PHP(3) PHP 関数を段階的に学習します
1. メソッドの概要
まず、誰でも確認できる最も単純な関数を作成します。
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue"><</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">html</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
<</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">head</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
<</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">title</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">></SPAN>HelloPHP<SPAN style="COLOR: blue"></</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">title</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
</</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">head</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
<</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">body</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
<?</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">php
</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: red">function CustomPrint</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">str</SPAN>)
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">for</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">i</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=0;$i</SPAN><5;$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">i</SPAN>++)
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">str</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'<br/>'</SPAN>);
}
}
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"Hello"</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">?>
</</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">body</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
</</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">html</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">>
</SPAN>この例を通して、PHP での関数の一般的な記述方法が理解できたと思います。構文に関しては、while、for、if なども同様です。その他の違いについては、今後の記事で徐々に説明します。
それでは、このメソッドの重要なポイントを要約しましょう:
A. PHP メソッドは関数で宣言されます。これは、おなじみの Javascript に似ています。
B. 変数を使用する場合は、ドル記号 ($) で始める必要があります。
2. 参照によるパラメータの受け渡しと値の受け渡し
パラメータ値の受け渡しと参照の受け渡しは、C 言語を学習する際に誰もが触れたことがあると思います。以下は C# を使用した例です。
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">public void </SPAN>Swap(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">int </SPAN>a, <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">int </SPAN>b)
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">int </SPAN>temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">public void </SPAN>Swap(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">ref int </SPAN>a, <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">ref int </SPAN>b)
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">int </SPAN>temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}次に、ここに PHP のバージョンを記述します。
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue"><?</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">php
</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: red">function Swap1</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN>,$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN>)
{
$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">temp</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=$a;
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=$b;
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=$temp;
</SPAN>}
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">function Swap2</SPAN>(&$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN>,&$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN>)
{
$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">temp</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=$a;
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=$b;
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=$temp;
</SPAN>}
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">function CustomPrint</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">str</SPAN>)
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">str</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"<br/>"</SPAN>);
}
$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=1;
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=2;
</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: red">Swap1</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN>,$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"值传递的结果:"</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'$a='</SPAN>.$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'$b='</SPAN>.$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN>);
$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=1;
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=2;
</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: red">Swap2</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN>,$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"引用传递的结果:"</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'$a='</SPAN>.$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">CustomPrint</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'$b='</SPAN>.$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">b</SPAN>);
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">?>
</SPAN>この例では: 明確にする必要がある 2 つの点があります:
A. 値の受け渡しと参照の受け渡しの違いは、パラメーターの前の「&」です。
B. CustomPrint('$a='.$a); この文では、一重引用符について特別な説明が必要です。二重引用符の唯一の違いは、変数名が解析できるかどうかです。この例は、問題を説明するのに十分です:
