

AIxivコラムは、当サイトが学術的・技術的な内容を掲載するコラムです。過去数年間で、このサイトの AIxiv コラムには 2,000 件を超えるレポートが寄せられ、世界中の主要な大学や企業のトップ研究室がカバーされ、学術交流と普及を効果的に促進しています。共有したい優れた作品がある場合は、お気軽に寄稿するか、報告のために当社までご連絡ください。投稿メール: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com
この研究は、「Nature Computational Science」に掲載されました。共同執筆者は、中国アカデミー自動化研究所の研究者 Li Guoqi と Xu Bo です。科学博士、北京大学のティアン・ヨンホン教授。共著者は、清華大学の Qian Xuesen のクラスの学部生、He Linxuan (オートメーション研究所のインターン)、基礎数学および科学クラスの学部生、Xu Yunhui (オートメーション研究所のインターン) です。 、清華大学精密機器学科の博士課程学生、He Weihua 氏と Lin Yihan 氏。
より広範で普遍的な認知機能を備えたモデルを実現することは、人工知能 (AI) 分野の現在の発展における重要な目標です。現在普及している大規模モデル パスは、スケーリング則に基づいて、より大きく、より深く、より幅広いニューラル ネットワークを構築してモデルのパフォーマンスを向上させます。これは、「外生的な複雑さに基づく」一般的なインテリジェンスの実装方法と呼ぶことができます。ただし、この方法は、計算リソースの消費量やエネルギー消費量が多いなど、いくつかの克服できない困難にも直面しており、解釈可能性にも欠点があります。
人工知能と神経科学は長い間相互依存しており、協力して発展してきました。 「外生的複雑さに基づく」一般知能の実現というジレンマを克服するために、中国科学院オートメーション研究所のLi Guoqi氏とXu Bo氏の研究チームは、清華大学、北京大学などと協力して、脳ニューロンの複雑な動的特性を解明し、「内因性の複雑さに基づく」アプローチを提案しました。脳のようなニューロン モデルの構築方法 (図 1) は、従来のモデルの外向きの拡張によって引き起こされるコンピューティング リソースの消費問題を改善し、その例を提供します。人工知能を開発するための神経科学の効果的な利用。 Nature Computational Science 誌はこれについて次のようにコメントしています。「AI 研究は工学や応用に近いものですが、神経科学研究はより探索的なものです。研究チームはこの伝統的な見方に異議を唱え、より詳細で生物学的に現実的なニューロン モデルが深層学習のさらなる進歩を促進できることを示しました」 ”

論文リンク: https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-024-00674-9
コメントリンク: https:// /www.nature.com/articles/ S43588-024-00677-6
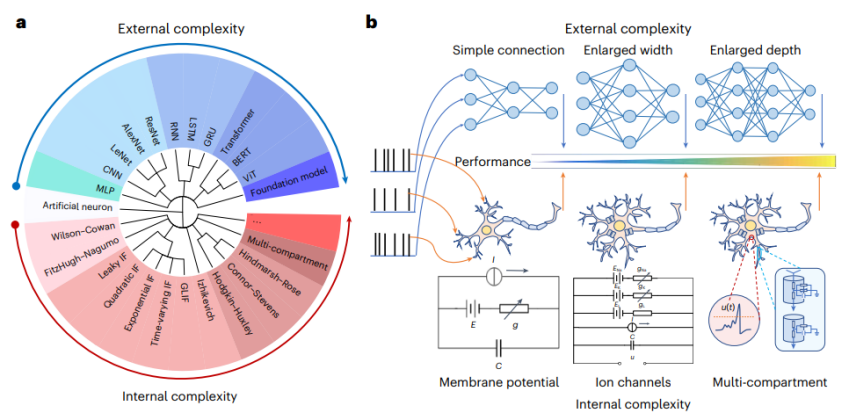
内因性の複雑性とは、脳ニューロンの複雑な動的特性を内部的に利用してニューラル ネットワークの原始モデルを構築することを指します
内因性の複雑性を備えた小さなネットワーク モデル: 生物学的ニューロンからのインスピレーション
生物学的ニューロンは、次のような複雑な内部構造を持っています。イオンチャネル、シナプス伝達機構など、これらの複雑な内部構造により、ニューロンは複雑な信号を処理し、多様な応答を生成することができます。対照的に、古典的な LIF (Leaky Integrate and Fire) ネットワークなど、現在の人工スパイク ニューラル ネットワーク モデルは、通常、単純な内部構造を採用しており、生物学的ニューロンの複雑なダイナミクスや機能をシミュレートすることが困難です。
この研究では、研究者らは「内因性の複雑さを備えた小さなネットワークモデル」という概念を提案しました。その中心的なアイデアは、生物学的ニューロンの複雑なダイナミクスをシミュレートすることによって、単一のニューロンに複雑な内部構造を導入し、それによってより効率的なAIモデルを構築することです。 。たとえば、この研究では、研究者らはスパイキング ニューラル ネットワークで HH (Hodgkin-Huxley) モデルを使用して、従来の LIF モデルを置き換えました。 HH モデルは、ニューロンの活動電位発生のメカニズムを記述する数理モデルであり、複雑な内部構造によってもたらされる微細なダイナミクスを持ち、さまざまな刺激に対するニューロンの応答をシミュレートできます。
外生的な複雑さから内生的な複雑さへの変換
理論的な力学の導出とシミュレーション
The research team theoretically proved that there is a certain equivalence relationship between the HH model and the LIF model in the action potential generation mechanism, that is, one HH neuron can be formed in a specific connection manner with four time-varying parameter LIF neurons (tv-LIF) The microstructural equivalent is that each LIF neuron describes an ion channel in the HH model. Based on this equivalence, the endogenous complexity of the computing unit can be improved by designing the microstructure, so that the HH network model can simulate the dynamic characteristics of the larger-scale LIF network model and achieve similar results on a smaller network structure. Calculation function.
