Le programme Java ouvre l'invite de commande et insère la commande
Cet article utilise différentes approches pour sélectionner les commandes insérées dans le fichier ouvert fenêtre de commande via le code Java. La fenêtre de commande est ouverte en utilisant 'cmd'. Ici, les méthodes pour faire de même sont spécifiées à l'aide du code Java. est d'abord ouvert à l'aide du programme Java. Il est ouvert en tant que processus enfant si le programme Java. est exécuté dans une fenêtre cmd existante, une autre est ouverte en tant que nouveau processus. différents types de commandes sont insérés et exécutés dans cette fenêtre de commande ouverte via du code Java.
Ces programmes ne peuvent pas fonctionner dans des environnements de programmation en ligne. Les détails sur la façon d'exécuter ces programmes à l'aide des commandes javac et java sont détaillés dans la section de sortie de cet article.
Algorithme
Étape 1 - Ouvrez la fenêtre CMD en utilisant le code Java.
Étape 2 - Sélectionnez la commande à exécuter. La commande sélectionnée est utilisée comme chaîne de texte.
.
Étape 3 - Exécutez la commande sélectionnée dans la fenêtre CMD ouverte via le programme Java.
Étape 4 − Vérifiez les résultats.
Plusieurs méthodes
Pour ces programmes, la sélection des commandes se fait via deux méthodes différentes.
En utilisant des commandes qui modifient la propriété de la fenêtre cmd.
En utilisant des commandes exécutables
Voyons le programme ainsi que sa sortie un par un.
Tout d'abord, le code java est donné pour démarrer la nouvelle fenêtre CMD.
Java Code (pour démarrer la nouvelle fenêtre CMD)
public class cmdprog1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try{
// cmd is a command that opens the command window
//CMD /C is used to run commands and then terminate the existing window while CMD /K will run the command and then it returns you to the given prompt. Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[] {"cmd", "/K", "Start"});
// the following line can also be used.....
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[] {"cmd", "/C", "Start"});
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
}
}
Sortie
C:\java\javaprgstu>javac cmdprog1.java C:\java\javaprgstu>java cmdprog1 Opening cmd window C:\java\javaprgstu>
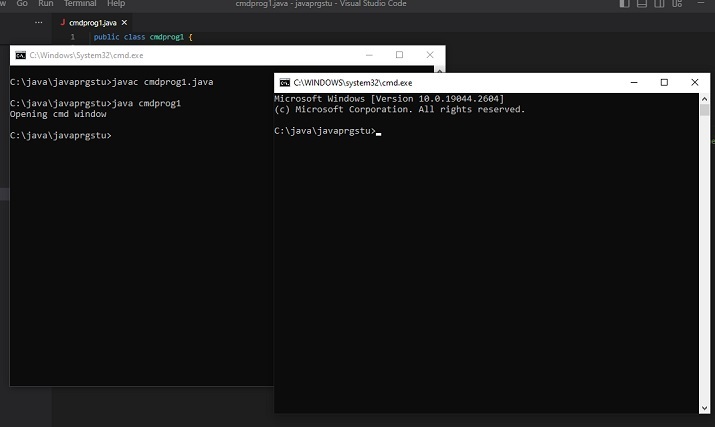
Méthode 1 : en utilisant la commande pour modifier les propriétés de la fenêtre cmd.
Dans cette approche, deux exemples différents sont utilisés.
Exemple 1 : Changez le titre lors de l'ouverture de la fenêtre CMD.
Exemple 2 : modifiez les couleurs d'arrière-plan et de premier plan lors de l'ouverture de la fenêtre CMD.
Exemple 1 : changez le titre lors de l'ouverture de la fenêtre CMD.
