
画像出典:medium
並べ替えは、データ構造とアルゴリズムの最も重要な部分の 1 つです。並べ替えアルゴリズムには多くの種類がありますが、ここでは最も簡単なアルゴリズムの 1 つであるバブル ソートを紹介します。
並べ替えアルゴリズムはコンピューター サイエンスの基礎であり、バブル ソートは最もシンプルで直感的な並べ替えアルゴリズムの 1 つです。この投稿では、バブル ソートがどのように機能するかを調査し、その時間計算量を分析し、JavaScript の実装について説明します。
このシリーズでは、完全な並べ替えアルゴリズムのデータ構造と Javascript を使用したアルゴリズムを共有し、バブル ソートから始めます。完全な並べ替えアルゴリズムを例とともに共有したい場合は、「いいね」とフォローをお願いします。皆さんのためにコンテンツを作成し、準備するモチベーションになります。
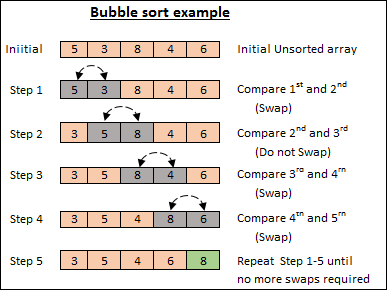
バブル ソートは、リストを繰り返しステップ実行し、隣接する要素 (次の要素) を比較し、順序が間違っている場合は入れ替える簡単な並べ替えアルゴリズムです。このプロセスは、リストがソートされるまで繰り返されます。このアルゴリズムの名前は、より小さい要素がリストの先頭に「バブル」することから付けられました。
コードを詳しく見て、JavaScript でバブル ソートがどのように実装されているかを見てみましょう:
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]

上記のコードの各行についてはすでにコメントを追加し、説明しています。ただし、完全なプロセスとコードを理解するのに役立つように、詳しく説明します。
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]
// optimized version:
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of the array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop run n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
let isSwapped = false;
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
//check if the first element is greater than the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
isSwapped = true;
}
}
//If no element swap by inner loop then break;
if (isSwapped === false) {
break;
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
バブル ソートの時間計算量は、最悪の場合と平均的な場合では (O(n²)) です。ここで、(n) は配列内の要素の数です。これは、各要素が他のすべての要素と比較されるためです。最良の場合、配列がすでにソートされている場合、スワップが必要ないときにアルゴリズムを停止する最適化が追加された場合、時間計算量は (O(n)) になります。
最良のシナリオでは、配列がすでにソートされている場合、isSwapped 最適化によりアルゴリズムが早期に終了する可能性があり、その結果、時間計算量は (O(n)) になります。
全体として、バブル ソートは二次時間計算量のため、大規模なデータセットに対しては効率的ではありませんが、小さな配列に対して、またはソート アルゴリズムを理解するための教育ツールとしては役立ちます。
バブル ソートは、そのシンプルさから教育目的に最適なアルゴリズムです。ただし、二次時間計算量があるため、大規模なデータセットには適していません。非効率ではありますが、バブル ソートを理解することは、より高度なソート アルゴリズムを学習するための基礎となります。
以上がバブルソートアルゴリズムを理解する: ステップバイステップガイドの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。