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue"><?</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">php </SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">a</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">=1; </SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"$a"</SPAN>); <SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"<br/>"</SPAN>); <SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'$a'</SPAN>); <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">?> </SPAN>ログイン後にコピー
最後に、値で渡すとき、PHP はそれをコピーして渡す必要があります。このように、大きなオブジェクトや文字列が使用されると、時間がかかるだけでなく、スペースも消費します。このとき、参照渡しをすると、パフォーマンスを消費するコピー操作を回避できます。パフォーマンスの向上に非常に適しています。
3. スコープの問題
C# では変数を使用する前に宣言する必要があるため、スコープやサブスコープという概念が存在しますが、PHP にはそのような概念はありません。
C# コードの一部を見てみましょう:
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">public class </SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: #2b91af">Student
</SPAN>{
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">private string </SPAN>name;
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">public void </SPAN>SayHello()
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: #2b91af">HttpContext</SPAN>.Current.Response.Write(<SPAN style="COLOR: #a31515">"Hello,I am " </SPAN>+ name);
}
}言い換えると、外部クラスによって宣言された変数にはメソッド内でアクセスできますが、PHP では異なります。
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue"><?</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: maroon">php
</SPAN>$<SPAN style="COLOR: red">name</SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: blue">="kym"</SPAN>;
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">function SayHello</SPAN>()
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">if</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: red">isset</SPAN>($<SPAN style="COLOR: red">name</SPAN>))
{
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">"Hello $name"</SPAN>);
}
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">else
</SPAN>{
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">'$name is undefined'</SPAN>);
}
}
<SPAN style="COLOR: red">SayHello</SPAN>();
<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">?>
</SPAN>
変数が定義されているか、空文字列であるかを検出できる関数「isset」を紹介します。
この結果は、関数本体内では外部変数 $name にアクセスできないことを示しています。
ここでもう 1 つ言及したいのは、unset に対応する関数: unset です。この関数は変数の値を削除するために使用されます。
簡単な例を書きます:
<SPAN style="COLOR: red"><?php </SPAN><SPAN style="COLOR: #660000">$name</SPAN>=<SPAN style="COLOR: #008200">"kym"</SPAN>; <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">if</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">isset</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #660000">$name</SPAN>)) { <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #008200">"Yes"</SPAN>); } <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">else </SPAN>{ <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #008200">"No"</SPAN>); } <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">unset</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #660000">$name</SPAN>); <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">if</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: blue">isset</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #660000">$name</SPAN>)) { <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #008200">"Yes"</SPAN>); } <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">else </SPAN>{ <SPAN style="COLOR: blue">echo</SPAN>(<SPAN style="COLOR: #008200">"No"</SPAN>); } <SPAN style="COLOR: red">?></SPAN>ログイン後にコピー
これらについては、後続のガベージ コレクションで詳しく説明します。

ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7445
7445
 15
15
 1374
1374
 52
52
 76
76
 11
11
 14
14
 6
6
 Ubuntu および Debian 用の PHP 8.4 インストールおよびアップグレード ガイド
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Ubuntu および Debian 用の PHP 8.4 インストールおよびアップグレード ガイド
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 では、いくつかの新機能、セキュリティの改善、パフォーマンスの改善が行われ、かなりの量の機能の非推奨と削除が行われています。 このガイドでは、Ubuntu、Debian、またはその派生版に PHP 8.4 をインストールする方法、または PHP 8.4 にアップグレードする方法について説明します。
 CakePHP データベースの操作
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP データベースの操作
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP でデータベースを操作するのは非常に簡単です。この章では、CRUD (作成、読み取り、更新、削除) 操作について理解します。
 CakePHP ファイルのアップロード
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP ファイルのアップロード
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
ファイルのアップロードを行うには、フォーム ヘルパーを使用します。ここではファイルアップロードの例を示します。
 CakePHP について話し合う
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP について話し合う
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP は、PHP 用のオープンソース フレームワークです。これは、アプリケーションの開発、展開、保守をより簡単にすることを目的としています。 CakePHP は、強力かつ理解しやすい MVC のようなアーキテクチャに基づいています。モデル、ビュー、コントローラー
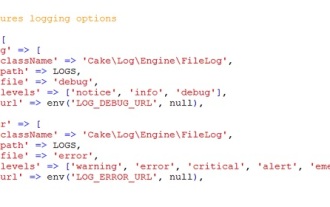 CakePHP のロギング
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP のロギング
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP へのログインは非常に簡単な作業です。使用する関数は 1 つだけです。 cronjob などのバックグラウンド プロセスのエラー、例外、ユーザー アクティビティ、ユーザーが実行したアクションをログに記録できます。 CakePHP でのデータのログ記録は簡単です。 log()関数が提供されています
 PHP 開発用に Visual Studio Code (VS Code) をセットアップする方法
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
PHP 開発用に Visual Studio Code (VS Code) をセットアップする方法
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code (VS Code とも呼ばれる) は、すべての主要なオペレーティング システムで利用できる無料のソース コード エディター (統合開発環境 (IDE)) です。 多くのプログラミング言語の拡張機能の大規模なコレクションを備えた VS Code は、