Programme
public class cmdprog22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command_to_playwith =" title 'The New Title of the New Command Window' ";
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try {
String command = "cmd /c" + " start" + command_to_playwith;
//Starting the new child process
Process childprocess11 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
System.out.println("The child process is Alive: " + childprocess11.isAlive());
System.out.println();
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
}
}
Sortie
C:\java\javaprgstu>javac cmdprog22.java C:\java\javaprgstu>java cmdprog22 Opening cmd window The child process is Alive: true
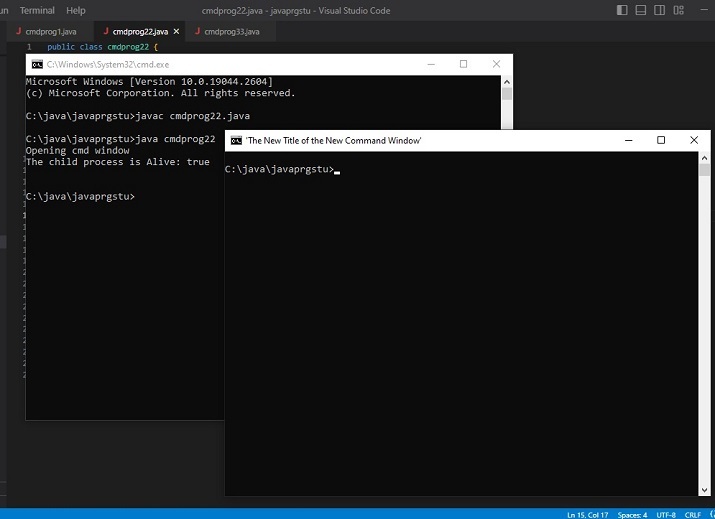
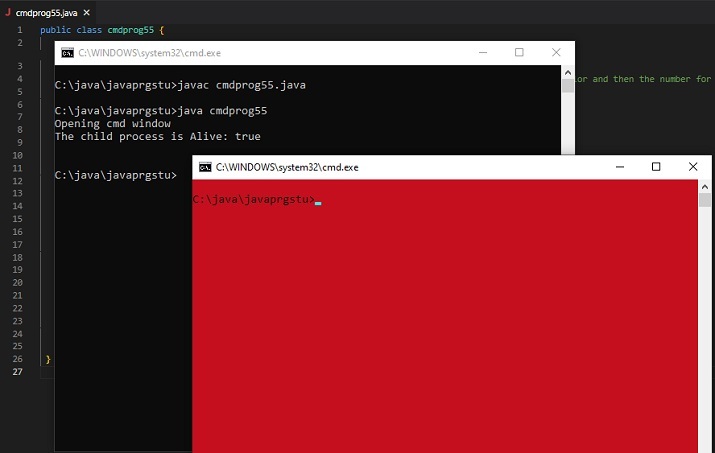
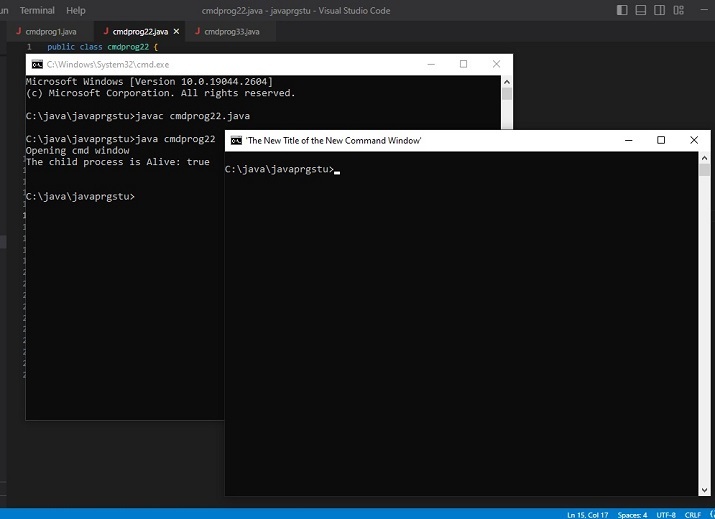
Exemple 2 : modifie la couleur d'arrière-plan et de premier plan de la fenêtre CMD lors de son ouverture.
public class cmdprog55 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//the following command will change the color of the cmd window. First the number for bg color and then the number for fg color is added.
// 4 means red color and 0 means black color
String command_to_playwith =" COLOR 40";
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try {
String command = "cmd /c" + " start" + command_to_playwith;
// starting the child process ....
Process childprocess11 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
System.out.println("The child process is Alive: " + childprocess11.isAlive());
System.out.println();
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
}
}
Sortie (Approche 1 : Exemple 2)
C:\java\javaprgstu>javac cmdprog55.java C:\java\javaprgstu>java cmdprog55 Opening cmd window The child process is Alive: true
Approche-2 : en utilisant les commandes exécutables
Une nouvelle fenêtre cmd s'ouvre en tant que processus enfant. Les résultats de la commande insérée ne peuvent être vus que dans une nouvelle fenêtre cmd. Dans cette approche, trois exemples différents sont utilisés.
Exemple 1 : Afficher un message dans la fenêtre CMD ouverte.
