜MySQL 5.6 introduit l'optimisation du pushdown d'index. Pendant le processus de parcours d'index, 🎜jugez d'abord tous les champs inclus dans l'index, filtrez les enregistrements qui ne remplissent pas les conditions, puis revenez à la table🎜, ce qui peut effectivement réduire le nombre. des retours de table. Après avoir utilisé l'optimisation du refoulement d'index, la requête ci-dessus correspond à l'index dont le nom commence par « LiLei » dans l'index conjoint, filtre également les deux champs d'âge et de position dans l'index, puis filtre les index restants. L'identifiant de clé primaire correspondant est. retourné à la table pour vérifier toute la ligne de données. 🎜🎜Le pushdown d'index réduira le nombre de retours de table. Le pushdown d'index de table du moteur innodb ne peut être utilisé que pour les index secondaires (index clusterisé) d'innodb stocke les données de ligne complètes sur les nœuds feuilles, donc à ce stade. Le refoulement de l'index temporel ne réduira pas le besoin d'interroger la ligne entière de données. 🎜🎜Pourquoi la recherche par plage n'est-elle pas optimisée avec le pushdown d'index ? 🎜🎜On estime que Mysql pense que l'ensemble de résultats de la recherche et du filtrage par plage est trop grand like KK% Dans la plupart des cas, l'ensemble de résultats filtré est relativement petit, donc ici Mysql choisit de donner like. L'optimisation de la baisse de l'index KK% est utilisée. Bien sûr, cela n'est pas absolu. Parfois, comme KK%, cela ne conduit pas à une baisse de l'index. 🎜🎜Comment choisir un index🎜🎜🎜Premièrement regardez les deux requêtes suivantes :🎜🎜
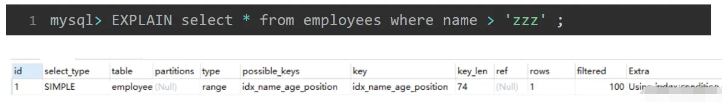
同样的表,同样的字段,因为条件的不同,选择的索引也不同,MySQL 是如何选择的呢?
MySQl 提供了一个工具,可以看到选择索引的计算过程, 用法如下:
mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; --开启trace mysql> select * from employees where name > 'a' order by position; mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;
下面是对 trace 字段的解析
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": { //第一阶段:SQL准备阶段,格式化sql
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `employees`.`id` AS `id`,`employees`.`name` AS `name`,`employees`.`age` AS `age`,`employees`.`position` AS `position`,`employees`.`hire_time` AS `hire_time` from `employees` where (`employees`.`name` > 'a') order by `employees`.`position`"
