
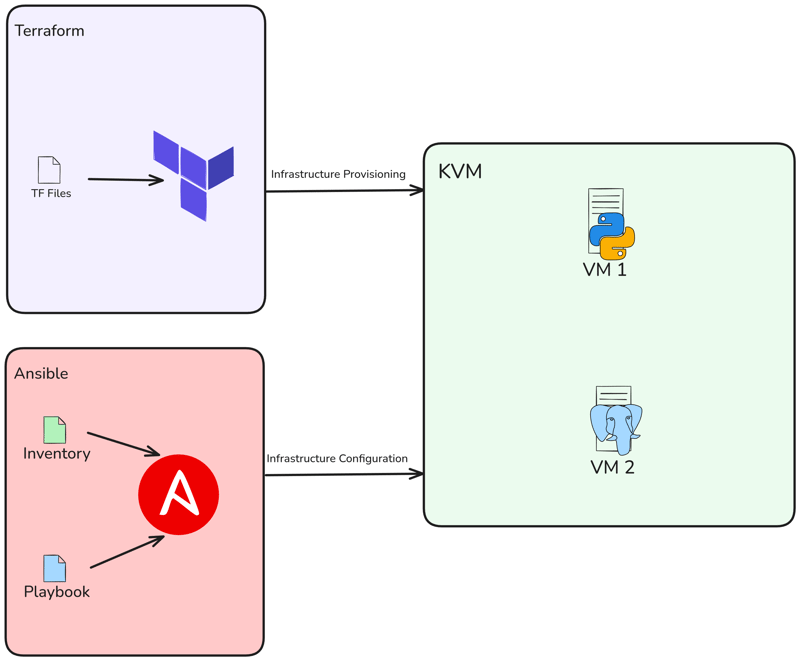
こんにちは、この投稿では、Terraform で Libvirt を使用して 2 つの KVM をローカルにプロビジョニングし、その後、Ansible を使用して Flask アプリと PostgreSQL をデプロイします。
そこで、Terraform を使用して 2 つの VM を作成し、Ansible を使用して Flask プロジェクトとデータベースをデプロイします。
このプロジェクトでは OS として Ubuntu 22.04 LTS を使用しました。別の OS を使用している場合は、必要な依存関係をインストールするときに必要な調整を行ってください。
このセットアップの主な前提条件は、KVM ハイパーバイザーです。したがって、システムに KVM をインストールする必要があります。 Ubuntu を使用している場合は、次の手順を実行できます:
sudo apt -y install bridge-utils cpu-checker libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon qemu qemu-kvm
次のコマンドを実行して、プロセッサが仮想化機能をサポートしていることを確認します。
$ kvm-ok INFO: /dev/kvm exists KVM acceleration can be used
$ wget -O - https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg $ echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.list $ sudo apt update && sudo apt install terraform -y
インストールを確認します:
$ terraform version Terraform v1.9.8 on linux_amd64
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install software-properties-common $ sudo add-apt-repository --yes --update ppa:ansible/ansible $ sudo apt install ansible -y
インストールを確認します:
$ ansible --version ansible [core 2.15.1] ...
