Scikit-Learn による完全な機械学習ワークフロー: カリフォルニアの住宅価格の予測
導入
この記事では、Scikit-Learn を使用した完全な機械学習プロジェクトのワークフローを示します。収入の中央値、住宅築年数、平均部屋数などのさまざまな特徴に基づいて、カリフォルニアの住宅価格を予測するモデルを構築します。このプロジェクトでは、データの読み込み、探索、モデルのトレーニング、評価、結果の視覚化など、プロセスの各ステップをガイドします。基本を理解したい初心者でも、復習を求めている経験豊富な実践者でも、この記事は機械学習テクニックの実際の応用についての貴重な洞察を提供します。
カリフォルニア住宅価格予測プロジェクト
1. はじめに
カリフォルニアの住宅市場は、その独特の特徴と価格動向で知られています。このプロジェクトでは、さまざまな特徴に基づいて住宅価格を予測する機械学習モデルを開発することを目的としています。カリフォルニアの住宅データセットを使用します。これには、収入の中央値、住宅築年数、平均部屋数などのさまざまな属性が含まれます。
2. ライブラリのインポート
このセクションでは、データ操作、視覚化、機械学習モデルの構築に必要なライブラリをインポートします。
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
3. データセットのロード
California Housing データセットをロードし、データを整理するための DataFrame を作成します。ターゲット変数である住宅価格が新しい列として追加されます。
# Load the California Housing dataset california = fetch_california_housing() df = pd.DataFrame(california.data, columns=california.feature_names) df['PRICE'] = california.target
4. サンプルをランダムに選択する
分析を管理しやすくするために、研究用にデータセットから 700 個のサンプルをランダムに選択します。
# Randomly Selecting 700 Samples df_sample = df.sample(n=700, random_state=42)
5. データを確認する
このセクションでは、データセットの概要を説明し、データの特徴と構造を理解するために最初の 5 行を表示します。
# Overview of the data
print("First five rows of the dataset:")
print(df_sample.head())
出力
First five rows of the dataset:
MedInc HouseAge AveRooms AveBedrms Population AveOccup Latitude \
20046 1.6812 25.0 4.192201 1.022284 1392.0 3.877437 36.06
3024 2.5313 30.0 5.039384 1.193493 1565.0 2.679795 35.14
15663 3.4801 52.0 3.977155 1.185877 1310.0 1.360332 37.80
20484 5.7376 17.0 6.163636 1.020202 1705.0 3.444444 34.28
9814 3.7250 34.0 5.492991 1.028037 1063.0 2.483645 36.62
Longitude PRICE
20046 -119.01 0.47700
3024 -119.46 0.45800
15663 -122.44 5.00001
20484 -118.72 2.18600
9814 -121.93 2.78000
データフレーム情報の表示
print(df_sample.info())
出力
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> Index: 700 entries, 20046 to 5350 Data columns (total 9 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 MedInc 700 non-null float64 1 HouseAge 700 non-null float64 2 AveRooms 700 non-null float64 3 AveBedrms 700 non-null float64 4 Population 700 non-null float64 5 AveOccup 700 non-null float64 6 Latitude 700 non-null float64 7 Longitude 700 non-null float64 8 PRICE 700 non-null float64 dtypes: float64(9) memory usage: 54.7 KB
概要統計の表示
print(df_sample.describe())
出力
MedInc HouseAge AveRooms AveBedrms Population \
count 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000
mean 3.937653 28.855714 5.404192 1.079266 1387.422857
std 2.085831 12.353313 1.848898 0.236318 1027.873659
min 0.852700 2.000000 2.096692 0.500000 8.000000
25% 2.576350 18.000000 4.397751 1.005934 781.000000
50% 3.480000 30.000000 5.145295 1.047086 1159.500000
75% 4.794625 37.000000 6.098061 1.098656 1666.500000
max 15.000100 52.000000 36.075472 5.273585 8652.000000
AveOccup Latitude Longitude PRICE
count 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000 700.000000
mean 2.939913 35.498243 -119.439729 2.082073
std 0.745525 2.123689 1.956998 1.157855
min 1.312994 32.590000 -124.150000 0.458000
25% 2.457560 33.930000 -121.497500 1.218500
50% 2.834524 34.190000 -118.420000 1.799000
75% 3.326869 37.592500 -118.007500 2.665500
max 7.200000 41.790000 -114.590000 5.000010
6. データセットをトレーニング セットとテスト セットに分割する
データセットを特徴 (X) とターゲット変数 (y) に分割し、モデルのトレーニングと評価のためにトレーニング セットとテスト セットに分割します。
# Splitting the dataset into Train and Test sets
X = df_sample.drop('PRICE', axis=1) # Features
y = df_sample['PRICE'] # Target variable
# Split the dataset into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
7. モデルのトレーニング
このセクションでは、トレーニング データを使用して線形回帰モデルを作成およびトレーニングし、特徴と住宅価格の関係を学習します。
# Creating and training the Linear Regression model lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
8. モデルの評価
テスト セットで予測を行い、平均二乗誤差 (MSE) と R 二乗値を計算してモデルのパフォーマンスを評価します。
# Making predictions on the test set
y_pred = lr.predict(X_test)
# Calculating Mean Squared Error
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"\nLinear Regression Mean Squared Error: {mse}")
出力
Linear Regression Mean Squared Error: 0.3699851092128846
9. 実際の値と予測値の表示
ここでは、実際の住宅価格とモデルによって生成された予測価格を比較するデータフレームを作成します。
# Displaying Actual vs Predicted Values
results = pd.DataFrame({'Actual Prices': y_test.values, 'Predicted Prices': y_pred})
print("\nActual vs Predicted:")
print(results)
出力
Actual vs Predicted:
Actual Prices Predicted Prices
0 0.87500 0.887202
1 1.19400 2.445412
2 5.00001 6.249122
3 2.78700 2.743305
4 1.99300 2.794774
.. ... ...
