Androidの単体テストとシミュレーションテストについて詳しく解説
テストと基本仕様
なぜテストが必要なのか?
安定性のために、開発が正しく完了したかどうかを明確に把握できます。
メンテナンスが容易になり、コードを変更した後に関数が破壊されないようにすることができます。
開発仕様を標準化し、コードをより安定させるためにいくつかのツールを統合します (ファブリケータ差分を介して diff を発行するときに実行する必要がある単体テストを送信するなど、開発プロセスにおけるリモート コードの安定性を確保できます)。
2. 何をテストするか?
一般的な単体テスト:
テストする例外をリストして検証します。
パフォーマンステスト。
シミュレーションテスト: ニーズに応じて、ユーザーの実際の使用中のインターフェイスのフィードバックと表示をテストするだけでなく、システムアーキテクチャに依存するいくつかのコンポーネントのアプリケーションテストも行います。
3.
読みやすさを考慮し、メソッド名には表現力豊かなメソッド名を使用し、RSpec スタイルなどのテスト パラダイムの仕様を使用することを検討してください。メソッド名は、[テストメソッド]_[テスト条件]_[期待される結果]のような形式にすることができます。
テスト メソッドでは、論理フロー キーワード (If/else、for、do/while、switch/case) を使用しないでください。必要な場合は、それらを個別のテスト メソッドに分割してください。
本当にテストする必要がある内容とカバーする必要がある状況をテストします。一般に、検証出力 (特定の操作後の表示内容や値など) のみが考慮されます。
消費時間を考慮して、Android Studio はデフォルトで消費時間を出力します。
プライベート メソッドのテストを考慮する必要はありません。プライベート メソッドをブラック ボックスの内部コンポーネントとして扱い、それによって参照されるパブリック メソッドのテスト (ゲッターやセッターなど) を考慮しません。
各単体テスト メソッドは、可能な限り分離すべきであり、テスト A とテスト B にタイミングがある状況があってはなりません。
4. テストを作成します
対応するクラスを選択します
クラス名にカーソルを置きます
ALT + ENTERを押します
ポップアップウィンドウで[テストの作成]を選択します
Android Studioとシミュレーションでの単体テストテスト
control + shift + R (Android Studio のデフォルトの実行単体テストのショートカット キー)。
1. ローカル単体テスト
開発マシンで直接テストを実行します。
依存関係がない場合、または単純な Android ライブラリの依存関係のみが必要な場合にのみ、このタイプの単体テストの使用を検討してください。
./gradlew check
(1) コードの保管場所
異なるフレーバーまたはビルドタイプに対応する場合は、テストの直後に対応するサフィックスを追加します (たとえば、myFlavor に対応する単体テストコードは src / に配置する必要があります)以下の testMyFlavor/java)。
src/test/java
(2)Google公式推奨リファレンス
dependencies {
// Required -- JUnit 4 framework,用于单元测试,google官方推荐
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
// Optional -- Mockito framework,用于模拟架构,google官方推荐
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1546.html
testCompile 'org.mockito:mockito-core:1.10.19'
}(3)JUnit
Annotation

2. シミュレーションテスト
Androidデバイス上で実行する必要があるテスト仮想マシン。
主にテストに使用されます: 単体 (Android SDK レイヤーの参照関係に関連する単体テスト)、UI、アプリケーション コンポーネントの統合テスト (サービス、コンテンツ プロバイダーなど)。
./gradlew ConnectedAndroidTest
(1) コードストレージ:
src/androidTest/java
(2) Google 公式推奨
dependencies {
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support:support-annotations:23.0.1'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:runner:0.4.1'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:rules:0.4.1'
// Optional -- Hamcrest library
androidTestCompile 'org.hamcrest:hamcrest-library:1.3'
// Optional -- UI testing with Espresso
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1546.html
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.1'
// Optional -- UI testing with UI Automator
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.uiautomator:uiautomator-v18:2.1.1'
}(3) 一般的な UI テスト
は Android システム環境をシミュレートする必要があります。
3 つの主要なポイント:
UI のロード後に表示される情報が正しいかどうか。
ユーザー操作後にUI情報が正しく表示されるかどうか。
ユーザーが操作できる正しいページを表示します。
(4)Espresso
Google公式がUIインタラクションテスト用に提供しています
import static android.support.test.espresso.Espresso.onView;
import static android.support.test.espresso.action.ViewActions.click;
import static android.support.test.espresso.assertion.ViewAssertions.matches;
import static android.support.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.isDisplayed;
import static android.support.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withId;
// 对于Id为R.id.my_view的View: 触发点击,检测是否显示
onView(withId(R.id.my_view)).perform(click())
.check(matches(isDisplayed()));
// 对于文本打头是"ABC"的View: 检测是否没有Enable
onView(withText(startsWith("ABC"))).check(matches(not(isEnabled()));
// 按返回键
pressBack();
// 对于Id为R.id.button的View: 检测内容是否是"Start new activity"
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1537.html
onView(withId(R.id.button)).check(matches(withText(("Start new activity"))));
// 对于Id为R.id.viewId的View: 检测内容是否不包含"YYZZ"