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_preparation */
},
{
"join_optimization": { //第二阶段:SQL优化阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"condition_processing": { //条件处理
"condition": "WHERE",
"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')",
"steps": [
{
"transformation": "equality_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
},
{
"transformation": "constant_propagation",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
},
{
"transformation": "trivial_condition_removal",
"resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
}
] /* steps */
} /* condition_processing */
},
{
"substitute_generated_columns": {
} /* substitute_generated_columns */
},
{
"table_dependencies": [ //表依赖详情
{
"table": "`employees`",
"row_may_be_null": false,
"map_bit": 0,
"depends_on_map_bits": [
] /* depends_on_map_bits */
}
] /* table_dependencies */
},
{
"ref_optimizer_key_uses": [
] /* ref_optimizer_key_uses */
},
{
"rows_estimation": [ //预估表的访问成本
{
"table": "`employees`",
"range_analysis": {
"table_scan": { //全表扫描情况
"rows": 10123, //扫描行数
"cost": 2054.7 //查询成本
} /* table_scan */,
"potential_range_indexes": [ //查询可能使用的索引
{
"index": "PRIMARY", //主键索引
"usable": false,
"cause": "not_applicable"
},
{
"index": "idx_name_age_position", //辅助索引
"usable": true,
"key_parts": [
"name",
"age",
"position",
"id"
] /* key_parts */
}
] /* potential_range_indexes */,
"setup_range_conditions": [
] /* setup_range_conditions */,
"group_index_range": {
"chosen": false,
"cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct"
} /* group_index_range */,
"analyzing_range_alternatives": { //分析各个索引使用成本
"range_scan_alternatives": [
{
"index": "idx_name_age_position",
"ranges": [
"a < name" //索引使用范围
] /* ranges */,
"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,
"rowid_ordered": false, //使用该索引获取的记录是否按照主键排序
"using_mrr": false,
"index_only": false, //是否使用覆盖索引
"rows": 5061, //索引扫描行数
"cost": 6074.2, //索引使用成本
"chosen": false, //是否选择该索引
"cause": "cost"
}
] /* range_scan_alternatives */,
"analyzing_roworder_intersect": {
"usable": false,
"cause": "too_few_roworder_scans"
