Comment Docker utilise nginx pour créer un cluster Tomcat
Créez d'abord le dossier tomcat. Afin de faciliter la configuration de docker, je vais le créer directement dans le répertoire racine. Étape 1 : Créer le dossier : Dossier Release
mkdir -p /docker/tomcat/webapp8081 mkdir -p /docker/tomcat/webapp8082 mkdir -p /docker/tomcat/webapp8083
#🎜🎜. ##🎜 🎜#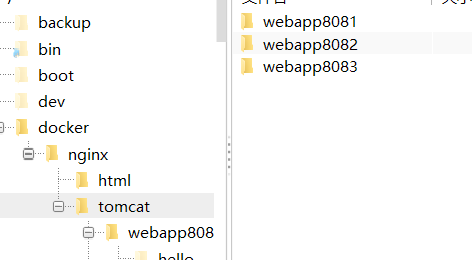 Étape 2 : Créez un conteneur Tomcat (le port peut être modifié en fonction de votre situation réelle)
Étape 2 : Créez un conteneur Tomcat (le port peut être modifié en fonction de votre situation réelle)
docker run -d --name tomcat8081 -p 8081:8080 -v /docker/tomcat/webapp8081:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ tomcat docker run -d --name tomcat8082 -p 8082:8080 -v /docker/tomcat/webapp8082:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ tomcat docker run -d --name tomcat8083 -p 8083:8080 -v /docker/tomcat/webapp8083:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ tomcat
Une fois la création terminée, utilisez la commande docker ps pour vérifier si la création est réussie et utilisez
# 🎜🎜#Étape 3 : Vérifiez l'adresse IP de Tomcat Utilisez la commande pour interroger ici Seul le premier exemple est utilisé#🎜🎜. #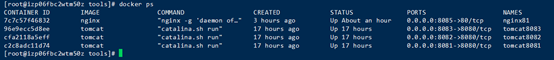
docker inspect tomcat8081</ code></p><p ><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/168526005746526.jpg" class="lazy" alt="Comment Docker utilise-t-il nginx pour créer un cluster Tomcat" /></p><p >Étape 4 : Afin de faciliter les tests, je ne téléchargerai pas le package war ici, mais créerai directement un hello/ index.html qu'il contient<code>docker inspect tomcat8081
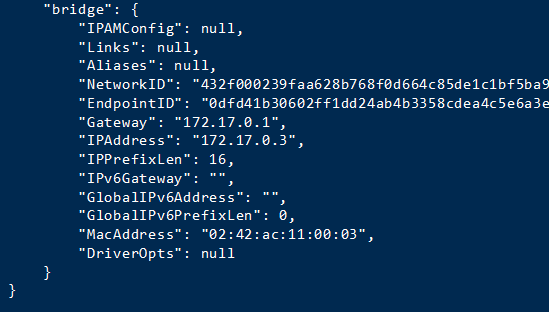
第四步:为了方便测试 我这里就不上传war包了,直接 在里面创建了一个hello/index.html 文件
注意:如果nginx为docker容器,必须使用tomact容器ip,否则连不上
首先在官网上下载nginx的官方版本
官网:
点击右边导航栏的download,进入下载界面 选择对应的版本 进行下载,我这里就使用nginx-1.6.2.tar
下载完成后,将文件放到自定义的文件夹,我这里放到/usr/local/tools/nginx-1.6.2

使用 这个命令将nginx 解压:
tar vxf nginx-1.6.2.tar.gz
 Remarque : Si nginx Pour le conteneur docker, vous devez utiliser l'ip du conteneur tomact, sinon vous ne pourrez pas vous connecter Téléchargez d'abord la version officielle de nginx sur le site officiel Site officiel : Cliquez sur Télécharger dans la barre de navigation de droite, entrez dans l'interface de téléchargement et sélectionnez la version correspondante à télécharger . J'utilise nginx-1.6.2.tar
Remarque : Si nginx Pour le conteneur docker, vous devez utiliser l'ip du conteneur tomact, sinon vous ne pourrez pas vous connecter Téléchargez d'abord la version officielle de nginx sur le site officiel Site officiel : Cliquez sur Télécharger dans la barre de navigation de droite, entrez dans l'interface de téléchargement et sélectionnez la version correspondante à télécharger . J'utilise nginx-1.6.2.tar Une fois le téléchargement terminé, placez le fichier dans un dossier personnalisé. Placez-le ici dans /usr/local/tools/nginx-1.6. 2
Une fois le téléchargement terminé, placez le fichier dans un dossier personnalisé. Placez-le ici dans /usr/local/tools/nginx-1.6. 2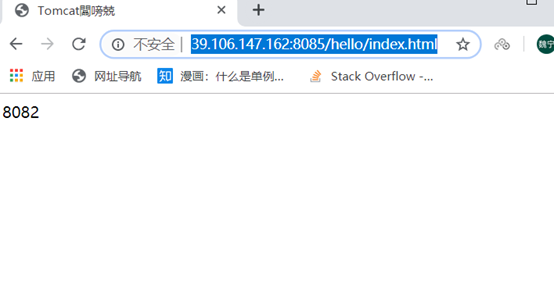
Utilisez cette commande pour décompresser nginx :
tar vxf nginx-1.6.2.tar .gz# 🎜🎜#Une fois la décompression terminée, je retourne dans le répertoire racine et crée un dossier hôte dans le répertoire racine. Le but est de créer des fichiers pour que nginx puisse être monté (vous pouvez aussi Définition)
. Créez le dossier hôte ici
mkdir -p /docker/nginx/ vim /docker/nginx/nginx.conf mkdir -p /docker/nginx/html