Terraform で libvirt プロバイダーを使用して、KVM 仮想マシンをデプロイします。
main.tf を作成し、使用するプロバイダーとバージョンを指定するだけです:
terraform {
required_providers {
libvirt = {
source = "dmacvicar/libvirt"
version = "0.8.1"
}
}
}
provider "libvirt" {
uri = "qemu:///system"
}
その後、terraform init コマンドを実行して環境を初期化します。
$ terraform init Initializing the backend... Initializing provider plugins... - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/template from the dependency lock file - Reusing previous version of dmacvicar/libvirt from the dependency lock file - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/null from the dependency lock file - Using previously-installed hashicorp/template v2.2.0 - Using previously-installed dmacvicar/libvirt v0.8.1 - Using previously-installed hashicorp/null v3.2.3 Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
次に、variables.tf を作成します。この variables.tf ファイルは、libvirt ディスク プール パス、VM の OS としての Ubuntu 20.04 イメージ URL、および VM ホスト名のリストの入力を定義します。
variable "libvirt_disk_path" {
description = "path for libvirt pool"
default = "default"
}
variable "ubuntu_20_img_url" {
description = "ubuntu 20.04 image"
default = "https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/releases/focal/release/ubuntu-20.04-server-cloudimg-amd64.img"
}
variable "vm_hostnames" {
description = "List of VM hostnames"
default = ["vm1", "vm2"]
}
main.tf を更新しましょう:
resource "null_resource" "cache_image" {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "wget -O /tmp/ubuntu-20.04.qcow2 ${var.ubuntu_20_img_url}"
}
}
resource "libvirt_volume" "base" {
name = "base.qcow2"
source = "/tmp/ubuntu-20.04.qcow2"
pool = var.libvirt_disk_path
format = "qcow2"
depends_on = [null_resource.cache_image]
}
# Volume for VM with size 10GB
resource "libvirt_volume" "ubuntu20-qcow2" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
name = "ubuntu20-${count.index}.qcow2"
base_volume_id = libvirt_volume.base.id
pool = var.libvirt_disk_path
size = 10737418240 # 10GB
}
data "template_file" "user_data" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
template = file("${path.module}/config/cloud_init.yml")
}
data "template_file" "network_config" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
template = file("${path.module}/config/network_config.yml")
}
resource "libvirt_cloudinit_disk" "commoninit" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
name = "commoninit-${count.index}.iso"
user_data = data.template_file.user_data[count.index].rendered
network_config = data.template_file.network_config[count.index].rendered
pool = var.libvirt_disk_path
}
resource "libvirt_domain" "domain-ubuntu" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
name = var.vm_hostnames[count.index]
memory = "1024" # VM memory
vcpu = 1 # VM CPU
cloudinit = libvirt_cloudinit_disk.commoninit[count.index].id
network_interface {
network_name = "default"
wait_for_lease = true
hostname = var.vm_hostnames[count.index]
}
console {
type = "pty"
target_port = "0"
target_type = "serial"
}
console {
type = "pty"
target_type = "virtio"
target_port = "1"
}
disk {
volume_id = libvirt_volume.ubuntu20-qcow2[count.index].id
}
graphics {
type = "spice"
listen_type = "address"
autoport = true
}
}
スクリプトは、Libvirt プロバイダーを使用して複数の KVM VM をプロビジョニングします。 Ubuntu 20.04 の基本イメージをダウンロードし、VM ごとにクローンを作成し、ユーザーおよびネットワーク設定用に Cloud-init を構成し、指定されたホスト名、1GB メモリ、および SPICE グラフィックスを備えた VM をデプロイします。セットアップは、var.vm_hostnames.
で指定されたホスト名の数に基づいて動的に適応します。前述したように、私はcloud-initを使用しているので、configディレクトリの下にネットワーク構成とcloud initをセットアップしましょう:
mkdir config/
次に、config/cloud_init.yml を作成します。構成内で ssh アクセス用の公開 ssh キーを必ず設定してください。
#cloud-config
runcmd:
- sed -i '/PermitRootLogin/d' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- echo "PermitRootLogin yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- systemctl restart sshd
ssh_pwauth: true
disable_root: false
chpasswd:
list: |
root:cloudy24
expire: false
users:
- name: ubuntu
gecos: ubuntu
groups:
- sudo
sudo:
- ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
home: /home/ubuntu
shell: /bin/bash
lock_passwd: false
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAA...
次に、config/network_config.yml のネットワーク構成:
version: 2
ethernets:
ens3:
dhcp4: true
プロジェクトの構造は次のようになります:
sudo apt -y install bridge-utils cpu-checker libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon qemu qemu-kvm
次に、計画を実行して、何が行われるかを確認します。
$ kvm-ok INFO: /dev/kvm exists KVM acceleration can be used
そして、terraform apply を実行してデプロイメントを実行します。
$ wget -O - https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg $ echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.list $ sudo apt update && sudo apt install terraform -y
virsh コマンドを使用して VM の作成を確認します:
$ terraform version Terraform v1.9.8 on linux_amd64
インスタンスの IP アドレスを取得します:
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install software-properties-common $ sudo add-apt-repository --yes --update ppa:ansible/ansible $ sudo apt install ansible -y
ubuntu ユーザーを使用して VM にアクセスしてみます:
$ ansible --version ansible [core 2.15.1] ...
