HTMLイベント属性
この記事では、HTML イベント属性について詳しく説明します。イベントは、ユーザーのアクションの結果として実行されるアクションです。たとえば、ユーザーがデータを読み取るためにキーボードを押したとき、それはキーボード イベントと言われます。これらのアクティビティは、ユーザーが Web サイトを調べてボタンをクリックしたとき、またはブラウザがページを操作して更新ボタンを押してページが読み込まれたときに実行されます。これらすべてのアクションはイベントであると言われます。ここでは、イベントの基本的な理解を説明し、ユーザーのアクションに対してイベントがブラウザーでどのように機能するかを説明します。ブラウザ ウィンドウ全体で発生するさまざまな種類のイベントについては、次のセクションで説明します。
上位 5 つの HTML イベント属性
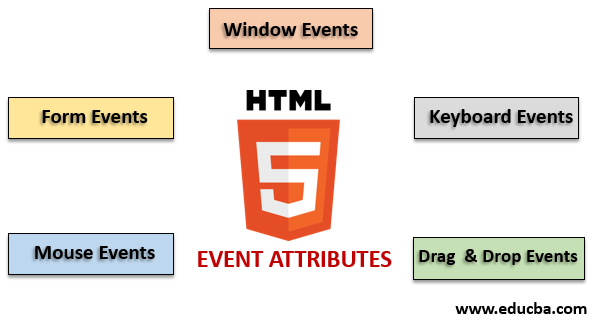
HTML では、別の種類のイベントを使用できます。これらすべてのイベントには、イベント アクションの実行時に起動されるイベント ハンドラーという名前の小さなコード ブロックがあります。これらは HTML 要素に添付されます。イベント ハンドラーまたはイベント リスナーは、HTML イベント属性において重要な役割を果たします。グローバルに宣言され、HTML 要素に適用されるさまざまなタイプのイベント属性とその動作を詳しく見てみましょう。主に 4 つの主要なイベント属性が使用されます。それらは次のとおりです:
- ウィンドウイベント
- フォームイベント
- マウスイベント
- キーボードイベント
- イベントをドラッグ アンド ドロップします
これらすべての属性を例を挙げて 1 つずつ説明します。まずは、
で行きます。1.ウィンドウイベント
- onafterprintEvent: この属性はすべての HTML タグでサポートされており、ページの印刷が開始され、単一値のスクリプトがあるときに機能します。 HTML コードの例を次に示します。この例は、ボタンが押されたときを示しています。ダイアログ メッセージに出力されるメッセージを出力します。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Windows onafterprint Event
</title>
</head>
<body onafterprint="myfun()">
<h1>Windows onafterprint Event </h1>
<p>This attribute works in IE and Mozilla</p>
<body style = "text-align:center">
<script>
function myfun() {
alert("Document is being printed");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:

- onbeforeprint: 印刷前に機能します。イベントは印刷プロセスの後に発生します。以下はサンプルコードです。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: #9370DB;
background-color: #BC8F8F;
text-align: center;
padding: 20px;
}
p {
font-size: 2rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body onbeforeprint="get()">
<h1> Attribute Demo</h1>
<p style="color:#0000FF;">trigger to print.</p>
<div class="show"></div>
<script>
function get() {
document.body.style.background = "#00BFFF";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:

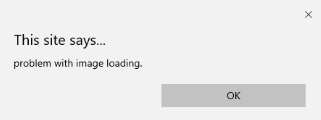
- onerror: この関数は、要素が存在しないときにエラーがスローされたときにトリガーされます。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<img src="p.jpg" onerror="myFun()">
<p>hello world.</p>
<script>
function myFun() {
alert("problem with image loading.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:
- onload: この関数はオブジェクトのロードに役立ち、Web ページが正しくロードされているかどうかを確認するのに適しています。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>onload event demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="pic.jpg" onload="ldImg()" width="50" height="92">
<script>
function ldImg() {
alert("image loaded without error");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:
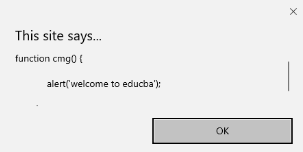
- onresize: このイベントは、ブラウザ ウィンドウのサイズが変更されたときにトリガーされ、任意の要素は、resize 属性でトリガーできます。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>onresize event</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function cmg() {
alert('welcome to educba');
}
window.onresize = cmg;
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="Click the button"
onclick="alert(window.onresize);">
</body>
</html>出力:

