 développement back-end
développement back-end
 C++
C++
 Dans le programme C, traduisez le contenu suivant en chinois : Programme pour trouver le nième nœud à partir du bas d'une liste chaînée
Dans le programme C, traduisez le contenu suivant en chinois : Programme pour trouver le nième nœud à partir du bas d'une liste chaînée
Dans le programme C, traduisez le contenu suivant en chinois : Programme pour trouver le nième nœud à partir du bas d'une liste chaînée
Étant donné n nœuds, la tâche consiste à imprimer le nième nœud à la fin de la liste chaînée. Le programme ne doit pas modifier l'ordre des nœuds dans la liste, mais doit uniquement imprimer le nième nœud du dernier nœud de la liste chaînée.
Exemple
Input -: 10 20 30 40 50 60 N=3 Output -: 40
Dans l'exemple ci-dessus, en commençant par le premier nœud, parcourez jusqu'à compter n nœuds, c'est-à-dire 10,20 30,40, 50,60, donc l'avant-dernier nœud est 40.
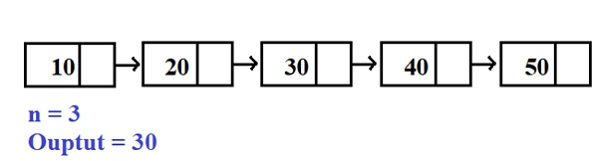
Au lieu de parcourir toute la liste de manière aussi efficace, l'approche que vous pouvez suivre -
- Obtenez un pointeur temporaire vers, par exemple, la température du type de nœud
- Définissez ce pointeur temporaire sur le premier pointeur de tête de nœud pointé
- Réglez le compteur sur le nombre de nœuds dans la liste
- Déplacez temp vers temp → next jusqu'à count-n
- show temp → data
Si nous utilisons cette méthode, le compte sera de 5 et le programme parcourra la boucle jusqu'à 5-3, soit 2, donc en commençant par 10 à la 0ème position jusqu'à 20 résultats en 1ère position et la 30ème position en deuxième position. Ainsi, avec cette approche, il n'est pas nécessaire de parcourir toute la liste jusqu'à la fin, ce qui permettra d'économiser de l'espace et de la mémoire.
Algorithme
Start
Step 1 -> create structure of a node and temp, next and head as pointer to a structure node
struct node
int data
struct node *next, *head, *temp
End
Step 2 -> declare function to insert a node in a list
void insert(int val)
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node))
newnode->data = val
IF head= NULL
set head = newnode
set head->next = NULL
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp->next!=NULL
Set temp=temp->next
End
Set newnode->next=NULL
Set temp->next=newnode
End
Step 3 -> Declare a function to display list
void display()
IF head=NULL
Print no node
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Print temp->data
Set temp=temp->next
End
End
Step 4 -> declare a function to find nth node from last of a linked list
void last(int n)
declare int product=1, i
Set temp=head
Loop For i=0 and i<count-n and i++
Set temp=temp->next
End
Print temp->data
Step 5 -> in main()
Create nodes using struct node* head = NULL
Declare variable n as nth to 3
Call function insert(10) to insert a node
Call display() to display the list
Call last(n) to find nth node from last of a list
StopExemple
Démonstration en direct
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head,*temp;
int count=0;
//function for inserting nodes into a list
void insert(int val){
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL){
head = newnode;
temp = head;
count++;
} else {
temp->next=newnode;
temp=temp->next;
count++;
}
}
//function for displaying a list
void display(){
if(head==NULL)
printf("no node ");
else {
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
}
}
//function for finding 3rd node from the last of a linked list
void last(int n){
int i;
temp=head;
for(i=0;i<count-n;i++){
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("</p><p>%drd node from the end of linked list is : %d" ,n,temp->data);
}
int main(){
//creating list
struct node* head = NULL;
int n=3;
//inserting elements into a list
insert(1);
insert(2);