Exemple 2 Afficher le contenu d'un fichier txt.
Exemple 3 : Afficher le contenu du dossier en grand format.
Exemple 1 : Afficher un message dans la fenêtre CMD ouverte.
public class cmdprog44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The following command will display the message specified.
String command_to_playwith =" ECHO 'Hi! Lets check the cmd commands ....'";
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try {
String command = "cmd /c" + " start" + command_to_playwith;
// starting the child process....
Process childprocess11 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
System.out.println("The child process is Alive: " + childprocess11.isAlive());
System.out.println();
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
}
}
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try {
String command = "cmd /c" + " start" + command_to_playwith;
// starting the child process ....
Process childprocess11 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
System.out.println("The child process is Alive: " + childprocess11.isAlive());
System.out.println();
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
Sortie (Approche 2 : Exemple 1)
C:\java\javaprgstu>javac cmdprog44.java C:\java\javaprgstu>java cmdprog44 Opening cmd window The child process is Alive: true
Exemple 2 : Afficher le contenu du fichier txt.
public class cmdprog33 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//The following command is the command that is needed to see the contents of the given text file
String command_to_playwith =" TYPE testfile.txt";
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try {
String command = "cmd /c" + " start" + command_to_playwith;
//Starting the new child process
Process childprocess11 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
System.out.println("The child process is Alive: " + childprocess11.isAlive());
System.out.println(" Now showing the content of testfile.txt ....\n");
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
}
}
Sortie
C:\java\javaprgstu>javac cmdprog33.java C:\java\javaprgstu>java cmdprog33 Opening cmd window The child process is Alive: true Now showing the content of testfile.txt ...
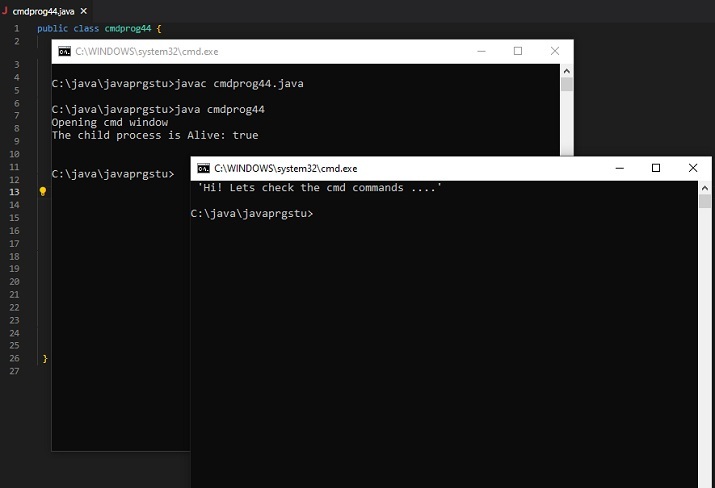
Exemple 3 : Afficher le contenu du dossier en grand format.
public class cmdprog66 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The following command will display the specified directory in wide format
String command_to_playwith =" dir .\applettest /W";
System.out.println("Opening cmd window");
try {
String command = "cmd /c" + " start" + command_to_playwith;
//Starting the new child process
Process childprocess11 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
System.out.println("The child process is Alive: " + childprocess11.isAlive());
System.out.println(" Now showing the directory in wide format ....\n");
}
catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " + e);
}
}
}
Sortie
C:\java\javaprgstu>javac cmdprog66.java C:\java\javaprgstu>java cmdprog66 Opening cmd window The child process is Alive: true Now showing the directory in wide format ...
Conclusion
Dans cet article, nous avons exploré différentes commandes à insérer dans la fenêtre cmd après l'avoir ouverte via le programme java. La sélection des commandes se fait en fonction des différentes catégories. Le premier ensemble de commandes modifie les propriétés de la fenêtre de commande lors de l'ouverture. celui-ci et le deuxième ensemble de commandes sont utilisés pour afficher les résultats dans la fenêtre de commande ouverte après son affichage. Dans les deux cas, la nouvelle fenêtre cmd est ouverte en tant que processus enfant.