onView(withId(R.id.viewId)).check(matches(withText(not(containsString("YYZZ")))));
// 对于Id为R.id.inputField的View: 输入"NewText",然后关闭软键盘
onView(withId(R.id.inputField)).perform(typeText("NewText"), closeSoftKeyboard());
// 对于Id为R.id.inputField的View: 清除内容
onView(withId(R.id.inputField)).perform(clearText());アクティビティを開くインテントを開始します
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
public class SecondActivityTest {
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule<SecondActivity> rule =
new ActivityTestRule(SecondActivity.class, true,
// 这个参数为false,不让SecondActivity自动启动
// 如果为true,将会在所有@Before之前启动,在最后一个@After之后关闭
false);
@Test
public void demonstrateIntentPrep() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("EXTRA", "Test");
// 启动SecondActivity并传入intent
rule.launchActivity(intent);
// 对于Id为R.id.display的View: 检测内容是否是"Text"
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1532.html
onView(withId(R.id.display)).check(matches(withText("Test")));
}
}(5)非同期インタラクション
「設定->開発者」でアニメーションをオフにすることをお勧めしますこれらのアニメーションは、非同期タスクの検出時に Espresso を混乱させる可能性があるため、デバイスの「オプション」を参照してください: ウィンドウ アニメーション スケール、トランジション アニメーション スケール、アニメーター期間スケール。
AsyncTask の場合、テスト中にクリック イベントがトリガーされた後に AsyncTask タスクがスローされた場合、テスト中に直接 onView(withId(R.id.update)).perform(click()) を実行して、それを直接検出します。この時点での検出は AsyncTask#onPostExecute の後です。
// 通过实现IdlingResource,block住当非空闲的时候,当空闲时进行检测,非空闲的这段时间处理异步事情
public class IntentServiceIdlingResource implements IdlingResource {
ResourceCallback resourceCallback;
private Context context;
public IntentServiceIdlingResource(Context context) { this.context = context; }
@Override public String getName() { return IntentServiceIdlingResource.class.getName(); }
@Override public void registerIdleTransitionCallback( ResourceCallback resourceCallback) { this.resourceCallback = resourceCallback; }
@Override public boolean isIdleNow() {
// 是否是空闲
// 如果IntentService 没有在运行,就说明异步任务结束,IntentService特质就是启动以后处理完Intent中的事务,理解关闭自己
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1531.html
boolean idle = !isIntentServiceRunning();
if (idle && resourceCallback != null) {
// 回调告知异步任务结束
resourceCallback.onTransitionToIdle();
}
return idle;
}
private boolean isIntentServiceRunning() {
ActivityManager manager = (ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
// Get all running services
List<ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo> runningServices = manager.getRunningServices(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// check if our is running
for (ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo info : runningServices) {
if (MyIntentService.class.getName().equals(info.service.getClassName())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
// 使用IntentServiceIdlingResource来测试,MyIntentService服务启动结束这个异步事务,之后的结果。
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
public class IntegrationTest {
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule rule = new ActivityTestRule(MainActivity.class);
IntentServiceIdlingResource idlingResource;
@Before
public void before() {
Instrumentation instrumentation = InstrumentationRegistry.getInstrumentation();
Context ctx = instrumentation.getTargetContext();
idlingResource = new IntentServiceIdlingResource(ctx);
// 注册这个异步监听
Espresso.registerIdlingResources(idlingResource);
}
@After
public void after() {
// 取消注册这个异步监听
Espresso.unregisterIdlingResources(idlingResource);
}
@Test
public void runSequence() {
// MainActivity中点击R.id.action_settings这个View的时候,会启动MyIntentService
onView(withId(R.id.action_settings)).perform(click());
// 这时候IntentServiceIdlingResource#isIdleNow会返回false,因为MyIntentService服务启动了
// 这个情况下,这里会block住.............