insert(3);
insert(4);
insert(5);
insert(6);
//displaying the list
printf("</p><p>linked list is : ");
display();
//calling function for finding nth element in a list from last
last(n);
return 0;
}Sortie
linked list is : 1 2 3 4 5 6 3rd node from the end of linked list is : 4
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Recherchez le nième nœud de la dernière liste chaînée en C++ à l'aide de la méthode récursive
Sep 15, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
Recherchez le nième nœud de la dernière liste chaînée en C++ à l'aide de la méthode récursive
Sep 15, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
Étant donné une liste à chaînage unique et un entier positif N en entrée. Le but est de trouver le Nème nœud à partir de la fin de la liste donnée en utilisant la récursivité. Si la liste d'entrée a des nœuds a → b → c → d → e → f et N vaut 4, alors le 4ème nœud du dernier sera c. Nous allons d'abord parcourir jusqu'au dernier nœud de la liste et au retour du nombre d'incréments récursifs (retour en arrière). Lorsque count est égal à N, un pointeur vers le nœud actuel est renvoyé comme résultat. Examinons différents scénarios d'entrée et de sortie pour cela - Entrée - Liste : -1→5→7→12→2→96→33N=3 Sortie − Le Nième nœud du dernier est : 2 Explication − Le troisième nœud est 2 . Entrée - Liste : -12 → 53 → 8 → 19 → 20 → 96 → 33N = 8 Sortie – Le nœud n'existe pas
 Interrogez le poids minimum dans le sous-arbre à partir du nœud X et la distance au plus D
Aug 25, 2023 am 11:25 AM
Interrogez le poids minimum dans le sous-arbre à partir du nœud X et la distance au plus D
Aug 25, 2023 am 11:25 AM
Lors de la programmation informatique, il est parfois nécessaire de trouver le poids minimum d'un sous-arbre provenant d'un nœud spécifique, à condition que le sous-arbre ne puisse pas contenir de nœuds éloignés de plus de D unités du nœud spécifié. Ce problème se pose dans divers domaines et applications, notamment la théorie des graphes, les algorithmes arborescents et l'optimisation des réseaux. Un sous-arbre est un sous-ensemble d'une structure arborescente plus grande, le nœud spécifié servant de nœud racine du sous-arbre. Un sous-arbre contient tous les descendants du nœud racine et leurs arêtes de connexion. Le poids d'un nœud fait référence à une valeur spécifique attribuée à ce nœud, qui peut représenter son importance, sa signification ou d'autres mesures pertinentes. Dans ce problème, l’objectif est de trouver le poids minimum parmi tous les nœuds d’un sous-arbre tout en limitant le sous-arbre aux nœuds situés au plus à D unités du nœud racine. Dans l'article suivant, nous approfondirons la complexité de l'extraction des poids minimum des sous-arbres.
 Ajouter 1 à un nombre représenté par une liste chaînée
Aug 29, 2023 pm 09:17 PM
Ajouter 1 à un nombre représenté par une liste chaînée
Aug 29, 2023 pm 09:17 PM
Une représentation par liste chaînée d'un nombre est fournie comme ceci : Tous les nœuds de la liste chaînée sont considérés comme étant un chiffre du nombre. Les nœuds stockent les nombres de telle sorte que le premier élément de la liste chaînée contienne le chiffre le plus significatif du nombre et que le dernier élément de la liste chaînée contienne le chiffre le moins significatif du nombre. Par exemple, le nombre 202345 est représenté dans la liste chaînée par (2->0->2->3->4->5). Pour ajouter 1 à cette liste chaînée représentant des nombres, il faut vérifier la valeur du bit le moins significatif de la liste. Si c'est moins de 9 c'est ok, sinon le code changera le numéro suivant et ainsi de suite. Voyons maintenant un exemple pour comprendre comment procéder, 1999 est représenté par (1->9->9->9) et l'ajout de 1 devrait le changer.
