
こんにちは!今日はThree.jsを使って太陽光発電システムを構築してみます。ただし、始める前に、この記事のインスピレーションは、私が現在取り組んでいるプロジェクトのクライアントの代表者から来ていることを知っておいてください。そう、それはあなたです。地球は平らだと信じている人です。
JavaScript/Node には、開発を簡素化する膨大な量の機能をカバーするライブラリの最大のエコシステムがあるため、目的に適したものをいつでも選択できます。ただし、3D グラフィックスについて話している場合、それほどクールなオプションはなく、three.js がおそらくすべての中で最高であり、最大のコミュニティを持っています。
それでは、Three.js に飛び込んで、それを使用して Solar System を構築してみましょう。この記事では以下について説明します:
まず最初に: プロジェクトを初期化するために、Vite を使用し、Three.js の依存関係をインストールします。さて、問題は Three.js をどのように設定するかです。このためには、シーン、カメラ、レンダラという 3 つのものが必要です。また、シーン内を移動できるようにする組み込みアドオン OrbitControls も使用しています。アプリを起動すると、黒い画面が表示されます。
import { Scene, WebGLRenderer, PerspectiveCamera } from "three";
import { OrbitControls } from "three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js";
const w = window.innerWidth;
const h = window.innerHeight;
const scene = new Scene();
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(75, w / h, 0.1, 100);
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.minDistance = 10;
controls.maxDistance = 60;
camera.position.set(30 * Math.cos(Math.PI / 6), 30 * Math.sin(Math.PI / 6), 40);
renderer.setSize(w, h);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
const w = window.innerWidth;
const h = window.innerHeight;
renderer.setSize(w, h);
camera.aspect = w / h;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
});
const animate = () => {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
animate();
コントロールを使用してズームを制限し、カメラのデフォルトの角度も変更していることに気づくかもしれません。これは、次の手順でシーンを適切に表示するのに役立ちます。
太陽系は星に囲まれているはずなので、簡単なスターフィールドを追加します。説明を簡単にするために、球があり、この球上で 1,000 個のランダムな点を選択すると想像してください。次に、これらのポイントに星のテクスチャをマッピングして、これらのポイントから星を作成します。最後に、アニメーションを追加して、これらすべての点が Y 軸の周りを回転するようにします。これで、スターフィールドをシーンに追加する準備が整いました。
import {
Group,
Color,
Points,
Vector3,
TextureLoader,
PointsMaterial,
BufferGeometry,
AdditiveBlending,
Float32BufferAttribute,
} from "three";
export class Starfield {
group;
loader;
animate;
constructor({ numStars = 1000 } = {}) {
this.numStars = numStars;
this.group = new Group();
this.loader = new TextureLoader();
this.createStarfield();
this.animate = this.createAnimateFunction();
this.animate();
}
createStarfield() {
let col;
const verts = [];
const colors = [];
const positions = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.numStars; i += 1) {
let p = this.getRandomSpherePoint();
const { pos, hue } = p;
positions.push(p);
col = new Color().setHSL(hue, 0.2, Math.random());
verts.push(pos.x, pos.y, pos.z);
colors.push(col.r, col.g, col.b);
}
const geo = new BufferGeometry();
geo.setAttribute("position", new Float32BufferAttribute(verts, 3));
geo.setAttribute("color", new Float32BufferAttribute(colors, 3));
const mat = new PointsMaterial({
size: 0.2,
alphaTest: 0.5,
transparent: true,
vertexColors: true,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
map: this.loader.load("/solar-system-threejs/assets/circle.png"),
});
const points = new Points(geo, mat);
this.group.add(points);
}
getRandomSpherePoint() {
const radius = Math.random() * 25 + 25;
const u = Math.random();
const v = Math.random();
const theta = 2 * Math.PI * u;
const phi = Math.acos(2 * v - 1);
let x = radius * Math.sin(phi) * Math.cos(theta);
let y = radius * Math.sin(phi) * Math.sin(theta);
let z = radius * Math.cos(phi);
return {
pos: new Vector3(x, y, z),
hue: 0.6,
minDist: radius,
};
}
createAnimateFunction() {
return () => {
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate);
this.group.rotation.y += 0.00005;
};
}
getStarfield() {
return this.group;
}
}
スターフィールドの追加は、シーンクラスの add メソッドを使用するだけで簡単です
const starfield = new Starfield().getStarfield(); scene.add(starfield);
テクスチャに関しては、このプロジェクトで使用されているすべてのテクスチャが、記事の最後にリンクされているリポジトリ内にあります。星と惑星の環のテクスチャを除いて、ほとんどのテクスチャはこのサイトから取得されました。
太陽には、正二十面体ジオメトリを使用し、その上にテクスチャをマッピングしました。改善されたノイズを使用して、太陽が脈動するエフェクトを実現し、実際の星が宇宙にエネルギーの流れを放出する方法をシミュレートしました。太陽は、マップされたテクスチャを持つ単なる図形ではありません。また、シーン内の光源である必要があるため、PointLight を使用してこれをシミュレートしています。
import {
Mesh,
Group,
Color,
Vector3,
BackSide,
PointLight,
TextureLoader,