// 直到IntentServiceIdlingResource#isIdleNow返回true,并且回调了IntentServiceIdlingResource#onTransitionToIdle
// 这个情况下,继续执行,这时我们就可以测试异步结束以后的情况了。
onView(withText("Broadcast")).check(matches(notNullValue()));
}
}(6) カスタムマッチャー
// 定义
public static Matcher<View> withItemHint(String itemHintText) {
checkArgument(!(itemHintText.equals(null)));
return withItemHint(is(itemHintText));
}
public static Matcher<View> withItemHint(final Matcher<String> matcherText) {
checkNotNull(matcherText);
return new BoundedMatcher<View, EditText>(EditText.class) {
@Override
public void describeTo(Description description) {
description.appendText("with item hint: " + matcherText);
}
@Override
protected boolean matchesSafely(EditText editTextField) {
// 取出hint,然后比对下是否相同
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1524.html
return matcherText.matches(editTextField.getHint().toString());
}
};
}
// 使用
onView(withItemHint("test")).check(matches(isDisplayed()));拓展工具
1. AssertJ Android
square/assertj-android
极大的提高可读性。
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
// 断言: view是GONE的
assertThat(view).isGone();
MyClass test = new MyClass("Frodo");
MyClass test1 = new MyClass("Sauron");
MyClass test2 = new MyClass("Jacks");
List<MyClass> testList = new ArrayList<>();
testList.add(test);
testList.add(test1);
// 断言: test.getName()等于"Frodo"
assertThat(test.getName()).isEqualTo("Frodo");
// 断言: test不等于test1并且在testList中
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1519.html
assertThat(test).isNotEqualTo(test1)
.isIn(testList);
// 断言: test.getName()的字符串,是由"Fro"打头,以"do"结尾,忽略大小写会等于"frodo"
assertThat(test.getName()).startsWith("Fro")
.endsWith("do")
.isEqualToIgnoringCase("frodo");
// 断言: testList有2个数据,包含test,test1,不包含test2
assertThat(list).hasSize(2)
.contains(test, test1)
.doesNotContain(test2);
// 断言: 提取testList队列中所有数据中的成员变量名为name的变量,并且包含name为"Frodo"与"Sauron"
// 并且不包含name为"Jacks"
assertThat(testList).extracting("name")
.contains("Frodo", "Sauron")
.doesNotContain("Jacks");2. Hamcrest
JavaHamcrest
通过已有的通配方法,快速的对代码条件进行测试
org.hamcrest:hamcrest-junit:(version)
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
// 断言: a等于b
assertThat(a, equalTo(b));
assertThat(a, is(equalTo(b)));
assertThat(a, is(b));
// 断言: a不等于b
assertThat(actual, is(not(equalTo(b))));
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(5, 2, 4);
// 断言: list有3个数据
assertThat(list, hasSize(3));
// 断言: list中有5,2,4,并且顺序也一致
assertThat(list, contains(5, 2, 4));
// 断言: list中包含5,2,4
assertThat(list, containsInAnyOrder(2, 4, 5));
// 断言: list中的每一个数据都大于1
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1507.html
assertThat(list, everyItem(greaterThan(1)));
// 断言: fellowship中包含有成员变量"race",并且其值不是ORC
assertThat(fellowship, everyItem(hasProperty("race", is(not((ORC))))));
// 断言: object1中与object2相同的成员变量都是相同的值
assertThat(object1, samePropertyValuesAs(object2));
