Imprimer la vue gauche de l'arbre binaire en langage C
La tâche consiste à imprimer le nœud gauche de l'arbre binaire donné. Tout d'abord, l'utilisateur insérera des données, générant ainsi un arbre binaire, puis imprimera la vue gauche de l'arbre résultant.
Chaque nœud peut avoir au maximum 2 nœuds enfants, ce programme doit donc itérer uniquement le pointeur gauche associé au nœud
Si le pointeur gauche n'est pas nul, cela signifie qu'il aura des données ou un pointeur associé, sinon ce sera la gauche enfant à imprimer et à afficher en sortie.
ExempleInput : 1 0 3 2 4
Output : 1 0 2
Copier après la connexion
Input : 1 0 3 2 4 Output : 1 0 2
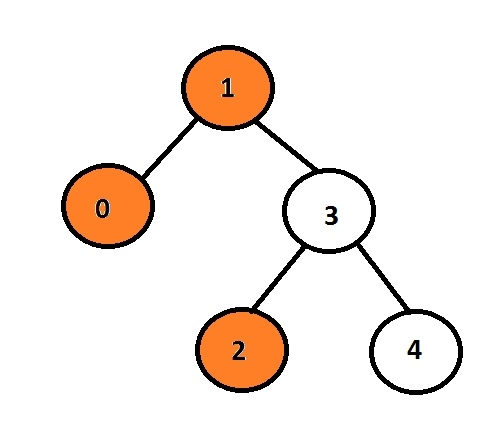
Ici, le nœud orange représente la vue gauche de l'arbre binaire.
Dans le graphique donné, le nœud avec les données 1 est le nœud racine, il sera donc imprimé, au lieu d'aller au nœud enfant gauche, il imprimera 0, puis il ira à 3 et imprimera son nœud enfant gauche, Cela fait 2.
Nous pouvons utiliser une méthode récursive pour stocker les niveaux des nœuds et les transférer à plusieurs reprises vers
Le code ci-dessous montre l'implémentation C de l'algorithme donné
algorithm
START
Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure
Declare int data
Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right
Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as new_data
Declare temp variable of node using malloc
Set temp->data = new_data
Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL
return temp
Step 3 -> declare function void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level)
IF root = NULL
Exit
End
IF *highest_level < level
Print root->data
Set *highest_level = level
End
Recursively call left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level)
Recursively call left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level)
Step 4 -> Declare Function void left(struct node* root)
Set int highest_level = 0
Call left_view(root, 1, &highest_level)
Step 5-> In main()
Call New passing value user want to insert as struct node* root = New(1)
Call left(root)
STOPExemple
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//create a structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right; //this pointer will point to the nodes attached with a node
};
struct node* New(int new_data) {
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
//allocating memory to a pointer dynamically
temp->data = new_data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) {
if (root == NULL) //if there is no node that means no data
return;
// this function will retrun the root node if there is only root node in a tree
if (*highest_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*highest_level = level;
}
// Recursive function
left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level);
left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level);
}
void left(struct node* root) {
int highest_level = 0;
left_view(root, 1, &highest_level);
}
int main() {
printf("left view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node* root = New(1);
root->left = New(0);
root->right = New(3);
root->right->left = New(2);
root->right->right = New(4);
left(root);
return 0;
}Output
Si nous exécutons le programme ci-dessus, it La sortie suivante sera générée.