} /* analyzing_roworder_intersect */
} /* analyzing_range_alternatives */
} /* range_analysis */
}
] /* rows_estimation */
},
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
] /* plan_prefix */,
"table": "`employees`",
"best_access_path": { //最优访问路径
"considered_access_paths": [ //最终选择的访问路径
{
"rows_to_scan": 10123,
"access_type": "scan", //访问类型:为scan,全表扫描
"resulting_rows": 10123,
"cost": 2052.6,
"chosen": true, //确定选择
"use_tmp_table": true
}
] /* considered_access_paths */
} /* best_access_path */,
"condition_filtering_pct": 100,
"rows_for_plan": 10123,
"cost_for_plan": 2052.6,
"sort_cost": 10123,
"new_cost_for_plan": 12176,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_execution_plans */
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')",
"attached_conditions_computation": [
] /* attached_conditions_computation */,
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`employees`",
"attached": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"
}
] /* attached_conditions_summary */
} /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */
},
{
"clause_processing": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"original_clause": "`employees`.`position`",
"items": [
{
"item": "`employees`.`position`"
}
] /* items */,
"resulting_clause_is_simple": true,
"resulting_clause": "`employees`.`position`"
} /* clause_processing */
},
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"steps": [
] /* steps */,
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`employees`",
"index_provides_order": false,
"order_direction": "undefined",
"index": "unknown",
"plan_changed": false
} /* index_order_summary */
} /* reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering */
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`employees`"
}
] /* refine_plan */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_optimization */
},
{
"join_execution": { //第三阶段:SQL执行阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
] /* steps */
} /* join_execution */
}
] /* steps */
}
// 结论:全表扫描的成本低于索引扫描,所以mysql最终选择全表扫描mysql> select * from employees where name > 'zzz' order by position; mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE; # 查看trace字段可知索引扫描的成本低于全表扫描,所以mysql最终选择索引扫描 mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; //关闭trace
