 développement back-end
développement back-end
 C++
C++
 Programme C++ : calculez le nombre d'opérations nécessaires pour atteindre n à l'aide de paiements par pièces
Programme C++ : calculez le nombre d'opérations nécessaires pour atteindre n à l'aide de paiements par pièces
Programme C++ : calculez le nombre d'opérations nécessaires pour atteindre n à l'aide de paiements par pièces

Supposons que nous ayons cinq nombres, N, A, B, C, D. On commence par le chiffre 0 et on termine par N. On peut changer un nombre par un certain nombre de pièces, comme suit :
- Multipliez le nombre par 2, payez les pièces A
- Multipliez le nombre par 3, payez les pièces B
- Multipliez le nombre par 5, payez les pièces C
- augmentez ou diminuez le chiffre 1, payez les pièces D
Nous pouvons effectuer ces opérations un nombre illimité de fois et dans n'importe quel ordre. Nous devons trouver le nombre minimum de pièces requis pour atteindre N
Donc si l'entrée est N = 1 ; B = 2 ; alors la sortie sera 19 car initialement x est ; 0.
Utilisez 8 pièces pour augmenter x de 1 (x=1).
Utilisez 1 pièce pour multiplier x par 2 (x=2).
Utilisez 2 pièces pour multiplier x par 5 (x=10).
Utilisez 8 pièces pour l'augmenter de 1 (x=11).
Étapes
Pour résoudre ce problème, nous suivrons les étapes suivantes :
Define one map f for integer type key and value Define one map vis for integer type key and Boolean type value Define a function calc, this will take n if n is zero, then: return 0 if n is in vis, then: return f[n] vis[n] := 1 res := calc(n / 2) + n mod 2 * d + a if n mod 2 is non-zero, then: res := minimum of res and calc((n / 2 + 1) + (2 - n mod 2)) * d + a) res := minimum of res and calc(n / 3) + n mod 3 * d + b if n mod 3 is non-zero, then: res := minimum of res and calc((n / 3 + 1) + (3 - n mod 3)) * d + b) res := minimum of res and calc(n / 5) + n mod 5 * d + c if n mod 5 is non-zero, then: res := minimum of res and calc((n / 5 + 1) + (5 - n mod 5)) if (res - 1) / n + 1 > d, then: res := n * d return f[n] = res From the main method, set a, b, c and d, and call calc(n)
Exemple
Voyons l'implémentation ci-dessous pour une meilleure compréhension −
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a, b, c, d;
map<long, long> f;
map<long, bool> vis;
long calc(long n){
if (!n)
return 0;
if (vis.find(n) != vis.end())
return f[n];
vis[n] = 1;
long res = calc(n / 2) + n % 2 * d + a;
if (n % 2)
res = min(res, calc(n / 2 + 1) + (2 - n % 2) * d + a);
res = min(res, calc(n / 3) + n % 3 * d + b);
if (n % 3)
res = min(res, calc(n / 3 + 1) + (3 - n % 3) * d + b);
res = min(res, calc(n / 5) + n % 5 * d + c);
if (n % 5)
res = min(res, calc(n / 5 + 1) + (5 - n % 5) * d + c);
if ((res - 1) / n + 1 > d)
res = n * d;
return f[n] = res;
}
int solve(int N, int A, int B, int C, int D){
a = A;
b = B;
c = C;
d = D;
return calc(N);
}
int main(){
int N = 11;
int A = 1;
int B = 2;
int C = 2;
int D = 8;
cout << solve(N, A, B, C, D) << endl;
}Input
11, 1, 2, 2, 8
Output
19
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
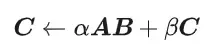 La multiplication matricielle universelle de CUDA : de l'entrée à la maîtrise !
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
La multiplication matricielle universelle de CUDA : de l'entrée à la maîtrise !
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
La multiplication matricielle générale (GEMM) est un élément essentiel de nombreuses applications et algorithmes, et constitue également l'un des indicateurs importants pour évaluer les performances du matériel informatique. Une recherche approfondie et l'optimisation de la mise en œuvre de GEMM peuvent nous aider à mieux comprendre le calcul haute performance et la relation entre les systèmes logiciels et matériels. En informatique, une optimisation efficace de GEMM peut augmenter la vitesse de calcul et économiser des ressources, ce qui est crucial pour améliorer les performances globales d’un système informatique. Une compréhension approfondie du principe de fonctionnement et de la méthode d'optimisation de GEMM nous aidera à mieux utiliser le potentiel du matériel informatique moderne et à fournir des solutions plus efficaces pour diverses tâches informatiques complexes. En optimisant les performances de GEMM
 Comment calculer l'addition, la soustraction, la multiplication et la division dans un document Word
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
Comment calculer l'addition, la soustraction, la multiplication et la division dans un document Word
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
WORD est un traitement de texte puissant. Nous pouvons utiliser Word pour éditer divers textes. Dans les tableaux Excel, nous maîtrisons les méthodes de calcul d'addition, de soustraction et de multiplicateurs. Ainsi, si nous avons besoin de calculer l'addition de valeurs numériques dans les tableaux Word, Comment soustraire le multiplicateur ? Puis-je utiliser uniquement une calculatrice pour le calculer ? La réponse est bien sûr non, WORD peut aussi le faire. Aujourd'hui, je vais vous apprendre à utiliser des formules pour calculer des opérations de base telles que l'addition, la soustraction, la multiplication et la division dans des tableaux dans des documents Word. Apprenons ensemble. Alors, aujourd'hui, permettez-moi de vous montrer en détail comment calculer l'addition, la soustraction, la multiplication et la division dans un document WORD ? Étape 1 : ouvrez un WORD, cliquez sur [Tableau] sous [Insérer] dans la barre d'outils et insérez un tableau dans le menu déroulant.
