HTML5 offline storage and cookie storage analysis
What are Cookies ("cookies")? To put it simply, cookies are information (text files in .txt format) that the server temporarily stores on your computer so that the server can use it to identify your computer. When you browse a website, the web server will first send a small amount of data to your computer. Cookies will record the text or selections you make on the website. The next time you visit the same website, the web server will first check to see if there is any cookie information it left last time. If so, it will judge the user based on the content in the cookie and send you specific web page content. Before HTML5, we would use cookies to cache some data on the browser side, such as logged in user information, historical search information, etc. However, the capacity supported by cookies is only 4k, and there is no dedicated API for operation. We can only rely on some open source libraries. Cookies.js is used here to store and obtain cookie information.
// 这是一个cookie值Cookies.set('key', 'value');
// 链式调用Cookies.set('key', 'value').set('hello', 'world');
// 可以额外设置一些参数Cookies.set('key', 'value', { domain: 'www.example.com', secure: true });
// 设置缓存时间Cookies.set('key', 'value', { expires: 600 });
// Expires in 10 minutesCookies.set('key', 'value', { expires: '01/01/2012' });
Cookies.set('key', 'value', { expires: new Date(2012, 0, 1) });
Cookies.set('key', 'value', { expires: Infinity });// 获取Cookies.get('key');It can be seen that using cookie storage has several disadvantages:
The amount of stored data is relatively small
There is no convenient API to operate it
Cookie information will be added to the request header when making an http request, which is both unsafe and increases bandwidth.
WEB Storage
HTML5 provides better local storage specifications localStorage and sessionStorage. They store data locally and do not carry the information in Storage when making http requests. The usage method is also Very simple:
localStorage.setItem('key', 'value'); localStorage.getItem('key'); localStorage.removeItem('key'); sessionStorage.setItem('key', 'value'); sessionStorage.getItem('key'); sessionStorage.removeItem('key');
sessionStorage and localStorage are basically the same in usage and features. The only difference is that sessionStorage is only valid within the session. When the browser window is closed, the sessionStorage cached data will be automatically cleared, while localStorage only needs If you don't clear it manually, it will be saved locally permanently.
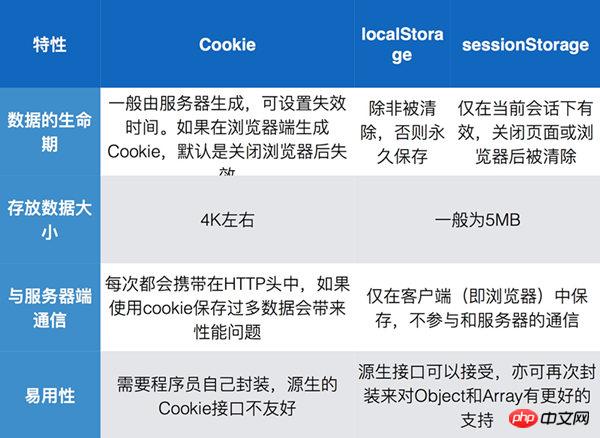
Here is a picture analyzing the differences between cookie, localStorage and sessionStorage
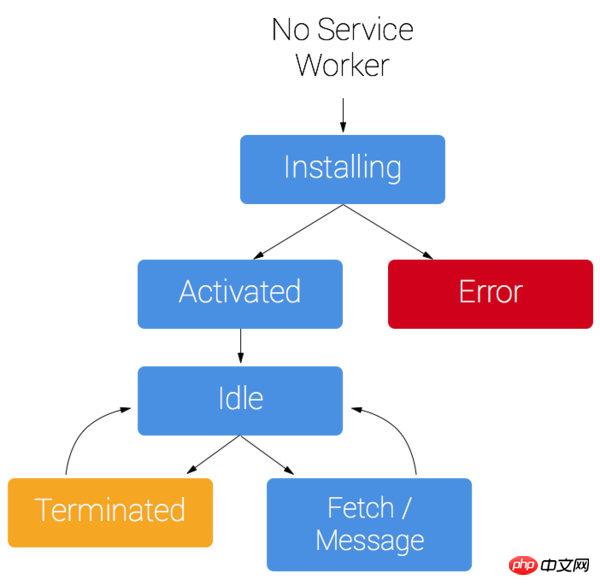
service work life cycle
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script>
navigator.serviceWorker.register("/service-worker.js").then(function(serviceWorker) { console.log("success!");
}); </script>
</head>
<body>
</body></html>
this.oninstall = function(e) { var resources = new Cache(); var visited = new Cache(); // Fetch them.
