 développement back-end
développement back-end
 Tutoriel Python
Tutoriel Python
 Vous apprendre étape par étape comment utiliser Flask pour créer un moteur de recherche ES (partie préparatoire)
Vous apprendre étape par étape comment utiliser Flask pour créer un moteur de recherche ES (partie préparatoire)
Vous apprendre étape par étape comment utiliser Flask pour créer un moteur de recherche ES (partie préparatoire)
/1 Préface/
Elasticsearch est un moteur de recherche open source, construit sur une bibliothèque de moteurs de recherche en texte intégral Apache Lucene™ Basé sur les bases.

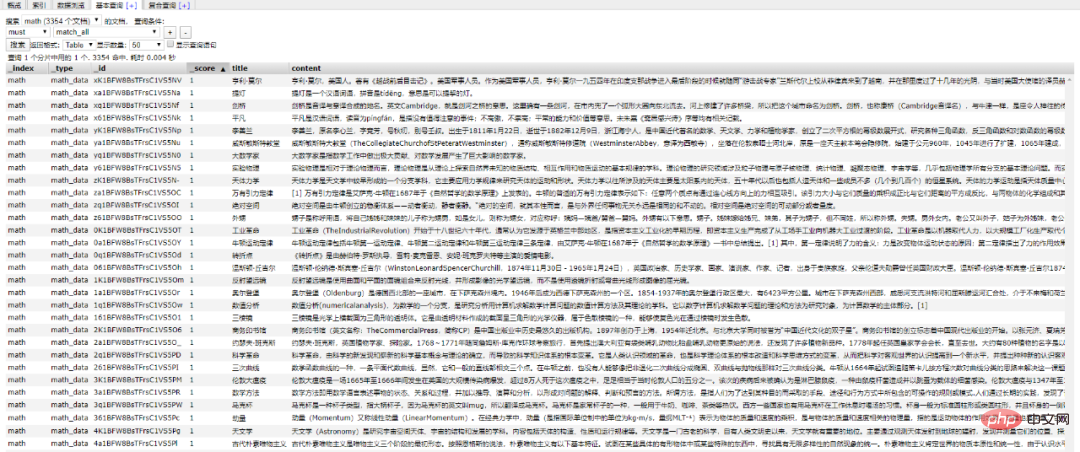
Elasticsearch et Python l'amarrage de est devenu une préoccupation pour nous (pourquoi avons-nous pour tout connecter ? /2 Interaction Python/ Donc, Python Il fournit également des bibliothèques de dépendances qui peuvent être connectées à Elasticsearch . Initialise une connexion à un objet d'opération Elasticsearch . Le port par défaut est 9200 Veuillez vous assurer que l'environnement local de Elasticsearch a été configuré avant l'initialisation. Obtenez les données du document en fonction de l'ID 插入文档数据 搜索文档数据 删除文档数据 好啊,封装 search 类也是为了方便调用,整体贴一下。 尝试一下把 Mongodb 中的数据插入到 ES 中。 到 ES 中查看一下,启动 elasticsearch-head 插件。 如果是 npm 安装的那么 cd 到根目录之后直接 npm run start 就跑起来了。 本地访问 http://localhost:9100/ 发现新加的 spider 数据文档确实已经进去了。 /3 爬虫入库/ 要想实现 ES 搜索,首先要有数据支持,而海量的数据往往来自爬虫。 为了节省时间,编写一个最简单的爬虫,抓取 百度百科。 简单粗暴一点,先 递归获取 很多很多的 url 链接 把全部 url 存到 url.txt 文件中之后,然后启动任务。 run.py 飞起来 黑窗口键入 哦豁 !! 你居然使用了 Celery 任务队列,gevent 模式,-c 就是10个线程刷刷刷就干起来了,速度杠杠的 !! 啥?分布式? 那就加多几台机器啦,直接把代码拷贝到目标服务器,通过 redis 共享队列协同多机抓取。 这里是先将数据存储到了 MongoDB 上(个人习惯),你也可以直接存到 ES 中,但是单条单条的插入速度堪忧(接下来会讲到优化,哈哈)。 使用前面的例子将 Mongo 中的数据批量导入到 ES 中,OK !!! 到这一个简单的数据抓取就已经完毕了。 好啦,现在 ES 中已经有了数据啦,接下来就应该是 Flask web 的操作啦,当然,Django,FastAPI 也很优秀。嘿嘿,你喜欢 !! 关于FastAPI 的文章可以看这个系列文章: 1、(入门篇)简析Python web框架FastAPI——一个比Flask和Tornada更高性能的API 框架 2、(进阶篇)Python web框架FastAPI——一个比Flask和Tornada更高性能的API 框架 3、(完结篇)Python web框架FastAPI——一个比Flask和Tornada更高性能的API 框架 /4 Flask 项目结构/ 这样一来前期工作就差不多了,接下来剩下的工作主要集中于 Flask 的实际开发中,蓄力中 !!pip install elasticsearch
def __init__(self, index_type: str, index_name: str, ip="127.0.0.1"):
# self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=('username', 'password'), port=9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch("localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_namedef get_doc(self, uid):
return self.es.get(index=self.index_name, id=uid)def insert_one(self, doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)
def insert_array(self, docs: list):
for doc in docs:
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)def search(self, query, count: int = 30):
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": ["title", "content", "link"]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=dsl, size=count)
return match_data
def __search(self, query: dict, count: int = 20): # count: 返回的数据大小
results = []
params = {
'size': count
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=query, params=params)
for hit in match_data['hits']['hits']:
results.append(hit['_source'])
return resultsdef delete_index(self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
except:
passfrom elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
class elasticSearch():
def __init__(self, index_type: str, index_name: str, ip="127.0.0.1"):