次に、Docker に Flask と Postgresql をデプロイするための Ansible Playbook を作成しましょう。まず、ansible ディレクトリと ansible.cfg ファイルを作成する必要があります:
terraform {
required_providers {
libvirt = {
source = "dmacvicar/libvirt"
version = "0.8.1"
}
}
}
provider "libvirt" {
uri = "qemu:///system"
}
$ terraform init Initializing the backend... Initializing provider plugins... - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/template from the dependency lock file - Reusing previous version of dmacvicar/libvirt from the dependency lock file - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/null from the dependency lock file - Using previously-installed hashicorp/template v2.2.0 - Using previously-installed dmacvicar/libvirt v0.8.1 - Using previously-installed hashicorp/null v3.2.3 Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
次に、hosts という名前のインベントリ ファイルを作成します。
variable "libvirt_disk_path" {
description = "path for libvirt pool"
default = "default"
}
variable "ubuntu_20_img_url" {
description = "ubuntu 20.04 image"
default = "https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/releases/focal/release/ubuntu-20.04-server-cloudimg-amd64.img"
}
variable "vm_hostnames" {
description = "List of VM hostnames"
default = ["vm1", "vm2"]
}
ansible ping コマンドを使用して VM を確認しています:
resource "null_resource" "cache_image" {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "wget -O /tmp/ubuntu-20.04.qcow2 ${var.ubuntu_20_img_url}"
}
}
resource "libvirt_volume" "base" {
name = "base.qcow2"
source = "/tmp/ubuntu-20.04.qcow2"
pool = var.libvirt_disk_path
format = "qcow2"
depends_on = [null_resource.cache_image]
}
# Volume for VM with size 10GB
resource "libvirt_volume" "ubuntu20-qcow2" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
name = "ubuntu20-${count.index}.qcow2"
base_volume_id = libvirt_volume.base.id
pool = var.libvirt_disk_path
size = 10737418240 # 10GB
}
data "template_file" "user_data" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
template = file("${path.module}/config/cloud_init.yml")
}
data "template_file" "network_config" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
template = file("${path.module}/config/network_config.yml")
}
resource "libvirt_cloudinit_disk" "commoninit" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
name = "commoninit-${count.index}.iso"
user_data = data.template_file.user_data[count.index].rendered
network_config = data.template_file.network_config[count.index].rendered
pool = var.libvirt_disk_path
}
resource "libvirt_domain" "domain-ubuntu" {
count = length(var.vm_hostnames)
name = var.vm_hostnames[count.index]
memory = "1024" # VM memory
vcpu = 1 # VM CPU
cloudinit = libvirt_cloudinit_disk.commoninit[count.index].id
network_interface {
network_name = "default"
wait_for_lease = true
hostname = var.vm_hostnames[count.index]
}
console {
type = "pty"
target_port = "0"
target_type = "serial"
}
console {
type = "pty"
target_type = "virtio"
target_port = "1"
}
disk {
volume_id = libvirt_volume.ubuntu20-qcow2[count.index].id
}
graphics {
type = "spice"
listen_type = "address"
autoport = true
}
}
ここで、playbook.yml とロールを作成します。この Playbook は、Docker、Flask、PostgreSQL をインストールして構成します。
mkdir config/
次に、roles/docker という名前の新しいディレクトリを作成します。
#cloud-config
runcmd:
- sed -i '/PermitRootLogin/d' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- echo "PermitRootLogin yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- systemctl restart sshd
ssh_pwauth: true
disable_root: false
chpasswd:
list: |
root:cloudy24
expire: false
users:
- name: ubuntu
gecos: ubuntu
groups:
- sudo
sudo:
- ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
home: /home/ubuntu
shell: /bin/bash
lock_passwd: false
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAA...