Copiez le index.html 50x.html dans le dossier html de negix que vous avez décompressé dans /docker/nginx/html Dans le dossier
, un Le fichier negix conf est fourni ici. Si vous ajoutez des commentaires, le format peut changer. N'oubliez pas de supprimer les commentaires
nginx.conf : #🎜🎜 #
user root;#. 🎜🎜#worker_processes 2; #Définissez votre nombre de threads ici
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数量
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
upstream mytomcat{
server 172.17.0.3:8080 weight=10;
# 另外mytomcat 这里名字和下方的名字保持一致 这里需要和你的tomcat ip保持一致
server 172.17.0.4:8080 weight=50;
server 172.17.0.5:8080 weight=10;
}
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name mytomcat;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
proxy_connect_timeout 50;
proxy_read_timeout 10;
proxy_send_timeout 20;
proxy_pass http://mytomcat;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the php scripts to apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the php scripts to fastcgi server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param script_filename /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of ip-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# https server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:ssl:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers high:!anull:!md5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}Créez et exécutez le conteneur#🎜🎜 #
81 : C'est le port pour l'accès au réseau externe. Celui-ci peut être modifié en fonction de la situation réelle /docker/nginx/nginx.conf fichier hôte local
/docker/nginx/nginx.conf fichier hôte local
docker run -d --name nginx81 -p 81:80 -v /docker/nginx/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf -v /docker/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html nginx
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Enseignement du nœud PI: Qu'est-ce qu'un nœud PI? Comment installer et configurer le nœud PI?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Enseignement du nœud PI: Qu'est-ce qu'un nœud PI? Comment installer et configurer le nœud PI?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Explication détaillée et guide d'installation pour les nœuds de pignon Cet article introduira l'écosystème de pignon en détail - nœuds PI, un rôle clé dans l'écosystème de pignon et fournir des étapes complètes pour l'installation et la configuration. Après le lancement du réseau de test de la blockchain pèse, les nœuds PI sont devenus une partie importante de nombreux pionniers participant activement aux tests, se préparant à la prochaine version du réseau principal. Si vous ne connaissez pas encore Pinetwork, veuillez vous référer à ce qu'est Picoin? Quel est le prix de l'inscription? PI Utilisation, exploitation minière et sécurité. Qu'est-ce que Pinetwork? Le projet Pinetwork a commencé en 2019 et possède sa pièce exclusive de crypto-monnaie PI. Le projet vise à en créer un que tout le monde peut participer
 Comment installer Deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
Comment installer Deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
Il existe de nombreuses façons d'installer Deepseek, notamment: Compiler à partir de Source (pour les développeurs expérimentés) en utilisant des packages précompilés (pour les utilisateurs de Windows) à l'aide de conteneurs Docker (pour le plus pratique, pas besoin de s'inquiéter de la compatibilité), quelle que soit la méthode que vous choisissez, veuillez lire Les documents officiels documentent soigneusement et les préparent pleinement à éviter des problèmes inutiles.
