Coprocessor access to HBase internals
By Lars Hofhansl Most folks familiar with HBase have heard of coprocessors. Coprocessors come in two flavors: Observers and Endpoints. An Observer is similar to a database trigger, an Endpoint can be likened to a stored procedure. This ana
By Lars HofhanslMost folks familiar with HBase have heard of coprocessors.
Coprocessors come in two flavors: Observers and Endpoints.
An Observer is similar to a database trigger, an Endpoint can be likened to a stored procedure.
This analogy only goes that far, though.
While triggers and stored procedures are (typically) sandboxed and expressed in a highlevel language (typically SQL with procedural extensions), coprocessors are written in Java and are designed to extend HBase directly (in the sense of avoiding subclassing the HRegionServer class in order to extend it). Code in a coprocessor will happily shutdown a region server by calling System.exit(...)!
On the other hand coprocessors are strangely limited. Before HBASE-6522 they had no access to a RegionServer's locks and leases and hence it was impossible to implement check-and-set type as a coprocessor (because the row modified would need to be locked), or to time out expensive server side data structures (via leases).
HBASE-6522 makes some trivial changes to remedy that.
It was also hard to maintain any kind of share state in coprocessors.
Keep in mind that region coprocessors are loaded per region and there might be 100's of regions for a given region server.
Static members won't work reliably, because coprocessor classes are loaded by special classloaders.
HBASE-6505 fixes that too. Now the RegionCoprocessorEnvironment provides a getSharedData() method, which returns a ConcurrentMap, which is held by the coprocessor environment as a weak reference (in a special map with strongly referenced keys and weakly referenced values), and held strongly by the environment that manages each coprocessor.
That way if the coprocessor is blacklisted (due to throwing an unexpected exception) the coprocessors environment is removed, and any shared data is immediately available for garbage collection, thus avoiding ugly and error prone reference counting (maybe this warrants a separate post).
This shared data is per coprocessor class and per regionserver. As long as there is at least one region observer or endpoint active this shared data is not garbage collected and can be accessed to share state between the remaining coprocessors of the same class.
These changes allow coprocessor to be used for a variety of use cases.
State can be shared across them, allowing coordination between many regions, for example for coordinated queries.
Row locks can be created and released - allowing for check-and-set type operations.
And leases can be used to safely expire expensive data structures or to time out locks among other uses.
Update:
I should also mention that RegionObservers already have access to a region's MVCC.
原文地址:Coprocessor access to HBase internals, 感谢原作者分享。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7455
7455
 15
15
 1375
1375
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 14
14
 9
9
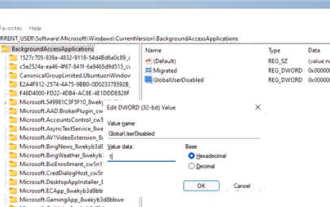 Windows 11 でバックグラウンド アプリケーションを無効にする方法_バックグラウンド アプリケーションを無効にする Windows 11 チュートリアル
May 07, 2024 pm 04:20 PM
Windows 11 でバックグラウンド アプリケーションを無効にする方法_バックグラウンド アプリケーションを無効にする Windows 11 チュートリアル
May 07, 2024 pm 04:20 PM