Integer[] ints = new Integer[] { 7, 5, 12, 16 };
// 断言: 数组中包含7,5,12,16
assertThat(ints, arrayContaining(7, 5, 12, 16));(1)几个主要的匹配器:
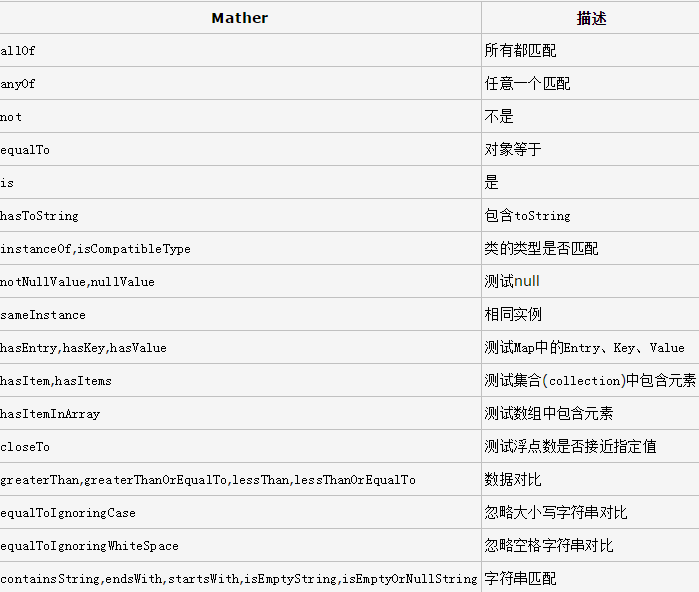
(2)自定义匹配器
// 自定义
import org.hamcrest.Description;
import org.hamcrest.TypeSafeMatcher;
public class RegexMatcher extends TypeSafeMatcher<String> {
private final String regex;
public RegexMatcher(final String regex) { this.regex = regex; }
@Override
public void describeTo(final Description description) { description.appendText("matches regular expression=`" + regex + "`"); }
@Override
public boolean matchesSafely(final String string) { return string.matches(regex); }
// 上层调用的入口
public static RegexMatcher matchesRegex(final String regex) {
return new RegexMatcher(regex);
}
}
// 使用
String s = "aaabbbaaa";
assertThat(s, RegexMatcher.matchesRegex("a*b*a"));3. Mockito
Mockito
Mock对象,控制其返回值,监控其方法的调用。
org.mockito:mockito-all:(version)
// import如相关类
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
// 创建一个Mock的对象
MyClass test = mock(MyClass.class);
// 当调用test.getUniqueId()的时候返回43
when(test.getUniqueId()).thenReturn(43);
// 当调用test.compareTo()传入任意的Int值都返回43
when(test.compareTo(anyInt())).thenReturn(43);
// 当调用test.compareTo()传入的是Target.class类型对象时返回43
when(test.compareTo(isA(Target.class))).thenReturn(43);
// 当调用test.close()的时候,抛IOException异常
doThrow(new IOException()).when(test).close();
// 当调用test.execute()的时候,什么都不做
doNothing().when(test).execute();
// 验证是否调用了两次test.getUniqueId()
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1503.html
verify(test, times(2)).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否没有调用过test.getUniqueId()
verify(test, never()).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否至少调用过两次test.getUniqueId()
verify(test, atLeast(2)).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否最多调用过三次test.getUniqueId()
verify(test, atMost(3)).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否这样调用过:test.query("test string")
verify(test).query("test string");
// 通过Mockito.spy() 封装List对象并返回将其mock的spy对象
List list = new LinkedList();
List spy = spy(list);
// 指定spy.get(0)返回"foo"
doReturn("foo").when(spy).get(0);
assertEquals("foo", spy.get(0));对访问方法时,传入参数进行快照
import org.mockito.ArgumentCaptor;
import org.mockito.Captor;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<Integer> captor;
@Test
public void testCapture(){
MyClass test = mock(MyClass.class);
test.compareTo(3, 4);
verify(test).compareTo(captor.capture(), eq(4));
assertEquals(3, (int)captor.getValue());
// 需要特别注意,如果是可变数组(vargars)参数,如方法 test.doSomething(String... params)
// 此时是使用ArgumentCaptor<String>,而非ArgumentCaptor<String[]>
ArgumentCaptor<String> varArgs = ArgumentCaptor.forClass(String.class);
test.doSomething("param-1", "param-2");
verify(test).doSomething(varArgs.capture());
// 这里直接使用getAllValues()而非getValue(),来获取可变数组参数的所有传入参数
