Java ArrayList クラス
ArrayList は List インターフェースの実装であり、Java のコレクション フレームワークの下にあり、配列のサイズを動的に、つまり実行時に拡大することができます。このクラスは内部的に java.util.package で使用でき、配列データ構造を使用します。 ArrayList では Java のラッパー クラスのみが許可され、ユーザーがクラスを定義します。
無料ソフトウェア開発コースを始めましょう
Web 開発、プログラミング言語、ソフトウェア テスト、その他
構文:
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList のインスタンスを直接使用するか、List 参照に割り当てることができます。
コンストラクター:
配列リストには、次の 3 つのコンストラクターが利用可能です。
- ArrayList(intInitialCapacity): ここで、配列リストの初期長を指定できます。ただし、サイズが前述のInitialCapacityを超えた場合は、ArrayList クラスが処理します。
- ArrayList(): これにより、初期容量なしの空のリストを作成できるため、この場合、デフォルトの初期容量は 10 になります。
- ArrayList(Collection c): コレクションのリスト。
Java ArrayList クラスのメソッド
次に、Java ArrayList クラスのメソッドを示します。
- void trimToSize(): This method will trim the list to the current list size.
- Object[] toArray(): Return the array of object.
- boolean remove(Object o): This method is used to remove the object, but it will remove the first occurrence as the list contain duplicate.
- boolean removeAll(Collection c): This method is used to remove all the elements of the list.
- Boolean removeIf(Predicate filter): This method is used to remove the predicate passed. Used as a filter.
- Add (E e): This method s used to add elements to the list.
- Void add(int index, E element): It takes two-parameter and adds elements t the specific index we mentioned.
- Boolean addAll(Collection c): This takes a list as an argument and adds all the elements to the end of the current list.
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection c): This method adds all the elements to the current list at the specified index we pass.
- Get (int index): This method is used to get the element. It will return the element present at the specified position in the list.
- Int indexOf(Object o): This method is used to get the element’s index passed. It will always return the first occurrence of the element into the list because the list can contain duplicate elements.
-
ListIterator
listIterator(int index): This method returns an iterator with the specific index. - Remove (int index): This method removes the element. It will remove the element with the corresponding index passed.
- Protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex): This removes the elements from a specified range.
- Boolean retainAll(Collection c): This method will retain all elements contained in the specified collection.
- Set (int index, E element): This method will set the element to the specified index.
- Void sort(Comparator c): This method is used to sort the collection element.
-
List
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex): This method will be used to return the sublist from the specified index. - Void clear(): This mentioned is used to clear the elements in the list.
- Object clone(): These methods create a copy of the list.
- Boolean contains(Object o): This method is used to check whether the passing object is present in the list or not.
- Void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity): This method is used to increase the capacity of the array list.
- Boolean isEmpty(): This method is used to check whether the array list is empty or not.
-
Iterator
iterator(): This method returns iterator. - int lastIndexOf(Object o): This method returns the last index of the object passed. If the object does not present in the list, it will return -1.
-
ListIterator
listIterator(): This methods return iterator.
Examples of Java ArrayList Class
Examples of Java ArrayList Class are given below:
1. add an element in ArrayList
The below example will show how to add an element to an array list.
Code:
package com.cont.article;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArratListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
System.out.println("list is :: " + list);
}
}Output:

2. Copying elements of list one to another list
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.addAll(list);
System.out.println("Elements in list one : " + list);
System.out.println("Elements in list two : " + list2);
}
}Output:
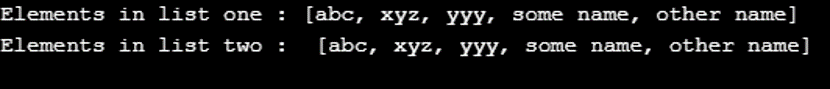
3. Remove element from ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
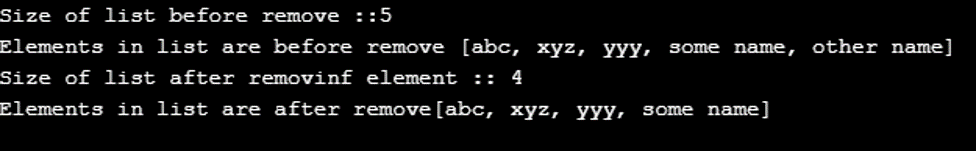
System.out.println("Size of list before remove ::" + list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are before remove " + list);
list.remove(4);
System.out.println("Size of list after removinf element :: " +list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are after remove" + list);
}
}Output:
4. Clear all the elements from ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
list.clear();
System.out.println("Clering all elements of list " +list.size());