The research team conducted simulation verification of this theory by simulating neuron stimulation input and comparing network output. Under the same input stimulus, the tv-LIF network with higher exogenous complexity is able to produce the same output response as the HH model. Furthermore, the team simplified the "HH model" (tv-LIF2HH) constructed from four tv-LIF neurons into the s-LIF2HH model, and verified through simulation experiments that this simplified model still retains the possibility of capturing the dynamic behavior of the HH model ( Figure 2).复 Figure 2. "Exogenous complexity" and "endogenous complexity" neurons can maintain equivalent dynamic behavior. In order
Comparison of network learning experiments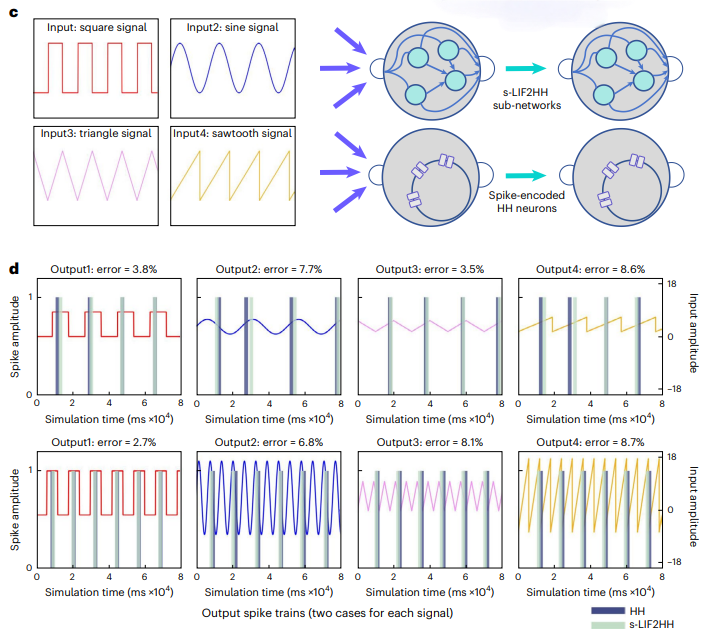
In addition to studying the dynamic behavior of different networks under the same stimulus through simulation, the researchers constructed a larger HH network model, the s-LIF2HH network model, and performed multi-task classification and deep enhancement Learn to experiment. The results show that the HH network model with endogenous complexity can have similar performance in representation ability and robustness to the larger-scale s-LIF2HH network model, and shows better performance than the larger-scale general LIF network. . Multi-task learning experiment: The researcher conducted a multi-task learning experiment using the Fashion-MNIST data set. The results showed that the HH network model can achieve equivalent performance to the larger s-LIF2HH network model, or even slightly better than the larger s-LIF2HH network model. scale of a general LIF network (Figure 3).
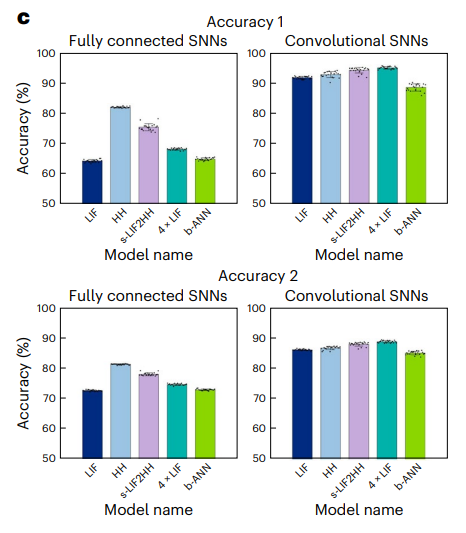 Temporal reinforcement learning experiments: research The researchers conducted sequential reinforcement learning experiments in Inverted Pendulum and Inverted Double Pendulum environments. The results show that the HH network model can perform stronger temporal information extraction than the larger LIF network model. capabilities (Figure 4).
Temporal reinforcement learning experiments: research The researchers conducted sequential reinforcement learning experiments in Inverted Pendulum and Inverted Double Pendulum environments. The results show that the HH network model can perform stronger temporal information extraction than the larger LIF network model. capabilities (Figure 4).
Experiments prove the effectiveness and reliability of the endogenous complexity model in handling complex tasks. At the same time, the study found that the HH network model is more efficient in computing resource consumption, significantly reducing the use of memory and computing time, thereby improving the overall computing efficiency. The research team explained the above research results through the information bottleneck theory. In addition, the external structure of a small-scale model is relatively simple, making it easier to understand its decision-making process, which also improves the interpretability and security of the model.
Conclusion and Outlook
Small models with endogenous complexity bring new opportunities for the development of AI. By simulating the complex dynamics of biological neurons and optimizing the local microstructure of the model to extend the endogenous complexity, we can build more efficient and powerful AI models and overcome the dilemma of large models with external complexity. In the future, expanding endogenous complexity may become an important direction in AI research and promote AI technology to wider applications.
This research provides new methods and theoretical support for integrating the complex dynamic characteristics of neuroscience into artificial intelligence, and provides a feasible solution for AI model optimization and performance improvement in practical applications. At present, the research team has carried out research on larger-scale HH networks and multi-branched multi-compartment neurons with greater endogenous complexity, which is expected to further improve the computing efficiency and task processing capabilities of large models and implement them in practical application scenarios. The quick landing.
以上がNature サブジャーナル | 内因性の複雑さに基づいて、オートメーション研究所の新しい脳のようなネットワークが人工知能と神経科学の間に架け橋を築くの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。