assertThat(varArgs.getAllValues()).contains("param-1", "param-2");
}(1)对于静态的方法的Mock:
可以使用 PowerMock:
org.powermock:powermock-api-mockito:(version) & org.powermock:powermock-module-junit4:(version)(For PowerMockRunner.class)
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({StaticClass1.class, StaticClass2.class})
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void testSomething() {
// mock完静态类以后,默认所有的方法都不做任何事情
mockStatic(StaticClass1.class);
when(StaticClass1.getStaticMethod()).andReturn("anything");
// 验证是否StaticClass1.getStaticMethod()这个方法被调用了一次
verifyStatic(time(1));
StaticClass1.getStaticMethod();
when(StaticClass1.getStaticMethod()).andReturn("what ever");
// 验证是否StaticClass2.getStaticMethod()这个方法被至少调用了一次
verifyStatic(atLeastOnce());
StaticClass2.getStaticMethod();
// 通过任何参数创建File的实力,都直接返回fileInstance对象
whenNew(File.class).withAnyArguments().thenReturn(fileInstance);
}
}或者是封装为非静态,然后用Mockito:
class FooWraper{ void someMethod() {
Foo.someStaticMethod();
}
}4. Robolectric
Robolectric
让模拟测试直接在开发机上完成,而不需要在Android系统上。所有需要使用到系统架构库的,如(Handler、HandlerThread)都需要使用Robolectric,或者进行模拟测试。
主要是解决模拟测试中耗时的缺陷,模拟测试需要安装以及跑在Android系统上,也就是需要在Android虚拟机或者设备上面,所以十分的耗时。基本上每次来来回回都需要几分钟时间。针对这类问题,业界其实已经有了一个现成的解决方案: Pivotal实验室推出的Robolectric。通过使用Robolectrict模拟Android系统核心库的Shadow Classes的方式,我们可以像写本地测试一样写这类测试,并且直接运行在工作环境的JVM上,十分方便。
5. Robotium
RobotiumTech/robotium
(Integration Tests)模拟用户操作,事件流测试。
@RunWith(RobolectricTestRunner.class)
@Config(constants = BuildConfig.class)
public class MyActivityTest{
@Test
public void doSomethingTests(){
// 获取Application对象
Application application = RuntimeEnvironment.application;
// 启动WelcomeActivity
WelcomeActivity activity = Robolectric.setupActivity(WelcomeActivity.class);
// 触发activity中Id为R.id.login的View的click事件
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1502.html
activity.findViewById(R.id.login).performClick();
Intent expectedIntent = new Intent(activity, LoginActivity.class);
// 在activity之后,启动的Activity是否是LoginActivity
assertThat(shadowOf(activity).getNextStartedActivity()).isEqualTo(expectedIntent);
}
}通过模拟用户的操作的行为事件流进行测试,这类测试无法避免需要在虚拟机或者设备上面运行的。是一些用户操作流程与视觉显示强相关的很好的选择。
6. Test Butler
linkedin/test-butler
避免设备/模拟器系统或者环境的错误,导致测试的失败。
通常我们在进行UI测试的时候,会遇到由于模拟器或者设备的错误,如系统的crash、ANR、或是未预期的Wifi、CPU罢工,或者是锁屏,这些外再环境因素导致测试不过。Test-Butler引入就是避免这些环境因素导致UI测试不过。
该库被谷歌官方推荐过,并且收到谷歌工程师的Review。
拓展思路
1. Android Robots
Instrumentation Testing Robots – Jake Wharton
假如我们需要测试: 发送 $42 到 “foo@bar.com”,然后验证是否成功。
(1)通常的做法

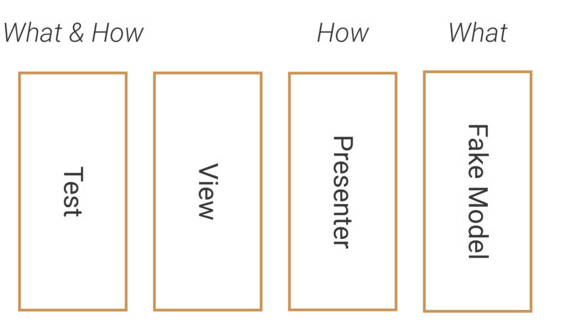
(2)Robot思想
在写真正的UI测试的时候,只需要关注要测试什么,而不需要关注需要怎么测试,换句话说就是让测试逻辑与View或Presenter解耦,而与数据产生关系。
首先通过封装一个Robot去处理How的部分:

然后在写测试的时候,只关注需要测试什么:
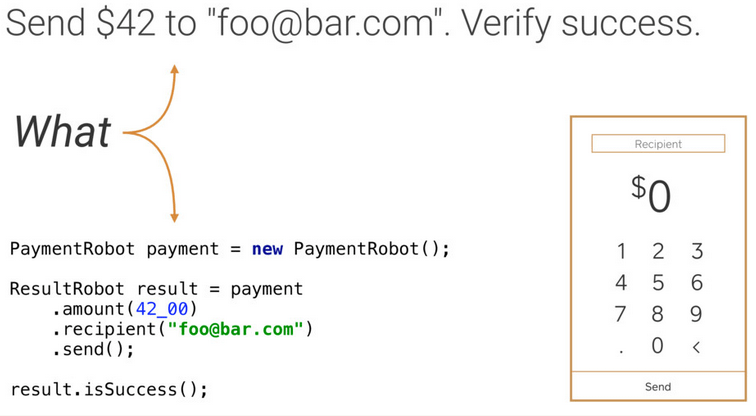
终的思想原理


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 7471
7471
 15
15
 1377
1377
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 19
19
 30
30