- onunload: このイベントは、Web ページのウィンドウが閉じられたとき、またはユーザーが Web ページから離れたときにトリガーされます。以下のコードは、ユーザーが離れるときにページをアンロードし、検索してくれてありがとうというアラートをスローします。このイベントはすべてのブラウザで機能する場合があります。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body onunload="onfunc()"><h1>Welcometo educba tutorial</h1>
<p>Leave the page .</p>
<script>
function onfunc() {
alert("Thank you for searching!");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:
2.フォームイベント
フォームコントロールで動作します。以下は、ユーザーがブラウザーを操作するときに発生する属性です。
- onblur: このイベントは、ユーザーの注意がフォーム ウィンドウから離れたときに発生します。次の例では、入力を小文字で受け取り、送信ボタンをクリックすると、出力が大文字に変わります。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> Form onblur </title>
<style>
body {
text-align:center;
}
h1 {
color:pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EDUCBA</h1>
<input type="text" name="fname" id="aaa"
onblur="myfunc()">
<button type="button">Submit</button>
<script>
function myfunc() {
var a = document.getElementById("aaa");
a.value = a.value.toUpperCase();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:


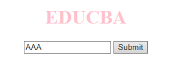
- onchange: このイベントは、ユーザーがフォーム内の既存の要素を変更すると発生します。これは要素がフォーカスを失ったときに発生します。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>HTML onchange</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="example" action=""> <input type="text" name="rahul" onchange="alert('input is changed')"><br>
<label>select the dress color</label>
<select onchange="alert('You have changed the selection!');">
<option>pink</option>
<option>Yellow</option>
<option>White</option>
</select>
<p><strong>Note:</strong> Select any option </p>
<label>Describe yourself in short : </label> <br/><textarea cols="15" rows="7" name="details" onchange="alert('description has changed')"> </textarea><br>
<button type="button" name="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>出力:
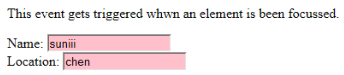
- onfocus: この属性は、ユーザーが Web ページ上の要素に注意を向けたとき、または入力がフォーカスされているときに有効になります。以下の例では、フィールドに入力するときに強調表示されます。
コード:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>This event gets triggered whwn an element is been focussed.</p>
Name: <input type="text" id="name" onfocus="onfoc(this.id)"><br>
Location: <input type="text" id="loc" onfocus="onfoc(this.id)">
<script>
function onfoc(a) {
document.getElementById(a).style.background = "pink";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>出力:
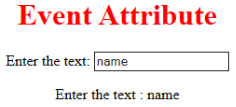
- oninput: This event triggers when the input is entered in the input field. It has been activated when the value in the text field is changed. It reflects once the value of the element is changed.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> HTML oninput </title>
</head>
<style>
body {
text-align:center;
}
h1 {
color:red;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1> Event Attribute </h1>
Enter the text:
<input type="text" id="EDUCBA" oninput="myon()">
<p id= "sid"></p>
<script>
function myon()
{
var x = document.getElementById("EDUCBA").value;
document.getElementById("sid").innerHTML = "Enter the text : " +x;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
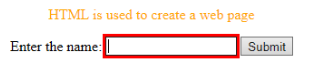

- oninvalid: This attribute calls the events when the text entered in the input type is invalid or remains empty. This event attribute must fill the input element.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> example oninvalid Event </title>
<style>
p {
color:orange;
}
body {
text-align:center;
}
</style> </head>
<body>
<p> HTML is used to create a web page</p>
<form method="get">
Enter the name:
<input type="text" oninvalid="alert('Fill the text form!');" required>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form> </body>
</html>Output:

- onreset: It is fired when a form is a rest. The following example says when you submit the button, a form is processed, and again when you click to reset, the form is being reset.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
body {font-family:calibri;}
label {font-variant:small-caps;}
ol {background-color:#610000; margin-top:35px;}
li {margin-top:3px; padding:3px; background-color:rose; font-size:15px;}
div {position:absolute;top:250px;left:70px; font-size:1.5em;
}
</style>
<body>
<ol>
<li>Form with input to reset and submit</li>
</ol>
<form action="" method="get" onreset="onRes()" onsubmit="onSub()">
<label>Enter input:<br /><input type="text" id="iv" oninvalid="onInva()" oninput="onInp()"></label><br /><br />
<input type="submit" value="press"> <input type="reset">
</form>
<div id="a_box"></div>
<script>
function onInva() {
alert("Input field cannot be empty!");
}
function onInp() {
var input_value = document.getElementById("iv").value;
document.getElementById("a_box").innerHTML = "Input value: <br />" + iv;
}
function onRes() {
alert("form is reset!");
}
function onSubmitEvent() {
alert("Form is loading");
location.reload();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