order by 和 group by 也会遵循左前缀法则, 如下例子 :
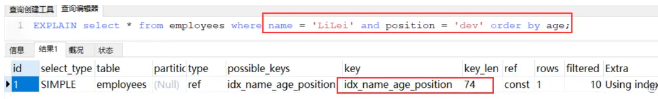
根据左前缀法则,用到了 name 字段的索引,同时使用 age 字段用来排序, 因为 extra 种没有 filesort
order by 或者 group by 用到的索引不会参与到 key_len 的计算,索引 key_len 仍然只是 74, 即 name字段的长度
再看下面一个例子:
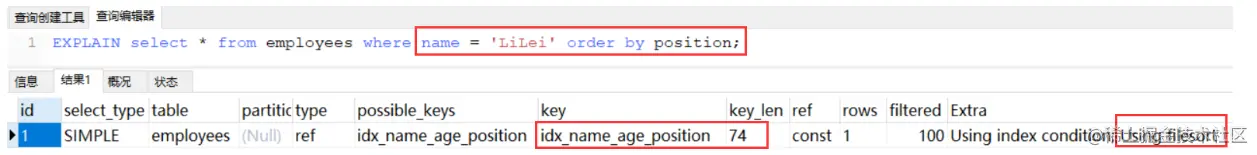
where 条件是name 排序字段是 position 跳过了age字段,所以只能用 name 索引,无法利用 position 索引进行索引排序,用到是文件排序
再看第三个例子:
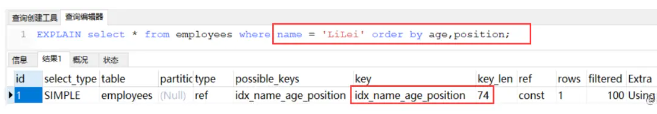
使用name条件查询, 同时使用 age position 双字段排序,没有跳过联合索引的字段. 所以可以用索引排序
然后颠倒一下排序顺序,先position 再 age:
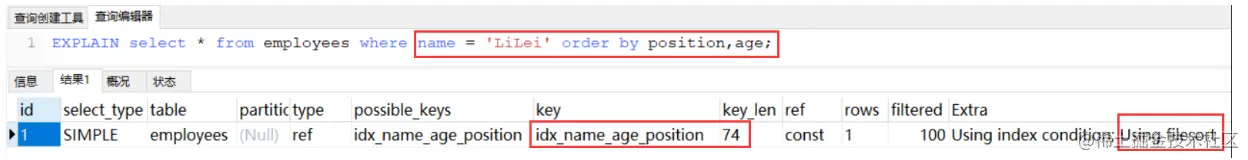
发现此时只能文件排序了
再看下面的例子
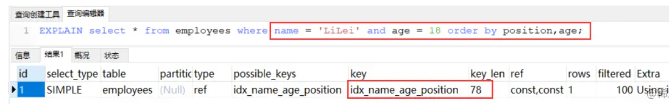
虽然排序字段与索引字段不一样,但仍然是索引排序, 因为查询条件中 用到是 (name, age)索引,排序中用到是 position 索引,并没有颠倒顺序。所以还是索引排序
如果一个正序一个倒序呢?
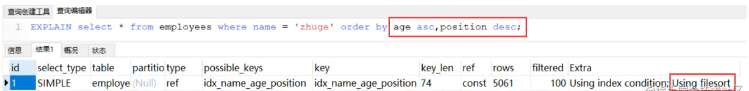
虽然排序字段与索引字段顺序相同, 但是 age 是正序, position 是倒叙,导致与索引的排序方式不同,无法利用索引。Mysql8及以上版本可以使用降序索引来支持文件排序。
先 in 查询:
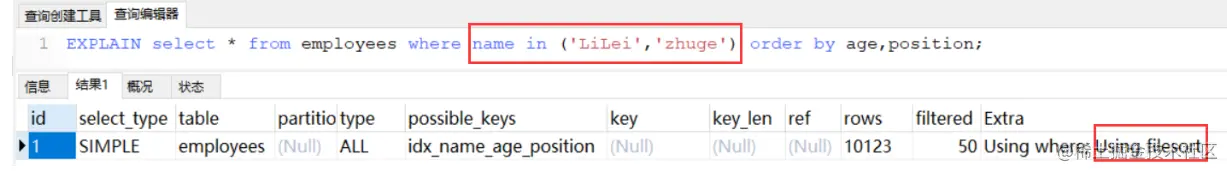
对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询, 无法利用索引排序
先范围查询:
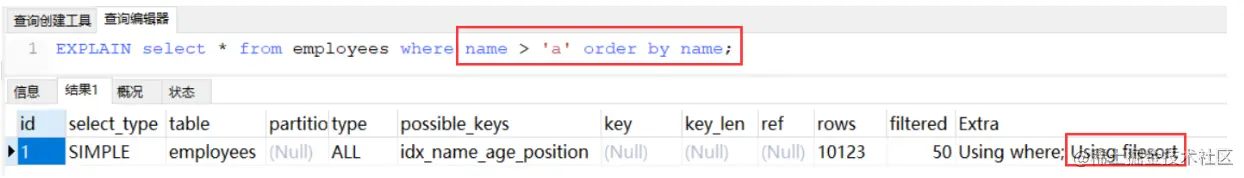
这里发生了全表扫描,没有任何索引,排序自然也无法利用索引了,可以使用覆盖索引优化:
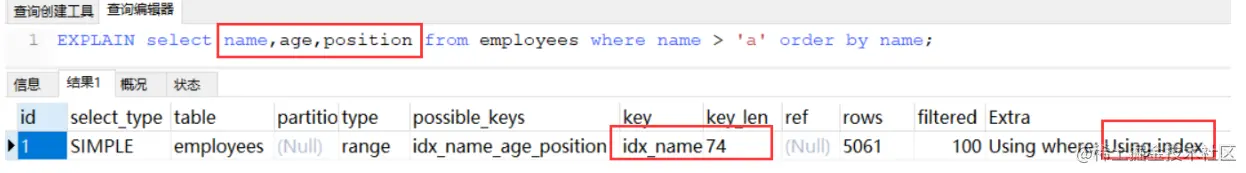
MySQL支持两种方式的排序filesort和index,Using index是指MySQL扫描索引本身完成排序。index效率高,filesort效率低。
2、order by满足两种情况会使用Using index。
order by语句使用索引最左前列。
使用where子句与order by子句条件列组合满足索引最左前列。
尽量在索引列上完成排序,遵循索引建立(索引创建的顺序)时的最左前缀法则。
如果order by的条件不在索引列上,就会产生Using filesort。
能用覆盖索引尽量用覆盖索引
group by与order by很类似,其实质是先排序后分组,遵照索引创建顺序的最左前缀法则。对于group by的优化如果不需要排序的可以加上order by null禁止排序。注意,where高于having,能写在where中的限定条件就不要去having限定了。
是一次性取出满足条件行的所有字段,然后在sort buffer中进行排序;用trace工具可以看到sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, additional_fields >或者< sort_key, packed_additional_fields >
是首先根据相应的条件取出相应的排序字段和可以直接定位行数据的行 ID,然后在 sort buffer 中进行排序,排序完后需要再次取回其它需要的字段;用trace工具可以看到sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, rowid >
MySQL 通过比较系统变量 max_length_for_sort_data(默认1024字节) 的大小和需要查询的字段总大小来判断使用哪种排序模式。
如果 字段的总长度小于max_length_for_sort_data ,那么使用 单路排序模式;
如果 字段的总长度大于max_length_for_sort_data ,那么使用 双路排序模·式。
有如下查询语句
select * from employees limit 10000,10;
该sql并不是只查询了10条,而是查找了10010条,然后把前10000条结果给舍弃掉, 因此要查询一个大表靠后的内容,执行效率是非常低的