docker に task という名前の新しいディレクトリを作成し、新しいファイル main.yml を作成します。このファイルは Docker と Docker Compose をインストールします:
version: 2
ethernets:
ens3:
dhcp4: true
$ tree . ├── config │ ├── cloud_init.yml │ └── network_config.yml ├── main.tf └── variables.tf
次に、psql という新しいディレクトリを作成し、vars、tempalates、tasks というサブディレクトリを作成します。
$ terraform plan data.template_file.user_data[1]: Reading... data.template_file.user_data[0]: Reading... data.template_file.network_config[1]: Reading... data.template_file.network_config[0]: Reading... ... Plan: 8 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy
その後、vars 内に main.yml を作成します。これらは、ユーザー名、パスワードなどの設定に使用される変数です:
$ terraform apply ... null_resource.cache_image: Creation complete after 10m36s [id=4239391010009470471] libvirt_volume.base: Creating... libvirt_volume.base: Creation complete after 3s [id=/var/lib/libvirt/images/base.qcow2] libvirt_volume.ubuntu20-qcow2[1]: Creating... libvirt_volume.ubuntu20-qcow2[0]: Creating... libvirt_volume.ubuntu20-qcow2[1]: Creation complete after 0s [id=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu20-1.qcow2] libvirt_volume.ubuntu20-qcow2[0]: Creation complete after 0s [id=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu20-0.qcow2] libvirt_domain.domain-ubuntu[1]: Creating... ... libvirt_domain.domain-ubuntu[1]: Creation complete after 51s [id=6221f782-48b7-49a4-9eb9-fc92970f06a2] Apply complete! Resources: 8 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed
次に、docker-compose.yml.j2 という jinja ファイルを作成します。このファイルを使用して、postgresql コンテナを作成します:
$ virsh list Id Name State ---------------------- 1 vm1 running 2 vm2 running
次に、タスクに main.yml を作成します。そこで、 docker-compose.yml.j2 をコピーし、 docker compose を使用して実行します:
$ virsh net-dhcp-leases --network default Expiry Time MAC address Protocol IP address Hostname Client ID or DUID ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2024-12-09 19:50:00 52:54:00:2e:0e:86 ipv4 192.168.122.19/24 vm1 ff:b5:5e:67:ff:00:02:00:00:ab:11:b0:43:6a:d8:bc:16:30:0d 2024-12-09 19:50:00 52:54:00:86:d4:ca ipv4 192.168.122.15/24 vm2 ff:b5:5e:67:ff:00:02:00:00:ab:11:39:24:8c:4a:7e:6a:dd:78
まず、flask というディレクトリを作成し、次にサブディレクトリを再度作成する必要があります。
$ ssh ubuntu@192.168.122.15 The authenticity of host '192.168.122.15 (192.168.122.15)' can't be established. ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:Y20zaCcrlOZvPTP+/qLLHc7vJIOca7QjTinsz9Bj6sk. This key is not known by any other names Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes Warning: Permanently added '192.168.122.15' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts. Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-200-generic x86_64) ... ubuntu@ubuntu:~$
次に、main.yml を vars に追加します。このファイルは、以前に posgtresql 変数を参照し、さらに VM2(データベース VM) の IP アドレスを追加しました:
$ mkdir ansible && cd ansible
次に、テンプレートに config.py.j2 を作成します。このファイルは、Flask プロジェクトの古い構成ファイルを置き換えます:
[defaults] inventory = hosts host_key_checking = True deprecation_warnings = False collections = ansible.posix, community.general, community.postgresql
次に、テンプレートに docker-compose.yml.j2 を作成します。このファイルを使用して、docker compose を使用してコンテナーを作成します:
[vm1] 192.168.122.19 ansible_user=ubuntu [vm2] 192.168.122.15 ansible_user=ubuntu
次にタスク内にmain.ymlを作成します。このファイルを使用して、Flask プロジェクトのクローンを作成し、compose ファイルを追加し、config.py を置き換え、docker compose を使用して新しいコンテナを作成します:
$ ansible -m ping all
192.168.122.15 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.122.19 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
プロジェクトの構造は次のようになります:
---
- name: Deploy Flask
hosts: vm1
become: true
remote_user: ubuntu
roles:
- flask
- config
- name: Deploy Postgresql
hosts: vm2
become: true
remote_user: ubuntu
roles:
- psql
- config
最後に、ansible-playbook を実行して PostgreSQL と Flask をデプロイしましょう:
$ mkdir roles $ mkdir docker
完了したら、エラーがないことを確認してください。すると、2 つ作成されていることがわかります。 VM1 は Flask で、VM2 は Postgresql です:
sudo apt -y install bridge-utils cpu-checker libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon qemu qemu-kvm
ブラウザを使用してアプリにアクセスしてみます。http://

新しいタスクを追加しようとすると、データがデータベースに追加されます:

最後に、この記事を読んでいただきありがとうございます。ご質問、ご提案、フィードバックがございましたら、お気軽にコメントを残してください。
注意: プロジェクト リポジトリ: danielcristho/that-i-write
以上がTerraform と Ansible を使用した KVM 上の Flask と PostgreSQL のデプロイメントの自動化の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。