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment exécuter un fichier JAR sous Windows 11 ou 10
May 12, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
Comment exécuter un fichier JAR sous Windows 11 ou 10
May 12, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
Windows 11 est capable d'exécuter un grand nombre de types de fichiers avec ou sans applications tierces externes. Non seulement il vous permet d'effectuer de nombreuses tâches dans le confort de votre PC, mais il garantit également que vous pouvez utiliser les capacités d'origine de votre PC. Aujourd'hui, nous allons examiner un type de fichier complexe, le jar, et vous expliquer comment l'ouvrir sur votre PC Windows 11 ou Windows 10. Qu'est-ce qu'un fichier jar ? jar est un format de package d'archives qui peut ou non contenir un programme Java exécutable. Ces archives peuvent contenir des applications Java ou du code source, qui peuvent ensuite être utilisés pour compiler et exécuter des applications sans avoir à écrire de code distinct pour chaque application. Vous pouvez utiliser diverses méthodes
 Comment installer les fichiers CAB sur Windows 11
Apr 30, 2023 pm 10:10 PM
Comment installer les fichiers CAB sur Windows 11
Apr 30, 2023 pm 10:10 PM
Qu'est-ce qu'un fichier CAB ? L'extension du fichier CAB est .cab, qui est l'abréviation du fichier WindowsCabinet. Il s'agit d'un fichier compressé généralement utilisé pour compresser les packages d'installation de logiciels tels que les pilotes de périphériques ou les fichiers de mise à jour. Les fichiers CAB prennent en charge la compression sans perte, ce qui rend le format idéal pour compresser des fichiers lorsqu'il est essentiel que les fichiers puissent être extraits avec précision, comme les pilotes et autres mises à jour. Comment installer un fichier CAB sur Windows 11 à l'aide de l'invite de commande Il existe plusieurs façons d'installer un fichier CAB sur Windows 11. L'une des méthodes consiste à utiliser l'invite de commande pour extraire et installer les fichiers. Vous pouvez également utiliser le nouveau Windows PowerShell
 Comment résoudre le problème dans Valorant qui nécessite un redémarrage du système avant de jouer ?
Apr 24, 2023 pm 11:58 PM
Comment résoudre le problème dans Valorant qui nécessite un redémarrage du système avant de jouer ?
Apr 24, 2023 pm 11:58 PM
La triche a toujours été un gros problème dans les jeux FPS en ligne, même si Valorant n'existait pas. Cela peut gâcher l’expérience de jeu et réduire l’intérêt des joueurs pour le jeu. Valorant a tenté de pallier cette lacune depuis ses débuts avec son propre système de protection RiotVanguard. Vous devez redémarrer le système après avoir installé le jeu une fois. Ceci est tout à fait normal et le système Vanguard démarrera automatiquement. Cependant, si vous redémarrez votre système et que le message « Votre jeu nécessite un redémarrage du système pour jouer. Veuillez redémarrer votre ordinateur. » Laisser un message sur la page d'accueil ? De nombreux utilisateurs ont rencontré ce problème, alors ne vous inquiétez pas. Suivez ces correctifs pour une solution rapide. Correctif 1 – Ne quittez pas Pioneer après le redémarrage de votre ordinateur
 Comment corriger l'erreur d'application 0xc0000906 sur un PC Windows
Apr 18, 2023 pm 10:55 PM
Comment corriger l'erreur d'application 0xc0000906 sur un PC Windows
Apr 18, 2023 pm 10:55 PM
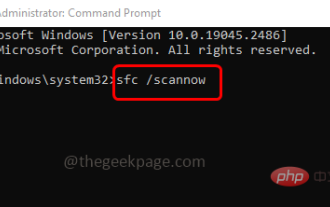
Certains utilisateurs rencontrent l'erreur « Erreur d'application 0xc0000906 » lorsqu'ils tentent d'exécuter l'application sur leurs systèmes et ne peuvent pas continuer. Une ou plusieurs applications sur votre système peuvent rencontrer cette erreur. Cela peut être dû à une corruption de fichiers, à des problèmes de mise en cache, à l'utilisation d'un logiciel antivirus tiers susceptible de bloquer des applications logicielles, etc. Dans cet article, nous proposons des solutions qui peuvent aider les utilisateurs à éliminer l'erreur. Essayez d'exécuter la commande pour analyser les fichiers système et désactiver le logiciel antivirus comme décrit ci-dessous. Alors commençons ! Méthode 1 : Exécutez l'analyse SFC et DISM Étape 1 – Ouvrez l'invite de commande en tant qu'administrateur. Pour ce faire, tapez cmd dans la barre de recherche de la fenêtre, puis maintenez les touches ctrl+shift enfoncées et appuyez sur Entrée.
 Comment définir en toute sécurité une priorité élevée pour les applications dans Windows 11 ?
