
アルゴリズムの実行時間またはスペース使用量の上限を記述する数学的表記。これは O(f(n)) として表されます。f(n) は、入力 n のサイズの関数として時間または空間を表す関数です。 .
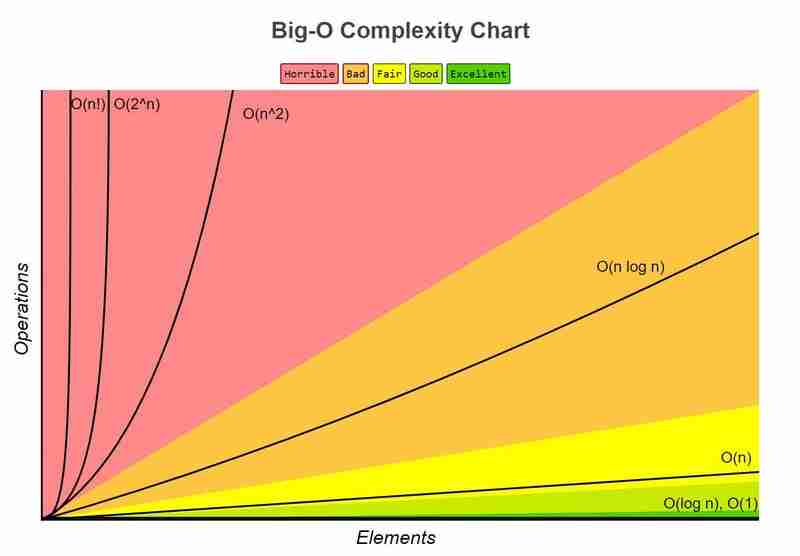
詳細については、http://bigocheatsheet.com
例:
import timeit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cProfile
# O(1)
def constant_time_operation():
return 42
# O(log n)
def logarithmic_time_operation(n):
count = 0
while n > 1:
n //= 2
count += 1
return count
# O(n)
def linear_time_operation(n):
total = 0
for i in range(n):
total += i
return total
# O(n log n)
def linear_logarithmic_time_operation(n):
if n <= 1:
return n
else:
return linear_logarithmic_time_operation(n - 1) + n
# O(n^2)
def quadratic_time_operation(n):
total = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
total += i + j
return total
# O(2^n)
def exponential_time_operation(n):
if n <= 1:
return 1
else:
return exponential_time_operation(n - 1) + exponential_time_operation(n - 1)
# O(n!)
def factorial_time_operation(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial_time_operation(n - 1)
# Function to measure execution time using timeit
def measure_time(func, *args):
execution_time = timeit.timeit(lambda: func(*args), number=1000)
return execution_time
def plot_results(results):
functions, times = zip(*results)
colors = ['skyblue', 'orange', 'green', 'red', 'purple', 'brown', 'pink']
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 8))
plt.bar(functions, times, color=colors)
for i, v in enumerate(times):
plt.text(i, v + 0.5, f"{v:.6f}", ha='center',
va='bottom', rotation=0, color='black')
plt.xlabel('Function Complexity')
plt.ylabel('Average Time (s)')
plt.title('Execution Time of Different Algorithm Complexities')
plt.grid(axis='y', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5, color='gray', alpha=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def main():
results = []
results.append(("O(1)", measure_time(constant_time_operation)))
results.append(("O(log n)", measure_time(logarithmic_time_operation, 10)))
results.append(("O(n)", measure_time(linear_time_operation, 10)))
results.append(("O(n log n)", measure_time(
linear_logarithmic_time_operation, 10)))
results.append(("O(n^2)", measure_time(quadratic_time_operation, 7)))
results.append(("O(2^n)", measure_time(exponential_time_operation, 7)))
results.append(("O(n!)", measure_time(factorial_time_operation, 112)))
plot_results(results)
if __name__ == '__main__':
cProfile.run("main()", sort="totime", filename="output_profile.prof")
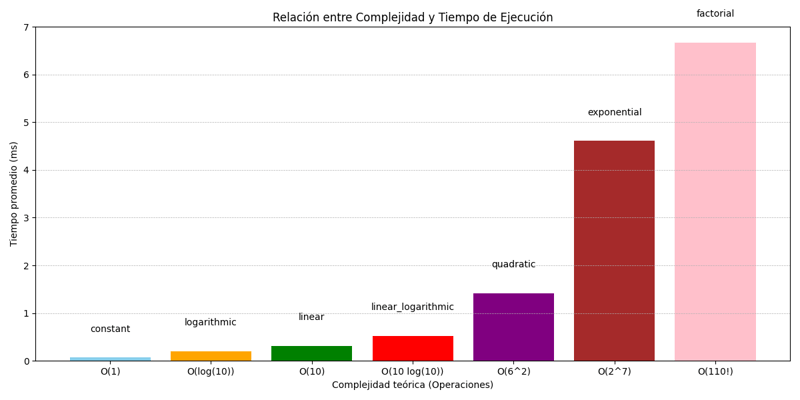
単純に大きな表記法を適用するだけでは十分ではないこと、または、これは最初のステップではありますが、メモリを最適化する他の方法があることを覚えておいてください。たとえば、スロット、キャッシュ、スレッド、並列処理、プロセスなど
読んでいただきありがとうございます!!
反応したり、意見を述べたりして私をサポートしてください。
以上がBig O 記法 - Pythonの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。