上面的下面的sql语句没有指定排序方式,默认使用ID排序。当使用ID排序时,我们可以使用下面的优化。
select * from employees where id > 90000 limit 5;
如果id是连续自增的,和limit 90000,5 结果没有差别,是 90001 ~ 90005 的数据。
但是如果在90000之前删除了一条数据,结果就不一样了,id > 90000 limit 5 的结果是 90001 ~ 90005, 但是limit 90000, 5 的结果是 90002 ~ 90006, 很明显 90002 ~ 90006 才是符合我们直觉的。所以这个优化只能限制与排序条件是连续的。如果id不是自增的呢?会出现什么情况,假如 90000 这条数据有两个,limit 90000, 5 的结果是 90000 ~ 90004,而 id > 90000 limit 5 的结果仍是 90001 ~ 90005, 会把 id= 90000 的数据漏掉一条。
所以这个优化只能用于排序的字段是连续自增的,并且不能重复
有如下查询语句
EXPLAIN select * from employees ORDER BY name limit 90000,5;

发现并没有用上name的索引,因为 select * ,扫描联合索引时,无法的到全部数据,需要回表,成本比全表扫描更高,所以优化器放弃使用索引。
可以使用索引覆盖的方法,使用分页查询仅仅找到少量的主键,然后在使用主键查找整行数据, 如下:
select * from employees e inner join (select id from employees order by name limit 90000,5) ed on e.id = ed.id;
看下执行计划:
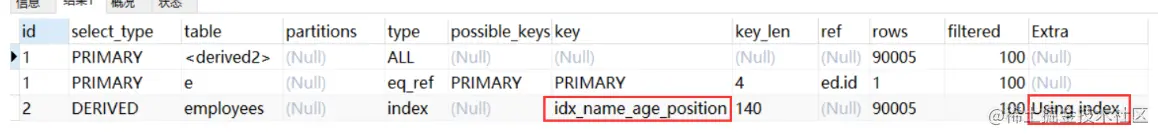
原 SQL 使用文件排序,优化后的使用索引排序
先造一些数据:
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_a` (`a`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
create table t2 like t1;
-- 插入一些示例数据
-- 往t1表插入1万行记录
drop procedure if exists insert_t1;
delimiter ;;
create procedure insert_t1()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=10000)do
insert into t1(a,b) values(i,i);
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call insert_t1();
-- 往t2表插入100行记录
drop procedure if exists insert_t2;
delimiter ;;
create procedure insert_t2()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=100)do
insert into t2(a,b) values(i,i);
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call insert_t2();新建 t1 t2 表,结构一样, 都在a字段上有索引,b字段没有索引,t1表有 10000 行记录,t2表只有100条记录。
内嵌循环连接算法 Nested-Loop Join
基于块的嵌套循环连接算法 Block Nested-Loop Join
一次一行循环地从第一张表(称为驱动表)中读取行,在这行数据中取到关联字段,根据关联字段在另一张表(被驱动表)里取出满足条件的行,然后取出两张表的结果合集。
一般关联字段有索引的时候使用这种算法, 示例:
EXPLAIN select * from t1 inner join t2 on t1.a= t2.a;
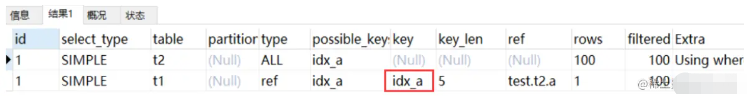
从执行计划中可以看到这些信息:
驱动表是 t2,被驱动表是 t1。先执行的就是驱动表;优化器一般会优先选择小表做驱动表,用where条件过滤完驱动表,然后再跟被驱动表做关联查询。所以使用 inner join 时,排在前面的表并不一定就是驱动表
当使用left join时,左表是驱动表,右表是被驱动表,当使用right join时,右表时驱动表,左表是被驱动表
使用了 NLJ算法。一般 join 语句中,如果执行计划 Extra 中未出现 Using join buffer 则表示使用的 join 算法是 NLJ。
上面sql的大致流程如下:
从表 t2 中读取一行数据(如果t2表有查询过滤条件的,用先用条件过滤完,再从过滤结果里取出一行数据);
从第 1 步的数据中,取出关联字段 a,到表 t1 中查找;