135 1.62100 2.246041
136 3.52500 2.626354
137 1.91700 1.899090
138 2.27900 2.731436
139 1.73400 2.017134
[140 rows x
2 columns]
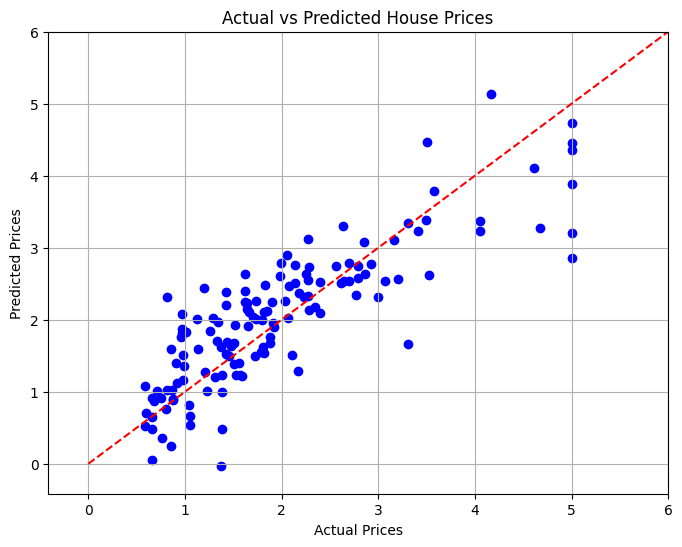
10. 結果の視覚化
最後のセクションでは、散布図を使用して実際の住宅価格と予測住宅価格の関係を視覚化し、モデルのパフォーマンスを視覚的に評価します。
# Visualizing the Results
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred, color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Actual Prices')
plt.ylabel('Predicted Prices')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted House Prices')
# Draw the ideal line
plt.plot([0, 6], [0, 6], color='red', linestyle='--')
# Set limits to minimize empty space
plt.xlim(y_test.min() - 1, y_test.max() + 1)
plt.ylim(y_test.min() - 1, y_test.max() + 1)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
結論
このプロジェクトでは、さまざまな特徴に基づいてカリフォルニアの住宅価格を予測するための線形回帰モデルを開発しました。モデルのパフォーマンスを評価するために平均二乗誤差が計算され、予測精度の定量的な尺度が提供されました。視覚化により、実際の値に対してモデルがどの程度優れたパフォーマンスを発揮するかを確認できました。
このプロジェクトは、不動産分析における機械学習の力を実証し、より高度な予測モデリング技術の基盤として機能します。
以上がScikit-Learn による完全な機械学習ワークフロー: カリフォルニアの住宅価格の予測の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7892
7892
 15
15
 1651
1651
 14
14
 1411
1411
 52
52
 1302
1302
 25
25
 1248
1248
 29
29
 中間の読書にどこでもfiddlerを使用するときにブラウザによって検出されないようにするにはどうすればよいですか?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
中間の読書にどこでもfiddlerを使用するときにブラウザによって検出されないようにするにはどうすればよいですか?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
fiddlereveryversings for the-middleの測定値を使用するときに検出されないようにする方法
 プロジェクトの基本と問題駆動型の方法で10時間以内にコンピューター初心者プログラミングの基本を教える方法は?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
プロジェクトの基本と問題駆動型の方法で10時間以内にコンピューター初心者プログラミングの基本を教える方法は?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
10時間以内にコンピューター初心者プログラミングの基本を教える方法は?コンピューター初心者にプログラミングの知識を教えるのに10時間しかない場合、何を教えることを選びますか...
 Python Asyncio Telnet接続はすぐに切断されます:サーバー側のブロッキング問題を解決する方法は?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:30 AM
Python Asyncio Telnet接続はすぐに切断されます:サーバー側のブロッキング問題を解決する方法は?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:30 AM
Pythonasyncioについて...
 Investing.comの反クローラーメカニズムをバイパスするニュースデータを取得する方法は?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:03 AM
Investing.comの反クローラーメカニズムをバイパスするニュースデータを取得する方法は?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:03 AM
Investing.comの反クラウリング戦略を理解する多くの人々は、Investing.com(https://cn.investing.com/news/latest-news)からのニュースデータをクロールしようとします。
 Python 3.6のロードピクルスファイルエラーmodulenotfounderror:ピクルスファイル「__builtin__」をロードした場合はどうすればよいですか?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:27 AM
Python 3.6のロードピクルスファイルエラーmodulenotfounderror:ピクルスファイル「__builtin__」をロードした場合はどうすればよいですか?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:27 AM
Python 3.6のピクルスファイルの読み込みエラー:modulenotfounderror:nomodulenamed ...
 Scapy Crawlerを使用するときにパイプラインファイルを書き込めない理由は何ですか?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:45 AM
Scapy Crawlerを使用するときにパイプラインファイルを書き込めない理由は何ですか?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:45 AM
SCAPYクローラーを使用するときにパイプラインファイルを作成できない理由についての議論は、SCAPYクローラーを学習して永続的なデータストレージに使用するときに、パイプラインファイルに遭遇する可能性があります...