 Comment compter le nombre d'éléments dans une liste à l'aide de la fonction count() de Python
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:53 PM
Comment compter le nombre d'éléments dans une liste à l'aide de la fonction count() de Python
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:53 PM
Comment utiliser la fonction count() de Python pour compter le nombre d'éléments dans une liste nécessite des exemples de code spécifiques. En tant que langage de programmation puissant et facile à apprendre, Python fournit de nombreuses fonctions intégrées pour gérer différentes structures de données. L'une d'elles est la fonction count(), qui peut être utilisée pour compter le nombre d'éléments dans une liste. Dans cet article, nous expliquerons en détail comment utiliser la fonction count() et fournirons des exemples de code spécifiques. La fonction count() est une fonction intégrée de Python, utilisée pour calculer un certain
 Compter le nombre d'occurrences d'une sous-chaîne de manière récursive en Java
Sep 17, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Compter le nombre d'occurrences d'une sous-chaîne de manière récursive en Java
Sep 17, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Étant donné deux chaînes str_1 et str_2. Le but est de compter le nombre d'occurrences de la sous-chaîne str2 dans la chaîne str1 en utilisant une procédure récursive. Une fonction récursive est une fonction qui s'appelle dans sa définition. Si str1 est "Je sais que vous savez que je sais" et str2 est "savoir", le nombre d'occurrences est de -3 Comprenons à travers des exemples. Par exemple, entrez str1="TPisTPareTPamTP", str2="TP" ; sortie Countofoccurrencesofasubstringrecursi.
 Comment utiliser la fonction Math.Pow en C# pour calculer la puissance d'un nombre spécifié
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:32 AM
Comment utiliser la fonction Math.Pow en C# pour calculer la puissance d'un nombre spécifié
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:32 AM
En C#, il existe une bibliothèque de classes Math, qui contient de nombreuses fonctions mathématiques. Il s'agit notamment de la fonction Math.Pow, qui calcule les puissances, ce qui peut nous aider à calculer la puissance d'un nombre spécifié. L'utilisation de la fonction Math.Pow est très simple, il suffit de spécifier la base et l'exposant. La syntaxe est la suivante : Math.Pow(base,exponent) ; où base représente la base et exponent représente l'exposant. Cette fonction renvoie un résultat de type double, c'est-à-dire le résultat du calcul de puissance. Allons
 Programme Java pour calculer l'aire d'un triangle à l'aide de déterminants
Aug 31, 2023 am 10:17 AM
Programme Java pour calculer l'aire d'un triangle à l'aide de déterminants
Aug 31, 2023 am 10:17 AM
Introduction Le programme Java pour calculer l'aire d'un triangle à l'aide d'un déterminant est un programme concis et efficace qui peut calculer l'aire d'un triangle à partir des coordonnées de trois sommets. Ce programme est utile à toute personne qui apprend ou travaille avec la géométrie, car il montre comment utiliser les calculs arithmétiques et algébriques de base en Java, ainsi que comment utiliser la classe Scanner pour lire les entrées de l'utilisateur. Le programme demande à l'utilisateur les coordonnées de trois points du triangle, qui sont ensuite lues et utilisées pour calculer le déterminant de la matrice de coordonnées. Utilisez la valeur absolue du déterminant pour vous assurer que l'aire est toujours positive, puis utilisez une formule pour calculer l'aire du triangle et l'afficher à l'utilisateur. Le programme peut être facilement modifié pour accepter des entrées dans différents formats ou pour effectuer des calculs supplémentaires, ce qui en fait un outil polyvalent pour les calculs géométriques. rangs de déterminants
 Programme Python pour calculer la somme des éléments diagonaux droits d'une matrice
Aug 19, 2023 am 11:29 AM
Programme Python pour calculer la somme des éléments diagonaux droits d'une matrice
Aug 19, 2023 am 11:29 AM
Python est un langage de programmation généraliste populaire. Il est utilisé dans divers secteurs, notamment les applications de bureau, le développement Web et l’apprentissage automatique. Heureusement, Python possède une syntaxe simple et facile à comprendre qui convient aux débutants. Dans cet article, nous utiliserons Python pour calculer la somme de la diagonale droite d'une matrice. Qu'est-ce qu'une matrice ? En mathématiques, nous utilisons un tableau ou une matrice rectangulaire pour décrire un objet mathématique ou ses propriétés. Il s'agit d'un tableau ou d'un tableau rectangulaire contenant des nombres, des symboles ou des expressions disposés en lignes et en colonnes. Par exemple -234512367574 Il s'agit donc d'une matrice de 3 lignes et 4 colonnes, exprimée sous la forme d'une matrice 3*4. Or, il y a deux diagonales dans la matrice, la diagonale primaire et la diagonale secondaire.
 Exemple de programme Java pour calculer le score total et le pourcentage
Sep 11, 2023 pm 06:01 PM
Exemple de programme Java pour calculer le score total et le pourcentage
Sep 11, 2023 pm 06:01 PM
Nous montrerons comment calculer les scores totaux et les pourcentages à l'aide d'un programme Java. Le score total fait référence à la somme de tous les scores disponibles, tandis que le terme pourcentage fait référence au score calculé divisé par le score total et multiplié par le nombre obtenu 100. percent_of_marks=(obtained_marks/total_marks)×100 Exemple 1 Il s'agit d'un programme Java qui montre comment calculer les scores totaux et les pourcentages. //Programme Java pour démontrer comment les marques totales et les pourcentages sont calculés importjava.io.*;publicclassTotalMarks_