取出表 t1 中满足条件的行,跟 t2 中获取到的结果合并,作为结果返回给客户端;
重复上面 3 步。
整个过程会读取 t2 表的所有数据(扫描100行),然后遍历这每行数据中字段 a 的值,根据 t2 表中 a 的值索引扫描 t1 表中的对应行(扫描100次 t1 表的索引,1次扫描可以认为最终只扫描 t1 表一行完整数据,也就是总共 t1 表也扫描了100行)。因此整个过程扫描了 200 行
当关联字段没有没有索引的时候会使用这种算法
把驱动表的数据读入到 join_buffer 中,然后扫描被驱动表,把被驱动表每一行取出来跟 join_buffer 中的数据做对比。
如下:
EXPLAIN select * from t1 inner join t2 on t1.b= t2.b;
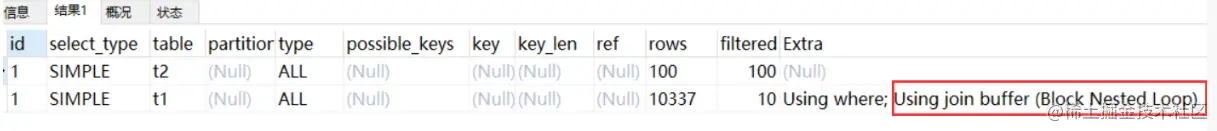
Extra 中 的Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)说明该关联查询使用的是 BNL 算法。
上面sql的大致流程如下:
把 t2 的所有数据放入到 join_buffer 中
把表 t1 中每一行取出来,跟 join_buffer 中的数据做对比
返回满足 join 条件的数据
整个过程对表 t1 和 t2 都做了一次全表扫描,因此扫描的总行数为10000(表 t1 的数据总量) + 100(表 t2 的数据总量) = 10100。并且 join_buffer 里的数据是无序的,因此对表 t1 中的每一行,都要做 100 次判断,所以内存中的判断次数是 100 * 10000= 100 万次。
这个例子里表 t2 才 100 行,要是表 t2 是一个大表,join_buffer 放不下怎么办呢?·
join_buffer 的大小是由参数 join_buffer_size 设定的,默认值是 256k。如果放不下表 t2 的所有数据话,策略很简单,就是分段放。
比如 t2 表有1000行记录, join_buffer 一次只能放800行数据,那么执行过程就是先往 join_buffer 里放800行记录,然后从 t1 表里取数据跟 join_buffer 中数据对比得到部分结果,然后清空 join_buffer ,再放入 t2 表剩余200行记录,再次从 t1 表里取数据跟 join_buffer 中数据对比。所以就多扫了一次 t1 表。
如果上面第二条sql使用 Nested-Loop Join,那么扫描行数为 100 * 10000 = 100万次,这个是磁盘扫描。
很显然,用BNL磁盘扫描次数少很多,相比于磁盘扫描,BNL的内存计算会快得多。
通常情况下,MySQL会采用 BNL 算法进行关联查询,当被驱动表的关联字段没有索引时。当存在索引时,使用NLJ算法可以获得比BNL算法更好的性能
关联字段加索引,让mysql做join操作时尽量选择NLJ算法,驱动表因为需要全部查询出来,所以过滤的条件也尽量要走索引,避免全表扫描,总之,能走索引的过滤条件尽量都走索引
小表驱动大表,写多表连接sql时如果明确知道哪张表是小表可以用straight_join写法固定连接驱动方式,省去mysql优化器自己判断的时间
straight_join解释:straight_join功能同join类似,但能让左边的表来驱动右边的表,能改表优化器对于联表查询的执行顺序。
比如:select * from t2 straight_join t1 on t2.a = t1.a; 代表指定mysql选着 t2 表作为驱动表。
straight_join只适用于inner join,并不适用于left join,right join。由于使用left join和right join已经明确了表的执行顺序
尽可能让优化器去判断,因为大部分情况下mysql优化器是比人要聪明的。使用straight_join一定要慎重,因为部分情况下人为指定的执行顺序并不一定会比优化引擎要靠谱。
在决定哪个表做驱动表的时候,应该是两个表按照各自的条件过滤,过滤完成之后,计算参与 join 的各个字段的总数据量,数据量小的那个表,就是“小表”,应该作为驱动表。不单单是表的总数据量
原则:小表驱动大表,即小的数据集驱动大的数据集
in:当B表的数据集小于A表的数据集时,in优于exists
select * from A where id in (select id from B)
#等价于:
for(select id from B){
select * from A where A.id = B.id
}exists:当A表的数据集小于B表的数据集时,exists优于in
将主查询A的数据,放到子查询B中做条件验证,根据验证结果(true或false)来决定主查询的数据是否保留
select * from A where exists (select 1 from B where B.id = A.id)
#等价于:
for(select * from A){
select * from B where B.id = A.id
}