# self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=('elastic', 'password'), port=9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch("localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_name
def create_index(self):
if self.es.indices.exists(index=self.index_name) is True:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
self.es.indices.create(index=self.index_name, ignore=400)
def delete_index(self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
except:
pass
def get_doc(self, uid):
return self.es.get(index=self.index_name, id=uid)
def insert_one(self, doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)
def insert_array(self, docs: list):
for doc in docs:
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)
def search(self, query, count: int = 30):
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": ["title", "content", "link"]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=dsl, size=count)
return match_dataimport json
from datetime import datetime
import pymongo
from app.elasticsearchClass import elasticSearch
client = pymongo.MongoClient('127.0.0.1', 27017)
db = client['spider']
sheet = db.get_collection('Spider').find({}, {'_id': 0, })
es = elasticSearch(index_type="spider_data",index_name="spider")
es.create_index()
for i in sheet:
data = {
'title': i["title"],
'content':i["data"],
'link': i["link"],
'create_time':datetime.now()
}
es.insert_one(doc=data)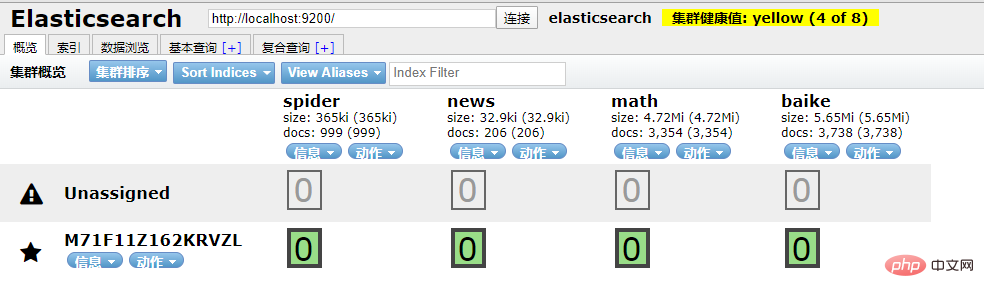
import requests
import re
import time
exist_urls = []
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/62.0.3202.62 Safari/537.36',
}
def get_link(url):
try:
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = 'UTF-8'
html = response.text
link_lists = re.findall('.*?<a target=_blank href="/item/([^:#=<>]*?)".*?</a>', html)
return link_lists
except Exception as e:
pass
finally:
exist_urls.append(url)
# 当爬取深度小于10层时,递归调用主函数,继续爬取第二层的所有链接
def main(start_url, depth=1):
link_lists = get_link(start_url)
if link_lists:
unique_lists = list(set(link_lists) - set(exist_urls))
for unique_url in unique_lists:
unique_url = 'https://baike.baidu.com/item/' + unique_url
with open('url.txt', 'a+') as f:
f.write(unique_url + '\n')
f.close()
if depth < 10:
main(unique_url, depth + 1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_url = 'https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%99%BE%E5%BA%A6%E7%99%BE%E7%A7%91'
main(start_url)# parse.py
from celery import Celery
import requests
from lxml import etree
import pymongo
app = Celery('tasks', broker='redis://localhost:6379/2')
client = pymongo.MongoClient('localhost',27017)
db = client['baike']
@app.task
def get_url(link):
item = {}
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/34.0.1847.131 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(link,headers=headers)
res.encoding = 'UTF-8'
doc = etree.HTML(res.text)
content = doc.xpath("//div[@class='lemma-summary']/div[@class='para']//text()")
print(res.status_code)
print(link,'\t','++++++++++++++++++++')
item['link'] = link
data = ''.join(content).replace(' ', '').replace('\t', '').replace('\n', '').replace('\r', '')
item['data'] = data
if db['Baike'].insert(dict(item)):
print("is OK ...")
else:
print('Fail')from parse import get_url
def main(url):
result = get_url.delay(url)
return result
def run():
with open('./url.txt', 'r') as f:
for url in f.readlines():
main(url.strip('\n'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()celery -A parse worker -l info -P gevent -c 10

Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment créer des applications Web simples et faciles à utiliser avec React et Flask
