
Java の多次元配列に関する完全なガイド。配列は、同様のデータ型を持つ要素のコレクションである同種データの多次元構造です。これらは連続したメモリ位置に保存されます。配列では、最初の要素はインデックス 0 に格納されます。 2 番目の要素はインデックス 1 に格納され、以下同様に続きます。配列は単一次元または多次元にすることができます。このドキュメントでは、Java の多次元配列について説明します。多次元配列は、複数の行と列を保持できる配列の配列です。ここで、次のセクションで多次元配列の構文と実装を見てみましょう。
広告 このカテゴリーの人気コース JAVA マスタリー - スペシャライゼーション | 78 コース シリーズ | 15 回の模擬テスト構文:
data_type[dimension 1][dimension 2][]…[dimension n] array_name= new data_type[size 1][size 2]…[size n]
Java で最も一般的な多次元配列は次のとおりです:
2D 配列は、スーパー マリオなどのプラットフォーム ビデオ ゲームで地形や画面を表すためによく使用されます。また、チェス盤の描画、スプレッドシートなどの構造の表現にも使用できます。
コード:
int[][] array1 = new int[2][2];//Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns
例:
9 10
7 66
これは 2 行 2 列の 2D 配列です。
3 次元配列はリアルタイム アプリケーションでは一般的に使用されません。したがって、プログラミング例でも 2 次元配列がより優先されます。
コード:
int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
例:
6 8 66
66 65 47
46 89 98
通常の配列がわかっていれば、Java の多次元配列を理解するのは簡単です。多次元配列は以下のように宣言できます:
まず、2D 配列の宣言を見てみましょう。
Java でのプログラミング中に適切な宣言が作成されていることを確認してください。
コード:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional 2D array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String args[]){
//2D array a is declared and initialized
int a[][]={{2,2,3},{8,4,5},{9,4,5}};
//Print the array elements
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}出力:

三次元配列の宣言について議論できます。
これらの配列には任意のデータ型を使用できます。以下は、さまざまなデータ型を持つ 3 次元配列の一部です。
コード:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3D array arr
int[][][] arr = { { { 1 , -9 , 3 } ,{ 2 , 7 , 4 } } , { { -45 , -5 , 6 , 75 } , { 88 } , { 29 , 30 } } };
// for..each loop to iterate through the elements of the 3d array arr
for (int[][] ar: arr) {
for (int[] a: ar) {
for(int finalarray: a) {
System.out.println(finalarray);
}
}
}
}
}出力:

多次元配列は複数の方法で初期化できます:
In a more traditional way, Initializing Array elements can be as follows.
int[][][] a = { { { 11 , 23 , 30 }, { 5 ,65 , 70 } , { 0 , 80 , 10 } ,{ 10 , 12 , 450 } } ,{ { 33 , 2 , 4 } , {11, 66, 6}, {55, 11, 22}, {11, 57, 43} } };In this case, even though the size of rows and columns are not mentioned, the java compiler is able to identify the size of rows and columns by counting the number of elements.
In the case of storing a large number of elements, Nested For Loop can be used as shown below:
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = i + j + k;} } }int a= new int[3][2][4]; a[0][2][1]= 33; a[0][1][2]= 73; a[0][1][1]= 88;
A three-dimensional array of size 3 levels * 2 rows * 4 columns is created, but values are assigned to some positions only. Since none of the other elements does have any value assigned, default values will be assigned.
Multidimensional Array in Java can perform several operations.
Let Us See the Matrix Addition of Two Arrays.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String args[])
{
int row, col, c, d;
//input the number of rows and columns
Scanner <u>in</u> = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows of matrix");
row = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns of matrix");
col = in.nextInt();
//initialization of two matrices and sum matrix
int firstmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int secondmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int summat[][] = new int[row][col];
//adding elements to first matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the first matrix");
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
firstmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//adding elements to second matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the second matrix");
for (c = 0 ; c < row ; c++)
for (d = 0 ; d < col ; d++)
secondmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//sum of the two matrices
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
summat[c][d] = firstmat[c][d] + secondmat[c][d];
System.out.println("Sum of the two given matrices is:");
//printing the sum matrix
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
{
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
System.out.print(summat[c][d]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:

If subtraction needs to be performed, replace ‘+’ with ‘-‘ in the code.
Let us see how Matrix Multiplication Works.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to perform matrix multiplication
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
static int N = 4;
// multiply matrices a and b, and then stores the result in c
static void mul(int a[][],
int b[][], int c[][])
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; //multiply a and b matrices
}
}
}
//main method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[][] = { {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2},
{9, 7, 2, 3}};
int b[][] = {{ 9, 7, 2, 3}, {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2}};
// Store the result in c
int c[][] = new int[N][N] ;
int i, j;
mul(a, b, c); //calling the mul method
System.out.println("Multiplication result matrix" + " is ");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
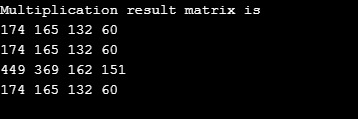
}Output:
Arrays are homogenous data structures that can store similar types of elements. It can be of single-dimensional or multidimensional. In this document, multidimensional arrays are discussed with explaining the syntax structure, initialization, etc.
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in Java. Here we discuss 2 types of the multidimensional array in java, how to declare, how to initialize and operation in it. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
以上がJavaの多次元配列の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。