1. Windows 11で設定を開きます。 Win+I ショートカットまたはその他の方法を使用できます。 2. 「アプリ」セクションに移動し、「アプリと機能」をクリックします。 3. バックグラウンドでの実行を禁止したいアプリケーションを見つけます。三点ボタンをクリックして、[詳細オプション] を選択します。 4. [バックグラウンド アプリケーションのアクセス許可] セクションを見つけて、目的の値を選択します。デフォルトでは、Windows 11 は電力最適化モードを設定します。これにより、Windows はアプリケーションがバックグラウンドでどのように動作するかを管理できるようになります。たとえば、バッテリーを節約するためにバッテリー セーバー モードを有効にすると、システムはすべてのアプリを自動的に終了します。 5. アプリケーションがバックグラウンドで実行されないようにするには、[なし] を選択します。プログラムが通知を送信していない、データの更新に失敗しているなどに気付いた場合は、次のことができることに注意してください。
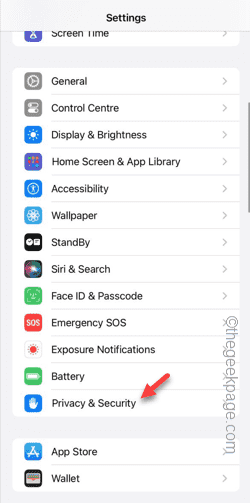 iPhoneのカメラとマイクへのアクセスを許可できません
Apr 23, 2024 am 11:13 AM
iPhoneのカメラとマイクへのアクセスを許可できません
Apr 23, 2024 am 11:13 AM
アプリを使用しようとすると、「カメラとマイクへのアクセスを許可できません」というメッセージが表示されますか?通常、カメラとマイクのアクセス許可は、必要に応じて特定の人に付与します。ただし、許可を拒否すると、カメラとマイクは機能しなくなり、代わりにこのエラー メッセージが表示されます。この問題の解決は非常に基本的なもので、1 ~ 2 分で解決できます。解決策 1 – カメラ、マイクの権限を提供する 必要なカメラとマイクの権限を設定で直接提供できます。ステップ 1 – [設定] タブに移動します。ステップ 2 – [プライバシーとセキュリティ] パネルを開きます。ステップ 3 – そこで「カメラ」権限をオンにします。ステップ 4 – 内部には、携帯電話のカメラの許可を要求したアプリのリストが表示されます。ステップ5 – 指定したアプリの「カメラ」を開きます
 DeepSeek PDFを変換する方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:24 PM
DeepSeek PDFを変換する方法
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:24 PM
DeepSeekはファイルを直接PDFに変換できません。ファイルの種類に応じて、異なる方法を使用できます。一般的なドキュメント(Word、Excel、PowerPoint):Microsoft Office、Libreoffice、その他のソフトウェアを使用してPDFとしてエクスポートします。画像:画像ビューアまたは画像処理ソフトウェアを使用してPDFとして保存します。 Webページ:ブラウザの「Print into PDF」関数を使用するか、PDFツールに専用のWebページを使用します。 UNCOMMONフォーマット:適切なコンバーターを見つけて、PDFに変換します。適切なツールを選択し、実際の状況に基づいて計画を作成することが重要です。
 Javaでフィールドは何を意味しますか
Apr 25, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
Javaでフィールドは何を意味しますか
Apr 25, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
Java では、「フィールド」は、データまたは状態を格納するために使用されるクラスまたはインターフェイスのデータ メンバーです。フィールドのプロパティには、タイプ (任意の Java データ型)、アクセス権、静的 (インスタンスではなくクラスに属する)、最終 (不変)、および一時 (シリアル化されていない) が含まれます。フィールドは、オブジェクト データの保存やオブジェクトの状態の維持など、クラスまたはインターフェイスの状態情報を保存するために使用されます。
 Oracleでdbfファイルを読み取る方法
May 10, 2024 am 01:27 AM
Oracleでdbfファイルを読み取る方法
May 10, 2024 am 01:27 AM
Oracle は、次の手順で dbf ファイルを読み取ることができます。外部テーブルを作成し、その dbf ファイルを参照し、データを Oracle テーブルにインポートします。
 Java リフレクション メカニズムはクラスの動作をどのように変更しますか?
May 03, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Java リフレクション メカニズムはクラスの動作をどのように変更しますか?
May 03, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Java リフレクション メカニズムを使用すると、プログラムはソース コードを変更せずにクラスの動作を動的に変更できます。 Class オブジェクトを操作することで、newInstance() によるインスタンスの作成、プライベート フィールドの値の変更、プライベート メソッドの呼び出しなどが可能になります。ただし、リフレクションは予期しない動作やセキュリティ上の問題を引き起こす可能性があり、パフォーマンスのオーバーヘッドがあるため、注意して使用する必要があります。
 メモリースティックはどのようなものですか?
Apr 21, 2024 pm 01:01 PM
メモリースティックはどのようなものですか?
Apr 21, 2024 pm 01:01 PM
コンピュータのメモリ モジュールはどのようなものですか? これは、コンピュータのグラフィック カードとメモリ モジュールの概要です。コンピュータの独立したグラフィックス カードはファン付きのグラフィックス カード スロットに挿入され、メモリ モジュールはコンピュータのマザーボード上の緑色の長方形の形をしたメモリ モジュール スロット内にあります。ラップトップのメモリ モジュールはデスクトップのメモリ モジュールとは異なるため、互換的に使用することはできません。外観の違い1:デスクトップメモリ、細身、長さ13〜14 cm。 2: ノートのメモリは短く、約 5 センチメートルです。メモリはコンピュータの橋渡し役であり、プロセッサとハードウェア (ハードディスク、マザーボード、グラフィックス カードなど) の間のデータ交換を担当します。途中の赤丸がメモリースティックで、CPUファンの横にありメモリースティックに差し込まれています。ほら、コンピューターのメモリースティックはこんな感じです。ドライバーを使用してデスクトップ コンピューターのカバーを開けます。中央の赤い丸がメモリ モジュールです。メモリースティックとは何ですか?
 Java関数開発における一般的な例外の種類とその修復方法
May 03, 2024 pm 02:09 PM
Java関数開発における一般的な例外の種類とその修復方法
May 03, 2024 pm 02:09 PM
Java 関数開発における一般的な例外の種類とその修復方法 Java 関数の開発中に、関数の正しい実行に影響を与えるさまざまな例外が発生する可能性があります。一般的な例外の種類とその修復方法は次のとおりです。 1. NullPointerException 説明: 初期化されていないオブジェクトにアクセスするとスローされます。修正: オブジェクトを使用する前に、オブジェクトが null でないことを確認してください。サンプル コード: try{Stringname=null;System.out.println(name.length());}catch(NullPointerExceptione){