- onsearch: It works when a user presses an enter button.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Write in the field.</p>
<input type="search" id="value1" onsearch="myF()">
<p id="sample"></p>
<script>
function myF() {
var k = document.getElementById("value1");
document.getElementById("sample").innerHTML = "search element is: " + k.value;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
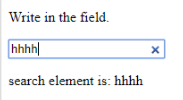
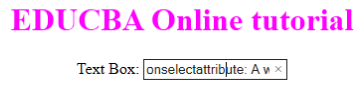
- onselect: It is triggered when a text has been selected in an input box. It throws a dialog box printing an alert message.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>onselect demo</title>
<style>
h1 {
color:magenta;
}
body {
text-align:center;
}
</style>
<script>
function eduhtml() {
alert("text highlighted!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EDUCBA Online tutorial</h1>
Text Box: <input type="text" value="onselectattribute: A well defined portal" onselect="eduhtml()">
</body>
</html>
</html>Output:
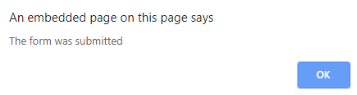
- onsubmit: The purpose of this event is to execute the action performed while pressing the submit button.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<head>
<title> Onsubmit Example</title>
</head>
<form action="demo_form.asp" onsubmit="myF()">
Enter name: <input type="text" name="fname">
<label>Email :</label>
<input id="email" name="email" type="text">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<script>
function myF() {
alert("The form was submitted");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
3. Key Board Attributes
- OnKeyDown: It is triggered when a user presses a down Arrow key.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Example for Onkeydown.</p>
<input type="text" onkeydown="mykedwn()">
<script>
function mykedwn() {
alert("key press is activated");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

- OnKeyPress: This event gets triggered when the user presses any key on the keyboard. Note: some browser doesn’t support pressing any key.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p> This example shows when a user type in the text area it triggers an event </p>
<form>
<textarea onkeypress="alert('triggering onkeypress event.')" placeholder="Place the cursor inside the textarea and press a key." " cols="30" rows="4" style="background-color:pink;">> </textarea> </form>
</body>
</html>Output:

- OnKeyUp: This attribute gets triggered when a user releases a cursor from the text field. Below comes the demonstration.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p> This example transforms the character to lower case.</p>
Fill the name: <input type="text" id="jjj" onkeyup="mykey()">
<script>
function mykey() {
var g = document.getElementById("jjj");
g.value = g.value.toLowerCase();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

4. Mouse Event Attributes
This action triggers a mouse event when a mouse is pressed either from a computer or any external devices like a smartphone or tablet. Some of the mouse events are given below:
- onclick: It is triggered when a user presses the button over the mouse. An input example is given below to show the event while clicking the mouse.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>HTML onclick Event</h1>
<p> Event plays a vital role in HTML.</p>
<button onclick="oncf()">Click </button>
<p id="sample"></p>
<script>
function oncf() {
document.getElementById("sample").innerHTML = "Hello World";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

- onmousemove: It is fired when a mouse is moved over an image in any direction.
Code:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head><title> Event onmousemove demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This event is activated when the pointer drags its direction.</p>
<body style="width:200px;height:80px;border:2px solid;" onmousemove="javascript:alert('mouse action');">Sample text</body>
</body>
</html>Output:

- Onmouseup: This event gives a notification when a user releases a button on an output.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: "#ff0000";
height: 120vh;
background-color: #610000;
text-align: center;
}
.polygon {
float: right;
shape-inside: polygon(0 0, 0 200px, 100px 200px);
clip-path: polygon(0 0, 0 250px, 100px 300px);
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background: linear-gradient(to bottom left, #7CFC00, #8B008B);
}
p {
margin: 30px auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML onmouseup Demo</h1>
<div class="polygon" onmouseup="mupfn()"></div>
<p> click below object</p>
<script>
function mupFn() {
document.querySelector('.polygon').style.transform = 'scale(2.2)';
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