ShaderMaterial,
AdditiveBlending,
DynamicDrawUsage,
MeshBasicMaterial,
IcosahedronGeometry,
} from "three";
import { ImprovedNoise } from "three/addons/math/ImprovedNoise.js";
export class Sun {
group;
loader;
animate;
corona;
sunRim;
glow;
constructor() {
this.sunTexture = "/solar-system-threejs/assets/sun-map.jpg";
this.group = new Group();
this.loader = new TextureLoader();
this.createCorona();
this.createRim();
this.addLighting();
this.createGlow();
this.createSun();
this.animate = this.createAnimateFunction();
this.animate();
}
createSun() {
const map = this.loader.load(this.sunTexture);
const sunGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(5, 12);
const sunMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
map,
emissive: new Color(0xffff99),
emissiveIntensity: 1.5,
});
const sunMesh = new Mesh(sunGeometry, sunMaterial);
this.group.add(sunMesh);
this.group.add(this.sunRim);
this.group.add(this.corona);
this.group.add(this.glow);
this.group.userData.update = (t) => {
this.group.rotation.y = -t / 5;
this.corona.userData.update(t);
};
}
createCorona() {
const coronaGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(4.9, 12);
const coronaMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xff0000,
side: BackSide,
});
const coronaMesh = new Mesh(coronaGeometry, coronaMaterial);
const coronaNoise = new ImprovedNoise();
let v3 = new Vector3();
let p = new Vector3();
let pos = coronaGeometry.attributes.position;
pos.usage = DynamicDrawUsage;
const len = pos.count;
const update = (t) => {
for (let i = 0; i < len; i += 1) {
p.fromBufferAttribute(pos, i).normalize();
v3.copy(p).multiplyScalar(5);
let ns = coronaNoise.noise(
v3.x + Math.cos(t),
v3.y + Math.sin(t),
v3.z + t
);
v3.copy(p)
.setLength(5)
.addScaledVector(p, ns * 0.4);
pos.setXYZ(i, v3.x, v3.y, v3.z);
}
pos.needsUpdate = true;
};
coronaMesh.userData.update = update;
this.corona = coronaMesh;
}
createGlow() {
const uniforms = {
color1: { value: new Color(0x000000) },
color2: { value: new Color(0xff0000) },
fresnelBias: { value: 0.2 },
fresnelScale: { value: 1.5 },
fresnelPower: { value: 4.0 },
};
const vertexShader = `
uniform float fresnelBias;
uniform float fresnelScale;
uniform float fresnelPower;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
vec4 mvPosition = modelViewMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec4 worldPosition = modelMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec3 worldNormal = normalize( mat3( modelMatrix[0].xyz, modelMatrix[1].xyz, modelMatrix[2].xyz ) * normal );
vec3 I = worldPosition.xyz - cameraPosition;
vReflectionFactor = fresnelBias + fresnelScale * pow( 1.0 + dot( normalize( I ), worldNormal ), fresnelPower );
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * mvPosition;
}
`;
const fragmentShader = `
uniform vec3 color1;
uniform vec3 color2;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
float f = clamp( vReflectionFactor, 0.0, 1.0 );
gl_FragColor = vec4(mix(color2, color1, vec3(f)), f);
}
`;
const sunGlowMaterial = new ShaderMaterial({
uniforms,
vertexShader,
fragmentShader,
transparent: true,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
});
const sunGlowGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(5, 12);
const sunGlowMesh = new Mesh(sunGlowGeometry, sunGlowMaterial);
sunGlowMesh.scale.setScalar(1.1);
this.glow = sunGlowMesh;
}
createRim() {
const uniforms = {
color1: { value: new Color(0xffff99) },
color2: { value: new Color(0x000000) },
fresnelBias: { value: 0.2 },
fresnelScale: { value: 1.5 },
fresnelPower: { value: 4.0 },
};
const vertexShader = `
uniform float fresnelBias;
uniform float fresnelScale;
uniform float fresnelPower;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
vec4 mvPosition = modelViewMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec4 worldPosition = modelMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec3 worldNormal = normalize( mat3( modelMatrix[0].xyz, modelMatrix[1].xyz, modelMatrix[2].xyz ) * normal );
