
二分探索木は、ソートされた数値リストを短時間で保持できるデータ構造です。各ツリー ノードは 2 つの兄弟のみを持つことができるため、バイナリ ツリーとも呼ばれます。二分探索ツリーは、数値の存在を検索するために使用できます。これは検索ツリーと呼ばれます。実行時間の複雑さは O(log(n)) 時間です。二分探索木と基本二分木を区別する特徴は次のとおりです –
無料ソフトウェア開発コースを始めましょう
Web 開発、プログラミング言語、ソフトウェア テスト、その他
1.左側のサブツリーのノードはすべてルート ノードよりも小さいです。
2.右側のサブツリーのノードはすべてルート ノードより大きくなります。
3.サブツリーの各ノードも同様に BST であり、ノード自体と同じ 2 つの性質を持っています。
1.指定された配列を次のようにします:
指定された配列: [8, 6, 2, 7, 9, 12, 4, 10]
2.最上位の要素 43 から始めましょう。ツリーのルートとして 43 を挿入します。
3.次の要素がルート ノード要素より小さい場合は、左側のサブツリーのルートとして挿入する必要があります。
4.そうでない場合は、右のサブツリーのルートとして挿入する必要があります。
下の画像は、提供された要素を使用して二分探索ツリーを構築するプロセスを示しています。
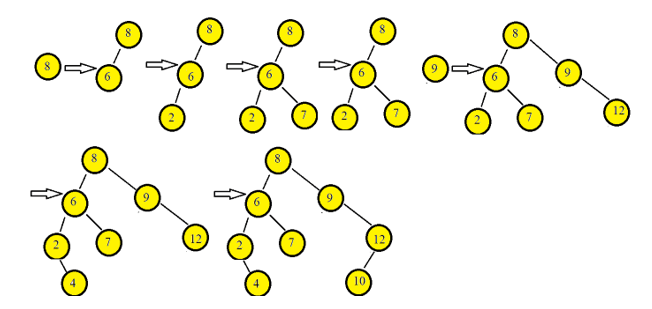
二分探索ツリー操作:
Java の二分探索木でサポートされている操作を以下のリストに示します –
1. BST での検索 – 二分探索木で、特定の要素の位置を見つけます。
2. BST への挿入 – 新しい要素をバイナリ検索ツリーの適切な場所に追加することで、バイナリ検索ツリーのプロパティが壊れないようにします。
3. BST での削除 – 二分探索ツリー内の特定のノードを削除します。ただし、ノードに含まれる子の数に応じて、さまざまな削除シナリオが考えられます。
二分探索木に対して操作を実行する Java の二分探索木の例 –
// プログラムは Eclipse IDE、JAVA 11 でテストできます
package jex;
import java.util.Scanner;
class binarySearchTree {
//node class that defines BST node
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data){
key = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
// binary search tree root node
Node root;
// Constructor for binary search tree, first empty tree
binarySearchTree(){
root = null;
}
//delete a node from binary search tree
void deleteKey(int key) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
//recursive delete function
Node delete(Node root, int key) {
// if tree is empty
if (root == null) return root;
//traverse the tree
if (key < root.key)
//traverse left subtree
root.left = delete(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
//traverse right subtree
root.right = delete(root.right, key);
else {
// if node having only one child
if (root.left == null)
return root.right;
else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
// if node has two children;
root.key = minKey(root.right);
// removing the inorder sibling
root.right = delete(root.right, root.key);
}
return root;
}
int minKey(Node root) {
// initially min is root
int min = root.key;
// find minimum value
while (root.left != null) {
min = root.left.key;
root = root.left;
}
return min;
}
// insert a node in binary search tree
void insertKey(int key) {
root = insert(root, key);
}
// recursively insert a node
Node insert(Node root, int key) {
// initially, tree is empty
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(key);
return root;
}
// traverse the tree
if (key<root.key)
//insert in the left subtree
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
//insert in the right subtree
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
// return
return root;
}
// function to travel inorder of binary search tree
void inorder() {
inorder(root);
}
// recursively traverse the binary search tree
void inorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
boolean searchKey(int key) {
root = search(root, key);
if (root!= null)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//recursive insert function
Node search(Node root, int key) {
// If root is null or key is present at root
if (root==null || root.key==key)
return root;
// when val is greater than root's key
if (root.key > key)
return search(root.left, key);
// when val is lesser than root's key
return search(root.right, key);
}
}
public class client{
public static void main(String[] args) {
binarySearchTree t = new binarySearchTree();
// inserting 8, 6, 2, 7, 9, 12, 4, 10 data into the binary search tree
t.insertKey(8);
t.insertKey(6);
t.insertKey(2);
t.insertKey(7);
t.insertKey(9);
t.insertKey(12);
t.insertKey(4);
t.insertKey(10);
//print the binary search tree
System.out.println( "The binary search tree created with the input data :");
t.inorder();
//delete the leaf node
System.out.println( "\nThe binary search tree after deleting 4 leaf node :");
t.deleteKey(4);
t.inorder();
//delete the node with one child
System.out.println( "\nThe binary search tree after Delete 12 node with 1 child is :");
t.deleteKey(12);
t.inorder();
//search a key in the binary search tree
boolean res = t.searchKey (9);
System.out.println( "\n The node 9 found in binary search tree is :" + res );
res = t.searchKey (12);
System.out.println( "\n The node 10 found in binary search tree is :" + res );
}
}出力:
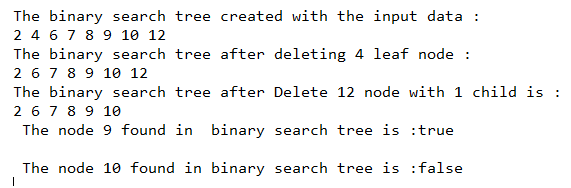
上記のプログラムと同様に、別の内部クラス Node とコンストラクターとメソッドを含む binarySearchTree クラスが作成されます。クラスで定義されているメソッドは、特定の操作を実行するための deleteKey()、delete()、minKey()、insertKey()、insert()、inorder()、searchKey()、および search() です。上記の出力に示すように、main 関数では、binarySearchTree クラス オブジェクトが作成され、そのオブジェクトにいくつかの要素が挿入され、次にそのオブジェクトに対してバイナリ Search Tree クラスのメソッドが呼び出されます。
二分探索ツリーは、各ツリー ノードが 2 つの兄弟のみを持つことができるため、バイナリ ツリーとも呼ばれます。二分探索ツリーは、ソートされた数値リストを短時間で保持できるデータ構造です。二分探索木に対して実行できる操作: 走査、挿入、削除、検索。
以上がJavaの二分探索木の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。