#A表与B表的ID字段应建立索引EXISTS (subquery)只返回TRUE或FALSE,因此子查询中的SELECT * 也可以用SELECT 1替换,官方说法是实际执行时会忽略SELECT清单,因此没有区别
EXISTS子查询的实际执行过程可能经过了优化而不是我们理解上的逐条对比
EXISTS子查询往往也可以用JOIN来代替,何种最优需要具体问题具体分析
有下面四条查询语句:
EXPLAIN select count(1) from employees; EXPLAIN select count(id) from employees; EXPLAIN select count(name) from employees; EXPLAIN select count(*) from employees;
只有 count(字段名) 不会把该字段为null 计入总数
其实上面四条的查询计划都一样,效率上没有太大的差别

count(*)≈count(1)>count(字段)>count(主键 id)
字段有索引,count(字段)统计走二级索引,二级索引存储数据比主键索引少,所以count(字段)>count(主键 id)
count(*)≈count(1)>count(主键 id)>count(字段)
字段没有索引count(字段)统计走不了索引,count(主键 id)还可以走主键索引,所以count(主键 id)>count(字段)
count(1)跟count(字段)执行过程类似,不过count(1)不需要取出字段统计,就用常量1做统计,count(字段)还需要取出字段,所以理论上count(1)比count(字段)会快一点。
count(*) 是例外,mysql并不会把全部字段取出来,而是专门做了优化,不取值,按行累加,效率很高,所以不需要用count(列名)或count(常量)来替代 count(*)。
为什么对于count(id),mysql最终选择辅助索引而不是主键聚集索引?因为二级索引相对主键索引存储数据更少,检索性能应该更高,mysql内部做了点优化(应该是在5.7版本才优化)。
自己维护的总行数
show table status 如果只需要知道表总行数的估计值可以用如下sql查询,性能很高 show table status like 'employee'

将总数维护到Redis里 插入或删除表数据行的时候同时维护redis里的表总行数key的计数值(用incr或decr命令),但是这种方式可能不准,很难保证表操作和redis操作的事务一致性
索引设计原则:
1、代码先行,索引后上
等到主体业务功能开发完毕,把涉及到该表相关sql都要拿出来分析之后再建立索引。
2、联合索引尽量覆盖条件
比如可以设计一个或者两三个联合索引(尽量少建单值索引),让每一个联合索引都尽量去包含sql语句里的where、order by、group by的字段,还要确保这些联合索引的字段顺序尽量满足sql查询的最左前缀原则。
3、不要在小基数字段上建立索引
索引基数是指这个字段在表里总共有多少个不同的值,比如一张表总共100万行记录,其中有个性别字段,其值不是男就是女,那么该字段的基数就是2。
如果对这种小基数字段建立索引的话,还不如全表扫描了,因为你的索引树里就包含男和女两种值,根本没法进行快速的二分查找,那用索引就没有太大的意义了。
一般建立索引,尽量使用那些基数比较大的字段,就是值比较多的字段,那么才能发挥出B+树快速二分查找的优势来。
4、长字符串我们可以采用前缀索引
尽量对字段类型较小的列设计索引,比如说什么tinyint之类的,因为字段类型较小的话,占用磁盘空间也会比较小,此时你在搜索的时候性能也会比较好一点。
当然,这个所谓的字段类型小一点的列,也不是绝对的,很多时候你就是要针对varchar(255)这种字段建立索引,哪怕多占用一些磁盘空间也是有必要的。
对于这种varchar(255)的大字段可能会比较占用磁盘空间,可以稍微优化下,比如针对这个字段的前20个字符建立索引,就是说,对这个字段里的每个值的前20个字符放在索引树里,类似于 KEY index(name(20),age,position)
Lorsque vous effectuez une recherche dans la condition où, si vous effectuez une recherche en fonction du champ de nom, vous rechercherez d'abord dans l'arborescence d'index en fonction des 20 premiers caractères du champ de nom et localiserez le préfixe des 20 premiers caractères après la correspondance. les données partielles, revenez à l'index clusterisé pour extraire la valeur complète du champ de nom à des fins de comparaison.