vec3 I = worldPosition.xyz - cameraPosition;
vReflectionFactor = fresnelBias + fresnelScale * pow( 1.0 + dot( normalize( I ), worldNormal ), fresnelPower );
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * mvPosition;
}
`;
const fragmentShader = `
uniform vec3 color1;
uniform vec3 color2;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
float f = clamp( vReflectionFactor, 0.0, 1.0 );
gl_FragColor = vec4(mix(color2, color1, vec3(f)), f);
}
`;
const sunRimMaterial = new ShaderMaterial({
uniforms,
vertexShader,
fragmentShader,
transparent: true,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
});
const sunRimGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(5, 12);
const sunRimMesh = new Mesh(sunRimGeometry, sunRimMaterial);
sunRimMesh.scale.setScalar(1.01);
this.sunRim = sunRimMesh;
}
addLighting() {
const sunLight = new PointLight(0xffff99, 1000);
sunLight.position.set(0, 0, 0);
this.group.add(sunLight);
}
createAnimateFunction() {
return (t = 0) => {
const time = t * 0.00051;
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate);
this.group.userData.update(time);
};
}
getSun() {
return this.group;
}
}
すべての惑星は同様のロジックを使用して構築されています。各惑星には軌道、テクスチャ、軌道速度、および回転速度が必要です。リングが必要な惑星については、リングも追加する必要があります。
import {
Mesh,
Color,
Group,
DoubleSide,
RingGeometry,
TorusGeometry,
TextureLoader,
ShaderMaterial,
SRGBColorSpace,
AdditiveBlending,
MeshPhongMaterial,
MeshBasicMaterial,
IcosahedronGeometry,
} from "three";
export class Planet {
group;
loader;
animate;
planetGroup;
planetGeometry;
constructor({
orbitSpeed = 1,
orbitRadius = 1,
orbitRotationDirection = "clockwise",
planetSize = 1,
planetAngle = 0,
planetRotationSpeed = 1,
planetRotationDirection = "clockwise",
planetTexture = "/solar-system-threejs/assets/mercury-map.jpg",
rimHex = 0x0088ff,
facingHex = 0x000000,
rings = null,
} = {}) {
this.orbitSpeed = orbitSpeed;
this.orbitRadius = orbitRadius;
this.orbitRotationDirection = orbitRotationDirection;
this.planetSize = planetSize;
this.planetAngle = planetAngle;
this.planetTexture = planetTexture;
this.planetRotationSpeed = planetRotationSpeed;
this.planetRotationDirection = planetRotationDirection;
this.rings = rings;
this.group = new Group();
this.planetGroup = new Group();
this.loader = new TextureLoader();
this.planetGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(this.planetSize, 12);
this.createOrbit();
this.createRings();
this.createPlanet();
this.createGlow(rimHex, facingHex);
this.animate = this.createAnimateFunction();
this.animate();
}
createOrbit() {
const orbitGeometry = new TorusGeometry(this.orbitRadius, 0.01, 100);
const orbitMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xadd8e6,
side: DoubleSide,
});
const orbitMesh = new Mesh(orbitGeometry, orbitMaterial);
orbitMesh.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
this.group.add(orbitMesh);
}
createPlanet() {
const map = this.loader.load(this.planetTexture);
const planetMaterial = new MeshPhongMaterial({ map });
planetMaterial.map.colorSpace = SRGBColorSpace;
const planetMesh = new Mesh(this.planetGeometry, planetMaterial);
this.planetGroup.add(planetMesh);
this.planetGroup.position.x = this.orbitRadius - this.planetSize / 9;
this.planetGroup.rotation.z = this.planetAngle;
this.group.add(this.planetGroup);
}
createGlow(rimHex, facingHex) {
const uniforms = {
color1: { value: new Color(rimHex) },
color2: { value: new Color(facingHex) },
fresnelBias: { value: 0.2 },
fresnelScale: { value: 1.5 },
fresnelPower: { value: 4.0 },
};
const vertexShader = `
uniform float fresnelBias;
uniform float fresnelScale;
uniform float fresnelPower;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
vec4 mvPosition = modelViewMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec4 worldPosition = modelMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec3 worldNormal = normalize( mat3( modelMatrix[0].xyz, modelMatrix[1].xyz, modelMatrix[2].xyz ) * normal );
vec3 I = worldPosition.xyz - cameraPosition;