May 06, 2023 pm 06:28 PM
Comment définir en toute sécurité une priorité élevée pour les applications dans Windows 11 ?
May 06, 2023 pm 06:28 PM
Windows fait un excellent travail en allouant des ressources système aux processus et aux programmes qui en ont le plus besoin en leur attribuant des priorités. La plupart des applications que vous installez fonctionneront parfaitement au niveau de priorité « normal » par défaut. Parfois, cependant, vous devrez peut-être exécuter un programme, tel qu'un jeu, à un niveau supérieur au niveau normal par défaut pour améliorer ses performances. Mais cela a un coût, et c’est une affaire qui mérite réflexion. Que se passe-t-il lorsque vous définissez une application comme étant prioritaire ? Windows dispose d'un total de six niveaux de priorité pour l'exécution de différents processus et programmes : faible, inférieur à la normale, normal, supérieur à la normale, élevé et en temps réel. Windows classera et mettra les applications en file d'attente en fonction de leur priorité. Plus la priorité est élevée, plus l'application
 Comment résoudre rapidement le code d'erreur d'activation de Windows 0xc004c020 ?
Apr 26, 2023 pm 03:19 PM
Comment résoudre rapidement le code d'erreur d'activation de Windows 0xc004c020 ?
Apr 26, 2023 pm 03:19 PM
Beaucoup de nos lecteurs ont signalé l'erreur 0xC004C020 lorsqu'ils tentaient de connecter leurs ordinateurs aux serveurs de leur organisation. Cette erreur empêche l'activation de son système d'exploitation Windows. Bien que les erreurs puissent être frustrantes, nous vous guiderons à travers l'erreur 0xC004C020 lorsque vous tenterez d'activer Windows sur un ordinateur lié à une organisation. Qu’est-ce qui cause l’erreur 0xC004C020 ? Si vous essayez d'activer Windows sur un ordinateur lié à une organisation et rencontrez l'erreur 0xC004C020, les causes possibles peuvent être les suivantes : Clés non MAK – Si une clé non MAK est utilisée sur un ordinateur lié à une organisation, les stratégies de l'organisation seront Il n'est pas permis de l'activer. Accès à la clé perdu après le formatage
 Comment réparer srttrail.txt sur Windows 11
Apr 18, 2023 am 10:43 AM
Comment réparer srttrail.txt sur Windows 11
Apr 18, 2023 am 10:43 AM
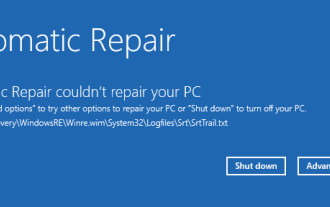
Pour les utilisateurs de Windows, il n'y a rien de plus ennuyeux que de devoir faire face à une erreur d'écran bleu, surtout si elle s'accompagne d'un crash du système. L'erreur srttrail.txt en fait partie. Bien qu'il ne s'agisse pas techniquement d'un BSOD, les bogues dans votre environnement de réparation automatique sont toujours les symptômes de problèmes plus profonds qui font dérailler Windows et nécessitent une intervention. Qu'est-ce que l'erreur srttrail.txt ? Le fichier texte srttrail.txt mentionné dans le message n'est qu'un journal que Windows conserve pour toutes les instances où il ne démarre pas correctement, et il continuera à apparaître si Windows reste bloqué au démarrage. Ce message d'erreur apparaît principalement au démarrage du système, mais peut également apparaître dans Windo
 3 façons d'ouvrir le dossier System 32 sous Windows 11 ou 10
May 04, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
3 façons d'ouvrir le dossier System 32 sous Windows 11 ou 10
May 04, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
Qu'est-ce que le dossier System32 ? System32 est l'un des principaux dossiers utilisés par Windows. Lors de l'installation de Windows, tous les fichiers et dossiers nécessaires au bon fonctionnement de Windows sont copiés dans ce dossier. Ceux-ci incluent des fichiers système importants, des fichiers exécutables associés utilisés par les utilitaires Windows, des bibliothèques de liens dynamiques (DLL) et même certains fichiers logiciels sont copiés dans ce dossier. Cependant, ne vous laissez pas tromper par le nom System32. Cela est vrai pour les ordinateurs 32 bits et 64 bits. Sur une machine 64 bits, le dossier System32 héberge les fichiers 64 bits, tandis que les fichiers 32 bits se trouvent dans