Mais si vous commandez par nom, alors comme votre nom ne contient que les 20 premiers caractères de l'arborescence d'index, ce tri est impossible d'utiliser l'index. Il en va de même pour le groupe par
5 , Quand il y en a. un conflit entre où et trier par, la priorité est donnée à où
Lorsqu'il y a un conflit de conception d'index entre où et trier par, l'index doit-il être conçu pour où ou pour trier par ? Doit-on laisser Where utiliser l'index, ou doit-on laisser commander en utilisant l'index ?
Généralement, à l'heure actuelle, la condition Where est souvent utilisée pour utiliser l'index pour filtrer rapidement une partie des données spécifiées, puis trier. il.
Parce que dans la plupart des cas, le filtrage basé sur l'index peut souvent filtrer une petite partie des données souhaitées le plus rapidement possible, et le coût du tri peut alors être beaucoup plus faible.
Il existe une table d'employés avec des colonnes de nom, d'âge, de sexe, de poste et un index conjoint (nom, âge, sexe, poste),
sexe : Gender, la valeur est 0 ou 1
comme suit Requête : sélectionnez l'identifiant des employés où nom = 'zhangsan' et âge = 18 et position = 'dev' Le champ sexe étant ignoré, le poste ne peut pas utiliser l'indexselect id from employees where name = 'zhangsan' and age = 18 and position = 'dev' 因为跳过了 sex 字段,position 无法利用索引
因为 sex 只有两个取值,我们在查询语句上把 sex 的值全部枚举出来, 如下:
select id from employees where name = 'zhangsan' and age = 18 and sex in (0, 1) and position = 'dev'
这样一来就可以利用全部索引了。
加入我们要查询最近一周登录的用户,首先想到的是 last_login_time > {一周之前的时间}
car le sexe a seulement deux valeurs. , nous énumérons toutes les valeurs du sexe dans l'instruction de requête, comme suit :
sélectionnez l'identifiant des employés où nom = 'zhangsan' et âge = 18 et sexe dans (0, 1) et position = 'dev '🎜🎜De cette façon, vous pouvez utiliser tous les index. 🎜🎜Un autre exemple🎜🎜Si nous voulons interroger les utilisateurs qui se sont connectés la semaine dernière, la première chose qui nous vient à l'esprit est last_login_time > requête de plage, tout ce qui suit Le champ ne peut pas utiliser l'index. Nous pouvons concevoir un autre champ, recent_login_flag (tinyint) pour identifier si l'utilisateur s'est connecté récemment. Utilisez une tâche planifiée pour mettre à jour régulièrement la valeur de ce champ. De cette façon, la requête par plage devient une requête équivalente. Les données peuvent ne pas changer dans le temps, selon que l'entreprise le permet. 🎜🎜En bref, il s’agit de trouver des moyens de maximiser l’utilisation des index. 🎜Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 mysql modifier le nom de la table de données
mysql modifier le nom de la table de données
 MySQL crée une procédure stockée
MySQL crée une procédure stockée
 La différence entre MongoDB et MySQL
La différence entre MongoDB et MySQL
 Comment vérifier si le mot de passe MySQL est oublié
Comment vérifier si le mot de passe MySQL est oublié
 mysql créer une base de données
mysql créer une base de données
 niveau d'isolement des transactions par défaut de MySQL
niveau d'isolement des transactions par défaut de MySQL
 La différence entre sqlserver et mysql
La différence entre sqlserver et mysql
 mysqlmot de passe oublié
mysqlmot de passe oublié