vReflectionFactor = fresnelBias + fresnelScale * pow( 1.0 + dot( normalize( I ), worldNormal ), fresnelPower );
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * mvPosition;
}
`;
const fragmentShader = `
uniform vec3 color1;
uniform vec3 color2;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
float f = clamp( vReflectionFactor, 0.0, 1.0 );
gl_FragColor = vec4(mix(color2, color1, vec3(f)), f);
}
`;
const planetGlowMaterial = new ShaderMaterial({
uniforms,
vertexShader,
fragmentShader,
transparent: true,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
});
const planetGlowMesh = new Mesh(this.planetGeometry, planetGlowMaterial);
planetGlowMesh.scale.setScalar(1.1);
this.planetGroup.add(planetGlowMesh);
}
createRings() {
if (!this.rings) return;
const innerRadius = this.planetSize + 0.1;
const outerRadius = innerRadius + this.rings.ringsSize;
const ringsGeometry = new RingGeometry(innerRadius, outerRadius, 32);
const ringsMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
side: DoubleSide,
transparent: true,
map: this.loader.load(this.rings.ringsTexture),
});
const ringMeshs = new Mesh(ringsGeometry, ringsMaterial);
ringMeshs.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
this.planetGroup.add(ringMeshs);
}
createAnimateFunction() {
return () => {
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate);
this.updateOrbitRotation();
this.updatePlanetRotation();
};
}
updateOrbitRotation() {
if (this.orbitRotationDirection === "clockwise") {
this.group.rotation.y -= this.orbitSpeed;
} else if (this.orbitRotationDirection === "counterclockwise") {
this.group.rotation.y += this.orbitSpeed;
}
}
updatePlanetRotation() {
if (this.planetRotationDirection === "clockwise") {
this.planetGroup.rotation.y -= this.planetRotationSpeed;
} else if (this.planetRotationDirection === "counterclockwise") {
this.planetGroup.rotation.y += this.planetRotationSpeed;
}
}
getPlanet() {
return this.group;
}
}
地球については、Planet クラスを拡張して、雲や惑星の夜側の夜のテクスチャなどの追加のテクスチャを追加します。
import {
Mesh,
AdditiveBlending,
MeshBasicMaterial,
MeshStandardMaterial,
} from "three";
import { Planet } from "./planet";
export class Earth extends Planet {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.createPlanetLights();
this.createPlanetClouds();
}
createPlanetLights() {
const planetLightsMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
map: this.loader.load("/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-2.jpg"),
blending: AdditiveBlending,
});
const planetLightsMesh = new Mesh(
this.planetGeometry,
planetLightsMaterial
);
this.planetGroup.add(planetLightsMesh);
this.group.add(this.planetGroup);
}
createPlanetClouds() {
const planetCloudsMaterial = new MeshStandardMaterial({
map: this.loader.load("/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-3.jpg"),
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.8,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
alphaMap: this.loader.load(
"/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-4.jpg"
),
});
const planetCloudsMesh = new Mesh(
this.planetGeometry,
planetCloudsMaterial
);
planetCloudsMesh.scale.setScalar(1.003);
this.planetGroup.add(planetCloudsMesh);
this.group.add(this.planetGroup);
}
}
Google で約 5 分間検索すると、シーンに惑星を追加するために必要な値をすべて記載した表が表示されます。
| Planet | Size (diameter) | Rotation speed | Rotation direction | Orbit speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 4,880 km | 10.83 km/h | Counterclockwise | 47.87 km/s |
| Venus | 12,104 km | 6.52 km/h | Clockwise | 35.02 km/s |
| Earth | 12,742 km | 1674.4 km/h | Counterclockwise | 29.78 km/s |
| Mars | 6,779 km | 866.5 km/h | Counterclockwise | 24.07 km/s |
| Jupiter | 142,984 km | 45,300 km/h | Counterclockwise | 13.07 km/s |
| Saturn | 120,536 km | 35,500 km/h | Counterclockwise | 9.69 km/s |
| Uranus | 51,118 km | 9,320 km/h | Clockwise | 6.81 km/s |
| Neptune | 49,528 km | 9,720 km/h | Counterclockwise | 5.43 km/s |
Now, all the planets and the sun can be added to the scene.