e.waitUntil(resources.add( "/index.html", "/fallback.html", "/css/base.css", "/js/app.js", "/img/logo.png"
).then(function() { // Add caches to the global caches.
return Promise.all([
caches.set("v1", resources),
caches.set("visited", visited)
]);
}));
};this.onfetch = function(e) {
e.respondWith( // Check to see if request is found in cache
caches.match(e.request).catch(function() { // It's not? Prime the cache and return the response.
return caches.get("visited").then(function(visited) { return fetch(e.request).then(function(response) {
visited.put(e.request, response); // Don't bother waiting, respond already.
return response;
});
});
}).catch(function() { // Connection is down? Simply fallback to a pre-cached page.
return caches.match("/fallback.html");
});
);
};service worker uses an event listening mechanism. The above code monitors the install and fetch events. When the server worker is successfully installed, Call this method, then cache the resource file of the page, fetch the page request event, and the server worker intercepts the user request. When it finds that the requested file hits the cache, it obtains the file from the cache and returns it to the page without going through the server, thereby achieving the purpose of going offline. .
Of course, the functions of service worker are far more than what they are now
indexedDB
indexedDB is a nosql database used to store data locally. It has extremely fast data query speed and can Save the js object directly. It is more efficient than web sql (sqlite), including indexing, transaction processing and robust query functions. indexedDB features:
1. A website may have one or more IndexedDB databases, and each database must have a unique name.
2. A database can contain one or more object stores
一个对象存储(由一个名称惟一标识)是一个记录集合。每个记录有一个键 和一个值。该值是一个对象,可拥有一个或多个属性。键可能基于某个键生成器,从一个键路径衍生出来,或者是显式设置。一个键生成器自动生成惟一的连续正整数。键路径定义了键值的路径。它可以是单个 JavaScript 标识符或多个由句点分隔的标识符。
基本使用方式如下:
var openRequest = indexedDB.open("auto_people", 3);var db; //数据库对象openRequest.onupgradeneeded = function(e)
{ console.log("Running onupgradeeded..."); var thisDB = e.target.result; if(!thisDB.objectStoreNames.contains("people")){
thisDB.createObjectStore("people", {autoIncrement:true}); //新建一个store并设置主键自增长
}
}//创建成功openRequest.onsuccess = function(e){ console.log("success!");
db = e.target.result; //Listen for add clicks}
openRequest.onerror = function(e){ console.log("error!"); console.dir(e);
}//这应该站在别的地方处理,这是做一个代码展示var transaction = db.transaction(['people'], "readwrite");
//创建一个连接var store = transaction.objectStore("people"); //获取storevar request = store.add({
name: 'myron',
email: 'test@qq.com',
created: new Date()
}); //添加信息request.onerror = function(e){
alert('error!'); console.dir(e);
} //当添加失败时调用request.onsuccess = function(e){ console.log('Did it!');
} //添加成功时调用request = store.get(1); //获取第一条数据request.onsuccess = function(e)
{ var result = e.target.result; console.dir(result); if(result){ //拿到存储的对象
}
}以上内容就是cookie和HTML5离线存储的分析,大家都了解了吗?
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of HTML5 offline storage and cookie storage analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.