- Onmouseover: Execute a JavaScript when moving the mouse pointer over an image
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<title>Example demonstrating Onmouseover.</title>
<h1 id="sample" onmouseover="A()" onmouseout="B()">Mouse over </h1>
<script>
function A() {
document.getElementById("sample").style.color = "yellow";}
function B() {
document.getElementById("sample").style.color = "green";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
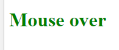
5. Drag Event Attributes
This application helps in the HTML window when the user drags the input element. Below are the different event listeners used in HTML to store dragged data.
- Ondrag: This is used when an element is being dragged from the web page.
- Ondragstart: This fires when the user begins to drag from the input field. The below example demonstrates about dragging the two-target area.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type = "text/css">
#b1, #b2 {
float:left;padding:11px;margin:11px; -moz-user-select:none;
}
#b1 { background-color: #FF6699; width:65px; height:85px; }
#b2 { background-color: #808000; width:180px; height:180px; }
</style>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function dStart(e) {
e.dataTransfer.effectAllowed = 'move';
e.dataTransfer.setData("Text", e.target.getAttribute('id'));
e.dataTransfer.setDragImage(e.target,0,0);
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>Drag demo</h2>
<div> Drag the box.</div>
<div id = "b1" draggable = "true"
ondragstart = "return dStart(e)">
<p>Drag it</p>
</div>
<div id = "b2">welcome</div>
</center>
</body>
</html>Output:
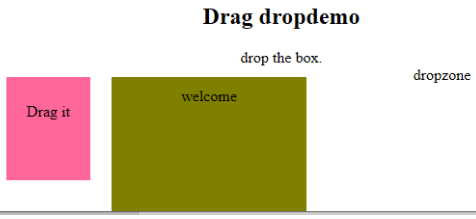
-
ondrop: Execute this attribute when a draggable element is dropped in element.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <style type = "text/css"> #b1, #b2 { float:left;padding:11px;margin:11px; -moz-user-select:none; } #b1 { background-color: #FF6699; width:65px; height:85px; } #b2 { background-color: #808000; width:180px; height:180px; } </style> <script type = "text/javascript"> function dStart(e) { e.dataTransfer.effectAllowed = 'move'; e.dataTransfer.setData("Text", e.target.getAttribute('id')); e.dataTransfer.setDragImage(e.target,0,0); return true; } </script> </head> <body> <center> <h2>Drag dropdemo</h2> <div> drop the box.</div> <div id = "b1" draggable = "true" ondragstart = "return dStart(e)"> <p>Drag it</p> </div> <div class="droptarget" ondrop="drop(event)" ondragover="allowDrop(event)"> </div> <div id = "b2">welcome</div> <span> dropzone </span> </center> </body> </html>ログイン後にコピーOutput:

Conclusion
This event attribute helps to make a web application very easier and attractive. The different occurrence of actions generates various events. Even though this approach is generally avoided, the programmer likes to learn the function assigned for the HTML attributes events. These event handlers are still executed to beautify the web pages.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to the HTML Event Attributes. Here we discuss the Introduction to HTML Event Attributes along with Code implementation and Output. you can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –
- HTML Frames
- HTML Style Attribute
- Applications of HTML
- HTML vs HTML5
以上がHTMLイベント属性の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 1673
1673
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 HTMLの表の境界線
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTMLの表の境界線
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML の表の境界線に関するガイド。ここでは、HTML でのテーブルの境界線の例を示しながら、テーブル境界線を定義する複数の方法について説明します。
 HTML のネストされたテーブル
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML のネストされたテーブル
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
これは、HTML でのネストされたテーブルのガイドです。ここでは、テーブル内にテーブルを作成する方法をそれぞれの例とともに説明します。
 HTML 左マージン
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML 左マージン
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML マージン左のガイド。ここでは、HTML margin-left の概要とその例、およびそのコード実装について説明します。
 HTML テーブルのレイアウト
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML テーブルのレイアウト
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML テーブル レイアウトのガイド。ここでは、HTML テーブル レイアウトの値と例および出力について詳しく説明します。
 HTML入力プレースホルダー
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML入力プレースホルダー
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML 入力プレースホルダーのガイド。ここでは、コードと出力とともに HTML 入力プレースホルダーの例について説明します。
 PHPでHTML/XMLを解析および処理するにはどうすればよいですか?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
PHPでHTML/XMLを解析および処理するにはどうすればよいですか?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
このチュートリアルでは、PHPを使用してXMLドキュメントを効率的に処理する方法を示しています。 XML(拡張可能なマークアップ言語)は、人間の読みやすさとマシン解析の両方に合わせて設計された多用途のテキストベースのマークアップ言語です。一般的にデータストレージに使用されます
 HTML の onclick ボタン
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML の onclick ボタン
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML オンクリック ボタンのガイド。ここでは、それらの紹介、動作、例、およびさまざまなイベントでの onclick イベントについてそれぞれ説明します。