Sep 27, 2023 am 11:09 AM
Comment créer des applications Web simples et faciles à utiliser avec React et Flask
Sep 27, 2023 am 11:09 AM
Comment utiliser React et Flask pour créer des applications Web simples et faciles à utiliser Introduction : Avec le développement d'Internet, les besoins des applications Web deviennent de plus en plus diversifiés et complexes. Afin de répondre aux exigences des utilisateurs en matière de facilité d'utilisation et de performances, il devient de plus en plus important d'utiliser des piles technologiques modernes pour créer des applications réseau. React et Flask sont deux frameworks très populaires pour le développement front-end et back-end, et ils fonctionnent bien ensemble pour créer des applications Web simples et faciles à utiliser. Cet article détaillera comment exploiter React et Flask
 Partez de zéro et vous guidez étape par étape pour installer Flask et créer rapidement un blog personnel
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
Partez de zéro et vous guidez étape par étape pour installer Flask et créer rapidement un blog personnel
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
En partant de zéro, je vais vous apprendre étape par étape comment installer Flask et créer rapidement un blog personnel. En tant que personne qui aime écrire, il est très important d'avoir un blog personnel. En tant que framework Web Python léger, Flask peut nous aider à créer rapidement un blog personnel simple et entièrement fonctionnel. Dans cet article, je vais repartir de zéro et vous apprendre étape par étape comment installer Flask et créer rapidement un blog personnel. Étape 1 : Installer Python et pip Avant de commencer, nous devons d'abord installer Python et pi
 Django vs Flask : une analyse comparative des frameworks Web Python
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs Flask : une analyse comparative des frameworks Web Python
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django et Flask sont tous deux leaders dans les frameworks Web Python, et ils ont tous deux leurs propres avantages et scénarios applicables. Cet article procédera à une analyse comparative de ces deux frameworks et fournira des exemples de code spécifiques. Introduction au développement Django est un framework Web complet, son objectif principal est de développer rapidement des applications Web complexes. Django fournit de nombreuses fonctions intégrées, telles que ORM (Object Relational Mapping), formulaires, authentification, backend de gestion, etc. Ces fonctionnalités permettent à Django de gérer de grandes
 Guide d'installation du framework Flask : étapes détaillées pour vous aider à installer Flask correctement
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:51 PM
Guide d'installation du framework Flask : étapes détaillées pour vous aider à installer Flask correctement
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:51 PM
Tutoriel d'installation du framework Flask : vous apprendrez étape par étape comment installer correctement le framework Flask. Des exemples de code spécifiques sont requis. Introduction : Flask est un framework de développement Web Python simple et flexible. Il est facile à apprendre, facile à utiliser et doté de fonctionnalités puissantes. Cet article vous guidera étape par étape pour installer correctement le framework Flask et fournira des exemples de code détaillés pour référence. Étape 1 : installer Python Avant d'installer le framework Flask, vous devez d'abord vous assurer que Python est installé sur votre ordinateur. Vous pouvez commencer à partir de P