left view of a binary tree is : 1 0 2
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Que dois-je faire si la ligne du cadre disparaît lors de l'impression dans Excel ?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Que dois-je faire si la ligne du cadre disparaît lors de l'impression dans Excel ?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Si lors de l'ouverture d'un fichier qui doit être imprimé, nous constatons que la ligne du cadre du tableau a disparu pour une raison quelconque dans l'aperçu avant impression. Lorsque nous rencontrons une telle situation, nous devons la traiter à temps si cela apparaît également dans votre impression. file Si vous avez des questions comme celle-ci, alors rejoignez l'éditeur pour apprendre le cours suivant : Que dois-je faire si la ligne du cadre disparaît lors de l'impression d'un tableau dans Excel ? 1. Ouvrez un fichier à imprimer, comme indiqué dans la figure ci-dessous. 2. Sélectionnez toutes les zones de contenu requises, comme indiqué dans la figure ci-dessous. 3. Cliquez avec le bouton droit de la souris et sélectionnez l'option "Formater les cellules", comme indiqué dans la figure ci-dessous. 4. Cliquez sur l'option « Bordure » en haut de la fenêtre, comme indiqué dans la figure ci-dessous. 5. Sélectionnez le motif de ligne continue fine dans le style de ligne de gauche, comme indiqué dans la figure ci-dessous. 6. Sélectionnez « Bordure extérieure »
 Mémoire ou espace disque insuffisant pour repaginer ou imprimer ce document Erreur Word
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:15 PM
Mémoire ou espace disque insuffisant pour repaginer ou imprimer ce document Erreur Word
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:15 PM
Cet article explique comment résoudre le problème de mémoire ou d'espace disque insuffisant pour repagener ou imprimer le document dans Microsoft Word. Cette erreur se produit généralement lorsque les utilisateurs tentent d'imprimer un document Word. Si vous rencontrez une erreur similaire, veuillez vous référer aux suggestions fournies dans cet article pour la résoudre. Mémoire ou espace disque insuffisant pour repagener ou imprimer ce document. Erreur Word Comment résoudre l'erreur d'impression Microsoft Word « Il n'y a pas assez de mémoire ou d'espace disque pour repagener ou imprimer le document. » Mettre à jour Microsoft Office Fermer les applications gourmandes en mémoire Changer votre imprimante par défaut Démarrer Word en mode sans échec Renommer le fichier NorMal.dotm Enregistrer le fichier Word sous un autre
 4 façons d'imprimer depuis un iPhone
Feb 02, 2024 pm 04:10 PM
4 façons d'imprimer depuis un iPhone
Feb 02, 2024 pm 04:10 PM
Dans ce monde numérique, le besoin de pages imprimées n’a pas disparu. Même si vous pensez peut-être qu'il est plus pratique d'enregistrer le contenu sur votre ordinateur et de l'envoyer directement à l'imprimante, vous pouvez faire la même chose sur votre iPhone. Avec l'appareil photo de votre iPhone, vous pouvez prendre une photo ou un document, et vous pouvez également stocker le fichier directement pour l'imprimer à tout moment. Vous pourrez ainsi matérialiser rapidement et facilement les informations dont vous avez besoin et les enregistrer dans un document papier. Que ce soit au travail ou dans la vie quotidienne, iPhone vous offre une solution d'impression portable. L'article suivant vous aidera à comprendre tout ce que vous devez savoir si vous souhaitez utiliser votre iPhone pour imprimer des pages sur une imprimante. Imprimer depuis un iPhone : demandez à Apple
 Impossible d'imprimer à partir de l'outil de capture sous Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Impossible d'imprimer à partir de l'outil de capture sous Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Si vous ne parvenez pas à imprimer à l'aide de l'outil Capture sous Windows 11/10, cela peut être dû à des fichiers système corrompus ou à des problèmes de pilote. Cet article vous fournira des solutions à ce problème. Impossible d'imprimer à partir de l'outil Snipping sous Windows 11/10 Si vous ne pouvez pas imprimer à partir de l'outil Snipping dans Windows 11/10, utilisez ces correctifs : Redémarrez l'imprimante PC Effacez la file d'attente d'impression Mettez à jour l'imprimante et le pilote graphique Réparez ou réinitialisez l'outil Snipping Exécutez SFC et DISM Scan utilise les commandes PowerShell pour désinstaller et réinstaller Snipping Tool. Commençons. 1] Redémarrez votre PC et votre imprimante Le redémarrage de votre PC et de votre imprimante permet d'éliminer les problèmes temporaires