 Déployer des applications JavaEE à l'aide de conteneurs Docker
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:29 PM
Déployer des applications JavaEE à l'aide de conteneurs Docker
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:29 PM
Déployez des applications Java EE à l'aide de conteneurs Docker : créez un fichier Docker pour définir l'image, créez l'image, exécutez le conteneur et mappez le port, puis accédez à l'application dans le navigateur. Exemple d'application JavaEE : l'API REST interagit avec la base de données, accessible sur localhost après déploiement via Docker.
 Comment utiliser PHP CI/CD pour itérer rapidement ?
May 08, 2024 pm 10:15 PM
Comment utiliser PHP CI/CD pour itérer rapidement ?
May 08, 2024 pm 10:15 PM
Réponse : Utilisez PHPCI/CD pour réaliser une itération rapide, y compris la configuration de pipelines CI/CD, de tests automatisés et de processus de déploiement. Configurer un pipeline CI/CD : sélectionnez un outil CI/CD, configurez le référentiel de code et définissez le pipeline de build. Tests automatisés : rédigez des tests unitaires et d'intégration et utilisez des frameworks de test pour simplifier les tests. Cas pratique : Utilisation de TravisCI : Installez TravisCI, définissez le pipeline, activez le pipeline et visualisez les résultats. Mettez en œuvre la livraison continue : sélectionnez les outils de déploiement, définissez les pipelines de déploiement et automatisez le déploiement. Avantages : améliorez l’efficacité du développement, réduisez les erreurs et raccourcissez les délais de livraison.
 Comment installer l'extension Docker dans vscode Étapes pour installer l'extension Docker dans vscode
May 09, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
Comment installer l'extension Docker dans vscode Étapes pour installer l'extension Docker dans vscode
May 09, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
1. Tout d'abord, après avoir ouvert l'interface, cliquez sur le bouton icône d'extension à gauche 2. Ensuite, recherchez l'emplacement de la barre de recherche dans la page d'extension ouverte 3. Ensuite, entrez le mot Docker avec la souris pour trouver le plug-in d'extension 4. . Enfin, sélectionnez le plug-in cible et cliquez à droite. Cliquez simplement sur le bouton d'installation dans le coin inférieur.
 L'accès au fichier du site WordPress est restreint: pourquoi mon fichier .txt n'est-il pas accessible via le nom de domaine?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
L'accès au fichier du site WordPress est restreint: pourquoi mon fichier .txt n'est-il pas accessible via le nom de domaine?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
L'accès au fichier du site WordPress est restreint: dépannage de la raison pour laquelle le fichier .txt ne peut pas être accessible récemment. Certains utilisateurs ont rencontré un problème lors de la configuration du nom de domaine commercial du programme MINI: � ...
 Pourquoi une erreur se produit-elle lors de l'installation d'une extension à l'aide de PECL dans un environnement Docker? Comment le résoudre?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Pourquoi une erreur se produit-elle lors de l'installation d'une extension à l'aide de PECL dans un environnement Docker? Comment le résoudre?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes et solutions pour les erreurs Lors de l'utilisation de PECL pour installer des extensions dans un environnement Docker Lorsque nous utilisons un environnement Docker, nous rencontrons souvent des maux de tête ...
 Comment faire coexister PHP5.6 et PHP7 via la configuration Nginx sur le même serveur?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
Comment faire coexister PHP5.6 et PHP7 via la configuration Nginx sur le même serveur?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
Exécuter plusieurs versions PHP simultanément dans le même système est une exigence commune, en particulier lorsque différents projets dépendent de différentes versions de PHP. Comment être sur la même chose ...