}
}Output:

5. Iterate all the elements of ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
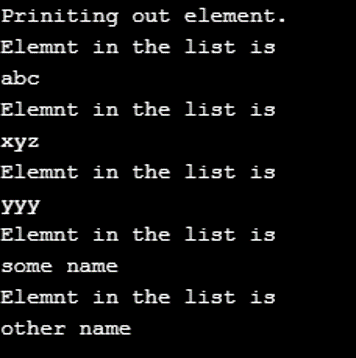
System.out.println("Priniting out element.");
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println("Elemnt in the list is");
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}Output:
The array list in java does not contain duplicate elements. Also, the insertion order is maintained in a list, which means we put over elements that will generate the output in the same sequence. Some detailed points which need to be remembered for the array list in java are as follows:
It implements various interfaces:
- Serializable,
- Iterable
, - Cloneable,
- Collection
, - List
, - RandomAccess
The class hierarchy is as follows:
java.lang.Object >> java.util.AbstractCollection<E> >> java.util.AbstractList<E> >> java.util.ArrayList<E>
By default, the array list is not synchronized in nature and is not thread-safe, But we can make them synchronized using the collections class synchronized method. The syntax is described below for reference :
List arrList = Collections.synchronizedList (new ArrayList(...));
以上がJava ArrayList クラスの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7899
7899
 15
15
 1651
1651
 14
14
 1411
1411
 52
52
 1303
1303
 25
25
 1248
1248
 29
29
 Java 8 Stream Foreachから休憩または戻ってきますか?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 Stream Foreachから休憩または戻ってきますか?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8は、Stream APIを導入し、データ収集を処理する強力で表現力のある方法を提供します。ただし、ストリームを使用する際の一般的な質問は次のとおりです。 従来のループにより、早期の中断やリターンが可能になりますが、StreamのForeachメソッドはこの方法を直接サポートしていません。この記事では、理由を説明し、ストリーム処理システムに早期終了を実装するための代替方法を調査します。 さらに読み取り:JavaストリームAPIの改善 ストリームを理解してください Foreachメソッドは、ストリーム内の各要素で1つの操作を実行する端末操作です。その設計意図はです
 PHP:Web開発の重要な言語
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:Web開発の重要な言語
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHPは、サーバー側で広く使用されているスクリプト言語で、特にWeb開発に適しています。 1.PHPは、HTMLを埋め込み、HTTP要求と応答を処理し、さまざまなデータベースをサポートできます。 2.PHPは、ダイナミックWebコンテンツ、プロセスフォームデータ、アクセスデータベースなどを生成するために使用され、強力なコミュニティサポートとオープンソースリソースを備えています。 3。PHPは解釈された言語であり、実行プロセスには語彙分析、文法分析、編集、実行が含まれます。 4.PHPは、ユーザー登録システムなどの高度なアプリケーションについてMySQLと組み合わせることができます。 5。PHPをデバッグするときは、error_reporting()やvar_dump()などの関数を使用できます。 6. PHPコードを最適化して、キャッシュメカニズムを使用し、データベースクエリを最適化し、組み込み関数を使用します。 7
 PHP対Python:違いを理解します
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP対Python:違いを理解します
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHPは、シンプルな構文と高い実行効率を備えたWeb開発に適しています。 2。Pythonは、簡潔な構文とリッチライブラリを備えたデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。
 PHP対その他の言語:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP対その他の言語:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHPは、特に迅速な開発や動的なコンテンツの処理に適していますが、データサイエンスとエンタープライズレベルのアプリケーションには良くありません。 Pythonと比較して、PHPはWeb開発においてより多くの利点がありますが、データサイエンスの分野ではPythonほど良くありません。 Javaと比較して、PHPはエンタープライズレベルのアプリケーションでより悪化しますが、Web開発により柔軟性があります。 JavaScriptと比較して、PHPはバックエンド開発により簡潔ですが、フロントエンド開発のJavaScriptほど良くありません。
 PHP対Python:コア機能と機能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP対Python:コア機能と機能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHPとPythonにはそれぞれ独自の利点があり、さまざまなシナリオに適しています。 1.PHPはWeb開発に適しており、組み込みのWebサーバーとRich Functionライブラリを提供します。 2。Pythonは、簡潔な構文と強力な標準ライブラリを備えたデータサイエンスと機械学習に適しています。選択するときは、プロジェクトの要件に基づいて決定する必要があります。
 カプセルの量を見つけるためのJavaプログラム
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
カプセルの量を見つけるためのJavaプログラム
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
カプセルは3次元の幾何学的図形で、両端にシリンダーと半球で構成されています。カプセルの体積は、シリンダーの体積と両端に半球の体積を追加することで計算できます。このチュートリアルでは、さまざまな方法を使用して、Javaの特定のカプセルの体積を計算する方法について説明します。 カプセルボリュームフォーミュラ カプセルボリュームの式は次のとおりです。 カプセル体積=円筒形の体積2つの半球体積 で、 R:半球の半径。 H:シリンダーの高さ(半球を除く)。 例1 入力 RADIUS = 5ユニット 高さ= 10単位 出力 ボリューム= 1570.8立方ユニット 説明する 式を使用してボリュームを計算します。 ボリューム=π×R2×H(4
 PHP:多くのウェブサイトの基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:多くのウェブサイトの基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHPが多くのWebサイトよりも優先テクノロジースタックである理由には、その使いやすさ、強力なコミュニティサポート、広範な使用が含まれます。 1)初心者に適した学習と使用が簡単です。 2)巨大な開発者コミュニティと豊富なリソースを持っています。 3)WordPress、Drupal、その他のプラットフォームで広く使用されています。 4)Webサーバーとしっかりと統合して、開発の展開を簡素化します。
 未来を創る: まったくの初心者のための Java プログラミング
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
未来を創る: まったくの初心者のための Java プログラミング
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java は、初心者と経験豊富な開発者の両方が学習できる人気のあるプログラミング言語です。このチュートリアルは基本的な概念から始まり、高度なトピックに進みます。 Java Development Kit をインストールしたら、簡単な「Hello, World!」プログラムを作成してプログラミングを練習できます。コードを理解したら、コマンド プロンプトを使用してプログラムをコンパイルして実行すると、コンソールに「Hello, World!」と出力されます。 Java の学習はプログラミングの旅の始まりであり、習熟が深まるにつれて、より複雑なアプリケーションを作成できるようになります。