 Comment suspendre l'impression sous Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:50 AM
Comment suspendre l'impression sous Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:50 AM
Vous avez imprimé un gros fichier par erreur ? Besoin d'arrêter ou de suspendre l'impression pour économiser de l'encre et du papier ? Il existe de nombreuses situations dans lesquelles vous devrez peut-être suspendre une tâche d'impression en cours sur votre appareil Windows 11. Comment suspendre l’impression sous Windows 11 ? Sous Windows 11, la suspension de l’impression mettra en pause la tâche d’impression, mais n’annulera pas la tâche d’impression. Cela offre aux utilisateurs un contrôle plus flexible. Il existe trois manières de procéder : Suspendre l'impression à l'aide de la barre des tâches Suspendre l'impression à l'aide des paramètres Windows Imprimer à l'aide du panneau de commande Examinons-les maintenant en détail. 1] Imprimer à l'aide de la barre des tâches Cliquez avec le bouton droit sur la notification de la file d'attente d'impression dans la barre des tâches. Cliquez pour ouvrir toutes les options d'imprimante actives. Ici, faites un clic droit sur le travail d'impression et sélectionnez Suspendre tout
 Le publipostage Word imprime une page blanche
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Le publipostage Word imprime une page blanche
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Si vous constatez que des pages vierges apparaissent lors de l'impression d'un document de publipostage à l'aide de Word, cet article vous aidera. Le publipostage est une fonctionnalité pratique qui vous permet de créer facilement des documents personnalisés et de les envoyer à plusieurs destinataires. Dans Microsoft Word, la fonctionnalité de fusion et publipostage est très appréciée car elle permet aux utilisateurs de gagner du temps en copiant manuellement le même contenu pour chaque destinataire. Afin d'imprimer le document de publipostage, vous pouvez accéder à l'onglet Mailings. Mais certains utilisateurs de Word ont signalé que lorsqu'ils essayaient d'imprimer un document de publipostage, l'imprimante imprimait une page vierge ou n'imprimait pas du tout. Cela peut être dû à un formatage ou à des paramètres d'imprimante incorrects. Essayez de vérifier les paramètres du document et de l'imprimante et assurez-vous de prévisualiser le document avant de l'imprimer pour vous assurer que le contenu est correct. si
 Comment imprimer toutes les pièces jointes dans Outlook
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Comment imprimer toutes les pièces jointes dans Outlook
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Outlook est l'un des clients de messagerie les plus riches en fonctionnalités et est devenu un outil indispensable pour la communication professionnelle. L'un des défis consiste à imprimer toutes les pièces jointes en même temps dans Outlook. Habituellement, vous devez télécharger les pièces jointes une par une avant de pouvoir les imprimer, mais si vous souhaitez tout imprimer en même temps, c'est le problème que la plupart des gens rencontrent. Comment imprimer toutes les pièces jointes dans Outlook Bien que la plupart des informations soient conservées en ligne dans l'application Outlook, il peut arriver que vous deviez imprimer les informations à des fins de sauvegarde. Doit signer des documents en personne pour satisfaire aux exigences légales telles que des contrats, des formulaires gouvernementaux ou des devoirs. Il existe plusieurs méthodes qui vous permettent d'imprimer toutes les pièces jointes dans Outlook en un seul clic au lieu de les imprimer une par une. Examinons chacun en détail. Perspectives
 Comment implémenter la fonction d'impression dans Vue
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
Comment implémenter la fonction d'impression dans Vue
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
Comment implémenter la fonctionnalité d'impression dans Vue nécessite des exemples de code spécifiques. Vue.js est un framework JavaScript progressif pour la création d'interfaces utilisateur. Dans de nombreuses applications Web, la fonctionnalité d’impression constitue un élément très important. Cet article expliquera comment implémenter la fonction d'impression dans Vue et fournira des exemples de code spécifiques. Pour implémenter la fonction d'impression dans Vue, vous devez d'abord clarifier quel est le contenu imprimé. Habituellement, nous mettrons le contenu à imprimer dans un élément HTML, comme un div. Puis, via Jav