const planets = [
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00048,
orbitRadius: 10,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.2,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.005,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/mercury-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xf9cf9f,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00035,
orbitRadius: 13,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.0005,
planetRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/venus-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xb66f1f,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00024,
orbitRadius: 19,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.3,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.01,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/mars-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xbc6434,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00013,
orbitRadius: 22,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 1,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.06,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/jupiter-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xf3d6b6,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.0001,
orbitRadius: 25,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.8,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.05,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/saturn-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xd6b892,
rings: {
ringsSize: 0.5,
ringsTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/saturn-rings.jpg",
},
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00007,
orbitRadius: 28,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.02,
planetRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/uranus-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0x9ab6c2,
rings: {
ringsSize: 0.4,
ringsTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/uranus-rings.jpg",
},
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.000054,
orbitRadius: 31,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.02,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/neptune-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0x5c7ed7,
},
];
planets.forEach((item) => {
const planet = new Planet(item).getPlanet();
scene.add(planet);
});
const earth = new Earth({
orbitSpeed: 0.00029,
orbitRadius: 16,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetAngle: (-23.4 * Math.PI) / 180,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.01,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-1.jpg",
}).getPlanet();
scene.add(earth);
In result all solar system will look sth like:
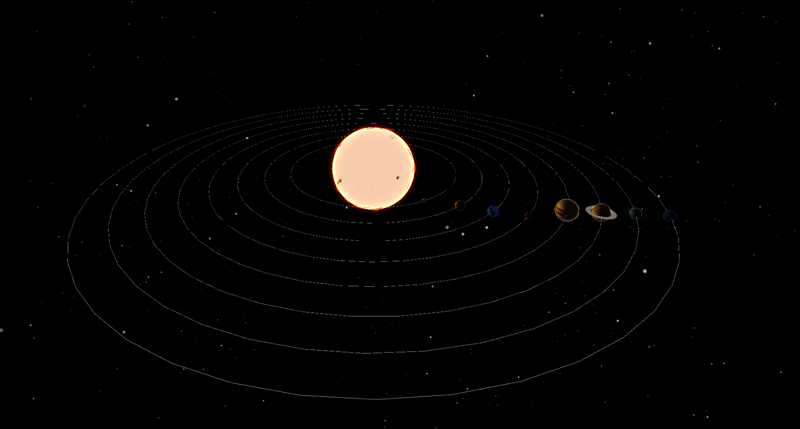
For deploying to set the correct base in vite.config.js.
If you are deploying to https://
If you are deploying to https://
Go to your GitHub Pages configuration in the repository settings page and choose the source of deployment as "GitHub Actions", this will lead you to create a workflow that builds and deploys your project, a sample workflow that installs dependencies and builds using npm is provided:
# Simple workflow for deploying static content to GitHub Pages
name: Deploy static content to Pages
on:
# Runs on pushes targeting the default branch
push:
branches: ['main']
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# Sets the GITHUB_TOKEN permissions to allow deployment to GitHub Pages
permissions:
contents: read
pages: write
id-token: write
# Allow one concurrent deployment
concurrency:
group: 'pages'
cancel-in-progress: true
jobs:
# Single deploy job since we're just deploying
deploy:
environment:
name: github-pages
url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
cache: 'npm'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Build
run: npm run build
- name: Setup Pages
uses: actions/configure-pages@v4
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v3
with:
# Upload dist folder
path: './dist'
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
id: deployment
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v4
That is it. If your deployment has not started automatically you can always start it manually in Actions tab in your repo. Link with deployed project can be found below.
That’s it for today! You can find the link to the entire project below. I hope you found this entertaining and don’t still believe the Earth is flat.
See ya!
Repository link
Deployment link
以上がThree.js を使用した太陽光発電システムの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。