
ファイル処理とは、Java でファイルを操作することを指します。ファイルの読み取りと Java ファイルへの書き込みは、Java ではファイル処理として知られています。ファイルは、さまざまな種類の情報を含めることができるコンテナです。ファイルにはテキスト、画像、ビデオ、表などを含めることができます。
広告 このカテゴリーの人気コース JAVA マスタリー - スペシャライゼーション | 78 コース シリーズ | 15 回の模擬テスト無料ソフトウェア開発コースを始めましょう
Web 開発、プログラミング言語、ソフトウェア テスト、その他
Java では、File クラスを使用してさまざまな種類のファイルを操作できます。 File クラスは java.io パッケージのメンバーです。 Java には、ファイルの読み取り、書き込み、更新、削除を行うためのさまざまなメソッドが用意されています。
ファイルに対して実行できるさまざまなタイプの操作を以下に示します:
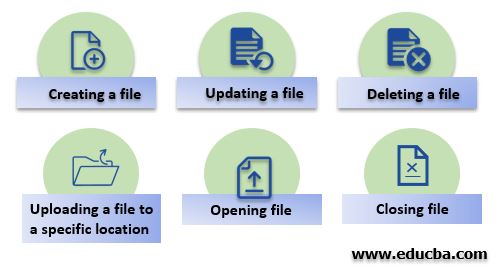
構文:
プログラム内でファイルを操作するには、java.io パッケージをインポートする必要があります。このパッケージをインポートすると、File クラスのコンストラクターでファイルを参照することで初期化できる File クラスが提供されます。
//importing file class
import java.io.File;
//File name passed to the object
File fileObj = new File("file.txt");Java では、ファイル処理はストリーミングの概念によって行われます。ファイルの入出力操作はストリーミングを通じて実行されます。ストリームとは、一連のデータを指します。
Java では、ストリームには 2 つのタイプがあります:
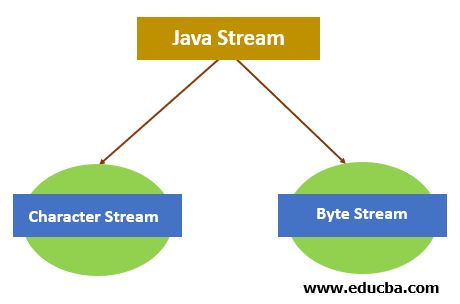
Java でさまざまな操作を実行するためのメソッドの一部を以下に示します。
以下は Java でのファイル処理の例です:
この例では、プログラムはさまざまなメソッドを使用して特定の詳細を取得します。このアプリケーションでは、次のようなさまざまなメソッドを使用してファイルに関連する情報を取得します。
コード:
io パッケージのさまざまなクラスをインポートしています。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileHandlingExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of a file
File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
if (fileObj.exists()) {
//retrieving the path of the specified file
System.out.println("\nSpecified file path: " + fileObj.getAbsolutePath());
//checking whether the file is writable or not
System.out.println("\nIs the file Writable: " + fileObj.canWrite());
//checking whether the file is Readable or not
System.out.println("\nIs the file Readable " + fileObj.canRead());
//retrieving file name
System.out.println("\nFile name: " + fileObj.getName());
//retrieving file size
System.out.println("\nFile size (in bytes) " + fileObj.length());
File fileDirObj = new File("D:/Programs/");
String[] fileList = fileDirObj.list();
//displaying here the list of files available in the directory
for (int i = 0; i < fileList.length; i++) {
System.out.print("\n" + fileList[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
else {
System.out.println("Specified file does not exist.");
}
}
}出力:
上記の例では、ファイルに関連するさまざまなチェックを実行するために必要な情報をさまざまなメソッドがどのように提供するかがわかります。
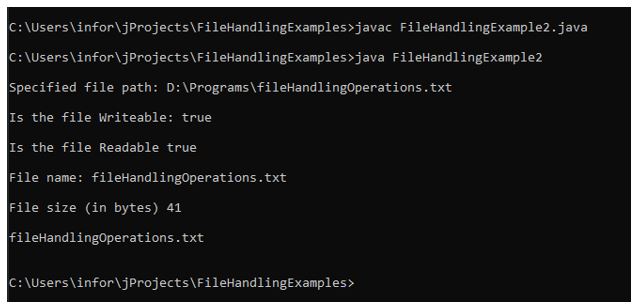
この例は、プログラム内でさまざまな種類の操作に対してさまざまなメソッドがどのように使用されるかを示しています。ファイルが存在するかどうかを確認するためにプログラムで使用されるexists()メソッドは存在しません。その後、if..else.. 条件が置かれます。
In the If condition, it checks first whether the existing file is writable or not; if the existing file remains writable, then the code block under the if section uses the FileWriter class method to write content into the existing file.
Code:
Importing io package different classes.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileHandlingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
if(fileObj.exists()){
System.out.println("File already exists.");
if(fileObj.canWrite()){
//creating object of FileWriter class to write things on file
FileWriter fwObj = new FileWriter("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
// Writes this content into the specified file
fwObj.write("It is a basic example of writing in file!");
//closing the files once writing completed
fwObj.close();
System.out.println("\nContent has been written to the file.");
}else{
System.out.println("\nFile is not in writable mode.");
}
;
}else{
if (fileObj.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("New File created: " + fileObj.getName());
}
}
}
catch (IOException ioError) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
ioError.printStackTrace();
}
}
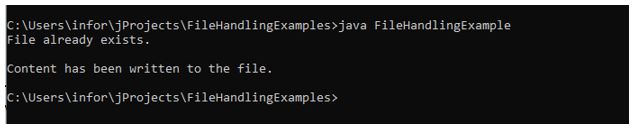
}Output:
In the above-given example, After compilation, running the program the first time will create a file with the specified name in the program.
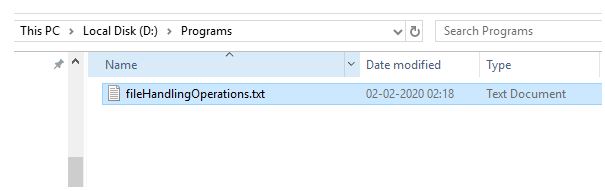
Running the program a second time will write the content in the existing file.
The article above explains what a file is, how to perform operations on it, and how file handling works. It was also demonstrated in the above section about classes & methods that can be used to work with files in java.
以上がJava でのファイル処理の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。