 Comparaison de la complexité temporelle des algorithmes des tableaux PHP et des listes chaînées
May 07, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Comparaison de la complexité temporelle des algorithmes des tableaux PHP et des listes chaînées
May 07, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Comparaison de la complexité temporelle de l'algorithme des tableaux et des listes chaînées : accès aux tableaux O(1), listes chaînées O(n), insertion de tableaux O(1)/O(n) ; ), listes chaînées O(n) (n); Tableau de recherche O(n), liste chaînée O(n).
 Structures de données PHP SPL : injectez de la vitesse et de la flexibilité dans vos projets
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:00 PM
Structures de données PHP SPL : injectez de la vitesse et de la flexibilité dans vos projets
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:00 PM
Présentation de la bibliothèque de structures de données PHPSPL La bibliothèque de structures de données PHPSPL (Standard PHP Library) contient un ensemble de classes et d'interfaces pour stocker et manipuler diverses structures de données. Ces structures de données comprennent des tableaux, des listes chaînées, des piles, des files d'attente et des ensembles, chacun fournissant un ensemble spécifique de méthodes et de propriétés pour manipuler les données. Tableaux En PHP, un tableau est une collection ordonnée qui stocke une séquence d'éléments. La classe de tableau SPL fournit des fonctions améliorées pour les tableaux PHP natifs, notamment le tri, le filtrage et le mappage. Voici un exemple d'utilisation de la classe array SPL : useSplArrayObject;$array=newArrayObject(["foo","bar","baz"]);$array
 Structure de données PHP : le charme des listes chaînées, exploration de l'organisation dynamique des données
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:53 PM
Structure de données PHP : le charme des listes chaînées, exploration de l'organisation dynamique des données
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:53 PM
Une liste chaînée est une structure de données qui utilise une série de nœuds avec des données et des pointeurs pour organiser les éléments, et est particulièrement adaptée au traitement de grands ensembles de données et aux opérations fréquentes d'insertion/suppression. Ses composants de base comprennent des nœuds (données et pointeurs vers le nœud suivant) et des nœuds principaux (pointant vers le premier nœud de la liste chaînée). Les opérations courantes de liste chaînée incluent : l’ajout (insertion de queue), la suppression (valeur spécifique) et le parcours.
 Comment implémenter les fonctions de copie et de coupure de nœuds des cartes mentales via Vue et jsmind ?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
Comment implémenter les fonctions de copie et de coupure de nœuds des cartes mentales via Vue et jsmind ?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
Comment implémenter les fonctions de copie et de coupure de nœuds des cartes mentales via Vue et jsmind ? La carte mentale est un outil de réflexion courant qui peut nous aider à organiser nos pensées et à trier notre logique de pensée. Les fonctions de copie et de coupe de nœuds sont des opérations couramment utilisées dans les cartes mentales, qui nous permettent de réutiliser plus facilement les nœuds existants et d'améliorer l'efficacité de l'organisation de la réflexion. Dans cet article, nous utiliserons les deux outils Vue et jsmind pour implémenter les fonctions de copie et de coupe de nœuds de la carte mentale. Tout d'abord, nous devons installer Vue et jsmind et créer
 Programme Python : ajouter des éléments à la première et à la dernière position de la liste chaînée
Aug 23, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
Programme Python : ajouter des éléments à la première et à la dernière position de la liste chaînée
Aug 23, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
En Python, une liste chaînée est une structure de données linéaire composée d'une séquence de nœuds, chaque nœud contenant une valeur et une référence au nœud suivant dans la liste chaînée. Dans cet article, nous verrons comment ajouter des éléments à la première et à la dernière position d'une liste chaînée en Python. LinkedList en Python Une liste chaînée est une structure de données de référence utilisée pour stocker un ensemble d'éléments. D'une certaine manière, cela ressemble à un tableau, mais dans un tableau, les données sont stockées dans des emplacements mémoire contigus, alors que dans une liste chaînée, les données ne sont pas soumises à cette condition. Cela signifie que les données ne sont pas stockées de manière séquentielle mais de manière aléatoire en mémoire. Cela soulève une question : comment pouvons-nous