 Intégration Flask et Intellij IDEA : conseils de développement d'applications Web Python (partie 2)
Jun 17, 2023 pm 01:58 PM
Intégration Flask et Intellij IDEA : conseils de développement d'applications Web Python (partie 2)
Jun 17, 2023 pm 01:58 PM
La première partie présente l'intégration de base de Flask et d'Intellij IDEA, les paramètres du projet et de l'environnement virtuel, l'installation des dépendances, etc. Nous continuerons ensuite à explorer d'autres conseils de développement d'applications Web Python pour créer un environnement de travail plus efficace : Utiliser FlaskBlueprintsFlaskBlueprints vous permet d'organiser le code de votre application pour une gestion et une maintenance plus faciles. Blueprint est un module Python qui regroupe
 Flask vs FastAPI : le meilleur choix pour un développement efficace d'API Web
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
Flask vs FastAPI : le meilleur choix pour un développement efficace d'API Web
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
FlaskvsFastAPI : Le meilleur choix pour un développement efficace de WebAPI Introduction : Dans le développement de logiciels modernes, WebAPI est devenu un élément indispensable. Ils fournissent des données et des services qui permettent la communication et l'interopérabilité entre différentes applications. Lors du choix d'un framework pour développer WebAPI, Flask et FastAPI sont deux choix qui ont beaucoup retenu l'attention. Les deux frameworks sont très populaires et chacun présente ses propres avantages. Dans cet article, nous examinerons Fl
 Créez des applications Web interactives de visualisation de données à l'aide de Flask et de D3.js.
Jun 17, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Créez des applications Web interactives de visualisation de données à l'aide de Flask et de D3.js.
Jun 17, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Ces dernières années, l’analyse et la visualisation des données sont devenues des compétences indispensables dans de nombreux secteurs et domaines. Il est très important pour les analystes de données et les chercheurs de présenter de grandes quantités de données aux utilisateurs et de permettre à ces derniers de comprendre la signification et les caractéristiques des données grâce à la visualisation. Pour répondre à ce besoin, il est devenu courant d'utiliser D3.js pour créer des visualisations de données interactives dans des applications Web. Dans cet article, nous verrons comment créer des visualisations de données interactives pour le Web à l'aide de Flask et D3.js.
 Flask-RESTful et Swagger : meilleures pratiques pour créer des API RESTful dans les applications Web Python (partie 2)
Jun 17, 2023 am 10:39 AM
Flask-RESTful et Swagger : meilleures pratiques pour créer des API RESTful dans les applications Web Python (partie 2)
Jun 17, 2023 am 10:39 AM
Flask-RESTful et Swagger : meilleures pratiques pour créer des API RESTful dans des applications Web Python (partie 2) Dans l'article précédent, nous avons exploré les meilleures pratiques pour créer des API RESTful à l'aide de Flask-RESTful et Swagger. Nous avons présenté les bases du framework Flask-RESTful et montré comment utiliser Swagger pour créer la documentation d'une API RESTful. Livre





